The purpose of a circuit breaker (hereinafter referred to as AB) is to protect electrical wiring and electrical equipment from short circuits (hereinafter referred to as short circuit) and overload. If you do not use such AVs in the network, then over time an accident may occur, that is, a short circuit in electrical wiring, electrical appliances or power tools. If not a short circuit, then an overload in the operation of electrical equipment.
In the first and second cases, the wire or cable will heat up, which means the insulation will melt. The wires will short out, a short circuit will occur, which means fire, sparks and ultimately a fire.
To prevent this from happening, AVs are used as protection against possible unpleasant consequences.
How does AB protect electrical wiring and electrical appliances and tools? If, simply put, there is a special device inside this switch that provides instantaneous shutdown of the voltage supply if there is a short circuit or overload problem.
Calculation of short circuit currents and selection of circuit breakers and fuses
Calculation of short circuit currents is necessary for the correct selection and adjustment of protective equipment.
Short circuit current occurs when the current-carrying parts of the phases are connected to each other or to the grounded body of the electrical receiver in circuits with a solidly grounded neutral and neutral wire. Its value, A, can be determined by the formula where U f
— phase voltage of the network, V;
Z p
— phase-zero loop resistance, Ohm,
R
— active resistance of one wire of the short circuit circuit, Ohm;
X
— inductive reactance, calculated based on specific inductive resistance equal to 0.6 Ohm/km;
Z
t is the total resistance of the phase winding of the transformer on the low voltage side, Ohm,
where UH ,
IH
are the rated voltage and current of the transformer;
UK%
— short-circuit voltage of the transformer, % of the rated one.
The values of UH
, lH
and Uk
% for
the corresponding transformer are given in Chapter 5.
The selection of an electrical device is carried out according to its functional purpose, the type of voltage and current, -> the amount of power.
It should be borne in mind the modern trend that when choosing between fuses and circuit breakers, preference is given to the latter due to their greater reliability, better protection against open-phase modes, versatility, etc.
The choice of devices based on voltage is based on the correspondence of the rated voltage indicated in the device’s passport and its type (AC, DC) to the rated voltage of the supply network. When choosing a device based on current, it should be taken into account that its rated current must be no less than the operating current of the installation.
Selection of circuit breakers
Circuit breakers
are selected primarily based on the nominal voltage and current values. Then the setting currents of the thermal and electromagnetic releases are determined.
The thermal
release
of the machine protects the electrical installation from prolonged overcurrent. The thermal release setting current is assumed to be 15-20% greater than the operating current:
where 1 R
— operating current of the electrical installation, A.
The electromagnetic
release
of the machine protects the electrical installation from short circuits.
The setting current of the electromagnetic release is determined from the following considerations: the machine should not be triggered by the starting currents of the electrical installation motor I start . dv .,
and the operation current of the electromagnetic release
I EMR
is selected as a multiple of the operation current of the thermal release:
where K
= 4.5—10 — current multiplicity factor of the electromagnetic healer.
The selected circuit breaker is tested for sensitivity and breaking capacity. Circuit breakers with a rated current of up to 100 A must operate under the following conditions:
where I O.K.Z.
— single-phase short circuit current.
The sensitivity of a machine that has only a thermal release is determined by the relation:
Circuit breakers with a rated current of more than 100 A must operate at
with an electromagnetic release is determined by the magnitude of the three-phase short circuit current I T.K.Z.
Fuse selection
The current of the fuse link is selected in accordance with the expression
The current of the fuse link used to protect a squirrel-cage induction motor is
where I start
is
the starting current of the motor, A;
β is a coefficient depending on the starting conditions, under average starting conditions (β = 2.5.
After a simple registration procedure, you will be able to use all services and create your own website.
My application.
total positions: 0.
Source
CIRCUIT BREAKERS AND RELEASES
The automatic protective switch (AB) is one of the most commonly used switching and protection devices in 0.4 kV networks. The protective functions of the machines are based on the operation of two types of releases:
- electromagnetic;
- thermal
The electromagnetic release operates without a time delay and provides protection against short circuit overcurrents.
The thermal release has an integral dependence of the response time on the current load. This is due to the use of a bimetallic element heated by a passing current load.
The greater the current value, the faster the thermal bending of the bimetal occurs, the latch is released and, accordingly, the machine is turned off. The thermal release protects the object from overload.
The basic principles of automatic protection of electrical circuits and electrical equipment are as follows.
Automatic protection elements AV do not have the ability to flexibly configure response parameters, like URZA. Therefore, to provide protection for loads of different properties, automatic circuit breakers are used that have different dependences of the response time on the current value. This relationship is called time-current characteristic (TCC)
circuit breaker.
In accordance with GOST R 50345 - 2010, the time-current characteristics of circuit breakers are divided into three types - B, C, D. The comparative characteristics of circuit breakers are most clearly demonstrated by VTX graphs. The horizontal axis of the graphs shows the current multiplicity values, that is, the ratio of the actual current to the nominal value of the machine; the vertical axis shows the shutdown time.
GOST regulates the procedure for conducting tests to check the time-current characteristics of a circuit breaker. The disconnecting characteristic is checked at five test current values.
The first three current values used during testing are intended to check the operation of thermal releases. One of them is the non-trip value, the other two are the trip currents. The last two tests are carried out to check the breaking capacity of the instantaneous magnetic release.
What is the machine used for?
A machine is installed in the power supply circuit to prevent overheating of the wiring. Any wiring is designed to carry a certain current. If the current passed exceeds this value, the conductor begins to heat up too much. If this situation persists for a sufficient period of time, the wiring begins to melt, resulting in a short circuit. A circuit breaker is installed to prevent this situation.
A packager or circuit breaker is necessary to prevent overheating of conductors and shutdown in the event of a short circuit
The second task of the circuit breaker is to turn off the power when a short circuit current (SC) occurs. When a short circuit occurs, the currents in the circuit increase many times over and can reach thousands of amperes. To prevent them from destroying the wiring and damaging the equipment included in the line, the circuit breaker must turn off the power as quickly as possible - as soon as the current exceeds a certain limit.
In order for the protective circuit breaker to properly perform its functions, it is necessary to correctly select the machine according to all parameters. There are not many of them - only three, but you need to deal with each one.
What types of circuit breakers are there?
To protect conductors of a single-phase 220 V network, there are single-pole and double-pole disconnecting devices. To single-pole wires, only one conductor is connected - phase, to double-pole wires, both phase and neutral. Single-pole circuit breakers are installed on 220 V indoor lighting circuits, on socket groups in rooms with normal operating conditions. They are also installed on some types of load in three-phase networks, connecting one of the phases.
For three-phase networks (380 V) there are three and four poles. These circuit breakers (the correct name is a circuit breaker) are installed on a three-phase load (ovens, hobs and other equipment that operate on a 380 V network).
In rooms with high humidity (bathroom, bathhouse, swimming pool, etc.) two-pole circuit breakers are installed. They are also recommended for installation on powerful appliances - washing machines, dishwashers, boilers, ovens, etc.
It’s just that in emergency situations - in the event of a short circuit or insulation breakdown - phase voltage can reach the neutral wire. If a single-pole device is installed on the power line, it will disconnect the phase wire, and the zero with dangerous voltage will remain connected. This means there is still a possibility of electric shock when touched. That is, the choice of machine is simple - single-pole switches are installed on some lines, and double-pole switches on others. The specific amount depends on the network condition.
Automatic machines for single-phase networks
For a three-phase network, there are three-pole circuit breakers. Such a machine is installed at the entrance and at consumers, to which all three phases are supplied - an electric stove, a three-phase hob, an oven, etc. The remaining consumers are equipped with two-pole circuit breakers. They must disconnect both phase and neutral.
Example of three-phase network wiring - types of circuit breakers
The choice of circuit breaker rating does not depend on the number of wires connected to it.
Types of circuit breakers
Circuit breakers are produced for single-phase and three-phase circuits. For a single-phase network there are two types of packets - single-pole and double-pole. Only the phase wire is connected to single-pole ones and, when triggered, only the phase is disconnected. It is recommended to install such machines in houses and apartments in rooms with normal operating conditions. Usually they are installed on lighting lines, socket groups, which are located in living rooms, corridors, and kitchens.
Circuit breakers - single-pole, double-pole and three-pole
Both phase and neutral wires are connected to two-pole circuit breakers. He breaks both chains. The degree of protection here is much higher since the shutdown is complete and not partial. Such a machine will ensure safety even if during an accident voltage reaches the neutral conductor. It is recommended to install two-pole circuit breakers on dedicated lines to which powerful household appliances are connected. They are also installed in rooms with difficult operating conditions. These include a bathroom, swimming pool, sauna.
For three-phase networks, three-pole and two-pole circuit breakers are used. All three phases are turned on to three-pole ones. Accordingly, they all turn off at the same time. Such packets are placed at the entrance to a house or apartment, as well as on the lines to which three-phase consumers are connected - a hob, an oven and other similar equipment. For the same consumers, four-pole circuit breakers can be installed. They will also disconnect the neutral wire.
An example of using circuit breakers on a three-phase network
On other power lines, on which one of the phases is used, two-pole packets are installed. Simultaneous disconnection of phase and zero is more preferable. And only on the lighting line can single-terminal circuits be installed.
Deciding on the denomination
Actually, from the functions of the circuit breaker, the rule for determining the rating of the circuit breaker follows: it must operate until the current exceeds the capabilities of the wiring. This means that the current rating of the machine must be less than the maximum current that the wiring can withstand.
For each line you need to choose the right circuit breaker
Based on this, the algorithm for selecting a circuit breaker is simple:
- Calculate the wiring cross-section for a specific area.
- See what maximum current this cable can withstand (see the table).
- Next, from all the ratings of the circuit breakers, we select the nearest smaller one. The ratings of the machines are tied to the permissible long-term load currents for a particular cable - they have a slightly lower rating (see the table). The list of denominations looks like this: 16 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 63 A. From this list you choose the appropriate one. There are smaller values, but they are practically not used anymore - we have too many electrical appliances and they have considerable power.
Example
The algorithm is very simple, but it works flawlessly. To make it clearer, let's look at an example. Below is a table that shows the maximum permissible current for conductors that are used when laying wiring in a house and apartment. Recommendations regarding the use of machines are also given there. They are given in the column “Nominal current of the circuit breaker”. This is where we look for the ratings - it is slightly less than the maximum permissible for the wiring to work normally.
Selecting a circuit breaker by current
According to the rated current AB
The industry produces a wide variety of automatic machines with rated current: 0.5A; 1A; 1.6A; 2A; 3.15A; 4A; 5A; 6A; 10A; 16A; 20A; 25A; 32A; 40A; 50A; 63A. In everyday life, it is mainly used from 6A to 40A.
When purchasing an AV, you need to choose a rating so that it operates until the moment when the current does not exceed the capabilities of the wiring.
Therefore, you need to know what cross-section you need to lay the wire (cable) to the consumer or group of consumers and their power. The nominal value of AB will depend on this.
Table 1.
| Rated current of the circuit breaker, A | Electrical circuit load, 220 V |
| 10 | Lighting, alarm |
| 16 | General purpose sockets |
| 25 | Air conditioners, water heaters |
| 32 | Electric stoves, ovens |
| 40; 50 | General input |
Selecting the breaking capacity
The selection of a packager based on the maximum permissible load current is described above. But the network circuit breaker must also turn off when a short circuit (short circuit) occurs in the network. This characteristic is called breaking capacity. It is displayed in thousands of amperes - this is the order currents can reach during a short circuit. Selecting a machine based on its breaking capacity is not very difficult.
This characteristic shows at what maximum value of the short-circuit current the circuit breaker remains operational, that is, it will not only be able to turn off, but will also work after being turned on again. This characteristic depends on many factors and for accurate selection it is necessary to determine the short-circuit currents. But for wiring in a house or apartment, such calculations are done very rarely, and are based on the distance from the transformer substation.
Breaking capacity of automatic protective switches
If the substation is located close to the entrance to your house/apartment, take a circuit breaker with a breaking capacity of 10,000 A; for all other city apartments, 6,000 A is enough. If the house is located in a rural area or you are choosing a circuit breaker for a summer residence, it may well be enough and a breaking capacity of 4,500 A. The networks here are usually old and short-circuit currents are not large. And since the price increases significantly with increasing breaking capacity, the principle of reasonable savings can be applied.
Is it possible to install bags with a lower breaking capacity in city apartments? In principle, it is possible, but no one guarantees that after the first short circuit you will not have to change it. He may have time to turn off the network, but will be inoperative. In the worst case scenario, the contacts will melt and the machine will not have time to turn off. Then the wiring will melt and a fire may occur.
Type of electromagnetic release
The machine must operate when the current rises above a certain level. But short-term overloads periodically occur in the network. They are usually associated with inrush currents. For example, such overloads can be observed when turning on the refrigerator compressor, washing machine motor, etc. The circuit breaker should not turn off during such temporary and short-term overloads, because they have a certain delay for operation.
But if the current has increased not because of an overload but because of a short circuit, then during the time that the circuit breaker “wait”, its contacts will melt. This is what an electromagnetic automatic release is for. It operates at a certain current value, which can no longer be an overload. This indicator is also called cut-off current, since in this case the circuit breaker cuts off the line from the power supply. The magnitude of the operating current can be different and is displayed by letters that appear in front of the numbers indicating the rating of the machine.
There are three most popular types:
- B - triggers when the rated current is exceeded by 3-5 times;
- C - if it is exceeded by 5-10 times;
- D - if 10-20 times more.
Class of machine or cut-off current
What characteristics should you choose? In this case, the choice of a circuit breaker is also based on the distance of your household from the substation and the state of the electrical networks; the choice of a circuit breaker is carried out using simple rules:
- With the letter “B” on the body they are suitable for dachas, houses in villages and towns that receive power supply through air ducts. They can also be installed in apartments of old houses in which the internal electrical network has not been reconstructed. These circuit breakers are not always on sale; they cost a little more than category C, but can be delivered to order.
- Bags with a “C” on the body are the most widely used option. They are installed in networks with normal condition, suitable for apartments in new buildings or after major renovations, in private houses near the substation.
- Class D is installed in enterprises and workshops with equipment with high starting currents.
That is, in essence, the choice of a circuit breaker in this case is simple - type C is suitable for most cases. It is available in stores in a large assortment.
Selecting AV based on short circuit current
You can purchase AVs with short circuit ratings: 3,000, 4,500, 6,000, 10,000 Amperes. The choice of AV with the required rating depends on the length of the cable or overhead line from the transformer substation (TS) to your house, apartment or cottage.
If the transformer substation is located nearby, then the short-circuit currents are very high, so you need to purchase a circuit breaker with a cutoff of 10,000 A. In the private sector of households, there is a large length of overhead power lines, so you need to use a circuit breaker with a short-circuit current of 4,500 A. In other cases, the average value is 6 000 A.
Electromagnetic release
An electromagnetic release is a part inside the AB that, in the event of a short circuit (SC), opens the electrical circuit. Releases are divided into categories. We will look at the categories that are used most often:
B – the circuit opens when the rated current is exceeded by 3–5 times;
C – exceeded by 5–10 times;
D – exceeded by 10–20 times.
Selecting a circuit breaker for short circuit current
The shutdown current of the circuit breaker during a short circuit is a multiple of the current in the circuit during a short circuit (short circuit), at which the circuit breaker will disconnect the circuit from the power supply.
The circuit breaker must turn off the electrical circuit in case of any short circuit. There is such a thing as the calculated value of short circuit current. You don't need this technique to practice.
To select a circuit breaker for short circuit current, the type of circuit breaker was introduced. The type of machine contains the required values of the circuit breaker current in relation to the probable short circuit current. The current depends on the types of network load. For apartment electricians, type B and C circuit breakers are used, at input D. An extended table with the types of circuit breakers is in the article: Circuit breakers, why they are needed.
Let me remind you that the cut-off current value of the circuit breaker during a short circuit should be from 3 to 5 values of the rated current in the circuit for light (type of machine B) or from 5 to 10 values of the rated current in the network in power socket circuits (type of machine C).
Modular circuit breakers
This is a unique, modern device that is provided today by many manufacturers. In such circuit breakers, two types of network releases are most often installed:
- A specialized thermal release that trips at the moment of overload. In fact, the design is equipped with a fairly high-quality bimetallic plate. When heated, due to the special qualities of the material, it straightens, which causes the chain to disengage. Note that depending on the amount of current supplied to the plate, its heating rate is formed. Accordingly, in this situation, the speed of operation of the machine will depend on the current strength that is passed through the plate;
- There is also an option for a magnetic circuit breaker. This element is triggered when short circuit currents arrive, which are not one-time, but multiple times exceed the established parameter standards.
Selecting an overcurrent protection circuit breaker
The circuit breaker must protect the electrical wiring cable and the connecting contacts of the circuit from overload. Network overload is the inclusion of such a number of household appliances in the circuit that their total power will lead to such a current in the network that will heat the network wires and contact connections.
From here we get the first selection rule: choosing an overload protection machine :
In its characteristics, the installed circuit breaker must have an overload shutdown current (rated current of the circuit breaker) equal to or greater than the maximum rated current in the circuit.
Let me explain with an example.
Suppose you have a group electrical circuit of n sockets in your apartment. You know what household appliances will be powered from them. This means you can calculate their total power consumption, and from it the maximum load current.
By default, the voltage is 220 Volts.
So we found out that according to the norms and rules, the rating of the circuit breaker must be equal to or greater than the maximum possible load current, that is, the current at which all devices are connected to the circuit.
But such a condition cannot be correct. According to this condition, it turns out that the circuit breaker can have any rating higher than the rated current of the circuit. Therefore, on the other hand, the rated current of the circuit breaker is limited by the permissible current that the electric cable can withstand without heating. Hence the second rule for choosing a circuit breaker for overload protection:
The rated current of the circuit breaker must be no more than the permissible cable current.
Permissible current values for conductors are taken from Table 1.3.4. PUE ed. 7 (rules for electrical installations) and depend on the type of electrical wiring (open wiring or hidden wiring).
Here I will give part of the table for apartment electrics.
Important! In apartments, you cannot use a cross-section of TPG (current-carrying cable cores) less than 1.5 mm 2, and you cannot use TPG with a cross-section of less than 16 mm 2 made of aluminum, only copper:
selection of circuit breaker based on wire cross-section and current
We combine both rules and get a general rule for choosing the rating of a circuit breaker for protection against network overloads:
The rated current of the circuit breaker must be no less than the maximum load current in the circuit and no more than the maximum permissible current for the conductors used in the circuit.
It is better to read an example of a detailed calculation of a circuit breaker in the article: Calculation of a circuit breaker.
Selecting the cut-off time of the circuit breaker
The second most important indicator of a circuit breaker is the cut-off time during a short circuit, that is, the time during which it will disconnect the circuit from the power supply.
Protection circuit breakers are divided into instantaneous circuit breakers and delayed cut-off circuit breakers (selective circuit breakers). Since selective circuit breakers are rarely used in residential networks, and if they are used, then only at level B (protection level on the power input side), we will mean instantaneous circuit breakers.
So, the longest response time of the circuit breaker (shutdown time) in the TN system should be from 0.1 sec. (at a supply voltage of more than 380 Volts) up to 0.8 seconds (at 127 Volts). For 220 volts, the cut-off time should not exceed 0.4 seconds. (PUE table 1.7.1.)
Selection of circuit breaker by power: table
To select a circuit breaker based on power (P), you need to calculate the load current using the formula, then, based on the data obtained, select a circuit breaker of a larger value.
AB selection example
First you need to calculate the sum of all powers for which you need to select an AB. A wire is connected to the machine in the apartment panel, which goes to the kitchen, where a 2.2 kW kettle, a 700 W microwave oven, and a 720 W bread maker are connected through sockets. The total power of electricity consumers is 3,620 W = 3.62 kW. We will calculate the current using the formula:
I = P/U
Where:
I – current consumption;
P – total power of consumers;
U – network voltage.
I = 3,620/220 = 16.4A
As you can see, the consumed load current is 16.4 A. And based on this, you can select AB. You can take a 16 A automatic machine, but it will work at the very limit. Any machine is designed in such a way that the specified rated current is increased by 13% and if overloaded it will work for some time. Why take an AB that will work to the limit. You need to take it with a reserve. The next AB rating is 20 A.
To determine a more accurate load, you need to look at the passport or take data from the nameplate, which is on all electrical appliances.
Look at the power table to select an AB by rating.
Table 2.
| Connection type | Single phase 220 V, | Three-phase (delta), 380 V | Three-phase (star), 220 V |
| Machine rating, A | |||
| 1 | 200 W | 1 100 W | 700 W |
| 2 | 400 W | 2,300 W | 1,300 W |
| 3 | 700 W | 3,400 W | 2,000 W |
| 6 | 1,300 W | 6,800 W | 4 000W |
| 10 | 2,200 W | 11,400 W | 6,600 W |
| 16 | 3,500 W | 18,200 W | 10,600 W |
| 20 | 4,400 W | 22,800 W | 13,200 W |
| 25 | 5,500 W | 28,500 W | 16,500 W |
| 32 | 7,000 W | 36,500 W | 21,100 W |
| 40 | 8,800 W | 45,600 W | 26,400 W |
| 50 | 11,000 W | 57,000 W | 33,000 W |
| 63 | 13,900 W | 71,800 W | 41,600 W |
Marking of circuit breakers
Let's see where to look on the body of the circuit breaker, the above-mentioned values of cut-off currents and response times.
Breaking capacity is a characteristic of the reliability of a circuit breaker. For example, in the photo you see a marking of a breaking capacity of 10,000 Amperes. This means that after the machine is triggered with a short circuit current of less than 10,000 amperes, the machine will remain in good condition and can continue to operate after the fault is eliminated.
GOST R 50345 defines standard values for the breaking capacity ratings of circuit breakers: 1500 A, 3000 A, 4500 A, 6000 A, 10,000 A.
Current limiting class . A circuit breaker with a current limiter does not allow the short circuit current to reach its maximum value, and the shutdown occurs faster.
The current limiting class is marked with numbers:
Class 2 – reduction of shutdown time by half a half cycle;
Class 3 – reduction by a third of the half-cycle.
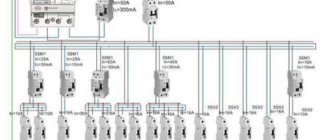
At the end of the article, it should be mentioned that the choice of circuit breaker will have to be made from the following AZ ratings for mounting on a DIN rail:
Purpose of the circuit breaker
The main purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect the wiring from overheating and the insulation from melting. And it does this by turning off the power supply at those moments when the conductor heats up to critical temperatures due to connecting an excessively high power load. The second task of the package operator is to disconnect the line during short-circuit currents. The goal is the same - to protect the wiring from destruction.
Selecting a circuit breaker begins with determining the number of wires to be disconnected
Turning off the power in a timely manner in the event of problems is very important, as it prevents damage to the wiring and fire. Therefore, choosing a circuit breaker is a responsible task. You need to choose according to the rules, and not according to the principle “so that it turns off less often.” This method may cause a fire. In general, the selection of a circuit breaker is carried out according to three parameters:
- denomination;
- breaking capacity (cut-off current);
- type of electromagnetic splitter (time-current characteristic).
Each parameter is important and is selected depending on the load connected to a particular line, the location of the electrical wiring relative to the distribution substations.