The principle of operation of microwave waves
Microwaves require dipole molecules to operate. They are charged both positively and negatively. There are more than enough such molecules in vegetables, fruits and meat products. The average concentration in, for example, a kilogram of fish is several million particles. In an ordinary environment, without an electric field, molecules are in a chaotic state. But as soon as the magnetron starts working in the microwave oven, the particles line up in a certain order. Positively charged ones go in one direction, and negatively charged ones go in the other. At the moment of polarity change, the molecule changes its direction to the opposite, turning 180 degrees.
Microwave waves cause molecules to turn around
Microwaves in classic microwave models move at a frequency of 2450 MHz, where each hertz is equal to one cycle per second. The field change occurs 2 times during the period of one wave. After turning on the stove, the particles accelerate and begin to rub against each other, increasing the temperature in the chamber. Moreover, the waves affect only the surface layer, penetrating into food no deeper than 3 cm.
How does a microwave oven work?
To understand this, a little background information is needed. Most food products contain the following substances: salts, fats, sugar, water. In order for microwaves to “work”, that is, to heat food, the food must contain dipole molecules.
On the one hand they have a positive electrical charge, on the other - negative. There are enough of these molecules in food - these are fats and sugar, but the main dipole is a water molecule.
Vegetables, meat, fruits and fish contain a large number of dipole molecules, the number of which reaches millions. If there is no electric field, the molecules are arranged in a chaotic order.
In microwave ovens, microwaves have a frequency of 2450 MHz
In the presence of an electromagnetic field, they begin to “line up”: “plus” is directed in one direction, “minus” in the other. When the field changes polarity, the molecules “unfold” 180 degrees.
In microwave ovens, microwaves have a frequency of 2450 MHz. 1 hertz = 1 oscillation per second. Megahertz is a million vibrations. The polarity changes twice during one wave period.
When food is exposed to microwave radiation, the molecules in it begin to rotate more often, literally rubbing against each other. This releases heat, which serves as a source of heating for the food.
The heating of food by microwaves can be compared to the way your palms heat up when you rub them together. “Waves” affect only the surface layer of food, penetrating no deeper than 1–3 cm.
But the heat “goes” further – the physics of thermal conductivity comes into play. This also leads to advice: if you need to heat up a large piece of meat, it is better to set the microwave oven to medium power. This way it will warm up better, although it will take longer. Heat from the outer layers will begin to penetrate inside.
The situation is similar with soups: it is better to periodically remove them from the oven and stir them, helping the heat to penetrate inside.
The stove models currently being produced may have a “Double Radiation” function - this indicates a bifurcated radiation source. Thanks to this separation, the products are heated more evenly, and the microwave oven has increased efficiency.
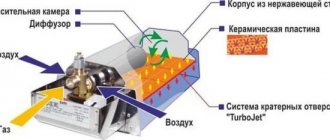
Microwave technology device
All microwave ovens, without exception, include a number of required elements: a chamber, a control interface, a microwave wave generation unit and protective systems. Functionality, cost and other performance qualities are influenced by individual design features. Let's look at the main elements of the equipment.
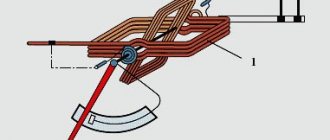
Magnetron
It is this device that generates waves in the chamber that affect the molecules in the food, resulting in heating. Moreover, any external thermal stimulation is not needed to heat food. Therefore, the temperature inside the chamber never exceeds 100⁰C.
The anode of the device has the shape of a cylinder with separate planes. Inside the structure there is a cathode with an incandescent element. Ring-shaped magnets run along the edges of the magnetron. The created field prevents electrons from moving from the cathode to the anode, creating a rotation effect.
As a result, due to the wire loop, a microwave field penetrates into the chamber. The magnetron becomes active as soon as it receives sufficient voltage, which is about 3000-4000 V. Such indicators require the presence of a high-voltage transformer.
Magnetron and other microwave elements
Electrical diagram
All household models of microwave ovens are made according to the same design, and the main blocks are located in standard places. The technology of previous generations differs only in the design of the control interface. Modern devices are equipped with an electronic unit, and the power transformer is replaced with a more efficient inverter.
Additional items
On sale you can find three types of appliances: classic, with grill, with convection and grill. In a regular oven you can heat up food, defrost it, and that’s it. While the presence of grill and/or convection expands the capabilities of the equipment. Naturally, additional elements significantly add to the cost of the furnace and increase energy consumption.
Models with convection are equipped with a fan, allowing you to fry food efficiently. The food is baked evenly and ends up with a crispy crust. In ovens with grills you can fry chicken, pies and other dishes. This tandem easily replaces a conventional oven.
The fan distributes heat evenly throughout the chamber
Grills in microwave ovens can be of three types - quartz, charcoal or heating element. In the first case, we have an element hidden behind a metal mesh that heats up quickly, consumes noticeably less energy than other types, and does not require maintenance.
Charcoal grills are good because they almost completely replicate an open fire. The resulting dishes are as juicy as if they were cooked on the grill or in a gas oven. The heating element is made of carbon fiber and is fastidious in maintenance.
Grills on heating elements are universal. They are relatively easy to maintain - clean and change. The tubes can be located either at the top or bottom. But there are models with two heating elements and even with a movable grill, where the heating element lowers during cooking and snaps back into place when the equipment is turned off.
How does a microwave grill work?
A grill allows you to microwave food using regular heat rather than microwaves. It is she who creates an appetizing crust on dishes, which does not appear during conventional microwave processing.
The grill spiral is located at the top of the oven and comes in two types:
- Heating elements (thermal electric heaters). A heating element is a metal tube, inside of which there is a thin spiral made of an alloy of nickel and chromium. Current passes through the coil and it heats up.
- Quartz . A quartz grill is also a heating element, but instead of a metal tube there is a glass shell, and between the spiral and the tube there is insulating quartz sand.
Conventional metal heating elements can often be adjusted - moved to the back wall or lowered, but the glass surface of a quartz grill is easier to clean (grease and carbon deposits do not eat into the glass as they do into metal).
There are designs of microwave ovens with grill and convection. Convection is simply blowing hot air over your food as it cooks. For such airflow, a fan is installed in the microwave, blowing heated air from the grill spiral towards the dish.
Most microwave oven models allow you to use both heating elements and microwaves at the same time. However, be aware that this combination can cause a lot of heat in the outlet and wires in your premises.
Read the following article about the principles of choosing a microwave oven to suit your needs:.
Important function of the microwave door
No less attention is paid to the door during production. In microwave ovens, the door is not only a decorative element, but also acts as a kind of fuse. The principle is very simple: if you open the door, the lock is activated and the operation of the units stops. Despite its apparent simplicity, the design of the door is quite complicated, because it is associated with the safe operation of the entire device.
So, let's take a closer look at how a microwave oven door works:
- Firstly, the manufacturer needs to ensure that the door and body of the device fit perfectly against each other with a minimum angle. Large gaps prevent the device from being used. The reason is simple: the door serves as a kind of shield against microwave radiation, and if the gap is large enough, the radiation can penetrate beyond the cooking chamber. What radiation is and what its dangers are has been known for a long time.
- Secondly, the perimeter of the door is equipped with a high-frequency throttle. This device is used to reduce radiation to an acceptable level.
- Thirdly, at the time of casting the door body, many additives are added, with the help of which a high percentage of radiation absorption is achieved. Of course, one cannot be completely sure of 100% absorption of radiation, but there is no doubt that residual waves do not pose a danger or significant harm to human health.
Microwave operating frequency
Most magnetrons emit waves at a frequency of 2450 MHz (megahertz, or millions of vibrations per second). These are waves of decimeter length (12.25 cm long). Some industrial installations, for example in the USA, operate at 915 MHz. Forced vibrations of water molecules are not resonant vibrations, since for them the resonant frequency is an order of magnitude higher - 22.24 GHz (gigahertz, or billions of vibrations per second).
There is no need to be afraid of harmful radiation from a microwave. The first mass production of microwave ovens was made in Japan in 1962. Many years have passed since then, tens of millions of Japanese have been heating food in microwave ovens for decades, and the average life expectancy of the Japanese is the envy of the whole world.
At a distance of half a meter from a microwave oven, the impact of microwaves weakens 100 times, so if you are afraid of getting radiation, it is enough to stay at arm's length from the microwave. More information about the effects of microwave ovens on humans can be found here. Only scientific facts!
Are microwaves dangerous?
Disputes about the dangers of microwave ovens have not subsided since their launch into mass production. To date, there is no reliable information confirming the harm from the use of this type of device.
Do not forget that a microwave oven does not emit radioactive waves. On the contrary, a microwave allows you to cook foods without losing their beneficial properties. The food is healthier because... it retains up to 80% of vitamins and minerals.
Traditional ovens and stoves cannot boast of this result. If you operate the device strictly according to the rules, then there is no danger from its operation. This conclusion is confirmed by the way the microwave oven is designed, as mentioned above.
It is not healthy food cooked in a microwave oven (so-called fast food) that can cause harm, and thermal microwave exposure has absolutely nothing to do with it. The harm of pies (and other flour products) lies not in the fact that they are cooked in the oven, but in their increased calorie content and slow absorption by the body.