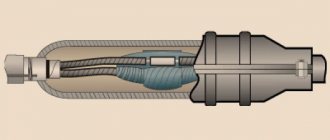
What is AABL wire
AABL cable is one of the most common types of power cable products with an aluminum sheath and impregnated paper insulation.
AABL cable
Decoding AABL:
- A - current-carrying conductor made of aluminum.
- A - aluminum shell.
- B - armor made of galvanized steel strips.
- L - polyethylene terephthalate tapes as a layer in the cushion under the armor.
ААБл 3х120-10
Explanation of cable brand AABl 3x120-10
A - Aluminum conductor
A - Aluminum sheath
B - Armor made of two steel strips
l - The cushion under the armor has a layer of plastic tapes
Structural elements of cable brand AABl 3x120-10
1. Aluminum conductor:
- single-wire (class 1) with a cross-section of 25-240 sq. mm.,
- stranded (class 1 or 2) with a cross section of 70-800 sq. mm.;
2. Phase paper insulation, impregnated with a viscous or non-drip insulating impregnation composition;
core markings:
- digital: 1, 2, 3, 4,
- color: white or yellow, blue or green, red or crimson, brown or black;
3. Filling with paper tows;
4. Belt paper insulation impregnated with a viscous or non-drip insulating impregnating composition;
5. Screen made of electrically conductive paper for cables designed for voltages of 6 kV or more;
6. Aluminum shell;
7. Cushion made of bitumen, PVC film and crepe paper;
8. Armor made of steel tapes;
9. An outer cover made of glass or cable yarn and a coating that protects the cable from sticking.
The cable is manufactured according to GOST 18410-73
Scope of application of cable brand AABL 3x120-10
Cables of the AABl 3x120-10 brand are intended for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy in stationary installations in electrical networks designed for voltages up to 10 kV with a frequency of 50 Hz. Cables with two copper control conductors and a cross-section of 1.5 sq. mm are intended for networks of all types of electrified transport.
Cables of this type are intended for use in macroclimatic areas with moderate and cold climates. They are also intended for use in the ground (trenches) with low and medium corrosive activity with the absence of stray currents, provided that the cables are not stretched or deformed during operation.
Cables with non-draining insulating impregnation composition (CAABl) are intended for laying on vertical and inclined sections of routes without limiting the difference in levels.
Cable AABL 3x120-10 in stock. Order and buy AABL 3*120-10
To clarify the availability of cable AABL 3x120-10, call or send a request. Cable AABL 3x120-10 (mn) and AABL 3x120-10 (mp) is an analogue of AABL 3x120-10. These indices mean that the cores of the AABL 3x120-10 cable are made in a multi-wire design. Price AABL 3x120-10 - price list You can find out the cost of AABL 3x120-10 by sending us a request.
List of complete documents upon delivery of AABL 3x120-10 in Podolsk
— TORG-12 (delivery note) — Invoice — Passport/test report for cable AABL 3x120-10 — Certificate of conformity from the manufacturer — Delivery agreement (upon conclusion) — Specification for the contract — Certificate of unwinding of cable AABL 3x120-10 (upon request )
Weight AABL 3x120-10 Estimated weight of cable AABL 3x120-10: 1 km - 3700.131 kg * *Weight of cable AABL 3x120-10 is calculated and may differ slightly from the actual one. Outer diameter AABL 3x120-10 Outer diameter of cable AABL 3x120-10: - 51.3 mm * *The diameter of the cable AABL 3x120-10 is calculated and may differ slightly from the actual one. The service life of cable brand AABl 3x120-10 is at least 30 years.
Specifications
An electrical cable is an element designed to conduct electricity. The main material from which they are made is copper (due to its high degree of conductivity), although aluminum is sometimes used. Its conductivity is lower, but it is cheaper than copper.
The AABL cable has the following technical characteristics:
- The bending radius during installation should not exceed 25 outer diameters of the shell.
- Operating temperature range from -50 to +50 degrees.
- The wire can withstand prolonged heating up to +80 degrees.
- The cable is designed for 30 years of operation.
- Rated voltage - from 1 to 10 kilovolts at a current frequency of 50 hertz.
- Insulation resistance – 100 MOhm per km.
- The installation temperature should not be below 0 degrees.
- Normal operating conditions are humidity 98% at a temperature of +35 degrees.
- For one core the temperature should not be higher than +80 degrees.
Electrical cables consist of a conductor, insulation, filling layer and sheath. Each of these elements performs its own function:
- Electrical conductor. This is the part of the cable that carries electricity and may consist of one or more copper or aluminum wires.
- Insulation. Covers the conductor, ensures that electric current does not exit the cable and is transported through the metal along the entire length of the product.
- Filling layer. Located between the insulation and the conductor. Ensures that the cable maintains a rounded appearance, since in many cases the conductors have several wires, which is why their cross-sectional shape is far from ideal. The layer achieves a rounded and uniform appearance.
- Shell. Material that protects the cable from bad weather and external influences.
When choosing aluminum as a conductor material, there are several considerations to take into account. Aluminum's lower conductivity requires conductor cross-sections to be approximately 30% larger than copper construction - an aspect to consider if robust cabling is required.
You might be interested in this Description of the KG cable
Important! Aluminum is about 70 percent lighter than copper. This not only means a reduction in the weight of all components required in many applications, but also makes it easier to install the power supply system.
In addition, in cases where flexible cable connection is required, the primary choice should be aluminum.
Structural elements of cable AABL 3x120(ozh)-1:
1. Aluminum conductor: • single-wire (class 1) with a cross-section of 25-240 sq. mm., • multi-wire (class 1 or 2) with a cross-section of 70-800 sq. mm.;
2.Phase paper insulation impregnated with a viscous or non-draining insulating impregnation composition;
core markings: • digital: 1, 2, 3, 4, • color: white or yellow, blue or green, red or crimson, brown or black;
3. Filling with paper tows; 4. Belt paper insulation impregnated with a viscous or non-drip insulating impregnating composition; 5. Screen made of electrically conductive paper for cables for voltages of 6 kV and more; 6.Aluminum shell; 7. Cushion made of bitumen, PVC film and crepe paper; 8. Armor made of steel tapes; 9. An outer cover made of glass or cable yarn and a coating that protects the cable from sticking.
Purpose of the AABL marking wire
These wires are used in a wide variety of industries. AAB is needed in wiring that requires increased reliability, for example, in high-voltage transmission lines. The widest range of power cables is a consequence of the diverse range of applications. The technical characteristics of the cable allow it to be used in cable mezzanines, shafts, dry and damp rooms, collectors, and on technological racks. The cable is laid in explosive and fire hazardous areas. Can be used in cold climates.
AABL cable in high-voltage transmission lines
Scope of application of cable AABL 3x120(ozh)-1:
The cables are intended for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy in stationary installations in electrical networks for voltages up to 10 kV with a frequency of 50 Hz. Cables with two copper control conductors with a cross-section of 1.5 sq. mm are intended for electrified transport networks.
The cables are designed for use in macroclimatic areas with moderate and cold climates. The cables are intended for use in the ground (trenches) with low and medium corrosive activity with the absence of stray currents, if the cables are not subjected to tensile forces during operation. Cables with non-draining insulating impregnation composition (CAABl) are intended for laying on vertical and inclined sections of routes without limiting the difference in levels.
The service life of cable AABL 3x120(ozh)-1 is at least 30 years.
| 95 and 120 | 250-400 |
| 150 or more | 200-350 |
How to choose AABL wire
An insulated conductor is exactly the same as a non-insulated conductor with the only difference being that the core is covered with a layer of insulation so that the metal does not come into contact with any other elements such as other conductors, people or metal objects. Insulated wire is used much more often than bare copper in both homes and offices. The advantages and disadvantages of using aluminum or copper conductors have been debated for many years. Most of the concerns on the part of users are related to the fact that reliable information about them does not exist, or it is long out of date.
Note! Aluminum has a higher thermal expansion than copper and steel, but it is important to know which aluminum alloy is used.
To understand the differences in use of these two materials, it is necessary to know their mechanical and electrical characteristics. Three materials are used as conductors in electrical distribution boards: copper, aluminum and silver.
Due to the fact that copper is becoming increasingly scarce, and the demand for it is only growing, the cost of this metal has increased proportionally in recent years, so the use of aluminum is becoming increasingly popular. In the case of silver, due to its high cost, it is only used to coat joints and contact surfaces. Copper is also sometimes used in its pure form, as its commercial conductivity is 98%. On the other hand, pure aluminum cannot be used as an electrical conductor because it is too soft for mechanical components, so it is always used in alloy with other materials.
You might be interested in this Features of the VBBShV cable
Important! Regardless of the material used, the appropriate conductor size must be considered to meet the above requirements. In the case of aluminum, its cross-section must be larger to achieve conductivity levels similar to those of copper.
When choosing a cable, you need to pay attention to the following aspects:
- Number of cores
- Core cross-section.
- Presence of copper cores.
- The presence of protective covers.
Power cable AABL
It should be noted right away that the AABL power cable is the basic version of this type of cable in the “simplest” design. For example, the AAB2l cable has not one, but two PET tapes under the armor. The AAB2lShv cable, among other things, is covered with a protective PVC hose.
AABL cable design
The standards for marking cable products make it clear to us that this cable has aluminum conductors (the first letter “A”), an aluminum sheath (the second letter “A”), armor (the letter “B”) and some kind of protective tape.
In fact, everything is so, but on the cross-section everything is much more interesting.
Firstly, the cable cores are made of soft electrical aluminum. They can be a single wire (“ozh”) or a bundle of twisted thin wires (“mzh”). In cross-section, the cross-sections of the cores can be round (“ok”) or in the form of an almost triangular sector (“os” or “ms”). The small letters listed may appear on cable markings.
Read: 5 main advantages of industrial automation
Thirdly, in this cable, single-wire conductors can have a cross-section from 25 to 250 mm2, multi-wire conductors can have a cross-section from 70 to 800 mm2. The core insulation is marked with color or numbers;
Fourthly, the insulation of the cable cores is paper-oil, that is, paper impregnated with a dielectric compound is used for it. The consistency of the impregnation composition can be viscous (the letter “B” may appear in the marking) or non-draining (the letter “H” in the marking.” A cable with viscous impregnation has a 15-25 meter limit on cable laying levels. Cable for vertical and inclined installation is marked TSAABl, where the letter “C” denotes ceresin impregnation.
The insulation of all cable cores is also paper-oil.
Fifthly, in 6 and 10 kV cables, the entire structure is covered with an electrically conductive paper screen.
And only sixthly, all this is covered with an aluminum shell.
Next, the aluminum is covered with a cushion of bitumen, paper and PVC film.
And only then all this is covered with strips of galvanized steel (armor).
Read: Features of the design and installation of an attic roof
If you look at the following photo of the AABL cable, you will not see the armor. This is because in cable construction, the armor strips are covered with cable or glass yarn and a layer of anti-stick coating (it is whitish in color).
Drum photo
As you can see in the next photo, the cable design is very different from the “simple” abbreviation AABL.
Photo of the cut
You can see the basic technical characteristics of the cable in the table.
Wire structure
Power cable layers:
- Outer layer.
- Aggregate. Special paper used for insulation, collected into bundles.
- An element that conducts current.
- Insulation layer. It is made from special paper, which is impregnated with a viscous mixture.
- Armor. Steel tapes.
- Paper screen. High current conductivity is necessary on wires rated at 6000 volts or more.
- Belt insulator made of paper.
- Aluminum shell.
- Crepe paper, polyvinyl chloride film and bitumen pad.
Layers of wire
Wire composition
The AABL power cable consists of several layers:
- The current-conducting element can be single- or multi-wire. In the first case, class I wire with an area of 25 to 240 mm2 is used. In the second case, class I and II wire is used with an area of 70 to 800 mm2.
- An insulating layer made of special paper impregnated with a viscous non-drip mixture. In this case, a numerical identification is applied to the insulator, and they also differ in color. Depending on the number of cores, the following colors are used: white (yellow), brown (black), red (crimson), blue (green).
- Filler – strands of special paper used for the insulating layer.
- Belt insulator made of paper impregnated with a similar mixture.
- A paper screen with high current conductivity, installed on wires rated for 6000 volts or more.
- Aluminum shell.
- Bitumen pad, polyvinyl chloride film and crepe paper.
- Armor – a pair of steel strips.
- The outer layer is a yarn of glass or cable, as well as a coating that prevents cable turns from sticking during transportation and storage.
How to use the wire correctly (+ how to connect)
This cable is mainly used for laying in earthen trenches. There is no need to use supporting structures, which is very suitable for power supply of objects in urban areas with dense buildings. The technical characteristics of the cable line are improved, external influences cause less mechanical damage. Installation is carried out in accordance with the project, which is necessary to determine the depth, route and profile of the trench for installation. According to building codes, the cable is laid in a sand bed.
Installation
In principle, it is important to use the correct installation elements when laying cables and pipes. But it is also very important to pay attention to certain rules and basics of electrical installation. These include, for example:
- Installation zones.
- Classification of circuits.
- Installation in concrete ceilings.
- Outdoor seating.
- Installation in plasterboard and wooden walls.
Important! When laying cables and lines, you need to ensure that they are protected from mechanical damage.
In recent years, many reasonable standards have been established to make the modern home safe. Modern circuit breakers instantly cut off power in the event of an overload and prevent fires in power cables. So-called residual current protection devices (RCDs) protect lives. They react like lightning to overvoltage or residual currents, such as when a child inserts a paperclip into an outlet. Such switches are now mandatory, especially in wet areas such as bathrooms. The same applies to outdoor sockets in the garden.
Description
AABL cable stands for:
- A – aluminum conductor;
- A – aluminum shell;
- B – armor made of two steel strips;
- l – in the cushion under the armor there is a layer of plastic tapes.
The picture shows the abbreviation (full explanation of the cable) AABL.
Decoding of the AABL markings
Important! Pure aluminum conducts electricity better than any other cheap conductor. The problem is that aluminum wires are not particularly strong. Therefore, for some installation methods (for example, in an earthen trench), they are made in steel armor.
AABL cable design elements:
- Aluminum conductor:
- single-wire (class 1) with a cross-section of 25-240 sq. mm,
- stranded (class 1 or 2) with a cross section of 70-800 sq. mm,
- phase paper insulation impregnated with a viscous or non-drip insulating impregnation composition.
- Core markings:
- digital: 1, 2, 3, 4;
- color: white or yellow, blue or green, red or crimson, brown or black.
- Filling from paper bundles;
- Belt paper insulation impregnated with a viscous or non-drip insulating impregnation compound;
- Screen made of electrically conductive paper for cables for voltages of 6 kV and more;
- Aluminum shell;
- Armor made of steel strips;
- An outer cover of glass or cable yarn and a coating that prevents the cable from sticking together.
Cable trench
For information. Aluminum has two properties that make it useful: cost and density. By density, using it you can gain 1/3 of the weight for the same volume. This provides a major mechanical advantage if it is possible to increase the cross-sectional area.
What are the problems when using wire?
Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity and is in strong demand due to its high electrical conductivity, corrosion and temperature resistance. These characteristics of this metal put it in first place when carrying out electrical installation work.
You may be interested in this Junction box
On the other hand, aluminum has very noticeable disadvantages when it comes to conducting electricity and especially in the production of electrical and electronic circuits. Due to its greater ductility, aluminum is less preferred than copper.
Problems during operation
The most notable disadvantage of aluminum cables is that they tend to deform more as temperatures change than their copper counterparts, so they are not recommended for use in applications that operate at high temperatures.
Another disadvantage to add is that aluminum is only 60% conductive compared to copper, which means using a larger diameter to conduct the same amount of electricity as copper. In addition, aluminum quickly oxidizes and breaks down upon contact with wet surfaces.
Important! Most problems can be avoided before the facility starts operating. To do this, you just need to choose the most suitable cable and carry out installation according to all the rules.
Main advantages
When operating an AABL cable, a number of necessary components are taken into account:
- the main provisions should not have stray currents;
- soil activity in relation to corrosion;
- Stretching on flat and curved areas is not recommended;
- resistance to short circuit currents and heating during their flow reaches up to +2000C.
Before purchasing conductors of this type, you need to study the properties of the cable. Since it is laid in the ground, it is necessary to take into account the location of the installation, namely the properties of the soil, because such cables can only be laid in conditions of medium and low corrosive activity. It is also necessary to take into account factors such as the appearance of stray currents, stretching, and bending. When laying conductors, it is necessary to artificially create conditions for height differences.
Today, cables of this type are used in various fields of activity, as they have the necessary technical characteristics and are easy to install, transport and operate. But these are not their main advantages; they are also able to withstand the most aggressive environmental conditions.
Manufacturers of AABL brand wire
The best manufacturers of AABl cable are Kamkabel, Kavkazkabel and Saranskkabel. These are the best factories, their consumers are the largest companies in Russia.
Cable production
"Kamkabel"
Located in the city of Perm, the plant has a powerful testing base and modern technological equipment, which ensures the production of the highest quality cables with different types of insulation. Cables are produced according to both Russian and foreign standards. Power cables produced at this plant account for 35% of the Russian cable market. The plant employs 3 thousand employees.
Kamkabel produces products in the following types of insulation:
- Glass threads.
- Cross-linked polyethylene
- Fluoroplastic films.
- PVC plastic.
- Paper-impregnated.
- Rubber.
All products of the plant can be found in the catalog on the website
"Kavkazkabel"
Although the plant received its current name in 2004, the history of the enterprise begins in 1958. Today Kavkazkabel is a dynamically developing company with extensive experience. All products are manufactured in accordance with GOST and certified.
On
Important! Winding wires is one of the main specializations. Kavkazkabel has the widest range of this type of product. Products are manufactured in the shortest possible time thanks to the use of modern technologies. His achievements are marked by numerous diplomas.
Saranskcable
The history of the plant begins in 1950. A wide range of cable and wire products are produced for many industries. The plant has close partnerships with many Russian and foreign companies.
AABL type wires are excellent for use in urban areas, cold climates, damp or fire hazardous areas. A variety of industries require high-quality aluminum and copper electrical conductors, and modern production fully satisfies this demand.
Technical characteristics of cable ААБл
Now let's look at the technical characteristics of the AABL cable and its operational properties.
- The work is carried out at air humidity of 30-350C.
- The cable service life is 35 years.
- AC voltage is used at 50 GHz.
- The highest temperature at which the cable can operate is 600C.
- The operating voltage used is 25 kV.
- The temperature of the ground in which the conductor can be laid varies from +50 to -500C.
- Insulation resistance – 200 Ohm per 1 km.
Design
Cables with voltages of 6 and 10 kV are made with three cores. Cables with a voltage of 1 kV - three- and four-core. The current-carrying conductor is aluminum single-wire - with a cross-section of 35-240 mm2, multi-wire - 70-240 mm2. Insulation - cable paper impregnated with a viscous or non-drip impregnating composition. Cables with non-draining impregnating composition are manufactured with a cross-section of 35-185 mm2 for voltages of 6, 10 kV. Aluminum shell. AAG
cable -
without protective cover;
— cables AAShv, TSAAShv
— sheath made of PVC plastic;
— cables AAShng, TsAAShng
— sheath made of PVC plastic compound of reduced flammability;
- cables AABl, AAB2l, AABlG, AABnlG, TsAABL, TsAABLG, TsAAB2l, TsAABnlG
- cushion under armor (bitumen, PVC film, PET-E film, crepe paper, glass yarn), armor (steel tape), external protective cover (except AABlG , TsAABLG, AABnlG, TsAABnlG) - bitumen, glass yarn, chalk;
— cables AAPl, AAPlG, AAP2l, TSAAPl, TSAAPlG, TSAAP2l
— cushion under armor (bitumen, PVC film, PET-E film, crepe paper, glass yarn), armor (galvanized steel wires), outer protective cover (except AAPlG, TSAAPlG) — bitumen, glass yarn, chalk;
— cable AAB2lShv
— cushion under armor (bitumen, PET-E film, crepe paper), armor (steel tape), outer protective cover (PVC sheath);
- cables AABv, AABvG, TSAABv, TSAABvG
- armor cushion (bitumen, PET-E film, PVC sheath, crepe paper), armor (steel tape), outer protective cover (except AABvG, TSAABvG) - bitumen, glass yarn , chalk.