Purpose of the PUNP wire
PUNP is intended for laying lighting and socket networks in residential, administrative and industrial facilities, for connecting low-current devices with a voltage of no more than 250 V. It can be laid in various ways:
- Open wiring method;
- In cable channels;
- In corrugated pipes;
- In grooves under plaster;
An example of laying PUNP wire in grooves
- By air between supports on steel cables and underground in plastic, metal or asbestos pipes.
In all cases, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of the PUE for each type of wiring. In some cases, the Electrical Installation Rules restrict the use of open wiring PUNP, in bathhouses, swimming pools and other objects with high humidity. In these cases, it is recommended to use rubber-insulated wires, PUGNP or PRGN, which have better moisture protection properties. There may be other restrictions related to technological processes in production.
Technical characteristics and scope of application of PUNP wire
The PUNP wire, which was widely used in its time, is an electrical product known in the past, belonging to a special class and intended mainly for domestic needs. Its direct purpose is to serve as the basis for the manufacture of power cords in lighting fixtures and other household consumers. Today it is considered an outdated cable product and is not recommended for practical use. Despite this, the PUNP brand is valued by most specialists and attracts them due to its ease of installation and comparative cheapness.
- Decoding and labeling
- Design features and selection rules
- Characteristics and scope
- Reasons for refusing PUNP
- When is it allowed to use
- Verification methods
Technical characteristics of PUNP wire
PUNP wires can be used in the temperature range from – 25 ̊С to + 45 ̊С with a humidity of 98%. When testing the voltage between the cores, the wire can withstand 1.5 thousand volts for 1 minute. A trouble-free operating time has been established, subject to the permissible operating conditions, of 5 thousand hours of continuous operation.
Weight and dimensions of different types of PUNP:
| Brand | Weight kg/1km | External dimensions in, mm |
| PUNP 2x0.75 | 34 | 3,4:5,1 |
| 2x1 | 38 | 3,5:5,3 |
| 2x1.5 | 53 | 4,0:6,4 |
| 2x2.5 | 74 | 4,4:7,1 |
| 2x4 | 110 | 5,1:8,4 |
| 2x6 | 151,2 | 5,6:9,4 |
| 3x0.75 | 44,2 | 3,4:7,1 |
| 3x1 | 55,3 | 3,5:7,5 |
| 3x1.5 | 73,5 | 4,0:8,7 |
| 3x2.5 | 107,6 | 4,4:10 |
| 3x4 | 160,8 | 5,1:12 |
| 3x6 | 223,1 | 5,6:13,5 |
If we compare the characteristics of PUNP with the characteristics of PUGNP, which it is often replaced with, we can see that the dimensions of the wire do not differ significantly, but the weight is significantly greater.
Appearance of PUGNP
The cross-section and number of wires are the same, the weight increases due to denser insulation, which ensures reliable tightness. Weight and dimensions of different types of PUGNP:
| Brand PUGNP | Weight kg per 1 km | External dimensions in mm |
| 2x0.75 | 34,5 | 3,5:5,5 |
| 2x1 | 40,1 | 3,6:5,5 |
| 2x1.5 | 54,8 | 4,1:6,5 |
| 2x2.5 | 81,1 | 4,6:7,5 |
| 2x4 | 116,1 | 5,3:9 |
| 2x6 | 159,5 | 5,8:10 |
| 3x0.75 | 47,4 | 3,5:7,5 |
| 3x1 | 57,4 | 3,6:7,5 |
| 3x1.5 | 79,1 | 4,1:9 |
| 3x2.5 | 118,5 | 4,6:10,4 |
| 3x4 | 170 | 5,3:12,4 |
| 3x6 | 235 | 5,8:14,1 |
Technical characteristics and reason for the danger of PUNP wire
The decoding of the abbreviation PUNP is as follows: P - wire, UN - universal, P - flat.
This type of conductor has become famous for its electrical and fire hazard and, as a result, has received many negative reviews on the Internet.
Next, we will tell readers of the Sam Electric website about the technical characteristics of the PUNP wire and the reason for the ban on the domestic market of cable products.
Main settings
So, first of all, let's talk about what technical characteristics this conductor has. Among the most important parameters for domestic use are:
- core material is copper, therefore the conductor is rigid;
- Core insulation/outer sheath – polyvinyl chloride plastic (PVC)/PVC;
- insulation color in accordance with the color marking of wires approved by GOST standards;
- rated voltage – up to 250 Volts;
- nominal frequency – up to 50 Hz;
- operating temperature - from -15°С to +50°С;
- permissible heating of wire cores – up to 70°C;
- cross-section of cores – from 1.0 to 4.0 mm2;
- number of current-carrying wires – 2 or 3;
- service life – up to 30 years;
As for the specific gravity per 1 meter of PUNP wire length, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with this technical characteristic in the table:
So we have provided a description of the most important parameters of this conductor
Now let's talk about a more important question - why PUNP was banned and where it can be used for domestic purposes
What are the dangers of using
The thing is that the PUNP wire is of very poor quality and, as a result, has more than once become the cause of fire and electric shock.
It has been clearly proven more than once by both experienced specialists and ordinary customers that the quality of the insulation and wire cores leaves much to be desired. But what can we say if the production of PUNP complies with the standards of TU 16.
K13-020-93, according to which the cross-section of the cores can vary up to 30% from that indicated on the marking (!).
As for the cross-section of current-carrying conductors, in most cases it is actually almost a quarter smaller than that declared by the manufacturer. As a result, instead of the wire you need 3*2.5, the output is 3*1.75 mm2.
Do you understand what the danger is? The fact is that a thinner conductor will not be able to withstand the current loads that are placed on it. The consequence of a low cross-section can be not only a short circuit, but also a fire in the house, because
PVC insulation is flammable, unlike VVGng cable.
The next danger concerns the high probability of electric shock. The fact is that the thickness of the insulation of the PUNP wire, according to the classics of the genre, does not correspond to that declared by the manufacturer. Instead of the 0.4-0.5 mm thickness of the PVC shell required by the GOST 23286-78 standard, in fact it is no more than 0.3 mm. In a dangerous situation, the electrical safety of this conductor leaves much to be desired.
To summarize, it should be noted that according to GOST 22483-77 and GOST 23286-78, PUNP does not pass a certificate of conformity for the cross-section of cores and insulation thickness.
This conductor is prohibited on the cable market and we hope that after the facts provided about the discrepancies in the technical characteristics of the PUNP wire, you understand why it is bad for domestic use.
We recommend reading:
overview of the problem of using this explorer
Decoding the abbreviation of the marking
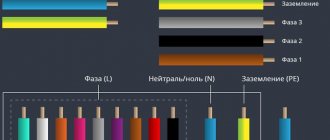
For the convenience of installation work, connecting wires to power supplies in distribution boards, to sockets and lighting fixtures, colored insulation is made in accordance with the requirements of the Electrical Installation Regulations. They use different colors, red, blue, white, black, yellow-green and others, the rules are determined by:
- A wire with blue or black insulation is connected to the neutral bus;
- Red, white, brown to phases;
- Yellow-green to the ground loop.
In addition to marking the wires with colored insulation, the brand and type of wire is signed on the outer PVC sheath, for example PUNP - 2X4, this means:
- P - wire;
- UN – universal purpose;
- P – flat shape.
The numbers 2x4 indicate the number of cores is 2, 4 - the cross-sectional area of the wires is 4 mm2. The number of cores and cross-section determine in which networks this type of wire can be used.
Criteria for choosing a PUNP wire
According to modern requirements, wiring in buildings is done according to a three-wire circuit, where phase, neutral and ground wires are used. Therefore, for laying socket and lighting networks, you must choose at least a PUNP with three wires. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the power and current load consumed by the electrical equipment that will be connected; these parameters determine the required thickness and cross-sectional area of the wires.
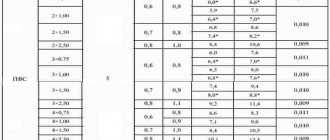
There are pre-calculated tables of the ratio of power and current loads to the cross-section of wires.
| Table 1.3.4. according to the requirements of the PUE, Long-term permissible current for copper wires in rubber or polyvinyl chloride insulation | |||||||
| Section Ø-S conductor, mm2 | Permissible current in A for wires laid parallel in a common insulating sheath | ||||||
| Open wiring | 2 cores | 3 cores | 4 cores | ||||
| 0,5 | 10 | — | — | — | |||
| 0,75 | 14 | — | — | — | |||
| 1,00 | 18 | 15 | 16 | 15 | |||
| 1,5 | 24 | 20 | 17 | 17 | |||
| 2,5 | 31 | 25 | 24 | 24 | |||
| 4,0 | 40 | 37 | 34 | 31 | |||
| 6,0 | 51 | 45 | 41 | 41 | |||
Taking into account statistics and many years of practical experience, for laying the socket group where ordinary household appliances, iron, refrigerator, TV, microwave oven are connected, use PUNP - 3x2.5 mm2. This is quite enough for high-power appliances, split systems, air conditioners, heating boilers with heating elements, electric stoves; separate lines with a wire cross-section of 4-6 mm2 are laid from the switchboard.
In order to save money for an apartment or house in lighting networks, you can use a two-wire PUNP with a cross section of 0.75 - 1.5 mm2. Often chandeliers, sconces and other lamp designs have plastic housings and there is simply nowhere to connect the grounding wire. In administrative and industrial buildings, lighting fixtures can be massive with a metal casing, with a large number of powerful lamps, so all requirements must be met. Calculate the number of lighting fixtures, their power consumption, select the appropriate cross-section and connect the lamp housings to the ground wire.
Features of application
According to the current rules of electrical installations (PUE), the PUGNP wire in domestic and industrial premises can only be used to supply electricity to devices, and the rated parameters of the supplied current must correspond to the tolerances of the conductor. However, in reality, this wire can often be found as a power cable. In Soviet times, it was quietly used for installing electrical networks in houses and apartments. Today, professional organizations are prohibited from doing this, but independent electricians continue to use PUGNP for these purposes.
The ban on the use of PUGNP is due to the fact that this wire is not produced in accordance with state standards. TU 16.K13-020-93, to which the conductor characteristics correspond, allows the manufacturer to make wires with a tolerance for cross-sectional area of up to 30%. Manufacturers take advantage of this, trying to reduce the selling price of the product by reducing production costs. As a result, a person buys a PUGNP with a nominal cross-sectional area of 2.5 mm2, but in reality it does not exceed 2 mm2. A good electrician, of course, will measure the wire before purchasing and refuse a thin conductor, but an inexperienced person will install the wire in a network where the load may be critical for a cable of such thickness.
In addition, PUGNP does not meet current requirements for electrical conductors in terms of insulation thickness. According to current standards, the thickness of the insulating sheath of the entire wire and conductive cores separately must be at least 0.4-0.5 mm, and in the specifications according to which PUGNP are produced, a PVC layer of 0.3 mm is allowed. The answer to the question of why the cable can still be found on the shelves of large construction hypermarkets is quite simple - a ban on use does not mean a ban on production, and the installation of wires that are unsuitable for specific conditions is a risk and the responsibility of the one who carries it out.
Despite all that has been said, it is neither possible nor advisable to categorically ban the PUGNP wire. Essentially, any cable, no matter how standardized it may be, will not be safe if used in the wrong conditions. This wire can be used, but only in conditions where you are completely sure that even an increased work load will not cause a fire. For example, to connect electrical appliances or supply light to a garage, cellar or bathhouse, when there are no plans to connect high-power devices to the network, such a cable will do. True, in this case it is advisable to lay it in corrugation. And you most likely won’t want to use such a weak material to power an electric stove or washing machine yourself, or the electrician doing the work will tell you that this is contrary to basic safety.
Disadvantages and advantages of PUNP wires
The flat design of the wire is very suitable for laying wiring indoors, double insulation and a wide choice of cross-section and number of cores attract consumers. But the main problem is that a large number of unscrupulous manufacturers do not follow production technologies. As a result, the products do not meet the stated technical specifications. According to statistics, 80% of PUNPs on the market are defective. Firefighters claim that 60% of fires caused by faulty electrical wiring occur in networks assembled with PUNP wire.
The reason for such negative statistics lies at the legislative level, TU 16.K13-020-93 allows you to make wires with a cross-section up to 30% smaller, which is successfully used by unscrupulous manufacturers. Wires with a cross-section designation of 2.5 mm2 may actually turn out to be 1.75 mm2. By installing such a wire in a network with a load designed for a cross-section of 2.5 mm2, the likelihood of wires and insulation melting increases, which leads to a short circuit and fire.
GOST 23286-78 establishes that the minimum thickness of the PVC insulating layer on wires should be 0.4-05 mm, contrary to this, TU 16.K13-020-93 allows the insulation thickness to be 0.3 mm. This significantly reduces the safety of operation of such wires.
Tip #1. If you decide to use PUNP wires when purchasing, you must carefully check these parameters.
All manufacturers claim a service life of at least 15 years. Price table for PUNP in various regions of Russia:
| Region | Price in $ per 1m. |
| Voronezh | 0,4 |
| Minsk | 0,5 |
| Saratov | 0,4 |
| Chelyabinsk | 0,4 |
| Petersburg | 0,5 |
| Ufa | 0,4 |
Reasons for prohibiting use
First of all, the PUGNP wire does not meet the requirements for the thickness of the conductor insulation. If the requirements of the PUE clearly indicate the need to use a shell with a thickness of at least 0.4-0.5 mm, the factory specifications allow the use of a layer of plastic compound of 0.3 mm.
In addition, TU 16.K13-020-93 is fairly liberal regarding tolerances on the cross-section of the cores - the permitted error is 30%. As a result, if you purchase a 2.5 mm² cable, then in fact there may be wires inside it with cores of 2.5 - 30% = 1.75 mm². It is clear that when even a rated load is connected to it, the cable may not withstand it and melt. According to statistics, more than 50% of all wire fires occurred when using the PUNP and PUGNP brands.
Formula for calculating the cross-section of PUNP wires
To correctly calculate the cross-section, you need to measure the diameter and multiply the square of this value by 0.785.
Checking the thickness of the wire insulation, measure the diameter of the conductive copper core, then the diameter of the wire with insulation, and calculate the difference between them. The Ø of the bare wire is subtracted from the Ø with insulation, the result will be the thickness of the insulating layer.
Analogs that can replace the PUNP wire
Analogue wires for PUNP are more expensive, but more reliable:
- NYM (NUM) - a round-shaped cable has two insulating sheaths: an outer non-flammable PVC and an inner melkolubricated one, in addition to the insulation of each wire, in fact, triple insulation. The best manufacturers of this brand are considered to be the companies Sevkabel and Concord;
- VVG - the design of this brand differs little from PUNP, single-strand conductors, double PVC insulation, cable shapes can be round or flat, insulation with non-flammable additives;
- PVA – round and flexible, multi-core wires with double PVC insulation.
Tip #2. If you want to install PUNP, then experienced electricians recommend purchasing products from Moscow manufacturers. They do not deviate from the declared characteristics; the parameters for insulation thickness and wire cross-section are observed.
PUNP cost
The price (in rubles/linear meters) is determined by the cross-section of the cores, their number and ranges from 9.1 to 33.5 (wire 3 x 4).
Attention! The use of PUNP wire in Russia is prohibited. It is on this point that there is a lot of controversy and there are discrepancies on the Internet
The reason why PUNP wire is prohibited is the discrepancy between the thickness of the sheath and insulation of each core with the requirements of GOST No. 23286 of 1978. It should be at least 0.4 mm, while manufacturers mainly rely on TU No. 16.K13-020 of 1993, which allow 0.3 mm.
Since reducing the thickness of the insulation allows you to reduce the cost of production, many companies take advantage of this, because it is impossible to make complaints about the quality of PUNP. But in terms of operation, they exist, and first of all this concerns electrical safety rules.
It should be taken into account that there is also some discrepancy between the actual cross-section of the cores and the characteristics declared by the manufacturer. The same specifications allow reducing this parameter to 30%. What does this mean? For example, the buyer takes a wire of 2.5 square meters, in accordance with the load calculations made. But in fact it will be only 1.75. Overheating, melting of insulation, short circuit, and even ignition of electrical wiring are guaranteed. This is another reason to doubt the advisability of the universal use of PUNP.
Conclusion The wire itself is good, and considering its cost, it is a good option for installing internal communications (in most cases). But when choosing a PUNP, you should focus on the specifics of the line’s operation and take into account the feature regarding the mismatch of the cross-section. That is, lay the wire with a margin according to its “quadrature”.