The road surface in Russia and abroad is different: in our country, highways for various purposes are made of asphalt, while in Europe and the USA they are mainly made of concrete. This is the obvious difference in their quality. In Russia, concrete roads have not become widespread due to their significant cost - after all, the country’s vast expanses and updating the road surface will cost the population another increase in taxes. However, no one forbids homeowners to build car parks and driveways from durable concrete.
Why are concrete roads needed?
The construction of concrete roads is advisable in places where there is no possibility of frequent repairs and there is a need for a durable road surface. In Russia it is:
- Autodromes;
- Runways and landing pads at airports;
- Parking of cars and other equipment;
- Pedestrian paths and sidewalks in cities;
- Coastal roads and embankments where high humidity and exposure to water prevail.
The service life of a concrete slab exceeds the service life of asphalt by up to 2-3 times. For this reason, it is advisable to replace asphalt concrete road pavements that cannot withstand climatic conditions with cement concrete ones everywhere, which is gradually happening in the USA.
Advantages of concrete roads
Such coatings have certain advantages:
- The concrete road is of good strength and does not require repair work. The coating can be used for at least four decades, and for asphalt this period is limited to a decade with annual repairs;
- Automotive vehicles consume less fuel. This is due to the fact that while a heavy-duty vehicle is moving, the road concrete is not subject to deformation, which means that the vehicle needs one-fifth less fuel to move;
- The coating is resistant to sudden changes in climatic conditions. It is not affected by heavy rains or sudden changes in temperature;
- air purity is maintained, because cars require less fuel, the exhaust gases of which pollute the environment;
- natural resources are used sparingly. Limestone is needed to make concrete, and petroleum is used to make asphalt.
The difference between asphalt and concrete
Why is asphalt road surface not as durable as concrete road surface? It's all about the quality of the basic materials:
- Asphalt is a composite of sand, crushed stone, mineral fillers, and their binder is bitumen polymers.
- Concrete is a sand and gravel mixture mixed with cement and additives.
The main difference between concrete and asphalt is the binder in their compositions. Bitumen, unlike cement, does not form a strong stone, sags under weak soils when loaded, softens in the sun and does not winter well. Concrete, if the technology of preparation and installation is followed, is free from these disadvantages.
Next, we will consider concrete roads: laying technology, advantages and applications.
Disadvantages you need to know about
To be fair, we note: concrete also has its disadvantages. And when starting to build a concrete road, you need to carefully weigh everything.
Concrete, compared to asphalt, has much higher requirements for precise adherence to technology. It is much safer to make mistakes when working with asphalt. In the case of concrete, errors can be discovered during the first winter season. If the work technology was violated, or low-quality materials were used, or the coating did not receive proper care, the road may begin to collapse literally before our eyes. The cost of a mistake is global - you will have to remove all the concrete and lay new one. What kind of contractor would want to take such risks?
In addition, on a concrete road it is necessary to use special reagents of the Nord Way brand - they cost 10 times more than conventional sodium chlorine used on an asphalt network. In addition to this, the use of studded tires in our country still has not been regulated in any way - it is unclear how the concrete surface will withstand damage from car studs.
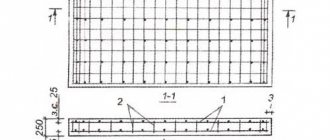
Road structure
The road surface consists of several layers:
- The underlying is crushed stone, draining water from the ground, and sand, compensating for loads coming from above and below from the ground.
- Strengthening – this is a layer of low-grade concrete that binds the bedding.
- The main road surface is a layer of concrete.
When laying highways with large traffic of heavy vehicles, the road must be made of unstressed and stressed reinforced concrete, the reinforcement cage in which does not allow the stone to crack under the weight of heavy trucks.
In private construction, as well as when organizing a road surface on soils saturated with water or with a high level, waterproofing for the road surface is laid on a sand and gravel embankment (roofing felt materials can be used). The layer prevents constant wetting of the concrete and, as a result, corrosion of the stone and reinforcement frame.
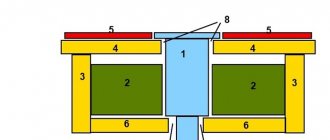
Concrete road structure
The canvas includes certain layers:
- underlying - for its construction, crushed stone is used, which drains groundwater, and sand, with the help of which the resulting loads are compensated;
- strengthening – represented by low-grade concrete that binds the backfill layer;
- road surface - concrete surface.
The construction of a concrete road for heavy vehicles is made of stressed and non-stressed reinforced concrete, the reinforcement frame in which does not allow the stone to crack from the weight of trucks.
In private types of construction work or when constructing concrete road surfaces on soils supersaturated with moisture, a waterproofing material is laid on the sand cushion to prevent severe wetting of the road surface and subsequent corrosion of stones and reinforcement. Ordinary roofing felt is used as a waterproofing material.
Types of canvas
The concrete road is good for both high-traffic highways and village driveways. For these cases, different types of canvas are chosen, differing in quality and cost:
- A high-quality single-layer coating for roads of any purpose, suitable for laying top and bottom layers;
- Concrete for the bottom layer of the canvas is cheap - it has low strength, and minimal requirements are imposed on its components. A coating made of such material can be used when arranging local areas with a small flow of passenger cars;
- Base concrete with average characteristics for heavy and advanced coatings. Can be laid on village roads;
- The organization of roads with ready-made concrete slabs can be included in a separate group.
Materials for filling the canvas
The universal material for laying roads is M400 concrete. Its strength is sufficient to withstand the pressure of the wheels of cars and trucks on city and village driveways.
The basis of the concrete is Portland cement, resistant to water (1 part). Plasticizers are also introduced into the solution, increasing the hydrophobicity of the coating and its strength. The working solution also includes:
- Crushed stone – 5 parts;
- Sand – 2 parts.
For concreting a road, it is rational to order ready-made concrete from a factory - even for a small site you will need a lot of mortar, which must be poured quickly, without allowing individual batches to set.
Road surfacing materials may differ in properties depending on the expected load and installation conditions.
Requirements for the quality of concrete roads
When choosing components for preparing road concrete, they are guided by SNiP 3.06.03-85 “Highways”. The document regulates the quality requirements for the finished fabric:
- Resistance to mechanical loads is the main requirement for a road surface. For roads for different purposes, the indicator is determined individually.
- No cracks in the coating after installation and during operation. Compliance with the technology for constructing concrete roads and the correctly selected composition of the working solution helps solve the problem.
- Water resistance and resistance to chemical reagents. Highways are located in different conditions of relief and soil quality, and in the absence of organized drainage (if construction technology is violated), water accumulates on the road surface, worsening its quality.
Requirements for concrete
The quality of the fabric is determined by the constituent components, which must also undergo careful selection in accordance with relevant GOSTs. For example, the strength of crushed stone, capable of ensuring reliable and long-term operation of the road, is at least 1200 kg/cm2. For a pillow, less durable crushed stone 800-1000 kg/cm2 will do.
The mobility of the concrete solution is 2 cm when testing with a cone. A large number of mineral inclusions of different fractions helps to avoid deviations from this parameter.
Another requirement for concrete is high bending strength; for this purpose, plasticizers are introduced into the solution and the canvas is additionally reinforced with reinforcement.
Pros and cons of concrete roads
Compared to asphalt roads, concrete roads have a number of advantages:
- High strength and rigidity of the coating;
- Resistance to higher dynamic loads;
- Resistance to heat and temperature changes;
- Long service life without the need for repairs;
- Good adhesion of the road surface and car wheels increases traffic safety.
The roads have fewer disadvantages, but they are significant:
- High construction cost;
- The need for strict adherence to technology when preparing solutions and selecting components;
- The need for the concrete to fully gain strength before starting the road.
Road maintenance
To protect roads of this type, it is recommended to treat concrete with a product that covers the canvas with a film and protects it from temperature changes and impregnation with water. These can be foams, films, hydrophobic liquids. Concrete roads are becoming popular. By giving preference to such roads, developers will forget about frequent repairs, as is the case with asphalt. In rural areas, roads are built with your own hands from scrap materials, but progress does not stand still.
Previously, people tried to neglect concrete roads because they were considered expensive. Over time, everything has changed. Nowadays it is much more practical to fill roads with concrete. Due to the availability of machines that are multi-functional and highly productive, the need for DIY construction is eliminated. In a few years, the construction of concrete roads will come to the fore.
Construction of a concrete road
Let us consider in detail the stages of constructing concrete roads, since the service life of the coating depends on compliance with the laying technology.
Soil preparation
Excavation work is one of the most expensive and complex. Before they begin, a detailed project is drawn up, based on a geological study of the relief. If possible, the laying plane of the road is made horizontal - the mounds are removed, and a board is made into the recesses with rock compaction.
The fertile layer of soil is removed: for large-scale construction of a highway, completely; for private laying of adjacent areas, 15-20 cm is enough. The lower ones are compacted with rollers and vibrating plates with a large weight. This is one of the most critical stages - the rigidity and integrity of the coating under intense dynamic loads depends on the strength level of the base.
At the stage of preparatory work with the soil, a drainage system is thought out to drain groundwater and rainwater. To do this, the base is made not in an ideal plane, but at a slight angle of 2-4%. Concrete gutters or natural slopes can be installed along the road, along which water flows into a receiver or into the ground.
Laying the bedding layer
Crushed stone and sand are poured onto the compacted soil. They perform the function of load compensator and water drainage.
The thickness of the bedding layers depends on the type of relief and the properties of the foundations and fluctuates around 20-40 cm. When laying intercity roads, geotest is often laid between sand and crushed stone - it does not allow the factions to mix and the embankments perform their functions better.
On foundations with a high groundwater level, it is rational to make the crushed stone mound thicker - it does not wash out and drains water well. Sand must be placed under layers of concrete - it forms a dense cushion.
Both sand and crushed stone layers must be compacted with a roller or vibratory pits to achieve high cushion strength.
For convenience, the bedding layer is sometimes covered with a thin concrete screed up to 5 cm thick, and a waterproofing sheet is laid on top.
Installation of formwork and reinforcement
Concrete is weak to bending loads, so the use of reinforcement is never superfluous - the choice of its type again depends on the characteristics of the base. In some cases, reinforcement may not be used at all.
The diameter of the reinforcement for the concrete sheet is taken only structurally according to calculations. Usually these are rods from 10 mm, welded into a mesh with a cell from 150 mm. The reinforcement products are laid in a concrete layer at a height of at least 4 cm from the bottom plane. It is important that the mesh is in the lower part of the slab, since it is there that the destructive load is concentrated and cracks form.
The easiest way to make formwork is to use thick boards with a cross-section of 50x150 mm (the choice of height depends on the design layer of the concrete base and coating). Thick plywood will also work. Boards and plywood are fixed with reinforcing pegs stuck into the ground from the outside of the sheet. When laying paths for pedestrians and parking lots for cars, the formwork can be replaced by curb stone installed at the stage of preparation for pouring.
Laying concrete pavement
Pouring the road with concrete must be carried out continuously, so the materials for the roadbed are prepared immediately in the required quantity. It is advisable to order concrete from the factory; during the construction of large roads, temporary mobile workshops for the production of mortar are installed near the sites, which reduces delivery costs.
If necessary, low-grade concrete (for example, M200) is laid on the base with bedding, then with finishing mortar M400 with additives.
Laying the top covering occurs in 2 stages: first, a 30-40 mm substrate is poured, reinforcing mesh is laid on it and the remaining thickness is poured.
The total layer thickness is about 12 cm, sometimes more or less.
Concrete is poured for preparation without interruption and the surface is immediately leveled. Material is constantly being delivered, work goes on around the clock.
After laying, the concrete must be compacted using vibrocompression. The procedure expels air bubbles and compacts the structure of the finished coating.
Cutting and sealing expansion joints
The construction of a concrete road includes cutting the road surface into segments. This is possible, then the concrete will gain sufficient strength of 50-60% and will withstand the weight of a person and cutting equipment.
Seams are needed to compensate for thermal expansion, which the concrete stone is subjected to to varying degrees. When the volume of slabs changes seasonally, cracks do not form in the road surface.
Sawing is carried out with a special tool - a jointer.
Expansion joints are made at a distance determined by calculations. One of the determination formulas is coating thickness × 30.
To prevent water from penetrating into the slab through the seams, they are filled with bitumen-polymer sealants.
Reinforcement of concrete roads
Pavilonis Alexander
- (067) 238-09-88
Polyex Mesh fiber is a modern alternative to the steel reinforcement cage used in the construction of concrete road surfaces.
As you know, concrete is one of the most durable materials, so it is widely used in construction. Even steel cannot withstand its compression characteristics. But concrete, like any other material, has a number of its own disadvantages, among which is the lack of plastic characteristics. It is for this reason that reinforcement is produced in concrete products. If we focus on plasticity, viscosity, cracking and shrinkage, then the best material for reinforcement and for enhancing these properties is co-polymer fiber Polyex Mesh .
When laying a concrete road, the minimum recommended thickness of the concrete layer should be at least 17 cm, but the optimal thickness for heavy loads is 20-25 cm. Special devices, so-called anti-shrinkage anchors, must be installed in places where concreting is interrupted and in places where maps are separated. Anti-shrinkage anchors are special devices that absorb shrinkage and temperature expansion. Special notches are also applied to impart a rough, rather than smooth, base to the coating. This is achieved by running special brushes along the slopes of the road and roughening the surface of the concrete road to increase the adhesion of vehicles to the concrete surface.
Previously, when constructing concrete road surfaces, a continuous steel reinforcement cage or a discontinuous reinforcement cage was mainly used. With the growth of the level of current technologies, we can conclude that it is much better, more reliable, faster and cheaper to use co-polymer fiber Polyex Mesh . This fiber is a very durable material, i.e. This wire has the breaking characteristics of steel.
Polyex Mesh fiber has a huge number of advantages over steel: it is light, cheap and does not corrode. It can be supplied together with concrete mortar using conventional concrete pumps, and it does not damage the equipment. At the same time, its plasticity characteristics, which it imparts to concrete, allow coatings to serve for a very long time, preventing shrinkage and plastic cracking; accordingly, this material is ideal for reinforcing concrete surfaces and concrete roads.
In order to properly build a concrete road, you must first prepare the foundation, i.e. These must be stable draining soils, preferably river sand, with a coefficient of no lower than 1.6. Other types of soils can also be used, but with the obligatory use of geosynthetic materials in order to reinforce this embankment. Next, you must remember about the drainage layer and the underlying layer, i.e. you can make the base from crushed stone or from the same asphalt concrete or from lean concrete, i.e. from concrete preparation. Again, when constructing these layers, it is mandatory to use geosynthetic materials to reinforce the embankment. After this, concrete pavement is installed using concrete of a grade not lower than M400, i.e. There must be heavy road concrete. Also, in addition to all of the above, it is necessary to take into account that this concrete sheet must necessarily be divided into maps, i.e. depending on the coverage width, these cards can reach up to 6x6 or even more. In places where concreting is interrupted, anti-shrinkage anchors must be installed.
Very often we are accustomed to the fact that concrete roads are constructed using a very complex piece of equipment, special concrete pumps, concrete pavers, etc. But in fact, if there is a need, then you can build concrete surfaces and concrete roads with your own hands. Those. It is enough to compact the base with high quality and make reinforcement, carry out drainage and concrete preparations, and then set up the formwork. In this way, you can lay concrete roads and concrete surfaces without using heavy equipment. The most important thing is to choose the right thickness, concrete composition, and, according to the recommendations of our experts, to make reinforcement using Polyex Mesh fiber. After this, you need to pour it in a high-quality manner and monitor the hardening of the concrete so that this surface turns out to be of the highest quality.
Care and prevention of concrete pavement
To ensure that the work does not go in vain, according to technology, a concrete road can be opened for traffic only after the concrete has fully gained strength, that is, after 28 days.
To prevent destruction of the canvas, it is protected with polymer impregnations, which form a waterproof film on the surface. True, these reduce the roughness of the road and its grip on the wheels. This is a negative quality for highways, so in most cases the roadbed is left as is. If the soil preparation and laying technology have been followed, the seams are cut correctly, nothing threatens the integrity of the slabs for a long time.
Another way to prevent and repair concrete roads is to lay a wear layer. Asphalt is applied to the concrete, which provides traction between the wheels and the surface, and extends the service life of the highway itself several times. In addition, repairing asphalt concrete pavement is much cheaper.
If cracks appear, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate them. To repair small damage, special putties are used, and to repair deeper damage, concrete mortar is used. In all cases, the crack is cleaned and moistened before introducing the filler.
If a fault occurs, the entire section of the canvas will have to be removed. The cause of such deformations is insufficient compaction of the soil base or embankment.