Purposes of wire markings
The designation of cable lines and wires is carried out in order to simplify installation work, repairs and preventive maintenance of objects during operation. To improve safety measures that reduce the likelihood of accidents and injuries to operating personnel.
- the number and cross-section of wires in the cable;
- type of insulation;
- what metal are the wires made of?
- about the material of the outer insulation layer and much more.
All these measures are insufficient to achieve maximum safety and do not provide maintenance personnel with information about the purpose of cable lines and individual sections of electrical wiring. During installation in switchgears, additional markings are applied to cables and wires, which display not only the characteristics of the cable, but also its purpose in a given circuit.
A list of main parameters is indicated:
- cable brand;
- from what object does it come;
- length;
- appointment and other data as required.
To make marking convenient and quick, several methods have been invented for wires with different characteristics, diameters and insulation. Marker designs vary, but all provide clear, long-lasting writing.
Marking devices
Wiring designation is a serious and responsible matter. Each cabinet or panel inside must contain special labels that give an understanding of the connection diagram and arrangement of circuit elements. The difficulty is that the tags must be firmly fixed and the inscriptions must be preserved for a long time. Therefore, for convenience, special devices are used that mark cables and wires in the panel.
An electrical panel wiring printer is a device that is used to print tags and labels that display markings when wiring is installed. The photo shows a mini printer with which you can mark a wire or cable.
The video shows how to use this printer:
If you are not involved in professional electrical installation work, then there is no point in purchasing a special marking printer. An alternative to this device is cable markers, for example from IEK, shown in the photo below:
With their help, you can quickly mark power and low-current lines in cabinets. A more expensive pleasure is to use the graphoplast marking system, which you can learn about by watching this video:
Wire and cable marking methods
Depending on the conditions and capabilities, availability of equipment and material, installers select the optimal marking options:
Before installing the wire
- PVC cambrics (tubes) of various diameters with inscriptions, you can additionally wrap them with transparent tape for reliable fastening and protection of the inscriptions;
- Heat-shrinkable insulating tubes;
- The most accessible and cheapest way is to make an inscription on a thick paper tag, place it on the cable and wrap it with transparent tape.
These methods ensure a tight fit to the cable sheath and eliminate the possibility of marker breakage when pulling through pipes and other installation work.
After installing the wire
When wires and cables are inserted into distribution devices, marking is done in the following ways:
- Before connecting the wires to the contacts, you can use PVC casings and heat-shrinkable tubes;
- Self-laminating markers are self-adhesive, on one side the plate is not transparent, on the other side there is a matte surface for inscriptions. The tag is glued to the wire insulation and wrapped with transparent self-adhesive tape, almost like tape. The materials of the plates and glue can withstand high temperatures and are resistant to aggressive environments.
- Tags are sometimes this method is the most optimal, they are made from polymers of different formats, several ways of attaching to the cable sheath. Plastic is able to withstand high temperatures while maintaining inscriptions on its surface. The dimensions of the tags and the content of the inscriptions comply with the requirements of the PUE, PTE EP, SNiP;
- For small-diameter wires, flags made of a polymer plate are used with inscriptions of standard designations, which are established by the guidelines for the design of electrical equipment;
- Self-adhesive nylon markers;
- Sleeves and containers consist of two components, a plastic carrier is attached to a wire (container), into which a polymer tape (marker) is inserted, and the necessary information is printed on it with a special printer;
- Clips and locking rings with pre-printed values, these can be individual numbers or letters, short content of 1-3 characters. This technique does not require the use of printing devices.
Rings RU Clips RA Clips R
| Type | Profile | Description | Dimensions |
| PA | Closed profile rings for medium and large diameter wires. | 4 sizes Ø 1.3 - 16.0 mm Section 0.2 - 70.0 mm2 | |
| PY | Closed profile rings for small diameter wires. | 1 size Ø 1.0-2.0 mm Section 0.2 - 0.7 mm2 | |
| PC | Open profile clips for fixed wires. | 5 sizes Ø 2.4-7.2 mm Section 1.0 - 10.0 mm2 | |
| PK | Rings for PKH plate with clamps (to be ordered separately). There is an analogue made of steel. | For wires and harnesses of any diameter |
Main variety
Today, cords, cables and wires are used for electrical installation work. Before deciphering the markings, it is necessary to understand what these products are and what their differences are.
Wires
A wire is an electrical product consisting of one or more wires twisted together, without insulation or insulated. The core sheath is usually light and not made of metal (although wire wrapping is also common).
Such products can be used in electrical installation work (for example, installing electrical wiring in a wooden house), as well as in the manufacture of electric motor windings. Today there are wires with copper and aluminum conductors. The copper version quickly oxidizes in open space and has a high price, but at the same time it is capable of passing through higher current loads. In addition, copper is more elastic, which means it will not break as quickly. Aluminum ones are more fragile and are not connected to copper ones (except perhaps through terminals), but for that they have a low cost. Today, aluminum wiring is used less and less.
It should also be noted that the contacts may be insulated or bare. The latter option is used for power lines. An insulated wire can be protected or unprotected. Protection is provided by another layer of insulation (made of plastic or rubber), which covers the sheath of the cores.
The last classification is carried out depending on the purpose: mounting, power and installation. The mounting wire must be copper; it is used, as a rule, to connect elements of an electrical circuit in a switchboard, as well as to connect circuits in radio equipment. Power (as well as installation) is better known to us, because used outdoors and indoors.
Cables
An electrical cable is a product made up of several wires that are located under one insulating sheath (PVC, rubber, plastic). In addition to this shell, there may be additional protection - an armored shell made of wire or steel tape, which must be indicated in the marking.
There are 5 main types of electrical cables:
- power;
- control;
- For driving;
- for communication;
- radiofrequency.
Let us briefly consider the conditions of use of each product.
Power is used to transmit electricity in power and lighting electrical appliances. There are products of various types and purposes. Power cables are mainly used for external (both overhead and underground) and internal electrical wiring (in residential and non-residential premises). Power cables can have both aluminum and copper conductors. It is recommended to give preference to the latter option. The insulating layer can be PVC, paper, rubber, polyethylene, etc.
The control is used for the operation of electrical devices that transmit an information signal to control any devices. This type can also be with aluminum and copper conductors.
The control cable is a copper electrical conductor with a protective shield. Used in various automation systems. The protective screen serves to remove interference and also protect against mechanical damage.
A communication cable is used to transmit information using currents of various frequencies. Transmission of local communication lines is carried out by low-frequency conductors, and long-distance lines - by high-frequency ones.
RF cable is used in radio engineering devices. The main purpose is the transmission of video and radio signals.
Cords
Cord for household electrical appliances
So we have figured out the main differences between all three types of electrical products. We hope that the information was accessible to you. We also recommend watching the video, which provides this information more clearly:
Main characteristics and differences of conductors
General Differences
All conductors may differ in the following ways:
- Cross section. There are cores with a cross section of 0.35 mm2. up to 240 mm.sq.
- Manufacturing material: copper, aluminum, aluminum-copper (a special composite of two metals).
- Rated voltage (for example, can withstand 220 or 380V).
- Number of cores (single-core or stranded).
- Insulation material (PVC, rubber, paper).
- Protective shell material (rubber, plastic, metal).
Printing devices and instruments
To apply inscriptions to marking elements, special devices have been developed, which can be divided into several types:
Portable automatic and semi-automatic devices
Canon MK 1500 printer
One of the modern devices for automatic printing on stickers, PVC casings and heat-shrinkable tubes is the Canon MK 1500 printer.
It is possible to select several types of fonts and set cropping modes at different intervals. Printing speed is 2.5 cm per minute, on a 20 mm tube you can print 35 markers per minute with 5 full-size characters.
Hotmarker M-3E
The Hotmarker M-3E printer prints characters on cables, casings and flat tapes using the hot stamping method. The printer's heated dies press the ink into the cable sheath. The matrix has the shape of a wheel, on which there are 10 + space symbols, a total of 7 matrices, this allows you to form thousands of combinations. This printer is capable of marking products with a diameter of 13 mm.
Stationary printers
Brady LabelMark
Used in large-scale production where it is necessary to mark large volumes of products with different types of markers. Brady's software allows LabelMark to quickly change from one program to another. Within 6.5 seconds, it prints characters and sticks a tag on the cable.
The program is placed on a regular PC and transferred from it to the printer. To operate the program and operate the printer, no special highly qualified training is required. The device has a high print resolution, up to 300dpi, which allows you to print small fonts and clear images of logos. Symbols are applied to wires with diameters of 1.5-15.2 mm, maximum marker dimensions 50.8 X 50.8 mm.
| Specifications | ||
| Printing technology | thermal transfer | |
| Print Resolution | 300 dpi (300 dpi) | |
| Production cycle duration, seconds | 4,5 — 6,5 | |
| Minimum wire diameter, mm | 1,52 | |
| Maximum wire diameter, mm | 15,24 | |
| Maximum print width, mm | 50,8 | |
| Maximum print length, mm | 41,3 | |
| Maximum label width, mm | 50,8 | |
| Maximum label length, mm | 76,2 | |
| Minimum label width, mm | 6,35 | |
| Minimum label length, mm | 19,05 | |
| Ribbon outer diameter | 68.58 mm | |
| Fonts, Barcodes, Graphics | Printing fonts, barcodes and graphics are consistent with LabelMark™'s label creation capabilities . For more information on this issue, check out LabelMark™ software. | |
| Interfaces and connectors | USB, Serial RS-232C, Ethernet, PCMCIA, CompactFlash | |
| Memory | Built-in 4Mb Memory expansion 32Mb RAM using PCMCIA or CompactFlash® | |
| Dimensions, mm | 571.5 x 368.3 x 450.9 | |
| Weight, kg | 38,5 | |
| Operating temperature | from 10° to 41° C | |
| Storage and transportation temperature | -18° to 60° C | |
| Humidity | from 20% to 80% without condensation | |
| Nutrition | 90-264 V AC, at 47-63 kHz | |
Office laser printers
Used when printing on sheets of self-adhesive stickers or regular sheets of A4 paper. Tags are placed on the cables and wrapped with transparent tape. This is a simple and cheap way for small volumes of marking.
Tip #1. Do not buy expensive marking equipment if you are not professionally involved in electrical installation work. Use low cost labeling methods.
Basic requirements for marking wires in switchgears (switchgears) and switchboards
Clause 1.1.30 of the PUE states that all wires in the control panel must correspond to the alphabetic, digital and color designations. The presence of a color designation does not exclude the installation of numbers and letters. It is allowed to apply markings not along the entire length of the line, but only at the connection points.
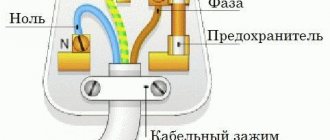
Marking begins with compliance with the rules during the installation process, when connecting wires according to the color of the insulation. This is the most clear example, which allows operating personnel to quickly navigate the purpose of each individual wire in the circuit. Sometimes cables with wires of the same color are used; in these cases, it is possible to paint the ends of the wires, put on cambrics of the corresponding color, or it is more practical to install a heat-shrinkable tube with alphabetic and digital values already applied. The length of the marker tube must be at least 2.5 cm.
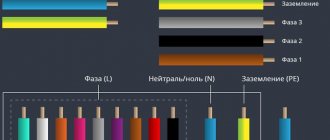
Wire marking by color
In three-phase networks, each phase is designated by the letters A, B, C, but in apartments and private houses single-phase power supply circuits are used, so there is no point in specifying which phase of the substation your panel is connected to.
Letter designations:
- The phase wire is marked with the letter “L”;
- The neutral wire is designated by the letter “N”;
- Grounding wires are marked with a symbol
- In circuits according to TN-CS system standards, it is allowed to connect the grounding conductor to the neutral wire. In such cases, “PEN” is written on the label.
- In DC power supply circuits, for individual consumer devices the polarities “+”, “-” and the voltage in volts “12V or 24V...” are indicated.
Marking DC circuits
Rules and standards for marking wiring in electrical panels
The colors for the wiring mark were chosen for a reason. All the variety of colors comes down to one standard - standard rules. They are prescribed in the rules for technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTEEP). It states that the conductors of electrical wires must be designated by color or letters and numbers, and the cabinet itself also requires designations. You can find out what types of wire color markings exist in our article.
The PUE states that:
- The electrical panel must have a name. This name is indicated on the body. In an apartment, the structure does not need to be marked with inscriptions. But for a private house, when the shield is placed on a pole, this is necessary.
- When installing it, you must leave a sheet inside the panel where all consumers (sockets and lamps) are indicated in table form.
- Also, inside there should be an assembly diagram for the input panel. This rule applies only to the device that was purchased assembled.
Note: if an electrician assembles a panel or cabinet, then you should definitely take the assembly diagram from him.
According to the same rules for the design and operation of electrical installations:
- The cable and aggregate circuits in a modular device must be marked.
- There is marking on the circuit breakers or on the information board of the installation indicating the wiring group. Also, according to the rules, the serial number and name of the room or the purpose of the group (for example, a kitchen or an air conditioner) must be indicated.
- In the event that there is no space for recording on a modular device, marking with the purpose of this installation is made in the table and passport, which each cabinet must have.
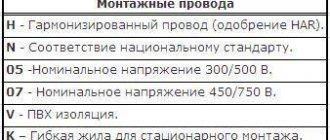
According to GOST, wires are designated:
- In accordance with GOST 23594–79 (marking), the wire or cable is marked with tags or PVC tapes. PVC and heat-shrinkable tubes can serve as tags.
- The inscriptions on the label are written in a legible font and must be clearly visible. The length of the tag itself should not be less than 25 mm.
- According to the standards, markings can be applied to a wire or cable (to its insulation). Only on condition that such an inscription will be clearly visible.
We have figured out the basic rules for applying identification marks. Now let's look at how you can mark wires during installation.
Features of digital wire designation
Digital designations in distribution boards require separate consideration. According to the requirements of the PUE, the distribution of power supply circuits in the distribution board is carried out in groups. Separate areas are fed from the group; these can be different objects:
- No. 1 lighting;
- No. 2 sockets;
- No. 3 air conditioner;
- No. 4 heated floors;
- No. 5 Boiler for heating water;
- No. 6 electric stove;
- No. 7 separate premises or structures (bathhouse, workshop, etc.)
In single-phase circuits, one phase L1-1 will arrive at the input of the circuit breakers; L1-2; L1-3, where 1,2,3 represent different lines. At the output of the switches, the wires are marked by group and line number, if there is one wire in a group, the marker writes Gr-1, if there are two Gr-1.2, indicating that this is the second wire of the first group.
Marking of wires in distribution boards by groups
On industrially assembled electrical panels, a connection diagram is pasted on the inside of the door indicating the markings of all wires; just to be on the safe side, you only need to sign the intended purpose. Wise people record this information on video or take photos during editing, save it on electronic media, even on social media servers. networks.
Tip #2. If you assembled the shield yourself or invited an electrician, such a diagram must be drawn up and glued to the door from the inside.
Types of electrical wires and their marking methods
What color and how are the neutral, phase and ground wires designated in electrical engineering?
The main models can be seen below:
Main types of electrical cables
- PBPP (PUNP) is a monocore cable of an installation type, with an internal and external sheath made of PVC material. The composition can contain cores from 1 to 4 with the largest cross-section being 4 squares. It is mainly used for lighting in residential premises, laid through sockets (used for low-power devices). The cores are made of both copper and aluminum;
- PBPPg (PUGNP). There were fairly thin wires inside. The “g” at the end of the name indicates that this cable is flexible;
- PPV. Copper monocore cable - used for hidden electrical installation or for installation in a corrugated or cable duct. The insulation is made in one layer;
- APPV - the same model as above, only with an aluminum core inside;
- PVA is one of the popular electrical cables with PVC protection. Inside it has a sector section and twisted wires. The cross-sectional area can be from 0.75 to 14 squares. Mainly used for residential wiring;
ShVVP cable 2×0.75
ShVVP is a mixed type electrical cable, used for household appliances. Its peculiarity is that there are both copper and aluminum conductors inside. These elements must be combined with a terminal block.
Features of marking of distribution boards and cables
According to the requirements of the PUE, the distribution devices themselves must also be marked; for apartments and private houses, the absence of names is allowed, due to the explicit definition of their purpose. When the shield is located outside the site on a power line pole or other structure, its marking must be indicated . It states:
- Manufacturer;
- Purpose and type of ASU, main switchboard, distribution switchboard, NKU;
- Voltage and current ratings;
- Degree of protection;
- There is a “Caution Voltage” sign on the doors;
- Lettering must be legible and environmentally resistant.
The following information is indicated on the markers of cables entering and exiting the distribution board:
- Poppy cable, it contains the number of cores, cross-section, metal of wires, insulation material;
- Cable purpose;
- Where does it come from?
- Where does it go;
- Length.
Tip #3. On the inside of the door there should be a detailed electrical diagram for connecting cables and the distribution of directions from the switchgear.
Marking wires in a switchboard: how to label wires and cables
Marking the wires in the switchboard is not only a matter of good manners and professionalism of the electrician, but must also be carried out in accordance with regulatory documents and in accordance with special GOSTs. Read about the rules for marking electrical cables in electrical panels of apartments and houses.
Is it necessary to mark cables and wires in the shield if the shield is in your apartment or house? If you do the installation according to the rules, then it is definitely necessary. If you installed the electrical wiring yourself and think that you have an eternal memory, then you can try not marking the wires in the panel and see what you remember in a year.
In fact, wires and cables are marked not for themselves, but for electricians who, sooner or later, will have to service or repair the switchboard.
Common labeling mistakes
- The most common mistake made by novice installers and experienced ones due to inattention. When the wires in the shield are screwed onto the terminals without first putting on labeled casings or heat-shrinkable tubes. Then you have to unscrew and put on the marking elements.
- They confuse the “PEN” conductor with the grounding wire, they have the same color markings, you need to look carefully.
- If the panel is located outside the site, but is on your balance sheet, this is determined by an agreement with the energy supply organization. It is imperative to have technical documentation of the circuit for it, and to fulfill all the requirements of the PUE, PTEEP and other documents. There may be claims from Rostechnadzor, up to disconnection of the consumer and fines.