Electrical wiring is very important for every home and apartment. It provides all appliances, appliances, lighting systems and other electrical components with the electrical energy they need to operate. You should never forget about protecting this very electrical network. For such purposes, various devices are used. The most popular of them is the RCD (residual current device). This material describes how an RCD is installed in a house without grounding and how to organize it correctly.
Is it possible to install an RCD if there is no grounding?
All experts talk about the importance of installing RCDs in places where there is an increased probability of electric shock, and this should not be neglected. Some experienced specialists argue that connecting this device without grounding it in two-wire electrical networks is impossible. This leads to the fact that you will have to upgrade your home network, but this is expensive. In addition, you will have to completely abandon protective shutdown devices.
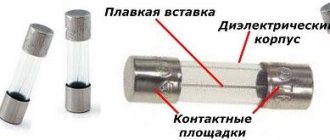
Appearance of the RCD
Note! This belief is incorrect, since the protection device has only two connectors for phase and neutral, and there is simply nowhere to insert the grounding. Moreover, the design features of these devices and their operating principle allow them to function quietly even without grounding.
This fact is confirmed by cases where the residual current device was connected to a three-wire electrical network and worked for a long time and without any failures, even in cases where the grounding cable was disconnected or broken.
Popular diagram for connecting an RCD without grounding in an apartment
RCD connection diagram without grounding
Perhaps everyone has heard about the need to install residual current devices in places where there is an increased risk of electric shock. However, many electricians, among whom there are often professionals, are for some reason convinced that connecting an RCD without grounding in a two-wire network is impossible, and that this leads either to an expensive modernization of the electrical network in the room, or to the abandonment of the RCD altogether.
However, such a prejudice is incorrect in its very essence, because the RCD has only two contact connectors, and there is simply nowhere to attach the grounding wire! And the principle of operation of such devices does not require connection to grounding at all.
This is confirmed not only by this article, but also by many cases when an RCD connected to a three-wire network in which there is a grounding works quite well and functioned for a long time, even despite damage to the grounding (for example, a break in the grounding wire) continues to perform its protective functions.
Is it possible to connect an RCD without grounding?
As we have already figured out, it makes sense to install an RCD even with a conventional two-wire connection diagram, where only phase and zero are present. And, for greater clarity and better understanding of the need to install additional protection, let’s define how an RCD works, and then imagine a typical everyday situation.
In fact, the RCD can be considered a kind of “calculator”. The connection diagram for an RCD without grounding is very simple - a phase and neutral wire pass through the device, the load on which is carefully monitored and compared.
In the event of damage to the wiring or consumer, a so-called leakage current appears in the electrical network - the same current that flows through the damaged insulation. The magnitude of this current is usually extremely small - tens and hundreds of milliamps - but is sufficient to cause serious damage to human health.
So, the residual current device compares the current passing through the phase and neutral wires, and, if these values deviate, it opens the contacts, thereby interrupting the supply of electricity to the damaged section of the network. From theory, let's move on to a completely understandable everyday situation.
For example, you have a washing machine installed in your bathroom at home. Electrical wiring is two-wire phase and zero, there is no grounding. The RCD has not yet been installed either. Now imagine that the insulation in the machine was damaged and the phase wire began to touch the metal body of the machine, i.e. The metal body of the machine was energized.
Now you approach the machine and touch its body. At this moment you become a conductor and electric current will flow through you. Electrical current will flow through you until you release the metal casing. In the meantime, you are cracking and pounding from the flowing current and there is no hope for protection that will turn off the damaged area. The only hope here is your own willpower (or you will lose consciousness and fall).
If an RCD had been installed, then when it touched a metal case that was energized, the RCD would have instantly sensed the current leak and tripped, turning off the damaged area.
Why? Because at the first sign of a “distortion” of the current on the phase and neutral wires, the automation would work and the machine would simply remain de-energized! And the person would barely have time to feel a slight tickling in the body and would be more puzzled by the sonorous click of the relay from the hallway than by the unusual sensations.
Moreover, this time is so short that a person practically does not feel the electric current. There is a video on the Internet on testing an RCD, and there a person specifically grabs a bare wire that is connected to a residual current device, the person touched the wire - the RCD instantly worked (he didn’t even feel any discomfort).
| So the benefits of RCDs are obvious, and in a two-wire power supply system, the presence of such devices in the most dangerous sections of the power network is simply necessary! |
How to connect an RCD without grounding
I hope the principle of operation of the RCD is clear and I have convinced you that the RCD must be installed, regardless of whether you have grounding in the house or not. In addition, if you have a two-wire power system, then even more so you need to install a residual current device. Don’t listen to advice that says it won’t work in such a network or will always work.
I hope the question of whether an RCD works without grounding has been sorted out. Now, before connecting the RCD without grounding, I would like to remind you of one important point.
A feature of residual current devices is the lack of overload protection. Therefore, they must be combined with conventional “automatic machines”. In this case, the connection diagram may be different.
We recommend: The lights in the apartment are flashing
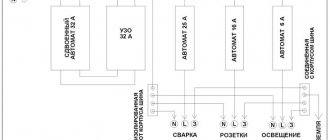
There are, in general, two options. You can install one common RCD for the entire house, thereby protecting even the bedside lamps. But only devices capable of passing 40-60A through themselves are noticeably more expensive than their less powerful counterparts, and even if the relay is triggered, it will be difficult to find out the reason - you will have to check each electrical device.
In addition, a power outage in the entire house immediately causes a lot of inconvenience - unsaved documents on the computer, a frozen air conditioner, a switched off water heating tank or washing machine - the list goes on for a long time!
If you decide to install one RCD for the entire group of consumers, then the RCD connection diagram without grounding will look like this:
The second option is to install a separate, less powerful RCD on each of the “dangerous” lines: bathroom, basement, garage, kitchen. In this case, more free space will be required in the panel, and the price of three or four devices will be even higher than one, but powerful one - however, the reliability of the entire power system increases, and the search for the cause of the shutdown will be reduced to only inspecting one or two outlets.
Experienced electricians advise taking the same judicious approach to choosing the power of the RCD - it should be slightly higher than the machine that will be paired with it.
The reason is simple - a circuit breaker with overload protection does not operate immediately (from several seconds to tens of minutes), and exceeding the rated current passing through the RCD can cause its breakdown.
Connecting an RCD in a two-wire network
I’ll tell you a little why I decided to write about such a topic as connecting an ouzo in a two-wire network. I chose this topic not by chance, as this issue also touched upon me.
Until recently, I lived in an apartment where the wiring was three-wire (a new building), i.e. phase, neutral and grounding were present. And recently I moved to another apartment in which the electrical wiring is two-wire, there is no trace of any PE neutral protective conductor.
Having settled in a little, I decided to look into the panel, which is located on the landing; there was no protection in the form of RCDs or automatic circuit breakers in my direction, there was only a 40 A package switch, a meter and two new 16 A circuit breakers.
Why I started a topic about connecting an RCD in a two-wire network, now I’ll tell you in more detail.
What confused me was the fact that in the bathroom there was a boiler (water heater) installed, which was powered by one of the 16-amp circuit breakers (2 kW boiler).
Moreover, this water heater was installed extremely carelessly: it was powered by a separate cable, this cable ran openly in the bathroom, without any protection in the form of a corrugation or box.
And when you take a shower (as they said in the movie “Moscow Doesn’t Believe in Tears” - sorry for such intimate details..) this cable, along with the boiler, becomes completely covered with moisture (condensation). My wife, of course, was not embarrassed by this fact, since she does not understand these issues, but it was very alarming to me. That's why I decided to install an RCD in a two-wire network.
So, there were two automatic machines in the panel, from one the entire apartment was powered (lighting and sockets), from the second only the boiler was powered. After thinking a little, I decided to install a separate residual current device on each line separately: a separate RCD for the sockets and a separate RCD for the water heater. Although of course it is a little expensive, safety is paramount.
Moreover, I would like to divide the network, i.e. Connect all sockets in the apartment and separate lighting to a separate machine. But for lighting it was necessary to run a separate cable from the panel to the apartment.
The maximum that can be done is to stretch a separate cable from the panel into the apartment to the first junction box and connect lighting only in the hallway; in other rooms it is not possible to connect lighting from this cable, since in the apartment all the wiring is walled up in the walls. Therefore, the lighting and sockets remained on the same machine.
To connect the residual current device, I chose the IEK brand VD1-63 series with a rated current of 16 A and a differential current of 30 mA.
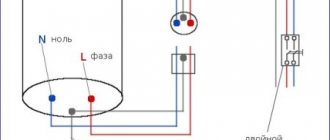
I already wrote in the article on errors when connecting an RCD that it is impossible to combine zeros after an RCD. The connection in the panel is made in such a way that the phase goes through the machine, and the zero is taken from the panel body. To connect the RCD, we disconnect the power cable from the circuit breaker (phase) and from the metal part of the panel (zero).
Having installed the RCD in the panel, we proceed to the connection. We immediately connect the phase and neutral of the supply cable to the output terminals of the device (for the apartment to one RCD, for the boiler to the second).
We start the phase at the input of the residual current device from the output terminal of the circuit breaker, and at the zero input we take zero from the panel body. Thus, the neutral conductors of the wires that came out of the RCD and go into the apartment are no longer combined with other neutrals (there is no connection with the panel body).
The connection is completed, you can check the residual current device itself, how it behaves in operation, and whether false alarms will occur if it is connected incorrectly. To do this, you need to turn on the circuit breaker in front of the residual current device and, of course, the device itself, then create a load (plug any device into the outlet). If no disconnection occurs, we can assume that all connections are made correctly.
Also, do not forget that after connecting the breaker or RCD, you must check them for leaks. How to check the RCD for tripping in this case? Of course, using the TEST button.
To do this, when the device is turned on, press the button; if, when you press the button, it turns off immediately, it means it’s working properly. This is how, using a personal example, I connected the RCD without grounding.
Source: electricvdome.ru
1
Electrical protection - what devices provide it
It is possible to connect an RCD without grounding, which is absent in old buildings, as in most private houses, and it will fully do its job. But electrical safety is not ensured by these devices alone. Almost everyone is familiar with plugs and circuit breakers that break the circuit when the load increases above the permissible level and a short circuit occurs. They protect wiring and home electrical devices from damage and more serious consequences - fire, fire.
When detecting a current leak, the residual current device turns off the electricity
Circuit breakers cannot protect against electric shock. This role is assigned to residual current devices. Damage is possible when a person, for example, touches both a current-carrying device and tap water, and a current passes through his body. If there is a current leak, the device immediately reacts by breaking the electrical circuit. The response time, which depends on the minimum current, is extremely important.
All current protective devices are installed in the distribution panel. It has installation containers where various modules are attached. Residents find it very convenient to use the devices together, especially when they are signed. Then the necessary devices turn on or off without error. The protection installed in the switchboard makes the connection diagram convenient and understandable.
We recommend
How to calculate the current strength How to connect machines after the meter How to connect an intercom - installation diagrams and installation tips
Will a difavtomat work without grounding?
A differential circuit breaker is a switching device that combines a circuit breaker and a residual current device. It can also easily operate in a two-wire network without a grounding wire. The principle of its operation is similar to the functioning of an analyzer, which compares the electric current readings of wires looking for the “phase” and “neutral” marks. If a short circuit or any other emergency situation suddenly occurs, the sensors detect this, and the device contacts automatically open and the wiring is de-energized.
You might be interested in this: Installation of a three-phase meter
Note! Let's take a washing machine as an example. If there is a break in the wires and one of them comes into contact with the body, the person will receive an electric shock. If the device detects that the electricity is not being distributed where it is needed, it will turn off the network and the user will not be harmed.
Connecting the difavtomat to an ungrounded network is carried out without problems
How to connect a water heater to electricity - errors, choice of cable, socket, machines
For a comfortable stay in the house, when you want to constantly use hot water, and not depend on the repair schedule of monopolists who can turn off this water for an unknown number of days, many people think about purchasing a boiler.
Most often, the choice falls towards a storage water heater. They come from different companies: Ariston, Drazice, Baxi, etc., shapes and designs - flat, cylindrical or elongated.
The installation of cold and hot water pipes may differ, but they are all connected to the 220V network in the same way.
Many people mistakenly believe that in order to connect the boiler, you just need to plug the plug into the socket and not worry about anything else. However, they forget that it is in the boiler that, in case of insulation failure, direct contact of electricity with a person can occur through water. What you should pay special attention to when connecting the boiler:
- selection of the cross-section of the supply cable (depending on the power of the boiler)
- selection of a circuit breaker for power supply to the boiler
When renovating new apartments, the boiler is usually wired separately directly from the panel. If you want to connect the boiler to the old common wiring, which already has several sockets connected, be sure to make sure that it can withstand the power of the boiler.
In most cases, with a power of up to 3.5 kW, wiring must be done with a 3-core copper cable VVGnG-Ls, with a cross-section of at least 2.5 mm2.
The three-core cable is required to ensure a permanent connection to ground.
Choose a two-pole boiler connection machine. The rated current of the machine is 16A (sufficient for boiler power up to 3.5 kW).
For loads up to 2 kW, a circuit breaker with a rated current of 10 A is suitable.
If the boiler is connected from an outlet, then the outlet must have a degree of protection IP44. These are sockets for rooms with high humidity levels.
Remember that the socket in the bathroom can only be placed in certain places. And there are areas where doing this is strictly prohibited. You can read more about this in the article “Socket in the bathroom - 5 placement rules.”
And for those water heaters that initially come with plugs, if you cut them off, you can sometimes void the warranty. Therefore, read the instructions.
If it says that this boiler can be connected in two ways
- and via the standard power cord
then you will not lose the guarantee here.
In addition, if you need to dismantle the device from the wall, if there is a plug, you will not need to call an electrician to disconnect it from the power supply. Pull out the plug, take it off, rearrange it, do whatever you want.
Powerful boilers over 3.5 kW should only be connected directly through a circuit breaker; a socket connection is not allowed here.
The cable must be routed so that there are no intersections with water pipes and places where the heater will be mounted.
It is mandatory to install an RCD - a residual current device - in the boiler supply line. Select its current one order of magnitude higher than the current of the machine.
Leakage current for RCD – 10mA or 30mA.
Why 10mA is better and not more can be understood from this sign of the effect of current on the human body:
A significant disadvantage here is that at 10mA the protection may falsely trigger. Especially if your water heater has been hanging for more than a year and such condensation and moisture often form in the places where the terminals are connected.
How can I check if this is a false positive or if the heating element itself is faulty? To do this, use a multimeter.
Turn off the power supply or pull out the plug from the socket and disconnect the standard grounding from the titanium body.
Then remove the terminal clamps from the heating element itself, and using probes, measure the resistance between the boiler body and the heating element.
If the heating element is working properly, the readings on the multimeter screen should tend to infinity, that is, they should be something like this:
In case of breakdown and damage to the heater, they will either be zero, but most often they can be several hundred or even kiloohms. In the photo below this is exactly the option ~ 500 kOhm.
Very often, in many of the latest boiler models, an RCD with a leakage current of 15 mA is already built into the cable for connecting to the outlet. In this case, it may not be necessary to install an additional leakage current protection device in the panel.
However, do not forget that such a built-in RCD will protect against leakage only if there is damage in the heater itself, but will not protect you in any way if there is a fault directly in the outlet or the supply wiring to it.
How to find these and other similar faults and what this can lead to can be found in the article “Electric shock in the bathroom. 5 reasons and what to do?”
What to do if you are not an expert in electricity and you yourself cannot or do not want to go into the electrical panel in order to install all the required protection devices there. But you still need to protect yourself.
Plug it into the existing outlet in the bathroom, and through it you plug the plug from the boiler cord.
Will the residual current device on the boiler trip if you do not have a ground connection? Will. These two systems, when working together, are designed to complement each other.
In the event of a current leak on a boiler without grounding, the protection device will only work when you directly touch the tank or the water from it (with the heating elements turned on). And if there is a grounding conductor, then the RCD will work immediately after voltage is applied to the titanium, without waiting for your touch. That's the whole difference.
How does an RCD work with and without grounding?
The RCD works as follows: when a breakdown occurs in the wiring or in a consumer device, the RCD will not work, since the body of the device is not grounded and does not have a path for current leakage to pass through. In this case, the electrical appliance will be under serious voltage, and under no circumstances should you touch it.
When a person touches the device, current will flow through his body into the ground. It is when its value equals the threshold value of the RCD that the network will be disconnected.
Note! Exactly how long a person will remain under voltage depends only on the time and threshold operation of the residual current device. In any case, this will happen quickly, but the victim, even in such a short period of time, can receive an electrical burn or other injury.
It's another matter when the case is connected to ground. In this case, the protection device would turn off instantly. From this we can conclude that the connection diagram for circuit breakers and RCDs without grounding can work safely, but this will not provide a 100% guarantee of human safety in the event of emergency situations
An example of how to connect a difavtomat to a two-wire network
Connect without grounding
How to properly connect an RCD
Connecting an RCD in the absence of grounding is done quite often in many apartments and old houses. Since in old-style houses there are usually power cables with one phase and zero, it is not possible to connect grounding. To make grounding, you will need to install a grounding protective loop around the perimeter of the building, and be sure to change all the wiring in order to place a new cable with “ground”. Only connecting such a core to a special conductor for sockets or individual contacts on powerful household appliances will allow grounding to be done in an apartment or private house. By combining such protective measures together with an RCD and a circuit breaker, it is possible to provide a residential building with all the necessary measures to prevent accidents.
However, many people simply do not have the opportunity to replace all the wiring in the apartment, since today this is an expensive update. For this reason, an RCD without grounding is installed. Despite the fact that the electrical network is not grounded, you should not ignore the connection of the residual current device. The protective equipment itself does not have terminals for the grounding conductor. It has places for connecting a phase and a working zero. Since this device has a completely different purpose, there is no need to make separate grounding points for it.
Connection diagram for a two-pole RCD
A connected RCD in the absence of grounding is expected to cut off the supply of electricity to the network when the potentials of the incoming and outgoing current change. Therefore, if there is no grounding structure in the house and a three-wire wire is not installed, there is also no reason to refuse to connect other types of protective equipment. It is advisable to simultaneously install a residual current device and a circuit breaker. The latter device will prevent short circuits in an apartment or private house if the cable is damaged, as well as prevent burnout of household appliances during voltage surges in the electrical network. An RCD cannot protect or warn against such things. It is designed to prevent AC leakage in the circuit.
According to the Electrical Installation Rules (PUE), you cannot use RCDs that react to differential current in three-phase circuits with four wires (the grounding is combined with the working zero). If you install a residual current device on the entire electrical network, then this circuit will be simpler. When connecting an RCD without grounding, you must know the parameters of the power cable that is laid in a private house or apartment, as well as the total current value, when calculating the simultaneous connection of all household appliances to the network.
Typically, the installation diagram of protective equipment provides for sequential connection of all elements. Even if changes are made to the new circuit by adding a new source or element, the sequence should not be broken. In this case, it will simply be connected to the appropriate section of the electrical circuit. For single-phase electrical wiring in which there is no grounding conductor, the residual current device must be placed in front of the distribution panel and in front of the energy supply meter. Then there are circuit breakers (if there is more than one) and a voltage equalizer. If you follow this scheme, you can exercise full control of all the wiring in the house, and not just its individual branch.
For individual branches with powerful electrical equipment, circuit breakers are installed that will respond to high voltage without turning off the power supply throughout the house. The most common scheme for connecting an RCD is the one designed for a single-phase power cable with a voltage of 220 volts. If the owners want to install less powerful protective equipment on each line with powerful equipment, then such a scheme will have a slightly different look. It is recommended to make connections separately for the bathroom, garage or workshop, basement, and also for the kitchen. There are often large studio kitchens where quite a lot of electrical appliances are connected to the circuit at the same time. In such a situation, it is advisable to divide the residential building and adjacent premises into separate areas with electricity consumption, providing each with independent protection.
Which is better: RCD or grounding
As has already become clear, an RCD is capable of measuring leakage current, but in a situation where a breakdown occurs on the device body, if it is not grounded and no one touches it, then the device will think that there is no leakage. It will appear only when touched, but this will be a fact of electric shock.
Speaking about which is better, we can say that these protection methods equally protect a person from emergency situations that can happen in the network, and when used together, they also warn him that the electrical installation used is faulty.
It is quite possible to connect an RCD to a circuit without grounding
Protection against electric shock
The operation of a differential circuit breaker or residual current device (sometimes called differential relays) is based on determining the difference in phase and zero currents.
If a difference exists, the device turns off the electricity supply. The difference can be recorded when a current leak occurs. When an electrical appliance or equipment is in good working order, there is no leakage in it, that is, the value of the current flowing through the phase conductor is equal to the value in the neutral conductor.
If the insulation of a phase wire is damaged, a potential difference arises between it and any grounded object. The same thing happens when there is a breakdown on the body of an electrical device. Grounding in this case will only help remove this potential difference from the housing, but the device itself will remain energized.
If a person touches the body, the latter most likely will not feel the impact of electricity, because the resistance of the body is greater than the resistance of the grounding conductor. You can imagine what would happen if the grounding is faulty or absent altogether.
If such a situation occurs, the differential machine will turn off the electricity supply and de-energize the device. A person, even if exposed to electricity, will not feel it, because the current value will not exceed 30 milliamps, and the shutdown time will not exceed 0.3 seconds. Such parameters for RCDs and automatic circuit breakers used in residential premises are determined by the standards.
How to properly connect an RCD without grounding
The connection process is as follows:
- De-energize the work site.
- Attach the RCD device to the DIN rail.
- Distribute the phase output of the RCD among all machines.
- Enable automatic input.
- Check that the connection is correct.
You might be interested in How RCD works and what it is
Diagram demonstrating how to install an RCD in an ungrounded network
Thus, it was explained how to connect an RCD in an apartment without grounding. You can connect the device to input machines, but this will not provide a 100% guarantee of safety. It is best to connect a difavtomat or RCD to already grounded networks.
Protective devices
A circuit breaker (circuit breaker) is a device designed to interrupt a circuit when a short circuit or significant overcurrent occurs. If a person receives an electric shock, such a device will not react, since the leakage current is small. To ensure safety from electric shocks, RCDs are used.
A residual current device is a device that is designed to protect a person from leakage currents. For example, if during operation a device that is used without grounding suddenly breaks through to the housing, then the residual current device will instantly operate and turn off the electricity. In other words, an RCD is designed to protect a person from electric shocks that can occur when wires are exposed.
Residual current device manufactured by ABB, model FH202-AC-40, 63 A
Rules for choosing ouzo
The most frequently asked question when installing and connecting washing machines: is it necessary to install an RCD for a washing machine? The answer is simple - yes, it is necessary. After all, the washing machine itself is a fairly energy-consuming device, and also operates in an environment with high humidity, due to which it belongs to the category of increased danger. That is why the installation of an RCD is necessary when connecting washing machines to the power supply network.
In order for the washing machine to serve for many years, and its operation to be safe, it is important to choose the right residual current device. To do this, you must follow the following rules:
- Device power. The choice of RCD for a washing machine based on power is based on the rated power of the electrical network. There are single-phase and three-phase devices.
- Mains voltage. Single-phase RCDs are designed for 220 V, and three-phase RCDs are designed for 380 V.
- Current strength. The most common RCDs, which are recommended by experts, have 30 mA protection. It can be set to 10 mA, but a similar degree of protection is not required for household electrical equipment.
- Design features of the RCD. Since the washing machine has a high level of power consumption, it is better to choose a class A residual current device. It is also possible to install class AC, but this type does not always perform its function well.
- Features of the release and marking of the machine. An RCD marked “C” is suitable for the electrical network in an apartment or private house. There are also devices with digital markings; in this case, the correct choice would be a device with a C16 marker or, more rarely, a C25.
- Additional levels of protection. Some RCD models do not have a protection system in case of a break in the neutral conductor, which leads to the device ignoring current leaks.
Is it dangerous!
Several reminders and warnings regarding safety precautions when doing electrical wiring yourself.
Attention! Installing sockets, switches, and electrical appliances in the bathroom without using a 10 mA RCD is deadly!
Do not voluntarily connect the neutral wire to your ground. That is, do not re-ground the neutral wire at the input and, accordingly, ground electrical appliances.
In case of emergency situations on the supply line, such as no contact; break of neutral conductor; conductor burnout; erroneous reversal of phase and neutral; overlapping of wires on overhead lines - the only neutral of all houses through your grounding can become your grounded neutral.
If re-grounding is done at home, without following the rules and appropriate qualified tests, the grounding is unlikely to withstand such accidents and may burn out. At best, there will be a fire, and even if it survives, there is no guarantee that it will provide safe touch voltage on open conductive surfaces.
In this connection, it is inevitably fatal and criminally liable for violation of the rules for operating electrical installations, electric shock through electrically connected open conductive surfaces and the risk of fire!
Always remember, when doing any work on electrical wiring, turn off the power supply to the lines, or better yet, the general apartment circuit breaker (this especially applies to old houses). In old houses, the more you work, the more you marvel at the intricacies of the old electrical wiring.
That's all about errors when connecting an RCD! Good luck to you in your endeavors!
What is the difference between a shutdown device and a difavtomat?
Both types of devices are designed to protect against electric shock when a leakage current to ground occurs, and to disconnect the load in this case. That is, they protect us from electric shock in case of damage to the insulation, and in the case of a bathroom, in case of breakdown through moisture. However, the differential circuit breaker has one more, perhaps main, function - disconnecting the consumer when the load current exceeds the rated one for a given circuit breaker and there is a short circuit.
Differences in Features and Settings
The main characteristics of an RCD are sensitivity (minimum leakage current at which it triggers) and rated operating current. For the bathroom, you should choose devices with a sensitivity of 100 to 300 mA and a rated current equal to the current consumption of all connected electrical devices. For example, if you plan to install a washing machine in the bathroom, the operating current of the device is selected equal to 16 amperes.
The main characteristics of an AV with a differential block are the operation (shutdown) current and the differential shutdown current. There are machines with operating currents from 1 to 300 A and settings for shutdown by leakage current of 10 and 30 mA.
So, the main differences between the RCD and the automatic differential switch:
- both devices will protect us from electric shock, but the machine will also turn off the load if the power consumption exceeds the norm; the first one will simply fail during long-term operation in this case.
- the difference in leakage response currents (for AVs is much less) also limits the scope of application of both devices.
- significant difference in cost.
How to distinguish RCD from differential. machine - watch the video:
What to use to protect electrics in the bathroom
In relation to the power supply of powerful devices in the bathroom, it is more advisable to install a separate RCD unit, as a device specially designed and intended for these purposes. In addition, the high sensitivity of differential protection in an AB can provoke false alarms when connecting a washing machine, mainly due to high-frequency interference from its electronic components; by the way, this is why it is not recommended to install differential circuit breakers in the computer’s power supply circuits. The area of application of differential circuit breakers is electrical lighting circuits.
Connection diagram of the residual current device. To connect the protection device, it is necessary to have a third protective conductor in the circuit. When turned on without this wire, the device will not perform its functions.