Nowadays, electrical wiring is carried out using wires with different insulation colors. And the point here is not about some fashion trends or the beauty of the product itself, but about the safety and ease of use of this electrical wiring.
After all, colored insulation can perform two functions simultaneously - protection against electric shock or protection against short circuits by applying insulating material to the conductor, and with the help of the color of this very insulating material, it helps the electrician determine the purpose of this conductor.
To avoid confusion, all color colors were reduced to a single standard, described in the PUE.
Color marking can be done both along the entire length of the conductor and at the connection points of the conductors or at their ends. To do this, colored electrical tape or heat-shrinkable tubes (cambrics) can be used.
In this article we will look at color marking in single-phase and three-phase circuits, as well as in DC circuits.
Wire colors in a single-phase network
Different colors of wire insulation become most relevant when the installation of electrical wiring is carried out by one person, and repairs and maintenance are carried out by another. The main purpose of color marking is to make it easy and quick to determine the purpose of any of the wires.
Phase wire colors
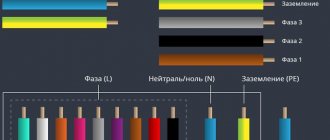
According to the PUE, phase wires in a single-phase electrical network can have the following insulation color - black, red, brown, gray, purple, pink, orange, white, turquoise. This color marking is quite convenient - when you see a wire with this color of insulation, it becomes clear that you have a phase in front of you (but it is still better to double-check, since in practice there are cases when the marking is not observed).
Zero working conductor or neutral
The neutral or neutral working conductor (N) is usually made with a wire with blue insulation.
Neutral protective conductor and neutral combined conductor
The neutral protective conductor (PE) has a yellow-green insulation color. The combined neutral and working conductor (PEN) has a blue color with yellow-green marks at the end, or vice versa - a yellow-green color with blue marks at the end.
If you do not have a wire of a suitable color, then installation can be done with a wire of any color (except for the protective PE conductor that is colored) by marking the ends of this wire with colored electrical tape or heat-shrink tubing, which have a color indicating the purpose of the conductor. You can also mark the ends of the conductor with the desired color in the case when the installation has already been carried out with a conductor of a different color.
Below are the colors that indicate phase, neutral, protective and combined conductors:
Colors of wires and buses in the AC network for a three-phase connection
To maintain the correct phase rotation when connecting three-phase consumers of electrical energy, color marking of buses and cables is also used. This makes life much easier for installers and repairmen, since by the color of the cable or bus, you can determine the phase that is connected or will be connected to this cable or bus. Unlike single-phase consumers, where the phase wire can be made of cables with different insulation colors (list above), for three-phase consumers the colors that can be used to indicate phases are strictly regulated by the PUE.
For a three-phase connection, phase A should be indicated in yellow, phase B in green, phase C in red. Zero working, protective and combined conductors have the same color as with a single-phase connection.
It is permissible to color code cables and buses not along their entire length, but only at the points where cables or buses are connected, as shown in the figure above.
Also, color codes may comply with the international standard IEC 60446 or may use the coding adopted within the country by the relevant regulatory documents. For example, in the USA and Canada, different color codes are used for grounded and ungrounded systems. Below is a table showing the color coding of cables and busbars in different countries for comparison:
Colors of wires and buses in DC circuits
DC circuits typically use only two buses, namely plus and minus. But sometimes DC circuits have a middle conductor. According to the PUE, buses and wires are subject to the following markings in DC circuits: positive bus (+) - red, negative (-) - blue, zero operating M (if available) - blue.
How are DC buses designated?
Answers from Rostechnadzor on electrical safety (ES) for electrical personnel of organizations operating consumer electrical installations on certification questions for test tasks. Questions with correct answers are confirmed by an excerpt from the regulatory documentation on which the Olympox tests were compiled.
How are DC buses designated?
• Positive bus (+) - in red, negative (-) - in blue and zero working M - in blue
• Positive bus (+) - in blue, negative (-) - in red and zero working M - in blue
• Positive bus (+) - green, negative (-) - red and zero operating M - blue
• Positive bus (+) - yellow, negative (-) - green and zero working M - blue
Excerpt from regulatory documentation:
Rules for electrical installations-1
1.1.30. The alphanumeric and color designations of tires of the same name in each electrical installation must be the same. Tires must be marked:
1) with alternating three-phase current: buses of phase A - yellow, phase B - green, phase C - red;
2) with single-phase alternating current, bus B, connected to the end of the power source winding, is in red, bus A, connected to the beginning of the power source winding, is yellow.
Single-phase current buses, if they are a branch from the buses of a three-phase system, are designated as the corresponding three-phase current buses;
3) at constant current: positive bus (+) - in red, negative (-) - in blue and zero operating M - in blue. The color coding must be carried out along the entire length of the tires if it is also provided for more intensive cooling or anti-corrosion protection.
It is allowed to carry out a color designation not along the entire length of the busbars, only a color or only an alphanumeric designation, or a color in combination with an alphanumeric designation at the points where the busbars are connected. If non-insulated busbars are not accessible for inspection during the period when they are energized, then they may not be marked. At the same time, the level of safety and visibility when servicing the electrical installation should not be reduced.
Electrical safety tests relevant for 2020 have been prepared and posted on the Test24.ru You can take online testing in the courses EB 1260.9, EB 1259.8, EB 1258.8, EB 1257.8, EB 1256.8, EB 1255.8, EB 1254.8 and EB 1547.3 to prepare for the exam on the unified testing portal of Rostechnadzor for the admission group up to and above 1000 V.
Changes in color marking of buses and wires
In the Russian Federation, GOST R 50462-92, which regulated the identification of conductors in electrical networks using digital and color designations from 01/01/2011, was replaced by GOST R 50462-2009, which has quite significant differences from GOST R 50462-92 and has some contradictions with PUE 7. Below is a table containing recommendations for color marking of busbars and cables in accordance with GOST R 50462-92:
How are zero working (neutral) conductors designated?
| Indicated by the letter N and green |
| Indicated by the letter N and white |
| Indicated by the letter N and blue color |
| Indicated by the letter N and the color yellow |
PUE clause 1.1.29. For color and digital designation of individual insulated or non-insulated conductors, colors and numbers must be used in accordance with GOST R 50462 “Identification of conductors by colors or digital designations”.
Protective grounding conductors in all electrical installations, as well as neutral protective conductors in electrical installations with voltages up to 1 kV with a solidly grounded neutral, including busbars, must have the letter designation PE and color designation in alternating longitudinal or transverse stripes of the same width (for busbars from 15 to 100 mm) yellow and green colors.
Zero working (neutral) conductors are designated by the letter N and the color blue. Combined neutral protective and neutral working conductors must have the letter designation PEN and a color designation: blue along the entire length and yellow-green stripes at the ends.
TICKET 5
Question 41
What letter and color designation is used for protective grounding conductors in electrical installations?
| Must have the letter PEN and a blue color along the entire length |
| Must have the letter designation PE and color designation with alternating longitudinal or transverse stripes of the same width for tires from 15 to 100 mm in yellow and green colors |
| Must have the letter PEN and color designation: blue along the entire length and yellow-green stripes at the ends |
| Indicated by the letter N and blue color |
PUE clause 1.1.29. For color and digital designation of individual insulated or non-insulated conductors, colors and numbers must be used in accordance with GOST R 50462 “Identification of conductors by colors or digital designations”.
Protective grounding conductors in all electrical installations, as well as neutral protective conductors in electrical installations with voltages up to 1 kV with a solidly grounded neutral, including busbars, must have the letter designation PE and color designation in alternating longitudinal or transverse stripes of the same width (for busbars from 15 to 100 mm) yellow and green colors.
Question 42
What letter and color designation is used for combined neutral protective and neutral working conductors?
| Letter designation PEN and blue color along the entire length |
| Letter designation PE and color designation with alternating longitudinal or transverse stripes of the same width (for tires from 15 to 100 mm) in yellow and green colors |
| Letter designation PEN and color designation: blue along the entire length and yellow-green stripes at the ends |
| Letter designation N and blue color throughout |
PUE P.1.1.29. For color and digital designation of individual insulated or non-insulated conductors, colors and numbers must be used in accordance with GOST R 50462 “Identification of conductors by colors or digital designations”.
Protective grounding conductors in all electrical installations, as well as neutral protective conductors in electrical installations with voltages up to 1 kV with a solidly grounded neutral, including busbars, must have the letter designation PE and color designation in alternating longitudinal or transverse stripes of the same width (for busbars from 15 to 100 mm ) yellow and green colors.
Zero working (neutral) conductors are designated by the letter N and the color blue. Combined neutral protective and neutral working conductors must have the letter designation PEN and a color designation: blue along the entire length and yellow-green stripes at the ends.
Question 43
What designations are used for buses for three-phase alternating current?
| Busbars phase A yellow, phase B green, phase C red |
| Buses of phase A - green, phase B - yellow, phase C - red |
| Busbars of phase A - red, phase B - white, phase C - blue |
| Buses of phase A - blue, phase B - white, phase C - red |
clause 1.1.30.PUE Alphanumeric and color designations of tires of the same name in each electrical installation must be the same.
Tires must be marked:
1) with alternating three-phase current: buses of phase A - yellow, phase B - green, phase C - red;
Question 44