A foundation is a structure that is designed to evenly distribute the weight load of a building on the ground. As a rule, it is installed below the freezing point in order to avoid the effect of frost heaving on the building. The condition of the foundation is an important factor on which the life of the building, its seismic resistance, integrity and appearance depend. The technology for examining the foundations of buildings and structures makes it possible to assess the current state of the structure, as well as determine a list of actions to eliminate defects.
When to do a foundation inspection
Unlike ground structures and building utilities, inspection of the foundation is complicated by its location below the site level. For this reason, assessment of the condition of foundations is almost never carried out as planned. Certain technical and other factors help to conduct the survey.
In particular, diagnostics of building foundations is carried out for the following reasons:
- Defects such as cracks, deflections and other types of deformations were discovered.
- A reconstruction of the building is planned, including the addition of additional floors or structures that will somehow increase the load on the foundation.
- Repurposing a building or structure.
- Reinforcement of the foundation is required.
- Long service life of the base.
- There was a need to equip a basement or deepen an existing one.
- Finding out the reasons for the increase in humidity in the lower part of the walls, in particular, if a violation of foundation waterproofing standards is not excluded.
- Expansion of a building without adding additional floors, but with a physical connection to the existing base.
- Major renovation of a building or structure.
- Before the construction of similar objects in order to determine how the current foundation configuration copes in specific conditions (local soil composition, groundwater level, freezing depth, etc.).
- Assessment of the general condition of a building in order to determine its resource, market value, profitability (for example, in commercial real estate transactions).
Most often, inspections of foundations and foundations are carried out for the same reason - the appearance of defects or their consequences. Professional expertise allows us to do more than just identify all the problems. A technical inspection of the condition of foundations carried out in the proper manner provides answers to questions about what caused the defects and, most importantly, how to eliminate them with minimal effort and investment.
How to check strip and column foundations?
A strip foundation is a base in the form of a strip, which is arranged along the perimeter of the building and the internal parts passing under the load-bearing walls of the future structure. Such a foundation can be made of monolithic reinforced concrete (the most commonly used option), concrete and other blocks, brick, rubble stone. To check the quality of such a foundation, it is necessary to take into account what kind of building material it is made of:
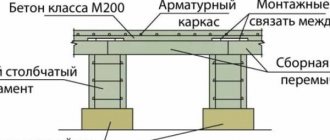
Diagram of a columnar foundation.
- You should check the horizontal position and the absence of cracks on the surface;
- for concrete strip – absence of chips, potholes, protruding parts of the reinforcing belt, delamination;
- for brick – no destruction of mortar joints, no loss of individual bricks, presence of a waterproofing layer;
- for stone and blocks - absence of destruction, loss of individual elements, their displacement, presence of a waterproofing layer.
A conventional pier foundation is a foundation of support pillars that rises above the soil. Such a foundation is not continuous, it is point-based, perfectly distributing the loads from the structure. The supports themselves are placed in the corners of the structure, the intersection points of load-bearing walls, and along the perimeter. The step between the supports should be at least two meters, but it all depends on the features of the structure.
This foundation is considered one of the most economical; there are quite a few varieties of it today. A similar base is used mainly for frame and small houses, bathhouses, and outbuildings.
During the inspection, the vertical level of installation of the pillars, the absence of defects in the piles, and distortions are monitored.
Inspection for defects in slab and column-and-strip foundations
Diagram of a slab foundation.
A slab foundation is the installation of a monolithic, most often reinforced concrete slab, which is installed in a pre-dug pit according to the parameters of the building. When checking the quality of such a base, it is necessary to determine whether there are cracks, signs of destruction, or severe distortions relative to the axes on its surface. You should pay attention to whether there is a layer of waterproofing, whether backfilling was done during the construction of the base.
A column-and-strip foundation for a house is made on soils that freeze to great depths in winter. To construct such a foundation, it is necessary to construct wells, the bottom of which will be located below the freezing point level. In this case, geological studies are carried out before starting work, otherwise the foundation will simply be pushed out in the winter, and this will lead to destruction. The lower part of the base is made wider, after which it is filled with concrete rather than covered with sand. The support piles must go perfectly level; deviations from the level are not allowed. The load that one pillar can withstand is from 5 to 10 tons; before starting construction, it is necessary to calculate exactly what total loads will be created by the structure of the house and the grillage tape.
Carrying out quality research involves checking the level of support pillars and the absence of defects on the pillars, tape, grillage.
Features of foundation inspection
Since visual inspection of foundations does not provide a complete picture of the condition of the structure, instrumental analysis is almost always performed. The difficulty of its implementation lies in the fact that the foundations of structures and buildings are located below ground level. To get to them, pits are excavated, and only after that the most thorough analysis is done. Both visually and using appropriate tools and methods.
Foundation inspection pits are excavations deep into the foundation, during which soil is excavated in order to provide access to problematic (including, presumably) areas of the structure. As a rule, pits are dug to the very bottom of the foundation. First of all, this is done in those places where there are visually visible foundation defects.
It often happens that the most serious defects can be identified only after excavating several pits. This requires a certain investment of time and money, however, only this approach allows you to most accurately identify defects that require elimination and the reasons for their occurrence. In this case, it is possible to see damage to the foundation even where the presence of defects was not expected at all.
Separately, we should consider the features of examining the foundations of buildings and structures of various types. Depending on the manufacturing technology of the foundation and its configuration, appropriate amendments are made to the examination plan, and a set of the most suitable methods, goals, tools and laboratory tests is determined.
Features of inspection of strip foundations
Despite the fact that, in terms of construction technology, a strip foundation is one of the simplest, its inspection is, on the contrary, complex and time-consuming. Primarily due to the fact that the excavation of pits is carried out not only outside the building, but also inside. Accordingly, the inspection of a strip foundation involves a large amount of excavation work, and is also complicated by the lack of direct access to the internal sides of the structure. If the base of the foundation is deep, instrumental research may be complicated by the influx of groundwater, without preliminary pumping of which it will not be possible to carry out a full analysis.
Features of inspection of pile foundations
Pile foundations are used mainly for the construction of buildings in problem areas. To circumvent some of these problems, including long-length piles. This makes it possible to reach stronger soil layers and ensure proper load-bearing capacity. Accordingly, when inspecting pile foundations, it is necessary to get to the base of the piles in order to assess their condition or the cause of defects - local subsidence, skew, tilt, and so on.
Features of inspection of support-column foundations
The examination of support-column foundations is carried out according to almost the same rules as in the case of strip foundations. The excavation of pits is carried out, first of all, in the most loaded places, as well as where a preliminary visual inspection has shown the presence of defects. After examining the condition of the foundation soil, the surface of the supports is dried and concrete samples are taken for laboratory analysis. An ultrasound scan may also be performed.
Foundation check - how to check the foundation
Checking the foundation - how to check the foundation In an ideal world, the customer who pays for the construction of the foundation should not worry about its final quality, but the reality is that even a high price does not guarantee a well-made foundation, so he must responsibly approach the issue of accepting the work himself and check the foundation at all stages of construction and installation work. For this purpose, customers of industrial and civil construction have separate technical supervision services, because the responsibility here is extremely high.
For low-rise construction, the same building codes and regulations apply. If you are not well versed in construction, then it is highly recommended that before starting construction you either consult with a construction expert or study the current SNiP and SP for established foundation requirements, tolerances and deviations.
Checking the foundation consists in the correct execution of all construction and installation works of the foundation.
Geology and foundation selection.
Construction must be carried out according to a specially developed house design. In order to save money, many customers buy a ready-made standard project. This option is acceptable, but the foundation of the building must be adapted to your geological conditions, otherwise in the future you may end up with settlement of the foundation and sedimentary cracks in the walls. To adapt you need:
- Research the geology at the site, or use an archived geology report.
- Calculate the foundation, taking into account the geology and climatic region, for the required bearing capacity, and adjust the foundation design. The calculation must be carried out by a qualified design engineer.
It also happens that construction companies enter into a contract for the construction of a standard house and carry it out completely without a project, according to a sketch. Most likely, the workers at some stages (if not at all) will do the work carelessly, because they do not build according to clearly developed drawings, but the way they know how.
Monitoring hidden work
A very important point is the acceptance of hidden work. These are works the quality of which will be either very difficult or completely impossible to check in the future, because subsequent work will cover them.
For example, for a strip foundation, this is the construction of a pit ( is the depth, level, thrombosing correct ), is the geometry of the axes laid out correct, the arrangement of underlying layers ( thickness of layers, design materials - sand, ASG, concrete preparation ), reinforcement device ( diameter and pitch of reinforcement , absence of corrosion, reliable binding ), arrangement of formwork ( horizontal and vertical levels, dimensions, reliability of fastening, thickness of the protective layer ), arrangement of concrete work ( is the formwork filled with concrete mixture smoothly and without interruptions, uniform vibration of the mixture with deep vibrators, subsequent measurement of the geometry of the foundation , testing the strength of concrete for 7 and 28 days ), maintaining a high-quality waterproofing device, backfilling without debris.
Geometry, checking the strength of the foundation.
You need to check the geometric dimensions and quality of the supplied materials for compliance with the project (provided that it is made in accordance with the requirements of SNiP, SP, GOST and correct structural calculations). If you identify deviations from the project, check with SNiP and SP to see if they are within acceptable values. If not, then you need to fix it while it is possible.
Geometry and level checks can be performed using tape measures, a level, or laser levels. To test the strength of concrete you already need specialized equipment. The minimum cheap and accessible thing that can be purchased is a sclerometer, but its accuracy is not too high, so it is better to order an assessment of the strength of concrete from a specialized organization with the necessary equipment (the most accurate methods are tearing off with chipping , drilling out cores and testing them on the press).
If the contractor refuses to correct the defects.
If you are responsible for checking the quality of work, you will already understand whether the team is working efficiently. Conscientious workers will correct their shortcomings immediately. But it happens that a company, not only does an outright “hack job”, but also does not want to correct anything, demands its money. In this case, it is necessary to seek justice only through the courts. You need to stop all work, order a construction examination if there are serious violations, and calculate the amount of repair and restoration work. Next, you need to present the expert organization’s conclusion to the contractor and try to negotiate compensation amicably, or file the claim in court if this does not lead to anything.
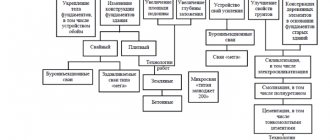
Foundation inspection methods
To fully determine the current state of the foundation, specialists use different methods of examining foundations:
- Visual inspection.
- Instrumental examination.
- Non-destructive testing - allows you to determine the strength of concrete without mechanical impacts on the foundation.
- Ultrasound diagnostics - performed using special tools, and allows you to identify hidden defects in the thickness of the base.
- Method of breakage with chipping.
- Elastic rebound.
- Shock pulse method.
- Laboratory analysis of selected samples.
- Measuring deformation of foundations.
- Determination of water resistance of concrete.
- Determination of frost resistance of concrete.
- Assessment of the degree of corrosion of the reinforcement frame.
The choice of foundation inspection methods is carried out taking into account the characteristics of each specific building, the type of foundation, the capabilities of the performing company and the tasks set by the customer.
Possible defects
Foundation inspections are performed to identify the following common defects:
- distortions;
- rolls;
- arches;
- cracks;
- schisms;
- shifts;
- uneven settlement;
- concrete getting wet;
- concrete corrosion;
- corrosion of metal piles;
- reinforcement cage corrosion;
- basement flooding;
- violation of external drainage.
The next step in examining the foundation is to find out the possible causes of the defects identified during the examination.
Causes of defects
The main causes of defects in the foundations of buildings and structures include the following factors:
- Construction without geological surveys - the composition and strength of the soil, the depth of groundwater and freezing, slope, etc. are not taken into account.
- Mistakes made during the design process - incorrect calculation of the required load-bearing capacity, burial depth, inappropriate type of foundation.
- Violation of the technology for arranging the selected type of foundation - insufficient soil compaction, tight deadlines, gross miscalculations, use of low-quality concrete, backfilling using soil prone to heaving.
- Incorrect operation of the foundation - exceeding the design load, mechanical damage, flooding, disruption of the movement of heavy vehicles near the building, temperature changes inside the premises.
- Failure of engineering water supply and sewerage systems.
- An unforeseen increase in seismic activity and other natural disasters that are not typical for the region in question.
- Making changes to the structure of a building without taking into account the original load-bearing capacity of the foundation.
- Untimely inspection of the foundation of a building - as a rule, is carried out when there are many defects, and most of them are critical.
Among other things, defects arise naturally as a result of long periods of operation and the inevitable exhaustion of structures. For such cases, timely repair of foundations, maintenance, updating of waterproofing and other measures, which are usually neglected, should be provided.
Stages of foundation inspection work
A comprehensive foundation inspection is carried out in four stages:
- Preparatory - data collection, familiarization with available documentation, preliminary selection of analysis methods.
- Field work - this stage includes a visual inspection of the foundation on site, development of pits, and assessment of the condition of the foundation using mobile tools.
- Laboratory analysis - taken samples of soil and, if necessary, foundation materials are subjected to it.
- Desk stage - analysis and synthesis of information collected during the survey, preparation of a report.
Some industrial facilities have their own specifics of conducting examinations, related to the peculiarities of the technological process and difficult operating conditions of the foundation.
How to check the quality of the foundation?
How to check the quality of the foundation? Sometimes a situation arises when you simply need to check the foundation. This question is very responsible and important. After all, the correctness of the assessment determines whether you will have problems in the future or whether they will be minimized.
So, the first step is a visual inspection. The presence of cracks in the walls, floor, or some incomprehensible deviations indicates that the foundation of the house is damaged. Streaks on the basement walls or salt deposits on the foundation walls indicate damaged waterproofing or no waterproofing at all. And problems are inevitable.
If a superficial inspection does not lead to any results, the concrete is tested for compression. For these purposes, a specialist with a Schmidt hammer is invited. He will be able to determine the compression ratio.
Next, check the cross-sectional size of the foundation: the stiffer the foundation is, and the less capable it is of bending from various uneven loads, the larger its reinforced concrete, monolithic part. The area of the base should also be taken into account. More area means less pressure on the ground. The next stage is to determine the quality of the materials used to build the foundation. It should be remembered that the minimum grade of concrete for the foundation is 200, and preferably 400. If foam concrete was used, then for grade 600 foam concrete, the thickness of the walls should be at least 45 cm, for foam concrete grade 800 at least 68 cm, and grade 1000 at least 94 cm It is worth checking the waterproofing, since if it is missing, the foundation will absorb moisture from the soil, and this is fraught with consequences.
An alternative is to let the foundation overwinter, in which case all the shortcomings will come to light: both the heaving of the soil and the foundation itself will show themselves in the freeze-thaw cycle. If the foundation is columnar, then you yourself will not be able to determine anything. Here you will have to call specialists to carry out an examination; by the way, here in parallel it will be possible to conduct a study: flaw detection of concrete floors for the presence of voids. For a slab foundation, almost the same actions: visual inspection, presence - absence of cracking, strength check, compliance with geometric dimensions, compliance with horizontal slab.
In cases of the slightest doubt about the integrity or defects of the foundation, do not be stingy, call specialists for an examination. Because if you made a mistake in assessing the foundation, the costs will continue to increase. Do you need it?
Examination result
Upon completion of the main stages of the foundation inspection, a technical report is drawn up, including:
- Explanatory note.
- Foundation inspection report.
- Inspection results in the form of defective statements.
- Roll charts, if available.
- Map of identified defects.
- Objective assessment of the current state of the foundation.
- Laboratory results.
- Strength assessment.
- Experts' conclusions and recommendations for builders.
The technical survey report is an official document, including one that allows for the further operation of the building or acts as a guide with recommendations for improving the condition of the foundation and increasing its service life.
Checking the quality of the foundation
Building a house is a complex process during which it is necessary to strictly follow the technology and recommendations given by experts. But even in this case, after about a year, it is recommended to inspect the condition of the foundation and the house to make sure that all work was carried out correctly and there are no defects or signs of destruction. How to check the quality of the foundation of a house? For this, various methods are used, which largely depend on what type of base was used. A columnar foundation perfectly distributes the loads from the building, provided that the distance between the supports is at least 2 meters.