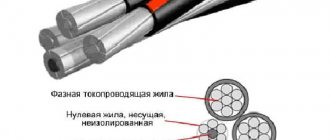
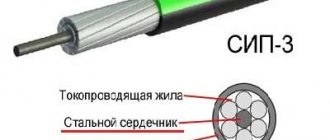
DESCRIPTION OF CABLE SHELL MATERIALS
PVC - POLYVINYL CHLORIDE
Thermoplastic material of mixed composition. Pros: elasticity, density and strength, water resistance, air tightness, heat resistance, sun resistance, non-oxidation, low cost, relatively long service life (from 5 to 15 years depending on use and characteristics).
PVC-UV Light-stabilized polyethylene is used for the sheathing of cables and wires that can be used outdoors. Light-stabilized polyethylene is obtained by adding carbon black and other light-stabilizing components to polyethylene. This polyethylene is frost-resistant! Not afraid of snow, hail or sun rays up to 4 years.
FR-PVC FLAME RETARDANT POLYVINYL CHLORIDE Flame retardant thermoplastic material (meets UL 1581 VW-1). General purpose insulation for applications meeting limited fire resistance requirements.
LSZH LOW SMOKE ZERO (NO) HALOGEN
LSZH, LS0H, LSOH, LSNH - a shell with low smoke emission and zero halogen content, does not emit aggressive acid gases during combustion. Cables with LSZH sheath are designed for use where low-smoke and low-corrosive gases are required. Used on board ships and computer communications centers and equipment.
FR-LSZH FIRE RESISTANT (FLAME RETARDANT - LOW SMOKE ZERO (NO) HALOGEN) Complies with DINVDE and ICE standards. Fire-resistant, low-smoke and halogen-free material. When burning, it does not emit aggressive acid gases.
FRNC/LSZH FIRE RESISTANT (FLAME RETARDANT NON CORROSIVE - LOW SMOKE ZERO (NO) HALOGEN)
Complies with DINVDE and ICE standards. Fire-resistant, non-corrosive, low smoke and halogen-free material. When burning, it does not emit aggressive acid gases.
FRNC FIRE RESISTANT (FLAME RETARDANT NON CORROSIVE)
The cable sheath is characterized as FR (non-flammable, non-flammable) and NC (non-corrosive). Cable sheaths can be marked as FRNC, or individually FR or NC, depending on the material used. There are designations FRNC/LSZH, FR/LSZH, FR/PVC and others.
FRNC Eca FIRE RESISTANT (FLAME RETARDANT NON CORROSIVE ECA)
Fire-resistant, with improved fire-resistant characteristics that prevent the spread of flame, emit a small amount of heat during combustion, and are not subject to corrosion. The material is included in the European Construction Product Regulation (CPR) and complies with the Eca class.
FRNC Dca FIRE RESISTANT (FLAME RETARDANT NON CORROSIVE DCA) Fire resistant, with improved fire-resistant characteristics that prevent the spread of flame, emit a small amount of heat during combustion, and are not subject to corrosion. The material is included in the European Construction Product Regulation (CPR - Construction Product Regulation), and corresponds to class Dca - s2, d2, a1 according to EN50575. FRNC-C FIRE RESISTANT (FLAME RETARDANT NON CORROSIVE)
Fire-resistant when laid in groups, does not emit aggressive acid gases during combustion, and is not subject to corrosion. Complies with VDE 0472 and IEC 60332-1, 60332-3 standards
PUR POLYURETHANE
Thermoplastic elastomer, characterized by excellent elasticity at ultra-low temperatures (below - 40ºC), with a low coefficient of friction, tensile strength, abrasion resistant, resistant to UV radiation, oils, hydrolysis and microbes, suitable for outdoor cables. Polyurethane coated cable is particularly suitable for industrial applications. Since such a shell has a higher degree of resistance to chemicals and hydrolysis.
PUR-FRZH POLYURETHANE (POLYURETANE - FLAME RETARDANT ZERO (NO) HALOGEN)
Thermoplastic elastomer, characterized by excellent elasticity at ultra-low temperatures (below - 40ºC), with a low coefficient of friction, tensile strength, abrasion resistant, resistant to UV radiation, oils, hydrolysis and microbes, suitable for outdoor cables. Also meets fire resistance and halogen-free requirements. When burning, it does not emit aggressive acid gases.
PE - POLYETHYLENE (POLYETHYLENE) Synthetic material with an extremely low degree of dielectric constant and complete waterproofness, plastic, flexible. Used for internal and external insulation of conductors in cables. Intended for use in an aquatic environment, as well as for street use. is resistant to ultraviolet radiation and low temperatures. UV-PE - POLYETHYLENE
Light-stabilized synthetic material with an extremely low degree of dielectric constant and complete waterproofness, plastic, flexible. Used for internal and external insulation of conductors in cables. Intended for use in an aquatic environment, as well as for street use. is resistant to ultraviolet radiation and low temperatures.
TPE - THERMOPLASTIC ELASTOMER
An excellent combination of high material characteristics with a minimum thickness of the resulting insulation, a high degree of tear resistance and shape retention, remains elastic in extreme temperatures, excellent electrical insulation characteristics, heat-resistant, chemically resistant. PVCRW Sheath material. Here PVC is a plastic compound based on PVC (polyvinyl chloride), RW - recycled white - recycled, white. Recycled is usually a mixture of primary and secondary PVC in different proportions.
LS PVC Low Smoke Polyvinyl Chloride. Operating temperature, from 0 to +75°C. PVCNC Polyvinyl Chloride, which does not emit corrosive products (Polyvinyl Chloride Non-Contaminating)
PVC-S Suspension polyvinyl chloride is a thermoplastic polymer of vinyl chloride, one of the most common plastics. It has low water absorption, good dielectric properties, better heat resistance and light fastness.
Fluoropolymers are the insulating material of the cable protective sheath. This material has high protection characteristics over a very wide temperature range (from -190 to +260 °C). This material is characterized by a high degree of resistance to chemical and other aggressive environments, and also has excellent electrical and mechanical properties.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): temperature range: -190 °C to +260 °C This material has excellent mechanical and electrical properties, as well as high chemical resistance. InBalt offers PTFE in extruded form and in the form of tape in a roll.
Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA): temperature range: -190 °C to +260 °C
Has the same properties as PTFE insulation. Used in extruded form. Fluoroethylenepropylene (FEP): temperature range: -100 °C to +205 °C
The material properties are similar to those of PTFE polymer, excluding the temperature range. Used in extruded form.
Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE): temperature range: -100 °C up to +150 °C
Chemical and mechanical properties are similar to those of PTFE insulation. Used in extruded form.
PVDF – Polyvinylidene fluoride A material consisting of 80% polyvinyl fluoride and 20% acrylic. The coating is durable, most resistant to UV radiation, practically does not fade, is highly resistant to aggressive environments and mechanical stress, and has a glossy surface.
It is advisable to use PVDF-coated fabrics in aggressive environments, such as the sea coast, chemical industry facilities, etc.
Main performance characteristics of FR PVDF fabric:
high mechanical resistance; high strength, even at low temperatures; chemical resistance; high permissible operating temperature (150 C); electrical insulating properties; physiological neutrality (PVDF is acceptable for direct contact with food products and in medicine); dimensional stability (PVDF does not change shape even in humid conditions); low flammability; resistance to UV radiation and weather conditions; compression resistance.
EPDM - Ethylene propylene diene elastomer
It has heat resistance, chemical resistance, as well as relatively high physical and mechanical properties
CPE - Chlorinated polyethylene
CSPE - Chlorosulfonated polyethylene
IP - Irradiated polyethylene A valuable property of irradiated polyethylene insulation is its high heat resistance. A wire insulated with irradiated polyethylene does not change its performance characteristics after exposure for 24 hours in molten tin at a temperature of +300°C
TPE - Thermoplastic elastomers
HFPE - Highly foamed polyethylene
GiFHDPE - Gas-filled high-density polyethylene foam (Gas injected FHDPE)
FHDPE - High Density Polyethylene Foam
PP - Polymer coating
PBT - Polybutylene terephthalate
A very tough, durable, wear-resistant, impact- and crack-resistant thermoplastic
For semiconducting shields of paper-insulated cables for voltages of 10, 20 and 35 kV, electrically conductive cable single-layer compacted paper of the KPU-80 and KPU-120 brands is used. Electrically conductive paper contains acetylene black. The specific electrical volumetric resistance of papers of the KPU-80 and KPU-120 grades is 1 × 103 - 9 × 104 Ohm m.
Semi-conducting screens made of PE, PVC plastic in cables with plastic insulation for a voltage of 6 kV are applied only over belt insulation, for 10 kV and above - on TPG and over the insulation (in some designs, insulation screens are made of electrically conductive rubberized fabric and layers of metal tape) . The material of the screen and electrical insulation must be the same to avoid differences in the temperature coefficient of expansion of the screen and insulation. Otherwise, cavities may form in the boundary layer in which partial discharges will occur.
Protective covers, usually consisting of a moisture-proof sheath and outer protective covers, are designed to protect all cable elements from mechanical, climatic and chemical influences.
Moisture-proof shells prevent moisture from penetrating into the insulation; they can be metal (lead, aluminum, corrugated steel), plastic (polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride plastic) or rubber. Metal shells provide complete protection of insulation from moisture and are therefore used in cases where the insulation material has the ability to absorb moisture (paper, porous materials, etc.), or for special requirements of increased reliability. Although polymer shells have very low moisture permeability coefficients (especially polyethylene), they nevertheless allow moisture to penetrate inside. Over the years of operation, this moisture diffuses through the sheath, which first leads to a deterioration in the quality of the insulation (a decrease in resistance, an increase in the relative dielectric constant (ε) and the dielectric loss tangent (tgδ)), and then to its breakdown in power cables or a significant deterioration in signal transmission in communication cables. For this reason, polymer moisture-proof shells are used in cases where the insulation is sufficiently moisture-resistant, i.e. in a variety of cables with continuous polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride insulation.
Aluminum shells are made by pressing (aluminum with a purity of at least 99.5% (grade A5) or by welding (grade AD1) smooth or corrugated. They are 2 - 2.5 times stronger than lead, so power cables are often used unarmored. The high conductivity of aluminum allows use the shell as a screen for protection from external influences or as a zero conductor.The thickness of the aluminum shells is selected according to Table 1.
Table 1.
Nominal thickness of aluminum cable sheaths, mm
| Diameter under the shell, mm | Pressed | Welded | ||
| smooth | corrugated | smooth | corrugated | |
| Up to 12.5 | 1,10 | — | 0,80 | — |
| 12,5-15,0 | 1,10 | — | 1,00 | — |
| 15,0-17,5 | 1,15 | — | 1,00 | — |
| 17,5-20,0 | 1,20 | — | 1,10 | — |
| 20,0-22,5 | 1,30 | — | 1,10 | 0,70 |
| 22,5-25,0 | 1,30 | — | 1,20 | 0,80 |
| 25,0-27,5 | 1,35 | — | — | 0,80 |
| 27,5-30,0 | 1,40 | — | — | 0,90 |
| 30,0-32,5 | 1,45 | — | — | 0,90 |
| 32,5-35,0 | 1,50 | — | — | 0,90 |
| 35,0-37,5 | 1,55 | 1,35 | — | — |
| 37,5-40,0 | 1,65 | 1,40 | — | — |
| 40,0-42,5 | 1,75 | 1,50 | — | — |
| 42,5-45,0 | 1,80 | 1,55 | — | — |
| 45,0-47,5 | 1,85 | 1,60 | — | — |
| 47,5-50,0 | 1,90 | 1,60 | — | — |
| 50,0-52,5 | 1,95 | 1,65 | — | — |
| 52,5-55,0 | 2,00 | 1,70 | — | — |
| 55,0-57,5 | 2,00 | 1,70 | — | — |
| 57,5-60,0 | 2,00 | 1,70 | — | — |
Lead shells are made from lead grades C-2 and C-3 or with additives (antimony - up to 0.8%, tin - up to 0.05%, tellurium - up to 0.05%, copper - up to 0.05%). Their thickness is selected according to the table. 2.
Table 2.
Nominal thickness of lead cable sheaths, mm
| Cable diameter under sheath, mm | With protective covers | Three-core with separate sheaths over insulated conductors | Without protective covers and for underwater installation |
| Up to 15.0 | 1,05 | 1,19 | 1,34 |
| 15,0-17,5 | 1,11 | 1,26 | 1,42 |
| 17,5-20,0 | 1,15 | 1,33 | 1,50 |
| 20,0-22,5 | 1,21 | 1,40 | 1,58 |
| 22,5-25,0 | 1,26 | 1,47 | 1,66 |
| 25,0-27,5 | 1,32 | 1,53 | 1,73 |
| 27,5-30,0 | 1,36 | 1,60 | 1,81 |
| 30,0-32,5 | 1,42 | 1,66 | 1,88 |
| 32,5-35,0 | 1,46 | 1,73 | 1,96 |
| 35,0-37,5 | 1,52 | 1,79 | 2,03 |
| 37,5-40,0 | 1,56 | 1,86 | 2,11 |
| 40,0-42,5 | 1,62 | 1,92 | 2,18 |
| 42,5-45,0 | 1,66 | 1,99 | 2,20 |
| 45,0-47,5 | 1,72 | 2,05 | 2,33 |
| 47,5-50,0 | 1,76 | 2,12 | 2,41 |
| 50,0-52,5 | 1,82 | 2,18 | 2,48 |
| 52,5-55,0 | 1,86 | 2,25 | 2,50 |
| 55,0-57,5 | 1,92 | 2,31 | 2,63 |
| Over 57.5 | 1,96 | 2,38 | 2,71 |
Steel shells are made from cold-rolled steel strip 08-KP or 08-Yu with a welded seam. The seam is welded in a high-frequency unit in an argon-arc atmosphere. Steel shells are corrugated and require anti-corrosion protection with bituminous compounds and plastic hoses.
Plastic (p) or rubber (r) shells, depending on operating conditions, are divided into three categories:
Ob-1 - portable cables and wires operating in difficult conditions (earthing machines);
Ob-2 - portable cables and wires operating in average conditions or laid permanently;
Ob-3 - portable cables and wires operating in light conditions (household electrical appliances and current collectors in the absence of mechanical loads).
The thickness of this group of cable sheaths is indicated in table. 3.
Table 3
Thickness of plastic and rubber cable sheaths, mm
| Diameter of the cable product under the sheath, mm | Nominal thickness of rubber and plastic wrappers for categories | |||||
| Obr-1 | Obp-1 | Obr-2 | Obp-2 | Obr-3 | Obp-3 | |
| Until 6 | 1,5 | 1,2 | 1,5 | 1,2 | 1,0 | 0,8 |
| St. 6 to 10 | 2,0 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,5 | 1,0 | 1,0 |
| St. 10 to 15 | 2,5 | 1,7 | 2,0 | 1,5 | 1,2 | 1,2 |
| St. 15 to 20 | 3,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 1,7 | — | — |
| St. 20 to 25 | 3,5 | 2,3 | 2,5 | 1,9 | — | — |
| St. 25 to 30 | 4,5 | 2,5 | 3,0 | 1,9 | — | — |
| St. 30 to 40 | 5,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 2,1 | — | — |
| Over 40 to 50 | 5,0 | 3,5 | 4,0 | 2,3 | — | — |
| Over 50 to 60 | 6,0 | 4,0 | 4,5 | 2,5 | — | — |
| St. 60 | 6,0 | — | — | 3,0 | — | — |
The thickness of armor and external protective coverings are given in the article “Armor and protective coverings of cables”.
You may also be interested in:
- Regulation of the electric field in cable joints
- Semiconducting coatings for equalizing the electric field
- Protective coatings for aluminum-copper electrical contacts
- Electroplating
- Plasma spraying