Greetings, friends!
Greetings, friends!
Many of you have heard about such a thing as a fuse, which is also called a fuse link.
Historically, such fuses were the first protective devices in electronic and other equipment.
Progress does not stand still, and something else has been invented for protection.
The traditional fuse is like a snail.
Let's delve a little deeper into this interesting topic!
The thermal fuse is switched on in series with the heating element of the device and it is placed as close as possible to the heating element. The operating temperature of the fusible element inside the thermal fuse is often indicated on its body, and the rating of the thermal fuse is chosen slightly higher than the operating temperature of the device itself.
How to check a thermal fuse with a multimeter or tester?
To check the thermal fuse you need a multimeter or a simple pointer tester.
It is enough to switch the device to the circuit continuity mode and check its integrity. If the arrow of the device does not budge or 1 lights up on the display, then we have an open circuit - such a thermal fuse is faulty.
Since imported household appliances are not cheap, repairs are often expensive. Therefore, in order to protect equipment from serious malfunctions in the event of all kinds of malfunctions, all kinds of fuses and protective devices are used. It is precisely such devices, which often cost pennies, that fail in a timely manner and thereby make further operation of the equipment impossible, which helps protect it from serious malfunctions.
Since imported household appliances are not cheap, repairs are often expensive. Therefore, in order to protect equipment from serious malfunctions in the event of all kinds of malfunctions, all kinds of fuses and protective devices are used. It is precisely such devices, which often cost pennies, that fail in a timely manner and thereby make further operation of the equipment impossible, which helps protect it from serious malfunctions.
The most common such protective devices are fuses, which protect against excessively high current levels. However, fuses are not effective protection for all modern equipment, so a thermal fuse is installed there, the principle of operation of which is not very different. If you don’t know what a thermal fuse looks like, it’s worth noting that its shape is practically no different from a regular fuse.
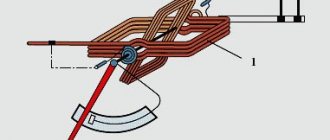
To operate effectively, the protection device must be located in close proximity to the winding wire, among the turns of the coils.
How to check if thermal protection is working properly
Checking the operation of a disposable fuse will lead to its operation and failure, so such elements are checked only with an integrity tester.
To test reusable thermal protection devices, in addition to the tester, you need a regular lighter;
- connect the tester to the terminals of the thermal fuse;
- check the resistance - it should be about 0 Ohm;
- heat the element with a lighter;
- during the heating process, the resistance of a working device increases sharply;
- After cooling, the instrument readings should return to their original values.
According to the principle of operation, they are similar to the thermal protection elements of automatic switches: inside there is a bimetallic plate, which opens the contacts of the power circuit when overheated. Under the action of a pre-compressed spring, the contacts open, and after the sensor cools down, the device returns to its original position by pressing a button. The contacts close and the spring compresses. It is again ready to open the contacts when overloaded.
Thermal fuse in transformers: description, types, replacement
The main reason for the failure of transformers is overheating due to overload or short circuit. Thermal fuses in the transformer turn it off when the temperature rises above the permissible level and protect the device from fire.
What is a thermal fuse and why is it needed?
A thermal fuse is an element of an electrical circuit that turns off the device not when the current exceeds the rated current, like a regular fuse, but when the temperature rises.
Transformer overheating occurs for various reasons, the main ones being overload or insufficient cooling of the device. In this case, the insulation of the winding wires is destroyed, which leads to a short circuit or fire of the windings.
The main task of the device is to break the circuit when overheated. It is connected in series with the primary winding and installed inside the transformer coils, under the outer insulation. When it overheats, it triggers and shuts down the device.
Operating principle of the device
There are several types of thermal fuses that perform the same functions, but differ in design:
- Disposable fuses. Inside the element there is a wire made of a low-melting alloy - Rose (+94°C.) or Wood (+60-68.5°C). The filler is quartz sand, which absorbs molten metal and extinguishes the arc that appears when the device is triggered.
- Self-resetting fuse. This is a polymer thermistor with a nonlinear change in resistance with increasing temperature. In a cold state, it is close to 0 and does not affect the operation of the circuit. When the temperature is exceeded, the resistance of the element increases, and it disconnects the transformer winding from the network. After cooling, the fuse returns to its original state.
- Bimetallic thermostats. The housing of these devices contains contacts and a bimetallic strip. When heated, it bends and opens the contact. There are two types - small-sized with flexible leads that are installed inside the windings and more massive ones that have terminals for connection and are placed outside the device on the magnetic core or radiator of the output transistors.
Where is the fuse placed in transformers?
To operate effectively, the protection device must be located in close proximity to the winding wire, among the turns of the coils.
In the winding
Installation in the primary winding is not used due to the fact that it is closer to the magnetic core, and the thermal fuse housing interferes with winding the secondary winding, and the temperature of the winding wires is the same throughout the entire device.
The exception is transformers with separate coils. In this case, it is possible to install two protection elements - one in each winding.
In the secondary winding
The most common place for installing thermal protection is the outer surface of the secondary winding, under the outer insulation of the transformer. In this case, the element is installed after winding the coils and does not interfere with the uniform winding of the wires.
In addition, in the event of a short circuit in the circuit, the secondary coil heats up more than the primary, especially if there are several windings.
Information! Thermal fuses, regardless of installation location, are always connected in series with the primary winding. This is necessary to completely shut down the device in an emergency.
What thermal fuses are used?
Depending on the purpose of the device, different types of thermal fuses are used in transformers.
In the transformer of the music center
Overheating of a music center is not always associated with failure of the electronic circuit. This may occur due to prolonged operation, insufficient cooling, installation of the center near a radiator and other reasons.
In addition, music equipment is more expensive than chargers and power supplies, so they are equipped with more expensive reusable self-resetting fuses and bimetallic thermostats.
Information! In some devices, thermal protection is installed not only in transformers, but also on the radiators of power transistors.
In the power supply transformer
Power supplies are relatively inexpensive devices, so disposable fuses with an insert made of low-melting metal are installed in power supplies.
How to check if thermal protection is working properly
Checking the operation of a disposable fuse will lead to its operation and failure, so such elements are checked only with an integrity tester.
To test reusable thermal protection devices, in addition to the tester, you need a regular lighter;
- connect the tester to the terminals of the thermal fuse;
- check the resistance - it should be about 0 Ohm;
- heat the element with a lighter;
- during the heating process, the resistance of a working device increases sharply;
- After cooling, the instrument readings should return to their original values.
How to make a homemade thermal fuse
It is impossible to make a full-fledged thermal protection device at home - this requires expensive and rare alloys. The common tin-lead solder POS-60 has a melting point of 190°C and will not provide reliable protection.
The replacement element is inexpensive and can be purchased in a store or ordered on Aliexpress. The choice is made according to three parameters:
- Response temperature. Should be similar to a blown fuse.
- Current. Must be no less than the current of the protected device.
- Voltage. During operation, the voltage at the fuse terminals is several millivolts, but when triggered it is equal to the mains voltage. Therefore, if the rated voltage of the element is insufficient, a short circuit will occur inside it and the transformer will remain in operation. For most electrical appliances, this parameter should be at least 250V.
Technological process of fuse repair and replacement
In many cases, the transformer stops working due to the thermal fuse tripping. This occurs not only due to overheating of the windings, but also due to a short-term increase in current. In this case, the thermal protection functions as a regular fuse.
To restore the functionality of the device, the protective element must be replaced with a similar or conventional fuse. There are two options for connecting thermal protection.
Connection of wires on the board
In this case, it is enough to short-circuit the thermal protection terminal or solder a working one parallel to the failed element on long wires. It is placed on the secondary winding and secured with tape.
Connection inside coils
In this case, the following is necessary:
- dismantle the transformer;
- disassemble the magnetic circuit;
- remove the outer layer of insulation from the secondary winding;
- separate the thermal fuse from the coil;
- unsolder it from the output of the primary winding;
- solder a working element instead and place it in place of the old one;
- wrap the entire structure with insulating material;
- assemble the transformer and connect it to the board.
Important! The reason for the thermal protection to operate may be a malfunction of the electronic circuit, so after assembly the operation of the device must be carefully checked.
Thermal fuses
According to the principle of operation, they are similar to the thermal protection elements of automatic switches: inside there is a bimetallic plate, which opens the contacts of the power circuit when overheated. Under the action of a pre-compressed spring, the contacts open, and after the sensor cools down, the device returns to its original position by pressing a button. The contacts close and the spring compresses. It is again ready to open the contacts when overloaded.
Thermal fuses are separated into independent devices, since the tasks they perform are limited. They allow you to protect household equipment from overloads that occur during operation. After the equipment has cooled down, the user will not need to change anything; just press a button and the device can be used again.
Similar devices are used in irons and electric stoves, but they do not have return buttons. The heating elements turn on automatically after the bimetallic plate has cooled. But this design is used not for protection against overheating, but for temperature regulation . To change the response threshold value, a regulator is connected to the bimetallic plate. With its help, you can mechanically change the current at which it will operate.
But there are other devices that have the same name. They work like temperature sensors: they open their contacts when it rises.
Temperature triggered thermal fuse
In the body of such a fuse there is an element that melts when the temperature rises and breaks the electrical circuit in the same way as the fuse insert.
If a part is “silent” when its temperature changes above the nominal and below the nominal, then it is most likely faulty.
Types of thermal fuses
The main option of a thermal fuse in comparison with a standard one is that it burns out not from high voltage, but from an increase in temperature.
The distinctive features of the thermal fuse are that there is a certain marking on the element body:
- series, code;
- response temperature;
- operating voltage;
- operating current.
There are two types of thermal fuses: disposable and reusable.
- The first type of thermal fuses is designed to perform its function once. If the temperature becomes extremely high, it breaks the power circuit of the heating element. This prevents damage to the entire device. This is how the system of multicookers and cars works.
By the way, read this article too: How to distinguish rechargeable batteries from regular ones
IMPORTANT
When disposable fuses blow, they become unusable and require replacement with new ones. Do not use equipment without a thermocouple, as it will be susceptible to overheating.
- Reusable thermal fuses are produced according to the bimetal principle. If the temperature is exceeded, the contact opens, interrupting the power supply circuit of the equipment. When the equipment cools down, the thermal fuse will return to its original position - the circuit of the heating element will close. A reusable thermal fuse protects the device from overheating and combustion. The action is typical for irons, dryers or heaters.
Method of checking for serviceability
There are several tips on how to check the thermal fuse. It all depends on whether you have a multimeter or a regular tester at hand.
The first tip is how to check a thermal fuse with a multimeter in resistance measurement mode:
- switch the device to resistance measurement mode;
- attach the probes to the fuse contacts - if the resistance is close to zero, then the contacts are closed;
- heat the metal part of the thermal fuse (with a lighter, soldering iron or put it in hot water) and check the resistance again - it should be infinitely large.
During the cooling process, a faint click may be heard - this is the contacts closing. If before heating the resistance is zero, and after heating it is infinity, then the part being tested is operational.
This verification method is the most accurate, but you don’t always have a measuring tool at hand. The following advice on how to check a thermal fuse gives an approximate result:
- heat the part being tested and listen - there should be a slight click when the heating temperature approaches the nominal one;
- There should also be a click when it cools down.
If a part is “silent” when its temperature changes above the nominal and below the nominal, then it is most likely faulty.
The design features of the thermal fuse allow it to respond to dangerous temperatures inside household appliances almost instantly. At the cost of its “life,” it saves modern expensive equipment from overheating and fire.
The most affordable protection for electrical appliances remains fuses, which allow you to protect devices from high current values. But there are still some devices that conventional fuses are not suitable for protecting.
You can select and buy a thermal fuse at https://electronoff.ua/termopredohraniteli at an excellent price.
How does a thermal fuse work?
The design features of the thermal fuse allow it to respond to dangerous temperatures inside household appliances almost instantly. At the cost of its “life,” it saves modern expensive equipment from overheating and fire.
You can get acquainted with the assortment and purchase a thermal fuse in the electronoff.ua online store.
Attention: when working with fuses, it is important to follow safety rules! Installing a fuse at home should only be done when the voltage is turned off. Under load, an electric arc may form, which can subsequently cause eye damage, burns and damage to the thermal fuse holder. In electrical installations up to 1000 W, replacement of a thermal fuse with exposed live parts is carried out by competent people with special protection.
These are electronic components designed to protect more expensive components and equipment. The operating principle of the thermal fuse is based on opening the electrical circuit if the permissible temperature is exceeded.
These are electronic components designed to protect more expensive components and equipment. The operating principle of the thermal fuse is based on opening the electrical circuit if the permissible temperature is exceeded.
The Dalincom store offers various types of thermal fuses and thermostats - regular blown thermal fuses, self-repairing fuses, for a multicooker, for a stove, and others.
The cost of delivery of regular parcels is cheaper for heavy orders, it depends on the distance. See the tariffs on the Russian Post website for your location.
You will receive the exact shipping cost in your invoice.
Thermal fuses are compact and reliable elements of electrical circuits that are designed to protect against overheating and short circuits, which can lead to failure of household appliances and electrical equipment.
- 20
- 40
- 60
Thermal fuses are compact and reliable elements of electrical circuits that are designed to protect against overheating and short circuits, which can lead to failure of household appliances and electrical equipment.
Operating principle: when the temperature of the conductors increases to a certain value, the fuse element overheats and melts, which is why the electrical circuit breaks and the current does not pass further along the circuit.
You can view and buy products from the “Thermal Fuses” group in our store in Minsk. Delivery of the order by mail throughout the Republic of Belarus, including the cities of Gomel, Mogilev, Vitebsk, Grodno, Brest, Bobruisk, Baranovichi.
To the Graciano
, about the reason for the burnout, I don’t believe it.
I believe barsenal
and my experience. This transformer will still work. Of course, if possible, I will buy a thermal fuse and replace this homemade one in the adapter. Then I'll test it for temperature. For now, temporarily, let it work.
How to make a thermal fuse with your own hands?
Most household appliances generate heat when operating.
Some of them are designed and designed to heat (an electric iron, an electric kettle or a boiler for heating water), and for most, a strong increase in the temperature of their body and internal filling is an undesirable side effect of their operation. To prevent overheating, a thermal fuse is installed in series in the power circuit of such devices.
Design and principle of operation
Structurally, this protective element consists of two parts:
- electrical with normally closed contacts;
- mechanical with a bimetallic plate connected to the contacts of the electrical part.
The electrical part is enclosed in heat-resistant plastic, and the mechanical part is enclosed in an aluminum housing.
How to check a thermal fuse with a multimeter in resistance measurement mode
- switch the device to resistance measurement mode;
- attach the probes to the fuse contacts - if the resistance is close to zero, then the contacts are closed;
- heat the metal part of the thermal fuse (with a lighter, soldering iron or put it in hot water) and check the resistance again - it should be infinitely large.
During the cooling process, a faint click may be heard - this is the contacts closing. If before heating the resistance is zero, and after heating it is infinity, then the part being tested is operational.
This verification method is the most accurate, but you don’t always have a measuring tool at hand.
What are fuses and why are they needed?
Protecting electrical circuits from short circuits and overloads is one of the most important tasks in electrical engineering.
For this purpose, many protective devices have been invented, which today are used both in power circuits and to protect electrical circuits in various devices.
In almost every complex electrical appliance you can find fuses - disposable switching devices that disconnect the circuit in an emergency. Purpose and principle of operation
The main task of fuses is to protect the electrical network and electrical equipment from overcurrents that occur during a short circuit or as a result of critical overloads. At the same time, they ensure uninterrupted operation of the protected circuits in nominal mode.
Unlike a circuit breaker, often used in electrical engineering, a fuse-link operates only once, after which it must be replaced.
However, such a device works with one hundred percent probability, while the automation may fail after repeated shutdowns. That is why fusible links are used to protect expensive equipment.
They do not refuse to use these protective devices in power circuits.
Design and principle of protection
The design of a fuse has two main elements: a body (holder) with contacts and a fuse insert (Figure 1). Strictly speaking, only a combination of these elements can be called a fuse. Very often the fuse link part (especially if it is replaceable) is called a fuse. In this article we will also sometimes adhere to this tradition.
Rice. 1. Fuse design
The working element of the insert is a conductor made of copper or a metal alloy. Thanks to this fusible element, circuit shutdowns occur in critical situations.
The fusible element can be one or more copper wires, a plate or a shaped part. These conductors are placed in a heat-resistant housing: glass, ceramic (Fig.
2) or plastic.
Depending on the purpose, the space around the fusible element can be filled with quartz sand or surrounded by an easily evaporating substance intended to extinguish the electric arc.
Rice. 2. Ceramic fuse links
When rated currents pass through the insert wire, it heats up slightly without reaching the melting point. But in short-circuit mode, the current increases sharply, which leads to melting of the inserts. This causes the chain to break.
Heating of the fuse also occurs during overloads, that is, as a result of exceeding the rated voltage in the protected section of the circuit. When the operating voltage reaches a value called the shutdown current, the temperature of the fuse element increases to the melting point and the circuit breaks. After restoring the circuit parameters, the fuse link must be replaced.
Fuse links have a certain response inertia. With a short circuit, the delay is unnoticeable, since in this case the fuse element heats up at lightning speed.
The situation is different in cases with overloads. It takes longer to reach the melting point. Therefore, in order to increase the response speed, the elements of the inserts are given a special shape and loaded with elastic forces (one end of the plate is connected to an extended spring).
In some models, under the action of a spring, a pin called an operation indicator comes out (Figure 3). It acts as an operation indicator and indicates that the insert needs to be changed.
Rice. 3. Structure of the fuse link
The numbers in the figure indicate:
- I – cartridge;
- 2 – fusible plate;
- 3 – tin balls;
- 4 – fuse link;
- 5 – quartz sand;
- 6 – spring;
- 7 – textolite washer;
- 8 – trigger mechanism of the trigger indicator;
- 9 – cap;
- 10 – rim of the cap;
- 11 – operation indicator;
- 12 – asbestos-cement gasket;
- 13 – cement filling.
In some cases, to increase the response speed, inserts with parallel tensioned wires of different diameters are used. Burning out the thinnest wire increases the load on the remaining elements, accelerating their melting.
In order to reduce overvoltages, some designs of inserts use wires with different sections of individual sections. When such a fuse is triggered, the section with the smallest cross-section of the insert burns out first. If vapors of molten metal provoke an electric arc at the breaking point, a section with a large cross-section will burn out.
The design features of fuses can be recognized by their markings. Unfortunately, time-current characteristics are not applied to all types of products. But models on which alphanumeric codes are applied can be easily classified according to their purpose.
Marking
When choosing fuses, it is important to know the protection range. There are only 2 of them: partial and complete. With partial protection, the fuse operates only against short-circuit currents. Full protection also includes overload tripping.
In the code marking, the protection ranges are designated by the letters “a” (partial) and “g” (full). These letters appear first before the numbers indicating the rated current.
In second place are placed English capital letters, which indicate:
- G - universal fuse. Used to protect equipment: transformers, cables, electric motors;
- L - for cables and distribution devices;
- B - protection of mining equipment;
- F - device for low-power circuits;
- M - device for protecting circuits of electric motors and switching devices;
- R - devices for protecting semiconductor circuits;
- S - instantaneous combustion during short circuit and average response time during overload;
- Tr—transformer fuses.
Types and device
Depending on the tasks being solved, the classification of fuses can be as follows (Figure 5):
- blade guards;
- low-current fuse links;
- plug fuses;
- quartz;
- cork type
- gas generating.
Rice. 5. Types of fuses
There are also self-resetting fuses, inertial and hinged (Fig. 6). Inertia-type products are designed to protect electric motors, which create heavy loads when starting. Fusible elements heat up but do not burn out. After the engine starts, the slow-blow fuse goes into standby mode.
Folding inserts are used to protect power lines. In emergency situations, the fusible element opens the circuit. Under the influence of high temperature, the insert elongates, resulting in pressure on the trigger mechanism, which throws the fuse out of its socket. This ensures reliable shutdown of the emergency section.
Rice. 6. Flip-up fuses
The design of a self-resetting fuse differs from other types of electrical devices. The working element of the product is a polymer with a positive temperature coefficient of expansion. The polymer contains carbon inclusions that conduct current.
When heated, carbon bonds are broken, resulting in an increase in electrical resistance. When the melting temperature of the polymer is reached, the resistance tends to infinity, that is, the circuit opens. When cooled, the electrical conductivity of the polymer resumes. The fuse is self-resetting.
Specifications
Fuse links are identified by two characteristics: rated voltage and rated current. In industrial equipment, these figures can reach tens of kilovolts and thousands of amperes.
Household appliances use fuse links, the rated voltage of the free contacts of which is:
- 110, 220 V – for direct currents;
- 220; 380 V – for alternating current.
At the contacts of common models, rated currents range from 10 to 2500 A, and at the ends of fuse links - from 2 to 2500 A.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of fuses include:
- full guarantee of disconnection of the emergency section of the circuit;
- stability of technical protection characteristics;
- can be used for selectivity;
- performance;
- reliability;
- simplicity of design.
Main disadvantages:
- in three-phase networks, phase imbalance is possible;
- probability of prolonged arc burning;
- influence of the environment (temperature) on the characteristics of fuse links;
- difficulty in setting up selective protection;
- the need to replace the insert after each protection operation.
in development of the topic
//www..com/embed/W4I95inI0H0?feature=oembed//www..com/embed/kCMW1pjWwyQ?feature=oembed
Sources:
Greetings, friends!
Many of you have heard about such a thing as a fuse, which is also called a fuse link.
Historically, such fuses were the first protective devices in electronic and other equipment.
Progress does not stand still, and something else has been invented for protection.
The traditional fuse is like a snail.
Until it crawls...
Let's delve a little deeper into this interesting topic!
Traditional fuses
A traditional fuse link consists of a lead filament placed in a glass or ceramic tube. The tube can be filled with quartz sand, which extinguishes the electric arc.
The lead thread has some resistance and heats up when an electric current passes through it.
In operating mode, when the current does not exceed a certain value, the lead thread does not prevent its passage. When the current (due to a malfunction or accident) increases, the lead thread heats up and melts, interrupting the circuit.
Thus, at the cost of its “death,” the fuse saves the device from much greater trouble.
But a conventional fuse link does not always perform its functions properly. Firstly, it takes some time for the lead thread to heat up to the melting point. Modern semiconductor products are quite “delicate” and can burn out safely during this time.
Secondly, there are devices and parts that heat up during operation to temperatures significantly higher than room temperature. One of such devices is a small-sized low-frequency transformer used in power supplies (adapters) of modems, LAN switches, etc.
These adapters provide their output with a constant or alternating voltage of several volts at a small current. Let's face it - manufacturers often save money in their production by using less copper and steel in the transformer.
The result is overload operation and quite severe overheating of the windings and core even under normal operating conditions.
How to make a thermal fuse with your own hands - Metalworker's Guide
Can a thermos boil water on its own? Of course it can if it is a thermopot. This is a combination of an electric kettle and a thermos. Like any piece of equipment, it is prone to breakdowns. Therefore, you need to figure out whether it is possible to repair a thermopot on your own?
Thermopot circuit
If you do not have knowledge or experience in repairing electronics, it is advisable to contact a service center. But it’s still a good idea to have a general idea of how the thermopot circuit works.
Then it will be possible to eliminate minor malfunctions without having any special education.
For example, fix the power cord, remove and replace a faulty capacitor, or replace a burnt-out heating element or pump yourself.
The thermopot has a power supply. It consists of a pulse transformer and a diode bridge. We do not recommend going inside. Even specialists are unlikely to want to do repairs.
Most likely, they will insist on a complete replacement. The elements of an electrical circuit connecting electrical parts include: capacitors, resistors, diodes, transistors, etc.
They are mounted on the electrical board.
We have already mentioned the electric pump, control module and thermal protection. They are also included in the scheme. Let's look at a few repair cases that do not require in-depth knowledge.
How to disassemble the device
Before attempting to repair anything, you must properly disassemble the unit. This is necessary, firstly, to find and get to the fault. Secondly, to properly assemble the device back. Otherwise, the already repaired thermopot simply will not work.
Almost all models are designed the same. Knowing the general principle, you can visually figure it out yourself. In order not to forget anything or confuse anything when dismantling, we will go step by step all the way:
- Before starting disassembly, unplug the thermos and empty the water from it. Then turn it upside down and remove all the screws.
- Use a flat-head screwdriver or other convenient object to remove the plastic ring from the clamps. There will be screws under it that also need to be unscrewed.
- Now you can remove the pan. We recommend photographing the entire process step by step. Then you won't get confused when assembling.
- We have opened access to the pump. To disconnect the hoses from the pump, you need to remove the mounting clamps from them. Cut them off with scissors.
- Remove the hoses from the pipes.
- Remove the top cover carefully and without unnecessary force.
- We install the unit firmly upside down and take hold of the printed circuit board. Unscrew it and move it to the side.
- We remove the gasket and remove two more screws.
- Now the metal tray is free and ready for removal. We take it out along with the bottom.
- Unscrew the last 8 screws that hold the protective cover. Then use a screwdriver to remove the protection. Access to the heating element is open.
- We disconnect and take out the heating element.
- Having disconnected the part we need, we need to check its functionality. We call all electronics with a tester. We check the housing visually for cracks through which liquid may leak.
Common faults
What may not work and how to understand the reasons.
- Not a single indicator light is lit on the display, and the kettle does not turn on. We check the power cord and each wire connection. We also check the thermostat, fuse, and control module.
- Pressing the button does not dispense water into the cup. The reason is the pump.
- Secondary boiling does not work, the thermos does not heat the water. We check the power module of the electrical board.
- Basic boiling doesn't work. Checking the thermostat.
- Only heating works. We check the heating element for boiling.
Replace the faulty thermal fuse. | Cheerful Pencil
There are often times when our favorite speaker system or other household electrical equipment goes silent.
A common and solvable problem in such cases may be a faulty electrical fuse protecting the power transformer from overheating or from exceeding the rated current consumption.
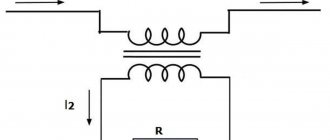
In modern household electrical equipment, in addition to protecting the electrical circuit from overvoltage of the supply network and short circuit in the secondary circuit, overheating protection is also used. A special element design is used, inside which a conductor made of a low-temperature alloy is placed.
When receiving heat from the elements it protects, the body of such a fuse heats up and the heat is transferred to the conductor located inside. As soon as the ambient temperature reaches the maximum safe level that guarantees the operation of the equipment, the conductor located inside the housing will melt and the electrical circuit will be open. The same thing will happen when the electrical current consumed by the equipment increases.
Location of the thermal fuse.
This fuse is convenient, safe and is used not only to protect transformers, but also to protect electric motors in fans, coffee grinders and many other electrical elements of household equipment. Often during repairs, the transformer is replaced with one with a working fuse, but there is not always something available to replace it. You can restore the operation of the equipment with minor repairs.
Replace the faulty thermal fuse with a tubular current one.
But what to do when the home craftsman does not have the necessary parts to replace the faulty ones? What can you come up with in this case, without resorting to going to the store or visiting a friend in the studio?
There is one solution. Before proceeding with repairs in such a situation, it is necessary to disconnect the electrical cord of the household equipment from the electrical outlet. This must be done always and without fail.
The process of the proposed repair itself consists of removing the faulty fuse and restoring the working network-transformer circuit through a mounted fuse designed for a maximum current consumption of 0.5A-1A and a voltage of 250V. There is nothing complicated. The main thing is accuracy, attentiveness, lack of haste and your equipment will work as before.
Sources
Source - https://vsbot.ru/lektronika/chto-takoe-termopredohraniteli.html Source - https://diodnik.com/kak-proverit-termopredoxranitel/ Source - https://kumar.dn.ua/publ/tekhnika /dlja_chego_nuzhen_termopredokhranitel/28-1-0-2147 Source - https://otransformatore.ru/svoimi-rukami/termopredohranitel-v-transformatore/ Source - https://electric-tolk.ru/klassifikaciya-predoxranitelej/ Source - https: //autogear.ru/article/383549/termopredohranitel-kak-proverit-v-domashnih-usloviyah/ Source - https://vp.donetsk.ua/ukraina-mir/nauka/83640-termopredohranitel-naznachenie-i-printsip- raboty Source - https://dalincom.ru/category-49-b0.html Source - https://www.chipdip.by/catalog/thermal-fuses Source - https://termopaneli59.ru/raznoe/aupo-bf121 -chem-mozhno-zamenit-xarakteristiki-princip-dejstviya-i-rabota-soprotivleniya-rasshifrovka-markirovki-kak-ego-proverit-i-prozvonit-multimetrom-gde-kupit-i-kak-zamenit-aupo-bf1.html