From the history of self-supporting insulated wire (SIP)
Self-supporting insulated wire (SIP) appeared on the Russian market as an imported development in the late 80s, and simultaneously in two ways - from Finland (Nokia Cables) and from France (Alkatel)
. It is difficult to determine now which of these manufacturers was the first to pay attention to Russia, but this is not so important. The main thing is that their SIP wire systems were different. And in those regions where these firms were most active, the corresponding systems were promoted. A little later, the production of SIP wires began to develop in Russia
And in those regions where these firms were most active, the corresponding systems were promoted. A little later, the production of SIP wires began to develop in Russia
Irkutskkabel became a pioneer, but in those years the plant produced an incompletely developed product. Only since 1997 did Sevkabel, Irkutskkabel, and a little later Moskabelmet begin to produce high-quality SIP wires. Now other cable factories are catching up to the level set by these enterprises. Due to the general positive consumer properties of SIPs, there is great interest in such wires. With a relatively small increase in costs (about 20 percent) compared to uninsulated “bare” wires, the reliability and safety of a line equipped with SIP increases to the level of reliability of cable lines. As part of the implementation of the long-term technical policy of RAO UES of Russia, RAO enterprises are transitioning to a power supply system via overhead lines with self-supporting insulated power supply
And in those regions where these firms were most active, the corresponding systems were promoted. A little later, the production of SIP wires began to develop in Russia. Irkutskkabel became a pioneer, but in those years the plant produced an incompletely developed product. Only since 1997 did Sevkabel, Irkutskkabel, and a little later Moskabelmet begin to produce high-quality SIP wires. Now other cable factories are catching up to the level set by these enterprises. Due to the general positive consumer properties of SIPs, there is great interest in such wires. With a relatively small increase in costs (about 20 percent) compared to uninsulated “bare” wires, the reliability and safety of a line equipped with SIP increases to the level of reliability of cable lines. As part of the implementation of the long-term technical policy of RAO UES of Russia, RAO enterprises are transitioning to a power supply system via overhead lines with self-supporting insulated insulation.
SIP wires are intended for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy in overhead power and lighting networks for voltages up to 0.6/1 kV (SIP-1A; 2A; 4; 5) and up to 20 kV (SIP-3).
The primary area of application of self-supporting insulated wires: for main overhead power lines and branches to inputs into residential buildings and outbuildings. Advantages of self-supporting insulated wires:
- A sharp reduction (up to 80%) of operating costs caused by high reliability and uninterrupted power supply to consumers, because Short circuits due to the clashing of wires during the vibration dance, breaks due to falling trees, ice formation and snow accumulation are excluded.
- Reduced costs for installation of VLI, associated with the cutting of a narrower clearing in a forest area, the ability to install wires along the facades of buildings in urban areas, the use of shorter (4 meters instead of 6) supports, the absence of insulators and expensive traverses (for VLI-0, 4 kV), the possibility of joint suspension on existing low and high voltage overhead lines and communication lines.
- Reduction of electrical losses in the line due to a more than threefold reduction in the reactance of insulated wires compared to non-insulated ones.
- Simplicity of installation work, the ability to connect new subscribers under voltage, without disconnecting the rest from the power supply and, as a result, reducing repair and installation time.
- High fire safety of VLI, associated with the exclusion of short circuits when phase conductors overlap and the use of lightning protection devices.
- Significant reduction in unauthorized line connections and incidents of vandalism and theft.
- Improving overall aesthetics in urban environments.
- Significant reduction in cases of electric shock during installation, repair and operation of the line.
Mechanical characteristics of SIP wire
| Brand and rated voltage of the wire | Nominal outer diameter, mm | Estimated outer diameter of the wire, mm" | Estimated weight of 1 km of wire, kg |
| SIP-1-0.6/1 | 1×16+1×25 | 15 | 135 |
| 3×16+1×25 | 22 | 270 | |
| 3×25+1x35 | 26 | 390 | |
| 3×35+1×50 | 30 | 530 | |
| 3×50+1×50 | 32 | 685 | |
| 3×50+1×70 | 35 | 740 | |
| 3×70+1×70 | 37 | 930 | |
| 3×70+1×95 | 41 | 990 | |
| 3×95+1×70 | 41 | 1190 | |
| 3×95+1×95 | 43 | 1255 | |
| 3×120+1×95 | 46 | 1480 | |
| 3x150+1x95 | 48 | 1715 | |
| 3×185+1×95 | 52 | 2330 | |
| 3×240+1×95 | 56 | 2895 | |
| SIP-2-0.6/1 | 3×16+1×25 | 24 | 308 |
| 3×16+1×54.6 | 28 | 427 | |
| 3×25+1×35 | 27 | 424 | |
| 3x25+1x54.6 | 30 | 512 | |
| 3×35+1×50 | 31 | 571 | |
| 3×35+1×54.6 | 32 | 606 | |
| 3×50+1×50 | 34 | 727 | |
| 3×50+1×54.6 | 35 | 762 | |
| 3×50+1×70 | 36 | 798 | |
| 3×70+1×54.6 | 39 | 973 | |
| 3×70+1×70 | 40 | 1010 | |
| 3×70+1×95 | 41 | 1087 | |
| 3×95+1×70 | 43 | 1240 | |
| 3×95+1×95 | 45 | 1319 | |
| 3×120+1×95 | 48 | 1553 | |
| 3×150+1×95 | 50 | 1787 | |
| 3×185+1×95 | 55 | 2403 | |
| 3×240+1×95 | 60 | 2968 | |
| SIP-3 -20 | 1×35 | 12 | 165 |
| 1×50 | 13 | 215 | |
| 1×70 | 15 | 282 | |
| 1×95 | 16 | 364 | |
| 1×120 | 18 | 445 | |
| 1×150 | 19 | 540 | |
| 1×185 | 21 | 722 | |
| 1×240 | 24 | 950 | |
| SIP-3-35 | 1×35 | 14 | 209 |
| 1×50 | 16 | 263 | |
| 1×70 | 17 | 334 | |
| 1×95 | 19 | 421 | |
| 1×120 | 20 | 518 | |
| 1×150 | 22 | 618 | |
| 1×185 | 24 | 808 | |
| 1×240 | 26 | 1045 | |
| SIP -4 0.6/1 kV | 2x16 | 15 | 139 |
| 4x16 | 18 | 278 | |
| 2x25 | 17 | 196 | |
| 4x25 | 21 | 392 |
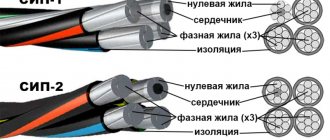
Brand SIP-2 and SIP-2A
The SIP-2 cable differs from the previous model only in the mandatory application of a protective sheath to the neutral core. The insulator itself provides improved protective properties due to increased strength.
The designation SIP-2A is not currently used. At the initial stages of cable production, this name was used to designate products with an insulated neutral core. Now the abbreviations SIP-1 or 1A are used to indicate a supporting wire with a bare or conventionally insulated neutral conductor. A cable coated with improved protection is usually labeled only as SIP-2.
There are also two more private designations for products manufactured outside the territory of the Russian Federation:
- SIP-2F, equipped with a load-bearing core made of stranded aluminum wire (without steel insert);
- SIP-2AF, which has a design without a load-bearing core.
Design of cables SIP-2 and SIP-2A
The cable consists of multi-core current-carrying conductors and an additional load-bearing core. By expanding the range of sections to 240 mm2, the wire is used in power lines with an operating current of up to 515 A. There are cables with an all-aluminum insulated multi-wire load-bearing core, as well as with a steel insert.
Examples of notation:
- SIP-2 3*16+1*54.6 - SIP wire of the second category, has an insulated zero core and three current-carrying conductors with sections of 54.6 and 16 mm2, respectively;
- SIP-2 4*50 - a cable with the following parameters - four cores of 50 mm2 each, no supporting conductor is provided in the design (a typical example of a product that does not comply with GOST 31946-2012).
The photo clearly shows the difference in the design of SIP-1 and SIP-2.
Features of cables SIP-1 and 2
Features of cables SIP-2 and SIP-2A
The design features of the SIP cable of the second model are:
- mandatory layer of insulation on the load-bearing core;
- use as a protective shell of especially durable cross-linked light-stabilized polyethylene with a thickness of up to 1.7 mm.
The polyethylene used for the sheath of SIP-2 cables is environmentally friendly and does not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere during long-term operation.
Scope of application of SIP-2 and SIP-2A cables
The wire is mounted on power lines with voltages up to 1000 V, and is also used to make taps for residential and industrial buildings. The cable can be used in various climatic zones, including salty sea air.
Main cable brands
To increase the pressure inside the network, the cable is pre-painted black. It provides reliable protection against various degrees of ultraviolet radiation. The neutral core contains a steel core
. It is first wrapped around an aluminum wire.
Important! Light-stabilized polyethylene is used as an insulating material.
The choice of section is key
SIP. In this case, attention should be paid to the insulating material. The supporting part must also exactly meet all the requirements of the internal system.
That is why several types are actively used in construction. Each of them has a number of advantages and disadvantages:
View 1 and 1A.
The cables contain an aluminum core that is used to conduct current through the system. The top is insulated using a polyethylene plate.
It will not deteriorate even when exposed to ultraviolet rays. Depending on the chosen model, the neutral core can be bare or insulated. If the client chose brand “A”, the cable will be additionally protected by a layer of insulation. The structure will continue to function normally even when heated to 70 degrees.
View 2.
The design of this wire is similar to the previous one.
However, polyethylene made from cross-linked fragments is used as an insulating material .
In terms of power and length, this cable is ideal for creating lines that will operate under a voltage of 1000 V. The design will not be damaged even in the presence of a large amount of precipitation.
The cross-section of cables of this type allows their use in the formation of trunk lines that go to individual areas of electricity consumption. The design provides for the operation of cables in cold and temperate climates.
SIP-2 have a more advanced structure, so they allow temperatures to rise up to 90 degrees. However, during the installation process you should pay attention to the bending radius. This figure should not exceed ten outer diameters.
View 3.
This type of cable is also formed from a steel tip. However, it is additionally wrapped with aluminum on top. For this purpose, a specially created AlMgSi alloy is used. The cross-section of SIP-3 is increased due to cross-linked polyethylene, which does not suffer even when exposed to direct sunlight.
This wire option is ideal for the construction of overhead lines.
Electricity transmission on it is subsequently carried out at a voltage of 20 kV.
Climate conditions can be temperate, cold and even tropical. The system functions normally at a temperature of 70 degrees. However, manufacturers assure that the range can be from -20 to +90 degrees.
Features and name decoding
Now we should consider the issue of wire marking. But before starting this issue with SIP wires, you should consider possible design features. Otherwise, you will simply get confused when decoding.
Design features of SIP brand wire
A SIP brand product may have several different types of cores. Each of them is marked differently, so let's figure out what they are called and what they are intended for. This issue is standardized by GOST 31946 - 2012.
SIP wire design
- Let's start our conversation with the zero core. It can be load-bearing or without a load-bearing element. It can be used as a neutral (N), protective (PE) or neutral and protective (PEN) conductor. The cross-section of the zero load-bearing core can be from 25 mm2 to 95 mm2.
- There is also a so-called main vein. It is this circuit that is designed to transmit electric current, and it is this circuit that is usually used as a phase circuit. There can be from one to four main cores, and as the instructions provide, their cross-section can be from 16 to 240 mm2.
- In addition, some brands of SIP wires provide for the presence of auxiliary conductors. They can be of two types - intended for connecting lighting devices, or used as controls for connecting various measuring or relay devices.
SIP wire with auxiliary control core
Auxiliary conductors are usually used for wires with a neutral conductor cross-section of at least 50 mm2. Their number can be from one to three. As for their cross-section, it all depends on the purpose. If these are conductors intended for connecting lighting devices, then their cross-section should be 16, 25 or 35 mm2. For control auxiliary cores this row is 1.5, 2.5 or 4 mm2.
SIP with auxiliary residential lighting
This is all we have discussed regarding the cores and their purpose, but here it is worth mentioning one more issue - insulation. It can be regular, or it can be sealed. Its difference is that even if moisture gets under the sheath, it will not spread throughout the entire wire, as is the case with conventional insulation. This, of course, is a better solution, which is why the price of sealed products is slightly higher.
Explanation of the name
Now we are ready to consider the question: “How to determine the brand and cross-section of SIP wire by marking.” After all, this abbreviation is printed directly on the wire, and if you understand what it is about, you can easily read it on the product itself.
SIP wire marking
- First of all, its type of cable product is applied to its shell. In our case, this is SIP, which translates as: self-supporting insulated wire. Then its class is indicated through a hyphen. We met this question in the first section of our article.
- Then the markings contain a continuous set of numbers. But everything becomes clear if you know what it is. And this is a designation of the number and cross-section of cores. First of all, the quantity and through the multiplier sign of the cross-section of the main core are indicated, then through the plus sign the number and cross-section of the zero load-bearing core, and only then the number and cross-section of the auxiliary cores.
SIP wire designation option
- Further in the marking, a dash sign indicates the rated voltage for which the wire is intended. Sometimes two values can be indicated here separated by a slash. For example, 0.6/1. This means that the wire is designed for voltages of 660 or 1000V.
- And the last thing in the marking is the technical condition according to which the wire is made. Usually this is a set of numbers after the abbreviation TU.
Calculation method
We take plate 10 and from it we find that one core is 16 sq. mm. withstands - 100 amperes. And then the most important thing is how much should this 100A be multiplied by - by 220 or 380? Here we need to look from the point of view of consumers who will be connected to the sip. If this is an ordinary residential building, then there are not so many three-phase appliances (well, the only thing that comes to mind is an induction cooker or electric oven, although they are essentially 220V), if this is some kind of repair shop, then there is already more three-phase equipment (lifts, welding, compressor).
At the beginning of the topic, the question was raised: “will a 4x16 15kW sip handle it?” Therefore, for a private house we multiply 220Vx100A = 22 kW per phase. But don’t forget that we have three phases. And this is already 66 kilowatts
total for a residential building.
Which is a 4-fold margin
relative to the issued technical conditions.
The main purpose of SIP cables is to transmit electricity over overhead lines. The cable is actively used in the removal of electricity from main highways to residential and commercial buildings, and in the construction of lighting networks on the streets of populated areas.
Self-supporting insulated wire (SIP)
SIP wire design
To know how to choose the right cable, you must first decide what designs it comes in. The first symbols of the marking, immediately following the abbreviation, indicate the type of SIP cable, which is marked as 1, 1A, 2, 2A, 4, 4n, 5 and 5n. They show what the neutral wires are made of, whether there is insulation on them and how the self-supporting property of the cable is ensured (steel core inside the neutral wire or the strength of the overall structure)
SIP-1 and SIP-1A
These brands of SIP electrical wire are almost identical in their characteristics. The only difference between them is the presence of insulation on the neutral core: SIP-1 does not have it, but SIP-1A does. Moreover, the neutral conductor itself has a steel core and can be of a larger, equal or smaller cross-section than the phase wires, depending on the brand and purpose of the cable. The insulation material is thermoplastic polyethylene with an operating temperature of -60 to +50 C°, which can withstand prolonged heating up to +70 C° without compromising its properties. Number of cores – 2-4.
SIP-2 and SIP-2A
It has exactly the same structure and conductive characteristics as wires of the SIP-1 brand, but it is designed for operation in more severe conditions, which is expressed in the use of insulation made of cross-linked light-stabilized polyethylene. This is a more durable material with improved heat resistance characteristics - operating temperatures from -60 to +50, but it can withstand prolonged heating up to +90 C° and can be used in regions with cold climates. Number of cores – 2-4.
SIP-3
Unlike other brands of SIP cables, this one is made exclusively single-core, used for power lines with a voltage of 10-35 kV. It consists of a steel core around which a wire made of aluminum alloy - AlMgSi - is wound. This material has high conductive and strength characteristics, and is also more resistant to corrosion. Light-stabilized polyethylene is used as insulation, which allows the use of SIP cables in regions with difficult climatic conditions.
SIP-4 and SIP-4n
Wire with cores of equal cross-section from 16 to 120 mm², the number of which can be 2-4 pieces. Load-bearing properties are equally distributed among all cores. Thermoplastic polyethylene is used as insulation. It can be used at temperatures from -60 to +50 C°, while withstanding prolonged heating up to +90 C°. The differences in markings are due to the material from which the conductors themselves are made - in SIP-4 it is pure aluminum, and in SIP-4n it is an aluminum alloy. The SIPn-4 marking is also used, which states that the insulation does not propagate fire.
SIP-5 and SIP-5n
By analogy with wires, SIP-1 and SIP-2 differ from cables SIP-4 and SIP-4n in the insulation material, which is made of cross-linked light-stabilized polyethylene. This makes it possible to increase its resistance to prolonged heating and hypothermia by 30%, which determines the scope of use for both temperate and cold climates.
Any SIP wire has a design life of 40 years and during installation it is required to maintain a bending radius of at least 10 diameters of the entire cable.
Types of SIP
SIP wire can be divided into several different categories depending on the material from which it is made and the design. The differences include the diameter of the conductor, the number of cores, and the insulation material. All types of SIP cables must have an insulating layer. Explanation of the name: S - self-supporting, I - insulated, P - wire.
SIP-1
Aluminum is used as the material for the cores. The cores are covered with insulating material PET - polyethylene terephthalate in the form of a synthetic film. This coating protects the wire from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation. The cable has a zero core. It can be insulated (then the letter A appears in the marking - SIP-1A) or without zero insulation (SIP-1).
SIP-2
It has a similar design to SIP-1, but a different material is used as insulation - polyethylene film. It is used in power lines up to 1000 V and in summer cottages with network voltage up to 380 Volts. Suitable for use as main and auxiliary lines. Recommended for use in northern regions and areas with temperate climates.
Also divided into SIP-2 and SIP-2A. Able to withstand temperatures up to 90°C. The minimum bending radius is 10 diameters.
SIP-3
SIP-3
This modification has significant differences from the previous two types. Structurally, it consists of a steel core with a braid of aluminum, silicon and magnesium. PET is used as insulation material. Single-core. Suitable for use in conditions up to 20 kV. Suitable for work in any climate with the exception of the Arctic and extreme continental ones. Operating temperature range from -20°C to +90°C.
SIP-4
SIP-4
The conductor is created from several pairs of cores without a neutral wire. The marking has the letter H, indicating that an alloy is used as the core material. If there is no sign, you can judge that the cores are made of pure aluminum. The insulation is thermoplastic PVC, which protects the wire from ultraviolet rays.
SIP-5
SIP-5
is similar in design to SIP-4, but PET is used as the insulation material. Thanks to this, it is possible to increase the maximum permissible temperature by 30%, which expands the climatic zone of application. It is used in power lines with voltages up to 2.5 kilovolts and connections to various buildings, street lighting, branches to cottages. Recommended for use in cold and temperate climates.
Cable Specifications
The rated voltage of the SIP wire depends on the thickness of the insulation and ranges from 0.22 to 32 kV. The current load is determined by the cross-sectional area of the current-carrying conductors.
Main technical characteristics:
- Operating temperature range from -60°С to +50°С;
- Permissible installation temperature without preheating is -20°C;
- Core cross-section 16 – 150 mm2
- The minimum bending radius during installation and operation is 10 Ø;
- Permissible long-term core temperature: during operation 70-90°C, during short circuit 135-250°C;
- Warranty period 5 years;
- Technical service life is at least 45 years.
The permissible current load at an ambient temperature of +25°C, a wind speed of 0.6 m/s and a solar radiation level of 1000 W/m2, as well as a short circuit current operating for 1 second, are shown in the table below.
You might be interested in Description of the ASB cable
| Cross-section of current-carrying conductors, mm2 | Permissible continuous load current, A | Short circuit current, A |
| 16 | 76 | 870 |
| 35 | 160 | 3200 |
| 50 | 195 | 4500 |
| 70 | 240 | 6500 |
| 95 | 300 | 8800 |
| 120 | 340 | 10900 |
The insulation of each core is distinctly color-coded with a colored stripe on a black background. Instead of color there may be raised stripes.
Raised markings
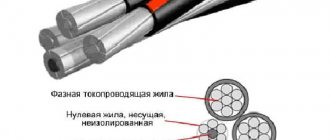
The cable cores are made of stranded aluminum. As a rule, one of the wires (central) in the load-bearing core is made of steel. This core takes on the load when hanging the wire between the supports. The cores are compacted during the manufacturing process and have a round cross-section.
Sectional view of the cable
In some cases, instead of pure aluminum, its alloy with other metals is used to increase mechanical strength.
The main advantages of SIP wires are as follows:
- The fundamental impossibility of phase overlap with subsequent short circuit;
- Smaller right-of-way (clearing width);
- Reduced losses by reducing reactance;
- Reducing the load on power line supports (especially during icy periods);
- No need to use insulators;
- Making illegal connections difficult;
- Reduced operating costs.
Fastening fittings The main requirements for an insulating coating are resistance to ultraviolet radiation and the ability to operate in a wide temperature range. Light-stabilized low-density polyethylene (LDPE) or light-stabilized cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) meets these requirements.
To attach wires to load-bearing surfaces or supports, special anchor and support clamps and hooks are used. To connect or install bends, cutting and stripping of insulation is not required, since piercing clamps are used.
Note! The use of specialized mounting hardware increases installation costs, but improves the quality of work and reduces the cost of ongoing operation of the electrical network
Technical characteristics of SIP 2 cable
SIP 2 wire is produced with the following technical characteristics:
- the number of conductors can be from 1 to 4;
- the cross section is in the range of 16-120 mm2;
- the zero core is made of aluminum alloy and has a steel core;
- rated voltage – 0.6-1 kV;
- insulation material – light-stabilized silanol cross-linked polyethylene;
- relative humidity of the operating environment – up to 98%;
- the minimum bending radius is 10D, where D is the diameter of the wire;
- installation of the wire is allowed at a temperature of at least -20°C;
Temperature parameters:
- Operating temperature range – -60°С – +50°С. Thanks to these properties, the cable can be used when laying electrical networks in a cold climate zone;
- Heating up to +90°C for 8 hours is allowed;
- Short-term heating up to 130°C is allowed;
- The permissible short circuit temperature is +250°C.
Attention! During operation, heating up to 90°C is possible. It is allowed to be allowed for no more than 8 hours per day, no more than 100 hours per year, and no more than 1000 hours for the entire period of work.
The warranty period is at least 3 years, the service life must be at least 40 years.
Strength characteristics of SIP 2
| Nominal cross-section of zero and main cores, mm2 | Core tensile strength, kN, not less |
| 25 | 7,4 |
| 35 | 10,3 |
| 50 | 14,2 |
| 70 | 20,6 |
| 95 | 27,9 |
| 120 | 35,2 |
| 150 | 43,4 |
| 185 | 53,5 |
| 240 | 69,5 |
Depending on the number of cores and their cross-section, cables have different weights and diameters.
Characteristics of the diameter and weight of SIP 2 wire
| Number and cross-section of cores | Outer diameter of wire, mm | Weight of 1 km of wire, kg |
| 1x16 + 1x25 | 16,4 | 167 |
| 3x16 + 1x25 | 24,1 | 307 |
| 3x25 + 1x35 | 27,1 | 424 |
| 3x35 + 1x50 | 30,8 | 570 |
| 3x50 + 1x50 | 34,1 | 729 |
| 3x50 + 1x70 | 36,1 | 799 |
| 3x70 + 1x70 | 40,0 | 1010 |
| 3x70 + 1x95 | 41,8 | 1086 |
| 3x95 + 1x70 | 44,2 | 1247 |
| 3x95 + 1x95 | 45,9 | 1323 |
| 3x120 + 1x95 | 48,1 | 1545 |
| 3x150 + 1x95 | 50,9 | 1812 |
| 3x185 + 1x95 | 55,0 | 2162 |
| 3x240 + 1x95 | 59,6 | 2652 |
| 4x16 + 1x25 | 24,1 | 377 |
| 4x25 + 1x25 | 27,1 | 522 |
Cable design SIP-4 4x16
Inside the product there is a cable core that acts as a conductor. It is made from aluminum alloy in accordance with GOST No52373-2004. The cable cores can be sectored or round and consist of a certain number of wires that are twisted into a tight bundle.
Power line installations
The internal cores are also made of aluminum, sometimes copper is used in the composition. External insulation is made of PVC materials. This shell may be flammable or non-flammable. The first option is used more often, which provides additional safety for the operation of power lines.
Everything about electrics is on our website
Mega-construction begins. Installation of ASU and dispute with builders
a mystery for professional electricians inside.
Comparing micro-levels for an electrician: STABILA Pocket Electric 17775 vs Stanley 0-42-130
Micro levels for an electrician - what to choose? Is it worth overpaying for the brand? Mini level functionality. Read my micro review.
Wiring in a wooden house
Using the example of a small bathhouse in Borisovsky. The material for sofa experts has arrived, trolls, I have poured you some fresh food - today we are discussing wiring in a wooden house, frame, log house, laminated veneer lumber, inside wooden structures - in general, everything that burns very well. Expectation and reality.
Super ladder Svelt Scalissima Plus 12+12
The best purchase over the past year, one might say my hope and support, like the great mighty Russian language. You can find out what is good about the stairs of Italian manufacturers in the article.
Operation and repair of VLI
When installing the wires, it is necessary to check the phasing; for this, they must have factory markings along the entire length every 50 cm. Before starting to operate the VLI, a test must be carried out. The test must also be carried out after the first year of operation, and then depending on operating conditions, routine and major repairs.
If there is an asymmetrical (uneven) load distribution on the line, then the measurement of the long-term permissible load must be carried out at the busiest phase. These measurements are carried out once every 1 year, the indicators are entered in a journal (VLI passport).
During operation of the VLI, the insulation may become damaged, which requires repair. Using special wedges and without relieving tension, the damaged core is dismantled. Then special glue is applied to the damaged area in two layers and the core is mounted back.
If the core on the branch to the residential building is damaged by more than 20%, then in this case repair is also necessary. It can be done with or without stress relief. In this case, the load in the house must be switched off.
Application area
Self-supporting insulated wires (SIP) are intended for use in overhead power lines (power lines) suspended on supports or facades of buildings and structures.
Climatic modification - UHL, placement categories - 1, 2 and 3, in atmospheres of type II and III according to GOST 15150-69.
As a result of generalizing domestic experience in the construction and operation in a number of regions of the country of overhead power lines with a voltage of 0.38 kV with self-supporting insulated wires, the technical and economic advantages of these lines were revealed in comparison with overhead power lines of 0.38 kV with uninsulated wires.
Based on the positive experience of using self-supporting insulated wires in power systems, the RAO UES of Russia directive document No. OB-5145 dated June 26, 2000 “On the use of self-supporting insulated wires in construction and reconstruction” was published.
Areas of use
The materials from which it is made, the design features, and therefore the scope of application depend on the brand of the product. In particular:
- SIP 1 wire is most often used in the construction of power lines and inputs into buildings;
- SIP 2 cables are also used for laying power lines and power supply to buildings. Their key feature is the type of atmospheric design, which allows them to be installed in places with high humidity, for example, on the shores of seas, lakes, in areas with poor environmental conditions and harsh climatic conditions, since their insulation is resistant to aggressive environmental influences;
- Products with the SIP 3 brand are used for laying sections of power lines with voltages from 10 to 35 kV. In addition, such a wire is used to connect equipment operating under high voltage. This is due to the cable design, which is able to withstand high-level loads;
- SIP 4 wires are used primarily for arranging various branches, since they have a higher level of flexibility. They are also distinguished by their frost resistance, which allows them to be used when laying power lines in the Far North;
- SIP 5 cable is used almost exclusively for installing branches.
Use of SIP brand products
So, the SIP cable, the decoding of which means that it is self-supporting (it has both phase and neutral wires) and insulated, is intended for laying power supply lines and branches from it. The operating voltage under which this product can be operated ranges from 0.4 to 1 kV, but for some brands it can reach 35 kV.
The main advantages of the described products are ease of maintenance and low weight, which can significantly reduce costs when laying power lines. At the same time, it meets all requirements regarding the safety and stability of energy supply.
What is SIP wire
To understand the purpose and design of the cable, you first need to decipher the markings:
- C – self-supporting;
- I – isolated;
- P – wire.
This cable is used for laying electrical transmission lines over the air. This is an ideal option when installation is carried out according to the “pole to house” system. On the other hand, the conductor cannot be led directly into the house or living quarters, since the insulation is not intended for such use. As a result, the SIP is extended to the distribution panel, which is the input node and is located on the street. An electric meter and an automatic input device are placed inside it. Other cables are laid from the panel into the house, usually with copper conductors and good insulation. Their diameter is much smaller and their flexibility is higher.
Structurally, a wire differs from a cable in the absence of insulation, which is why our product is called “self-supporting insulated wire.” There is no additional protection in the form of an outer shell or armor, and only the conductors are insulated. Thus, technically calling it a SIP cable is incorrect.
The adjective “self-supporting” indicates that for overhead lines there is no need to use a dielectric cable to which the remaining wires are attached. SIP of any brand is characterized by a high load-bearing capacity, which is sufficient for the cable to withstand its own weight and additional loads due to wind or precipitation (for example, snow settling on power lines).
Brand SIP-5
The cable model SIP-5 differs slightly from the previous version. Visually, the wires are practically indistinguishable even to a specialist. Some changes have been made to the design to extend the service life of the product at critical temperatures. A number of enterprises produce wiring with non-combustible insulation suitable for installation inside a building. Such cables are designated with the prefix NG.
The table shows the characteristics of some SIP-5 wires.
| Characteristic | 2*16 | 4*25 | 4*70 | 4*120 |
| Permissible load, A | 105 | 130 | 240 | 340 |
| Short circuit current for 1 second, kA | 1,5 | 2,3 | 6,9 | 11,2 |
| Resistance of a 1 km long conductor (with the passage of direct current), Ohm | 1,91 | 1,20 | 0,443 | 0,253 |
| Core diameter, mm | 4,8 | 6,0 | 9,8 | 13,0 |
| External diameter of wire, mm | 16,8 | 23,4 | 34,6 | 43,6 |
| Approximate weight of 1 km of wire, kg | 138,1 | 400,5 | 983,1 | 1624,4 |
| Force required for breaking, kN (not less) | 5,0 | 15,4 | 43,0 | 73,7 |
| Thickness of the insulating layer, mm | 1,2 | 1,2 | 1,6 | 1,7 |
SIP-5 cable design
The design contains several wires made of aluminum alloy. There is no separate steel guide; its role is played by the cable cores themselves. The product is supplied in a wide range, differing in the diameter of the conductors. It is possible to use single-phase and three-phase current in networks (the number of cores in the wire changes accordingly).
Internal structure of SIP-5 cable
Features of the SIP-5 cable
The design feature is only the external insulation, made of cross-linked polyethylene. The use of such material made it possible to expand the time range of exposure to critical temperatures by a third.
The material used has the following advantages:
- the ability to preserve characteristics when heated to a temperature of 90-130ºС for up to 8 hours;
- short-term performance when overheated up to 250ºС;
- the surface remains elastic at low ambient temperatures;
- restoration of the original configuration after bending or overheating.
Scope of application of SIP-5 cable
The insulated cable SIP-5 is used to transmit electric current with a voltage of up to 1000 volts. Due to the wide temperature range of operation, the product is used for making connections to buildings, as well as for street lighting lines. Manufacturers recommend using the cable in regions with temperate and cold climates. The NG wire version is used for wiring inside residential and industrial premises.
Wire (cable) SIP-4 4x50 description
Wire SIP-4 4x50 is a high-quality four-core wire that is used for laying overhead power lines. Its technical characteristics made the wire quite popular among buyers. The main purpose of using SIP cable 4-4x50 is to create subscriber branches and inputs into residential and utility premises.
Self-supporting insulated wire can be used in a temperature range from minus 60 to plus 50 degrees. Installation seems possible down to temperatures of minus 20 degrees. SIP is resistant to most types of external negative influences, including the influence of sunlight, precipitation and other atmospheric phenomena. For the production of wires, only the highest quality materials are used, which allows us to achieve high quality products.
How to connect
SIP cables are used to lay lines outdoors. This connection is a concentrated line. To independently connect this cable to the central line, you must coordinate the work with the relevant organizations to which these networks belong. Before doing this, be sure to develop a project.
Note! To install the cables you will need special equipment and tools. SIP fittings
SIP fittings
To insert the wire, you need a clamp that can be used to make the connection without stripping the cable insulation. To hang a wire longer than 25 m, you must stretch the cable between the terminals. The bracket is fixed to a support for convenient and quick cable installation.
Wire mounts
To guide cables along the outside wall of a building, special anchors are used in combination with standard cable kits. The number of anchors and clamps must correspond to the number of lead cores.
For your information! The cable can be laid throughout the building at a distance of no more than 1 m, and then inside the house. A special feature of insulated installation cables is that they can operate without turning off the power.
If the home's construction material is non-flammable, the SIP cable along the exterior wall can be left exposed. Of course, this does not add beauty to the facade, since the black cables are clearly visible on the walls. To avoid this, a plastic box or a special corrugated pipe is installed on the wall
This is important, especially if the house is wooden
Network connection to the house