The slab foundation of a private house is used if construction is carried out on difficult types of soil. In this situation, other options will not be suitable, since they will not withstand the load and vibration. A slab foundation is expensive, but usually if you choose it, then other options are simply not possible.
A slab foundation is a monolithic reinforced version that is laid under the entire area of the future building. It is used in cases where other types are not suitable, since they will affect the soil, causing severe shrinkage. The slab ensures uniform distribution of the load on the soil, so shrinkage is not observed.
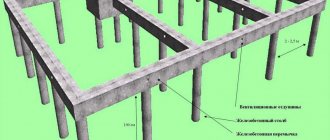
Construction of a slab foundation
The slab foundation structure includes a multilayer structure. In the list, the layers are presented in ascending order from the very bottom:
- Priming;
- Sand pillow. You can also use fine gravel if it is not possible to deliver or buy that amount of sand;
- Special geological textiles;
- Concrete preparation. This is a small layer of concrete that is poured onto geotextiles. It is not reinforced;
- Waterproofing so that the foundation base is not exposed to aggressive moisture;
- Reinforced concrete.
We make a slab foundation for a house with our own hands. Step-by-step instruction
To make a slab foundation with your own hands, first of all you need to think over the plan of the house, since you will have to fill the foundation for its entire area, including small extensions. After applying the markings, follow the instructions:
- Dig a hole to a certain depth (depending on the number of floors of the house).
- They compact the soil. If the ground is initially hard, compaction is not required. It is best to perform compaction using heavy special equipment.
- Sand or fine gravel is poured in, after which compaction is performed again. If there is no special equipment, the sand can be filled with water, and it will compact in a few days under its own weight.
- Dornite gasket (geotextile). It is laid to protect the concrete base from the underside from moisture.
- Concrete pad. Usually its thickness is approximately 5 cm. It is made to level the surface for the following work.
- Laying bitumen sheets for waterproofing. Construction stores sell rolled bitumen sheets, and they can be laid very quickly. No additional fastening is required; simply cover the entire surface.
- Assembly of the reinforcing frame. Can be made from old pipes or fittings. But you can also buy special reinforcing mesh in a ready-made version
- Pouring concrete mixture.
We make a slab foundation for a house. Step-by-step instruction
Installation of a slab for the foundation
To obtain a reliable, durable foundation for a house, it is important to choose the right material. Particular attention is paid to concrete. The following requirements for it should be highlighted:
- water resistance must correspond to at least category W8;
- In terms of strength, concrete with a grade of at least M300 is selected;
- frost resistance must correspond to F200;
- The mobility of the solution during manual pouring is sufficient P3.
To reinforce the slab, you can use any steel reinforcement with a periodic profile with a diameter of at least 12 mm. Often preference is given to A500C rods, which have the necessary strength and are designed for welded joints.
At the preparation stage, you should also prepare the necessary tools - a shovel, a crowbar, a grinder for cutting reinforcement, a knife and scissors for cutting rolled materials, a hacksaw for metal, a hacksaw and a hammer for making formwork, pliers, a hammer drill.
When preparing and pouring the solution, you will need a vibrator, a construction mixer, a trowel or trowel, a grater, and a rule. Quality control and measurements are provided by a building level, tape measure, metal ruler, square.
Earthworks and formwork
To build a slab foundation, it is necessary to carefully prepare the construction site. First of all, the fertile layer of soil is removed and the site is leveled using a level. If necessary, additional soil is brought in, which is backfilled on the site and compacted. It is advisable to use a vibrating platform for this.
The next step is digging a pit (“trough”). The size of the pit exceeds the dimensions of the slab by 20-30 cm for installing the formwork. Its depth is chosen to be 30-40 cm greater than the height of the buried part of the foundation. The bottom of the “trough” is carefully leveled horizontally and compacted.
drainage outlets on it . Next, the bottom is covered over the entire area with geotextiles. This layer will keep the cushion from migrating into the ground, while freely allowing moisture to pass through.
An important stage of preparatory work is filling the pillow. To do this, pour a layer of sand, and then a layer of crushed stone or gravel. The total thickness of the pillow is on average 30 cm.
If construction is carried out on highly heaving soils, then the thickness increases to 40-45 cm. Every 8-10 cm of backfill, compaction is performed (recommended with a vibrating plate). Communication pipes and drainage pipes are laid inside the cushion.
The preparatory stage ends with the installation of formwork. It is installed along the entire perimeter of the future foundation slab and strictly determines its dimensions. Installation begins with installing beams at the corners with a height equal to the height of the foundation.
A cord is stretched between the beams, following which intermediate beams are driven in increments of 1.5-2 m. Plank walls are nailed to the vertical beams. Boards 15-20 cm wide and 2.5-3 cm thick are used, which are tightly fitted to each other.
From the outside, the formwork is strengthened with jibs (supports). Particular attention is paid to the strength of the corners. When installing the formwork, you should remember that the surface of the slab is formed along the upper edge of the board, which means that the horizontalness of the foundation depends on the evenness of the installation.
We recommend reading: How to properly prepare a plot of land for construction?
How to properly prepare concrete?
The reliability of a slab foundation increases significantly in the presence of such an element as concrete preparation (concrete footing). Taking into account the large area of the main pour, the footing performs the following functions: preventing concrete from leaking, uniformly distributing the solution, mitigating the effects of sudden swelling of the soil, and simplifying the correct installation of the reinforcement system.
Concrete preparation parameters are determined by SNiP 52-01-2003 . Among the main provisions, the following norms should be noted:
- use of lean concrete based on a mixture of grade M50;
- layer thickness is 5-10 cm;
- exposure after pouring for 28 days for the material to gain strength.
Lean concrete for footings contains only 6-7% cement. The mixture contains a minimal amount of ingredients, which speeds up the hydration process, and therefore the hardening of the mass. The solution is poured into the formwork over the entire surface and carefully leveled using the rule. The evenness of the surface is controlled by the building level.
Laying waterproofing
Waterproofing a slab foundation is considered a mandatory structural element. It must reliably protect the concrete slab from soil moisture and flood waters. The waterproofing layer should protect the slab both from below and from the sides. Protection can be provided using rolled, coating and sprayed materials that are waterproof.
The most commonly used are roofing felt and thick polyethylene film . Bitumen coating is used as additional insulation . The rolled material is laid on top of the concrete preparation with overlapping strips. The overlap length is at least 15 cm.
To provide lateral protection, the material is lifted onto the formwork walls (from the inside). The modern construction industry offers improved polymer materials that effectively act as waterproofing.
Insulation
Thermal insulation in a slab foundation is an optional, but desirable element . Its installation is especially important during construction in cold regions. The insulation can be laid on top of the waterproofing or on top of the foundation slab when making a floor screed. It should not be forgotten that thermal protection is significantly deteriorated in the absence of end insulation.
We recommend: Building a foundation for a private house with your own hands. All stages of work from design to pouring
The following materials are used as thermal insulation for a monolithic foundation.
Styrofoam
It is technologically advanced, easy to install, does not rot, and is highly water resistant. Among the disadvantages are toxicity when heated above 50 degrees, fragility and flammability.
The material is available in the form of slabs of various thicknesses. It is widely used as insulation for foundation slabs, incl. due to low cost.
Extruded polystyrene foam
In appearance it resembles polystyrene foam, but differs in the manufacturing method. It has good thermal insulation properties and increased strength. Available in rolls and slabs.
Slab foundation for a house made of aerated concrete
When it is planned to arrange a slab base for an aerated concrete house, the following steps are performed:
- Calculate the required base thickness.
- Try to accurately calculate the mass of the house, taking into account the loads (even specialists cannot calculate it accurately, so the average value is usually taken as a basis).
- Determine the perimeter (based on the area of the future house).
- Calculate the mass of the base and, in accordance with the results, determine the amount of building materials.
- Determine the length and width of the reinforcement.
Next, the process is carried out according to the above instructions.
Step-by-step instructions for installing a slab foundation
Step-by-step diagram of the slab base installation
Surveys and calculations
Taking soil samples
When designing a monolithic slab, it is necessary to take into account the experience of similar structures in the region, the results of surveys (ground level, nature of the soil, bearing capacity of the layer), conditions of the technical specifications (number of storeys, wall, roofing materials). The survey includes a minimum of five geological pits (corners + middle of the slab).
The result of the research is the characteristics of strength, deformation of different layers of soil in the building area, prediction of changes in the chemical composition during the operation of the home, and the degree of aggressiveness of groundwater.
It is necessary to compare several solution options to identify the best combination of construction budget and technical characteristics. Step-by-step calculation instructions:
- concrete grade – M200 and higher for slabs, M50 for preparation, according to SNiP 2.02.01 for the foundations of structures and buildings;
- groundwater depth – anti-corrosion measures in the presence of high water;
- when calculating prefabricated loads, the weight of the slab on sandy soil is not taken into account;
- The load-bearing capacity and deformations that can destroy the structure are calculated.
For this purpose, special programs are used that have proven the performance of foundations manufactured based on their results in real operating conditions. The main documents at this stage are:
- soil classification – GOST 25100;
- enclosing and load-bearing structures – SP 70.13330;
- anticorrosive structure of the building's load-bearing frame - SP 28.13330;
- design, manufacturing MZF – VSN 29-85; 37-96.
Unlike strip foundations, the slab has an increased support area, prefabricated loads from the building are distributed evenly, and the strength margin is very large.
Marking and excavation work
Removing the fertile soil layer
It is forbidden to pour the slab over the fertile layer. The house layout diagram looks like this:
- axes - are carried out in the building area with a cord attached to pegs installed beyond the perimeter of the drainage system;
- the pit is 0.5 meters larger than the slab on each side (for drainage), the slab protrudes beyond the dimensions of the building by at least 10 cm (depending on the project).
Due to the small amount of work required to remove the fertile layer (20–40 cm) for a residential building, the work is carried out with one’s own hands without the use of special equipment. At this stage, it is necessary to ensure protection of the monolithic structure from soil moisture (overwater). To do this, drains are laid around the perimeter:
- geotextiles extending to the edges of the ditch;
- layer of compacted crushed stone;
- perforated pipe (corrugated or smooth in a dornite filter) with a slope towards the underground reservoir;
- backfilling with a natural filter (crushed stone fraction 10/20);
- covering with the remaining geotextile.
Drains must not be installed under a concrete preparation or foundation slab. The height of the backfill should be level with the crushed stone base cushion.
In addition, after pouring the slab into the building, it is impossible to enter communications, so cold water and sewage pipelines are laid at the same stage. They do not have to be buried below the freezing mark, since the thermal insulation of the base of the slab will retain geothermal heat and the ground under the cottage will not freeze. A depth of 1 - 1.2 m is sufficient.
Substrate
We arrange a sand cushion. Sealing is required.
Another measure to reduce heaving forces is the substrate. It is made by hand using the following technology:
- layer-by-layer compaction of sand - 10 cm backfill, abundant moisture, compaction with a vibrating plate, a second layer of similar thickness;
- layer-by-layer compaction of crushed stone - fraction 10/20, similar.
Lay a layer of crushed stone.
Instead of crushed stone or sand, a mixture of ASG can be used to a depth of 40 cm with compaction using the specified method. Only in this case will the monolithic foundation of the house receive reliable support on the lower layer.
Concrete preparation and waterproofing
We do concrete preparation.
A monolithic slab requires a lower waterproofing cutoff to prevent corrosion of the concrete and reinforcement inside it. Laying a waterproofing carpet made from roll materials over a layer of crushed stone does not satisfy the operating conditions:
- sharp edges of stones cut through the material;
- the seams cannot be properly sealed.
Therefore, when building the foundation of a house with your own hands, concrete preparation is often used. This is a regular screed that solves two problems:
- providing a flat surface on which it is easy to stick the bitumen base of Bicrost, Linokrom, Technoelast, and reliably seal the seams;
- creating a level base for the slab, strengthening its strength, and stabilizing its geometry.
We install waterproofing.
The method of pouring into the formwork is standard, the thickness of the screed is 5 cm, no reinforcement is required. Roll materials provide a minimum construction budget, impregnation, primers are not used here. The recommended overlap of the strips is 15 - 20 cm, the seams are treated with hot or cold bitumen-based mastics. The edges of the waterproofing carpet extend beyond the perimeter of the concrete preparation so that after pouring the slab, they can be launched onto the sides and top surface.
Insulation
We lay insulation under the entire area of the building.
Extruded polystyrene XPS is used as a heat insulator. It is laid in two layers (10 + 10 cm) close together for smooth slabs. If the project provides for stiffening ribs, the first layer is laid end-to-end with your own hands, in the second layer gaps are created along the width of the ribs:
- along the perimeter;
- perpendicular to the long wall after 3 m.
In this case, the monolithic slab has a large margin of safety, and the house is free from distortions during operation.
Reinforcement
We create a reinforcement frame in accordance with the project.
Reinforcement of the slab with reinforced belts is carried out in accordance with the regulatory documentation for reinforced concrete and concrete structures SP 63.13330. The reinforcement scheme looks like:
- production of clamps - a smooth 6 mm rod, bent in the form of a square or triangle;
- creation of reinforcing mesh - longitudinal, transverse bars of a periodic profile with a diameter of 12 - 16 mm, connected with knitting wire or connected by welding (cell 15 x 15 cm);
- reinforcement of stiffeners - four longitudinal rods connected with clamps;
- laying the lower chord - installed on concrete pads (thickness 15 - 25 mm, section 10 x 10 cm) to provide a protective layer (the reinforcement must be recessed in the concrete);
- installation of the upper belt - clamps are placed on the lower mesh, and the upper card is attached to them.
The slab is reinforced at the ends with U-shaped clamps.
It is not advisable to use separate rods inside the armored belt. They need to be bent in curved sections, in places where communications enter nodes with common grid maps. To save reinforcement, the cell in some cases is enlarged to 20 x 20 cm.
Formwork
We install and strengthen the formwork.
To fill a monolithic structure with your own hands, you need to install formwork around the perimeter. It is constructed from OSB, chipboard, plywood or edged boards in the form of panels. The inner surface is sheathed with roofing felt or film to prevent concrete from spalling during formwork removal. The main document for the construction of formwork are GOST R 52085 standards; 52086.
The panels are mounted around the perimeter; to protect the structure from freezing, 10 cm of polystyrene foam can be placed vertically inside them. This insulation is also laid under the blind area of the house to prevent lateral freezing. It is laid at the level of the base of the slab, flush with the bottom or top layer of heat insulation inside the formwork.
Pouring and maintaining concrete
Pour concrete into the formwork and level the surface. Sealing is required.
Requirements for the design and manufacture of MZF are specified in the VSN 29-85 standards; 37-96, according to which the work is carried out. When filling, the following conditions must be met:
- filling the formwork with concrete in one step;
- the maximum interval between feeding the mixture with a mixer after vibration compaction of the previous section is 2 hours in warm weather;
- It is forbidden to move concrete with shovels around the entire perimeter from one place - it is necessary to rearrange the mixer or use a concrete pump;
- vibration compaction is carried out until cement laitance appears, crushed stone is hidden and there are no bubbles;
- the step of lowering the nozzle of the deep vibrator cannot exceed its radius of action;
- in winter, the mixture is heated with a cable laid inside the formwork, covered with film materials, and heated with steam;
- vibrator attachments are prohibited from leaning against the mesh of armored belts;
- stripping is possible on the fifth – seventh day under normal conditions;
- The surface of the concrete must be protected from precipitation, covered with burlap, and wetted from a watering can in hot weather.
If technologies, recommendations for the selection of materials, and reinforcement sections are followed, the slab foundation will not require restoration and will serve at least three generations of property owners. All of the above technologies comply with the requirements of the specified regulatory documents and have operational experience in the regions of the Russian Federation.
Slab foundation for a two-story house
Considering that a two-story house provides a much greater load (especially if it is made of heavy materials like concrete or brick), the work ahead is much more difficult. There are several distinctive features when arranging the foundation for such a structure:
- Improved waterproofing. It is necessary to use several layers of waterproofing. It is also recommended to perform additional waterproofing during pouring.
- Increasing the thickness of the foundation to 30 cm.
- Using a monolithic slab with lower ribs to evenly distribute the load on the ground.
How thick should a monolithic foundation slab be?
The slab foundation is considered the most reliable and is chosen when building houses on unstable and floodable soils. This type has minimal impact on the ground and ensures that all weight loads are evenly distributed. The pouring technology itself is simple, the main emphasis is on calculating the parameters of the slab, namely: laying depth, cushion height, grade and thickness of concrete, reinforcement cross-section, and insulation needs. The range varies from 15 to 35 cm; if the calculated value is different, then other base options are considered.
Thickness of the foundation slab for an aerated concrete private cottage.
Features of a slab foundation.
It is a concrete monolith with two rows of mesh reinforcement, placed on top of a compacted sand cushion, and in particularly difficult cases, reinforced with stiffening ribs from below. The cost of its construction depends on the depth of the foundation: on stable soils it is practically equal to the ground and requires minimal investment and effort. On floating soils or if it is necessary to organize a basement space, up to 1/3 of the general construction budget is spent on a slab foundation, since the laying is carried out below the freezing level.
For stable soils.
For very heaving people.
The thickness of the slab for a wooden house depends on the number of storeys; when using well-dried materials, their specific weight does not exceed 600 kg/m3, which is 2.5-3 less than that of brick. As a result, the recommended value is 30 cm.
Thickness of the foundation slab for a one-story aerated concrete cottage.Slab foundation for a frame house
Since the frame house has a lightweight structure, you can relax a little when arranging the foundation. However, it still remains the basis of the house, so it should not be treated irresponsibly. When creating a foundation for a frame house, follow the standard instructions. But there are some additional tips:
- Use the “inverted bowl” foundation, because then it will be possible to think through the location of the load-bearing walls.
- Take the initial calculations responsibly. In such a house, communications are often combined with the foundation. But errors cannot be corrected later, so high accuracy of calculations is required.
Slab foundation for a brick house
A brick house is one of the heaviest. Even without furniture or decoration, it places a serious load on the foundation. Therefore, the approach should also be serious:
- Each stage of foundation formation must be carried out with the utmost responsibility.
- It is necessary to calculate the approximate load and take the maximum parameters as a basis. It is better if the foundation is stronger than the potential load on it than to crack under the weight of the house.
- Perform external and internal waterproofing and insulation to reduce negative impacts and extend service life.
Slab foundation for a timber house
Despite the fact that timber is not a heavy material, this does not mean that the foundation should be weak or absent altogether. It is necessary to pay special attention to several points:
- High quality waterproofing. It is recommended to purchase special materials to carry out this process, since wood is more sensitive to moisture than all other materials.
- Light foundation thickness, but using an "inverted bowl" format to distribute the load without spending too much on the foundation of the house.
In any construction, the foundation is the basis on which a lot of time and money are spent. It is also worth noting that you cannot proceed to the construction of the structure itself until the foundation dries well. This will take several days, or even weeks.
What does the indicator depend on?
The slab in this case is a monolithic reinforced base under the entire area of the structure.
The power structure consists of fundamentally significant layers:
- compacted cushion made of non-metallic materials;
- heat insulator and waterproofing;
- footings, as well as the concrete slab itself with an embedded reinforcement frame.
The thickness of the monolith determines the strength and reliability of the base and depends on a number of parameters, including:
- characteristics of the soil under the supporting base area;
- laying depths of the power structure;
- design loads, which are determined by the design features of the structure, operating conditions, and climatic conditions in the region.
Professional designers take into account all of the above factors, which requires a thorough understanding of the technology and experience in laying slab structures.
Private developers, in order to save on the services of specialists, use a simplified methodology, which is based on taking into account three parameters:
- reinforcement thickness;
- gap between reinforcing chords;
- thickness of concrete above and below the reinforcement cage.
As a rule, if you add up the three indicated parameters, you get a slab thickness value ranging from 0.2 to 0.3 m. The final indicator is adjusted taking into account the characteristics of the soil, the uniformity of rock occurrence and the complexity of the design of the future building.
In addition to the indirect assessment given by practicing builders, according to established standards, it is necessary to check the selected slab thickness in relation to the parameter - the optimal specific pressure of the structure on the ground (more details in the table).
If the pressure that the building will exert on the ground according to the design differs from the reference value by no more than 25% up or down, then it is considered that the thickness of the slab is chosen correctly.
| Optimal value of distributed load (kgf/cm²) depending on soil type | |
| plastic clays, sandy loams | 0,50 |
| dense sands, loams | 0,35 |
| medium density sands, hard clay | 0,25 |