Types of ouzo, the principle of operation of ouzo and differential machine, how to check the ouzo, errors when connecting it, how often checks are carried out. +3 Photos with differences between type A and AC RCDs
TEST:
A short test will show the level of knowledge on this topic and the importance of choosing the optimal electrical protection device.
- Do you need separate lines to connect powerful household electrical appliances?
a) yes;
b) no.
- With what leakage current should an RCD be installed for children's rooms?
a) 10 mA;
b) 30 mA;
c) 100 mA.
- Is there a difference which type of RCD to purchase for house A or AC?
a) yes;
b) no.
- What is more reliable than RCD+AV or AD?
a) RCD+AV;
b) BP.
Answers:
- Yes. Separately installed lines make it possible to relieve the load on input circuit breakers and create more reliable in-house electrical networks.
- 10 mA. The resistance of a child's body is less than that of an adult. 10 mA is the only permissible conditionally safe value of the flowing leakage current.
- Yes. Devices with characteristic A protect not only from alternating, but also from constant impulse potential.
- RCD+AV. Disabling the blood pressure does not determine the cause of the failure: short circuit or leakage current. In the case of a residual current device and a circuit breaker, it is different by re-switching on the circuit breaker in front of it to determine the presence of a short circuit in the system. Also, if the automatic machine fails, the unit will need to be replaced with a new one. In another case, it is necessary to replace the circuit breaker or the residual current device.
A residual current device is an electrical device designed to protect a person from injury from leakage currents. This is a key element in ensuring safe use of household electrical networks.
Modern intra-house wiring is made of three wires, and the requirements of the current Electrical Installation Rules require the mandatory presence of differential protection. Electrical distribution boards are equipped with differential switches (devices sensitive to leakage currents) and RCDs. The device is installed for socket groups and lighting networks, as well as for stationary household electrical appliances.
Incorrect connection of the device leads to a decrease in the security level of the electrical network and its incorrect operation (false alarms).
To properly connect an electrical device, you need to understand its operating principle and structure.
Fig.1 Multi-level protection against differential currents
The diagram shows a detailed diagram of the connection of a residential building: 1st level - fire-fighting models at 300 mA, 2nd level - introductory, 3rd level distribution RCDs for power networks, lighting and connection of individual electrical appliances.
Differences between RCD types A and AC
Residual current devices are divided into subtypes depending on the principle of operation and technical characteristics.
Type of leakage current. Devices are divided into 2 types:
- AC type. It only responds to alternating leakage current (which occurs in the primary circuits of electrical appliances).
- Type A. Responses to constant and alternating pulsed differential electric current, i.e. on leakage currents that occur in the secondary circuits of electrical devices (control boards, power supplies, etc.).
The abbreviation is indicated on the case: AC (“~”) or A.
Rice. 2. Appearance of the RCD
High-quality manufacturer markings help you quickly understand the circuit and select the required model of the protection device.
Performance. Selectivity is determined by the protection response time:
- Type G. The electrical device turns off after leakage current flows for 0.06..0.08 s.
- Type S. Time delay - 0.15-0.5 s. the best option when organizing multi-level protection. These are incoming protection and fire protection devices. They are triggered in case of incorrect operation or damage to group electrical protection.
Operating principle. There are two types of models:
- Electromechanical. Disabling the emergency section does not depend on the presence of voltage in the network.
- Electronic. The operation of the electronic amplifier is ensured in the presence of an external power supply. If the integrity of the neutral conductor is compromised, then such devices cannot provide protection against electric shock. Therefore, electronic models are less reliable.
Modern imported premium class devices are equipped with an electromagnetic relay that turns off the load when the potential disappears.
Programming and Comparator
The comporator is not only used as part of an electrical circuit for PWM, etc., it is often used to create individual programs or their components. For example, the device is often used to create java collections.
To work, you will need a special Maven program. First, you need to create a project; for full operation, you need an Internet connection. Create a new project, select two components in the structure: comparator and pojo. Availability is checked using the JUnit 4.11 utility; Install pom.xml and create a new file
Interrupting the process is unacceptable, so it is very important to save at every stage. Afterwards, a POJO is created and configured, where the necessary settings are specified
The parameters depend on the requirements for a particular library. This could be dates of birth, general information about accommodation, etc.; And only after that a comparator is created. This is a class that is used to verify data and distribute it to the required folders. Using this class is necessary if you need to sort certain information according to specified parameters (colors, sizes, dates). This ensures data protection and classification according to a certain principle.
You can buy a ready-made comparator at any radio equipment and electrical equipment store. The price of the device varies depending on its purpose and the number of channels.
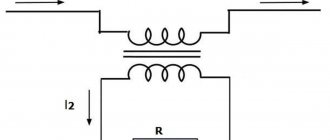
Operating principle of RCD. 2 main nodes
The operation of the electrical device is based on the principle of constant comparison of the current value at the input and output. If the values are equal, the network is considered stable and secure. If a difference appears, the sensitive element reacts to the change in parameters and the protection mechanism is activated.
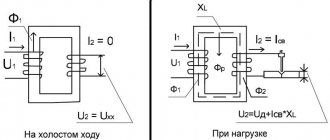
The main component of the device is a differential transformer, which responds to changes in parameters in the electrical network. In normal mode, the resulting current passing through the core is zero. When a leakage current appears, the magnitude of the current in the phase and neutral wires is different, which provokes the solenoid to turn off and the contacts of the electrical device to open.
A differential circuit breaker combines two devices: an RCD and a circuit breaker, simultaneously protecting electrical networks from leakage currents and short circuits.
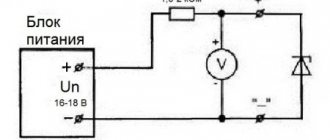
Rice. 3. Operating principle of RCD
The importance of choosing the right RCD?
Today there are a large number of different models of differentiated current switches on the market, which differ significantly from each other. The differences lie in the technical parameters, installation method and place of use.
If the RCCB (RCD) model is chosen incorrectly, with incorrect characteristics, then the following consequences are possible.
The automation will react erroneously, mistaking small current leaks, which usually exist in the home electrical network, for an emergency situation. In older wiring, these leaks are more common.
Often people choose VDT (RCD) with overestimated characteristics, as a result of which the VDT may operate with some time delay or may not sense an emergency situation at all. In this case, electrical injury may occur.
There are cases when the RCCB is connected according to the wrong diagram. Manufacturers display a connection diagram on the body of the device itself with the location of contacts for connecting phase and neutral conductors. If the connection is made incorrectly or power is supplied from the reverse side, this can also lead to “insensitivity” of the RCCB in the event of an emergency.
To avoid such errors, let's study the main characteristics of the RCD (RCD) before purchasing.
How to avoid incorrect operation of differential protection in the absence of grounding. 2 ways
During the construction of civil facilities during the Soviet period, there were no regulations requiring grounding in every apartment. The final grounding point in such cases is the house electrical panel. Using modern electrical appliances with a connection diagram without grounding is extremely dangerous. Using electrical protection reduces the risk of electric shock.
Without grounding, an electrical device ensures that the network is disconnected when leakage current flows through the human body. At the same time, the speed of the protection is such that the current does not have time to hit the body.
It is important to remember: if there is a grounding conductor, the electrical device disconnects the line with the leakage current instantly. Without grounding, shutdown occurs only after a person touches a faulty electrical appliance (washing machine, water heater, etc.).
In household networks, an RCD without grounding for fire protection works equally correctly, as in the case of three-wire lines.
Conventionally, we can consider connecting electrical protection without grounding as a special case of device operation when the grounding conductor is broken, while stably performing its main function.
Conclusion: RCD is the main element of protection in all circuits (with and without a grounding conductor). Provides fire safety at home and a high level of human protection from electric shock.
What is selective RCD
Selective RCDs differ from conventional protection devices in their long response time. This implementation makes it possible, in the event of any interruptions in the electrical circuit with series-connected protection devices, to disconnect not all wiring, but only a certain part of it.
Photo - principle of connecting a selective RCD
Since the protective devices responsible for a certain part of the electrical network operate before the selective RCD, the process of troubleshooting is greatly simplified.
To ensure selectivity, you need to do the following:
- Set the response time of the protection device (if such a function is available in a certain model);
- Set shutdown parameters for leakage current or short circuit (they must exceed those of other non-selective options).
Both of these parameters must be three times higher than the corresponding characteristics of other RCDs in the system, otherwise the device will not operate effectively.
Models are divided into the following types:
- AC;
- A;
- IN.
The first one is triggered at the slightest change in the supply current. It also instantly reacts to its smooth increase and exceeding the leakage current threshold. This option can be used both in an apartment panel and to ensure the safety of industrial or office electrical networks. This is the most accessible and popular type.
Photo - device connection diagram
The second type is triggered when the load is pulsating, as well as when the threshold leakage current value is exceeded. It is more expensive than AC, but its functionality is much higher. Scope of application: connecting a washing machine, power plants, refrigerators and other electrical appliances that require increased control.
The type B fire protection device allows monitoring of constant leakage current even at low ripple levels. This device is considered special, which is reflected in its scope of application (bridge circuits, industrial equipment, medical equipment, etc.).
Considering that the main task of operation is to maintain a certain time interval (it is by this parameter that the main classification is made), protection devices are:
- RCD S;
- RCD G.
The S marking is used for protection and shutdown devices that have a delay time interval of 0.15 to 0.5 seconds. This is an excellent choice for electrical networks where several protection devices are installed simultaneously and rapid shutdown of the current is required when necessary. For example, if in an apartment or private house there are several groups of loads, say 2, then a separate RCD (by type) is installed for each of them, and a selective RCD is installed at the input of the supply cable.
Then energy surges are not scary, because the “control” selective device will only work if any of the main ones does not respond. Based on which RCD has switched off, it will be possible to quickly find and fix the fault. Thanks to this, the protective device for a certain group will work first, and only after that the main one will work, which will turn off the power to the entire apartment.
Photo - S type
In some cases, RCDs that operate in groups may not work. Then the selective protective device will perform its function and de-energize the room in a split second.
Marking G indicates faster response. Here the time interval ranges from 0.06 seconds to 0.08. These are professional devices that provide an accurate and quick response to problems in electrical networks.
Classification [edit | edit code ]
By method of management [ edit | edit code]
- UDT without auxiliary power source
- UDT with auxiliary power source:
- performing automatic shutdown in case of failure of the auxiliary source with and without time delay:
- automatically restarting when the auxiliary source is restored
- not automatically restarting when the auxiliary source is restored
Read also: Construction of a polyurethane foam cylinder valve
- not producing automatic shutdown in case of failure of the auxiliary source:
- capable of shutting down if a dangerous situation arises after failure of an auxiliary source
- unable to shut down in the event of a hazardous situation following failure of an auxiliary source
- stationary with installation of fixed electrical wiring
- portable with installation by flexible wires with extension cords
By type of installation [edit | edit code]
By number of poles [edit | edit code]
- bipolar;
- four-pole.
If possible, regulate the disconnecting differential current [edit | edit code]
- unregulated;
- adjustable:
- with discrete regulation;
- with smooth regulation.
In terms of resistance to pulse voltage [edit | edit code]
- allowing the possibility of switching off during impulse voltage;
- resistant to impulse voltage.
According to the operating conditions in the presence of a direct current component [edit | edit code]
UDT type AC
: UDT, the operation of which is ensured by a differential sinusoidal alternating current by either its sudden application, or with a slow increase [9].
UDT type A
: UDT, the operation of which is ensured by both sinusoidal alternating and pulsating direct differential current by either sudden application or slow rise [9].
UDT type B
: UDT which guarantees operation as a type A device and additionally operates:
- with differential sinusoidal alternating current of frequency up to 1000 Hz;
- with a differential sinusoidal alternating current superimposed on a smoothed direct current;
- with a differential pulsating direct current superimposed on a smoothed direct current;
- with differential pulsating rectified current from two or more phases;
- with a differential smoothed direct current applied suddenly or gradually increasing, regardless of polarity [10].
UDT type F
: A RCD which guarantees operation as a type A device in accordance with the requirements of IEC 61008-1 and IEC 61009-1 and additionally operates:
- with a compound differential current applied suddenly or gradually increasing between phase and neutral or phases and the middle grounded conductor;
- with a differential pulsating direct current superimposed on a smoothed direct current [10] .