Explanation and main parameters of the PVS wire
The characteristics of PVA wires allow it to be used to solve a wide range of problems. And in order to make the right choice, you should know not only the technical characteristics of the wire, but also its operational features.
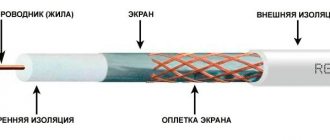
Decoding the PVS wire
For PVC wires, the decoding is quite simple - “P” means wire, “B” means the presence of vinyl insulation (this is an abbreviation for PVC) and “C” means the connection of all cores in a single sheath. In this case, the wire has a circular cross-section. The addition of the symbol “P” indicates a parallel arrangement of cores. In this case, the wire has an oval shape.
Decoding of PVS wires
So:
- The marking on the wire is applied to its outer surface. In addition to the designation of the wire brand, it also contains a number of numbers. Let's look at their meaning. And the video presented on the site will help us in this.
- The first digit after the letter marking is “2”, “3”, “4” or “5”. This number indicates the number of cores in the cable.
- After this comes the “×” sign and the second number, which can be “0.75”, “1.00”, “1.50”, “2.50”. This number means the cross-section of all wire cores.
Basic parameters of PVS wire
Now let's look at the main characteristics of the PVS wire. After all, it is on the basis of them that the choice of wire and location of its installation is made.
Technical characteristics of PVS wires
So:
- According to GOST 22483 - 77 cores of PVS wires belong to class 5. Based on this, the cross-section of individual wires in the total cross-section of the core is selected. For example, for a wire with a nominal core cross-section of 1.0 mm2, the cross-section of a single wire should be no more than 0.21 mm2. And for a core of 2.5 mm2, the value of a single wire should no longer be more than 0.26 mm2.
- As for insulation, GOST 7399 - 97 PVS sets values for wires that depend on the cross-section of the cores. So the thickness of the core insulation ranges from 0.6 to 0.8 mm. And the thickness of the shell ranges from 0.8 to 1.2 mm. In this case, the insulation must provide an insulation resistance not less than those given in this GOST.
- Operating temperatures for PVA wire are considered to range from - 25⁰С to +40⁰С. In this case, the maximum operating temperature should not exceed +70⁰С. And the minimum temperature for installation should not be lower than -20⁰С
- The instructions assume that the wire sheath does not spread fire. At the same time, it itself is exposed to temperatures.
- GOST measures the service life of PVA wires at 6 years. But usually this period is much longer, unless the wire is exposed to aggressive environments.
Where is it used?
They use PVS cable to connect stationary household appliances - washing machines, electric stoves, refrigerators, garden equipment, power tools, household machines, electrical extension cords and carriers.
The rather weak, from a mechanical point of view, PVA shell made of PVC plastic compound does not allow its use in industrial connections, but for everyday use it is practically irreplaceable. PVA is used in lighting and advertising.
Related articles: Cable sleeves: description, purpose, classification
It is worth noting that PVC plastic compound makes PVA wire resistant to acidic and alkaline environments. Also, PVC plastic compound does not burn and is ozone-resistant.
The use of the same materials, PVC plastic, for the shell of the entire cable and insulation of its current-carrying conductors, the absence of additional protection reduces its cost to an attractive one for the consumer.
In addition, the ease of working with it (due to flexibility) encourages some craftsmen to use it not only for the actual connection of household appliances, but also for installing power electrical wiring. To put it mildly, it is not recommended to do this due to the weak protective properties of PVC insulation and the complexity of the contact connections of stranded conductors.
PVS wire technical characteristics, structure, application
The widespread use of household electrical appliances, a variety of tools and devices designed to connect to a standard 220/380V network, led to the development of a standard wire specifically for these purposes.
Operating conditions required making it safe, flexible, strong and durable. This problem was successfully solved, and currently Russian companies offer sufficient quantities of PVS wire that fully meets these requirements.
All about PVS wire in GOST 7399-97
Domestic manufacturers of PVS wire working for the Russian and CIS markets strive to comply with the requirements of GOST 7399-97, since it has interstate status. In addition, this facilitates export operations to non-CIS countries, since the content of the document is synchronized with the relevant parts of the international standards IEC 60227-1-93 (97) and IEC 60245-1-94 (97).
Sections of GOST 7399-97 contain all the most important information about the range, mechanical and electrical characteristics of PVA wire, as well as safety requirements, a list of tests, etc.
Marking example:
PVA 2x0.75+1x0.75 GOST 7399-97
The wire of the PVA brand is designated here; it has two main conductors with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2 and one grounding conductor with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2.
PVA wire structure
The standard defines PVA wire as a flexible wire for voltage up to 380V with twisted copper conductors in polyvinyl chloride insulation, with a polyvinyl chloride sheath. Each core consists of copper conductors; the core class must be at least 5 according to GOST 22483-77.
This standard establishes the thickness of the wires of which the core of each section can be composed. For example, in a standard PVA wire, cores with a cross-section of 1 mm2 cannot consist of wires with a diameter greater than 0.21 mm.
The number of wire cores can be from two to five, the minimum cross-sectional area is 0.75 mm2, the maximum produced by cable factories is 16 mm2, however, it is worth noting that according to GOST 7399-97 standards, the PVA wire must have a cross-section of 0.72 mm, up to 2.5 mm. The twist direction is left, twisting is performed without filler.
Core insulation color: white, grey, blue, blue, green, red, brown and yellow. On top of them there is a sheath of PVC plastic, applied by extrusion and flame retardant when laid individually. It must fill the gaps between the wires, giving the wire a round shape.
PVS transcript
- the absence of the letter A at the beginning of the abbreviation means that the wire is copper;
- P - wire;
- B - PVC insulation;
- C - designation of the purpose of the wire, connecting.
PVC wire technical specifications
Threshold values of basic mechanical and electrical characteristics are standardized by GOST 7399-97; as for specific values for each manufacturer, they may differ within the specified limits.
Therefore, accurate data on diameters, insulation thickness, mass and other indicators must be taken from the documentation accompanying the batch or the manufacturer’s catalogs. As an example, the characteristics of a standard PVS wire from one of the largest Russian manufacturers are shown here.
High-quality dry PVA wire can withstand alternating current voltage of 2000V for 5 minutes, and after an hour in water (tO= 20 ± 5 °C) it can withstand it for 15 minutes. The strength requirements are the same as for the VVG cable, the breaking force must be at least 10 N/mm2, and the elongation before breaking must be at least 150%.
The life of the wire, defined as the number of alternating bending deformations at rated voltage, should not be less than 30,000 cycles.
Application of PVS wire
PVA wire is used in the production of household appliances and electrical tools and devices. In the design of washing machines, televisions, refrigerators, all kinds of plumbing and construction power tools, other machines and devices, it is used to connect to the network. It is also used for the manufacture of network adapters, extension cords, etc.
Other types of PVS wire
- PVSng(A)-LS - the same as PVS, but does not propagate combustion, with reduced gas and smoke formation;
- PVS-Tng(A)-LS - the same as PVSng(A)-LS, but lightweight;
- PVS-TTng(A)-LS - the same as PVSng(A)-LS, but has a thicker insulating layer;
- PVS-TSng(A)-LS - the same as PVSng(A)-LS, but is intended for stationary installation.
Operating conditions and technical specifications
An important condition for the operation of PVA wires of any model is maintenance in the operating temperature range, which ranges from -35 to +40 degrees. Celsius. If you follow this rule and exclude mechanical damage, the cable will last for ten years.
Due to its high technical and operational characteristics, PVS is significantly superior to wires of other brands. However, there is only one drawback - the price. However, the reasons for the higher cost are quite obvious.
We list the main technical parameters prescribed in GOST:
For production, cores with a flexibility class of at least five are used. In accordance with this requirement, the cross-section of the wires used to form the core is selected. For example, 0.21 sq. mm each for a cable with cores of 1.0 sq. mm or 0.26 sq. mm for 2.5 sq. mm. The specific thickness of the insulating layer for an individual core and the entire wire as a whole depends on their cross-section. For cores, the thickness range is 0.6-0.8 mm, for sheath - 0.8-1.2 mm. When choosing this value, you need to focus on the electrical resistance specified in GOST. The operating temperature range of PVA wire is from -35 to +45 degrees. Celsius (for some versions below - from -25 to +40). The maximum permissible value when heating the cable is +70 deg. Celsius, and installation must be carried out at a temperature of at least -20 degrees. Celsius. The polyvinyl chloride shell is flame retardant but may crack when exposed to extreme cold or heat. The service life in accordance with GOST, subject to strict compliance with the conditions, is at least six years. The wire sheath must not have any visible defects, including bulges or dents.
It is important to ensure that there is no free space between the cable cores, and if necessary, use additional materials as filler. In this case, the sheath is removed from the cores easily, without any difficulty.