A lead-acid battery is a power source whose design has remained unchanged since its invention. The main purpose of the battery is to assist in starting the engine and to provide power to the vehicle's on-board network when the engine is not running. The battery itself does not produce electric current; it accumulates it through a chemical reaction.
Sometimes we wonder - what's inside a car battery? And inside is an acid electrolyte containing sulfuric acid and lead plates. This is of course simplified, we will tell you in more detail later.
A car battery is a secondary galvanic cell. A careful study of its properties and structure will help us choose the right product when purchasing.
What are galvanic cells?
A galvanic cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The main components of any galvanic cell are two electrodes - the cathode and the anode, placed in a vessel made of non-conducting material and filled with electrolyte.
The whole variety of galvanic cells used can be divided into two main types: primary elements and secondary elements.
Primary elements include, for example, the well-known so-called “dry” elements. Secondary cells include batteries of all types. The difference between the types of elements is determined by the nature of the chemical reactions that occur in them during operation.
In secondary elements, the chemical reactions that occur are reversible. A used or discharged battery can be restored (charged) if a direct electric current is passed through it in the opposite direction. During the charging process, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy. During the next discharge cycle, a reverse reaction occurs.
The battery produces electric current as a result of a chemical reaction between sulfuric acid contained in the electrolyte and an active compound applied to the lead plates. The battery plates or grids are shaped like a mesh to better hold the spreading paste.
Battery grilles are produced in three ways:
- Casting method - casting into molds
- Expanding – rolling, followed by cutting and stretching.
- Stamping – rolling, followed by removal of part of the plate by stamping.
The casting method is used in the production of low-antimony batteries. The disadvantage of this method is the high material consumption and low production speed. Poor quality of grating surface treatment accelerates the corrosion process. The undoubted advantage is that the grille produced by casting has a frame around the perimeter and the thickness of the grille plate allows it to withstand large deformations during engine starting. Therefore, such plates are still used in most truck batteries capable of delivering high starting currents during vehicle starting.
The expander method is used in middle-class calcium batteries. Alloying lead with calcium made it possible to roll it to a very small plate thickness. Next, notches are made along the tape. After applying the perforations, the tape is stretched and a lattice is obtained with two smooth edges and two uneven ones. The main advantage of expanded metal technology is its low production cost and acceptable electrical and strength properties. The disadvantage is an increased susceptibility to corrosion, due to disruption of the crystalline structure of lead, and reduced strength at high starting currents, due to the lack of a full-fledged frame.
The advanced method of producing battery grids in our time is the stamping or punching method. The punching process begins with rolling lead tape, just like expanded metal technology. Next, a grating of a certain shape is stamped. The result is a strong plate with a full frame, which gives strength close to a cast lattice. At the same time as increasing strength, we received an excellently processed surface that is slightly susceptible to corrosion. The absence of disruption of the crystal structure of the lead alloy increased the electrical characteristics of the lattice.
When choosing a car battery, ask the seller about how the grid in the proposed battery is made. You can always get qualified advice from our master consultants. Contact Battery and get a high-quality battery selection service.
Types of car batteries
Battery types are serviceable and maintenance-free.
With a serviceable battery you can:
- physically just unscrew the caps from the cans;
- visually determine the electrolyte level and the condition of the lead plates;
- measure the density and boiling of the electrolyte during charging;
- add distilled water if necessary.
To put it in the language of a motorist - “get to the insides.” We can do whatever we want with the battery.
But serviced batteries have a number of disadvantages:
- due to the leakage of the battery during operation, the electrolyte may boil away, which leads to a decrease in its level and, as a result, the capacity drops, resulting in problems with starting the car;
- evaporation of water leads to an increase in the density of the electrolyte, resulting in the destruction of the plates;
- it is necessary to constantly monitor the electrolyte level;
- When the electrolyte is heated, a specific white coating forms on the outer cover of the battery (at the location of the plugs), which can lead to short-circuiting of the terminals and premature partial discharge.
All these shortcomings are problems of past years. Inventors worked for many years to solve these problems and finally found a way out - they made the battery maintenance-free.
Maintenance-free battery.
A distinctive feature is the absence of plugs on the top cover and no matter how much you want to look inside, nothing will work. It became completely sealed.
What are the advantages of this type?
- When the electrolyte is heated, the evaporated liquid in the form of condensate settles on the inner walls of the battery and flows down.
- The battery can be turned over in any way without fear of electrolyte spillage.
- The main problem has been solved - the plates are always in the electrolyte.
But there is no device without shortcomings.
On maintenance-free batteries, jumpers between banks are located inside the case. It is almost impossible to check the voltage on the banks.
So-called “emergency pressure relief valves” have begun to be installed on maintenance-free batteries. It works in emergency situations when there is a strong overcharge. Some of the evaporated electrolyte comes out, but there is no way to add it back to the battery. Several recharges and as a result, the battery loses capacity.
Why does the battery drain quickly?
There is nothing special about the car battery itself that breaks. The service life of a car battery depends to a very large extent on its operating mode.
A car battery can drain quickly for the following reasons:
- due to corrosion of battery plates,
- as a result of depletion of the active coating of the battery plates,
- battery electrolyte depletion.
Failure to follow the rules of battery care causes a number of malfunctions, such as:
- Sulfation of battery plates.
- Accelerated battery self-discharge.
- Short circuit inside the battery.
- Electrolyte leaks through cracks in the battery tank.
- Oxidation of battery poles.
Battery plate sulfation is the formation of a white coating of large lead sulfate crystals, called sulfate, on the battery plates. Sulfated battery plates no longer take part in the chemical reactions occurring in the battery. If sulfated plates appear in the battery, the battery capacity decreases. The battery becomes unusable. A sign of partial sulfation of the plates is the rapid discharge of a car battery under load.
Sulfation of battery plates occurs in the following cases. 1) When the battery is systematically undercharged. 2) When storing the battery in an uncharged state and with the electrolyte not drained. 3) When charging the battery below the permissible limit. 4) When the electrolyte level in the battery banks decreases. 5) When the electrolyte density in the battery is high.
Any battery has a natural self-discharge. Self-discharge of a battery occurs for many reasons, including due to the fact that the lattice of battery plates and the active mass on them themselves constitute a galvanic couple in which a local current arises. In a working battery, the self-discharge value does not exceed 2% of the battery capacity per day. The self-discharge of the battery increases if, during the operation of a car battery, contaminated sulfuric acid and water (undistilled), containing salts and alkalis, are used, or various substances get inside the battery, then additional galvanic couples will also form in the battery. If the battery self-discharges rapidly due to contamination of the electrolyte, it is necessary to replace the electrolyte and rinse the battery. Self-discharge of the battery also increases from high temperature, from dirt and from electrolyte (water) on its cover. Oxidized battery pins and terminals must be cleaned.
During the operation of a car battery, the following gradually occurs in it: - Destruction of the separators. — Loss of the active mass from the plate grids. The cause of loss of active mass may be prolonged recharging of the battery, poor fastening of the plates, vibration, etc. — Warping of battery plates. Warping of the plates occurs: with an increase in the charging current, with a short circuit, with a decrease in the electrolyte level, with frequent and prolonged activation of the starter, when the battery is loaded with a high discharge current. All this, in turn, leads to the contact of the plates, that is, to a short circuit between the plates and the termination of the battery.
The battery indicator is a very important part; as a rule, car batteries without plugs for adding electrolyte are equipped with an indicator.
Some plug batteries also come with a built-in indicator, which does not cause any inconvenience to the owner.
The battery indicator shows the owner the level of charge of the battery, also determines the density of the electrolyte and its charge, but the reading starts only from 65 percent. Unfortunately, it is impossible to determine the exact charge level, especially since it is necessary to take into account that the reading comes from only one battery cell.
Nowadays, special indicators are produced for cars, which are equipped with a scale and a reading sensor; they are conveniently placed in the car interior, you sit down and immediately see the condition of the car battery.
If the battery starts to drain quickly , you need to look for the cause in the circuit, most likely the wiring is loose somewhere in the car, you need to check all the connecting terminals for oxidation, as well as the wires for fraying. If everything is in order with the wires, you need to check the battery capacity; when increasing power, the outdated generator may not be fully charged. On the contrary, a powerful generator is overcharged, which has a bad effect on its functioning.
Another very important reason may be a malfunction of the battery itself, if it is already more than two years old, you need to pay attention to the operation of the battery, to the color of the electrolyte, if it is dark, this indicates a problem directly in the battery itself, peeling of the plates could have occurred.
Let's summarize the reasons for battery failure:
1. Malfunction of the vehicle’s electrical equipment, possible malfunctions in the electrical circuits.
2. Car manufacturers sometimes put a battery in a car that cannot cope with additional equipment; it simply does not have enough power.
3. Recharging the battery. The electrolyte in the battery begins to boil and, as a result, the electrolyte level decreases.
Once damage to the electrical equipment has been ruled out, you should move on to identifying the causes directly in the battery itself.
Let's summarize: the battery is charging quickly after a short stop, a leak in the electrical circuit, a faulty battery. When parking a car for a long time, experts recommend disconnecting the battery from the network. If this does not help, replacement is the only way out. As a rule, they can no longer be repaired, and even if so, then after service the battery will not last long.
The average battery life is two years on average, if that's how long the battery needs to think about replacing it.
| Similar articles | Popular articles | Selected articles |
|
|
|
Add a comment
JComments
Characteristics of lead-acid batteries
Surely more than 90% of motorists know about the structure of their battery only from school physics lessons. Yes, in everyday life this is no longer required. Bought - installed - forgotten.
Characteristics of rechargeable batteries that motorists pay attention to when choosing a battery: type of battery (maintained or maintenance-free), electrical capacity of the battery, rated voltage of the battery, self-discharge.
The term “electrical capacity of the battery” means the amount of electricity given off by the battery when discharged. Capacity is determined in ampere hours.
Discharge capacity CP - the amount of electricity in ampere-hours obtained when the battery is discharged to the permissible voltage. The discharge capacity is determined based on the formula:
CP = Iр* tr
The capacity of the SAB significantly depends on the temperature of the electrolyte, especially in starter discharge modes.
Battery capacity can be expressed in two ways: in ampere hours or in watt hours. The term "capacity" refers to the amount of electricity that can be obtained from a given power source. Capacity in watt-hours is a measure of energy or the ability to produce work.
When determining the capacity of any battery, it is necessary to note the mode in which the discharge is performed, the temperature and the final voltage. The battery capacity is mainly determined by three factors: discharge, temperature and final voltage, and when marked, it is set in ampere hours.
The standard nominal voltage of one battery cell is 2 volts. Batteries with a voltage of 12V are produced for passenger cars, and for trucks they are used with a voltage of 24V. For special equipment, batteries can be manufactured with a voltage set by the manufacturer.
Spontaneous battery discharge – loss of capacity during storage, disconnection of external consumers, temperature conditions of operation and quality of maintenance. At the same time, its performance characteristics are reduced.
It has been experimentally established that for lead-acid batteries, the self-discharge value varies from 1.5 to 3% per month.
One of the reasons for the increased self-discharge of serviced batteries is the use of non-distilled water containing impurities of iron, chlorine and various salts.
Also, when the battery is turned over or strongly shaken, the active substance falls off the plates.
Let's take a look what's inside?
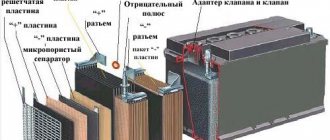
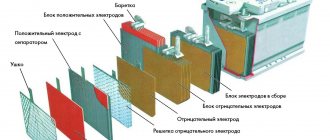
Fundamentally, the design of batteries has remained unchanged since their invention: lead plates and acid. The internal space is filled with an electrolyte consisting of 38% sulfuric acid and distilled water. Each battery alternates negative and positive electrodes. Plastic separators are placed between the plates. All jumpers between cells and batteries are made of lead.
How are car batteries made?
Have you ever looked inside car batteries? And we decided to look “inside” battery production. The only Belarusian enterprise that produces batteries for passenger cars is located in Pinsk and is 75% owned by the American corporation Exide. At the plant they speak two languages and make big plans. For example, they are going to produce batteries for the Volkswagen Polo Sedan, which are produced at a plant in Kaluga.
The plates are delivered from the warehouse, “impregnated” with a special paste (lead oxide with additives). They act as guides. Yellowish in color - with a positive charge, greenish-gray - with a negative charge. The plates are the most important component of the battery, an element of the electrical circuit. Like the filament in a light bulb. The amount of paste determines such an important characteristic of the battery as capacity. And the surface area of the plates is the inrush current.
The thinner the plates and the more of them, the higher the inrush current. Starter batteries (they are the only ones produced in Pinsk) - they have a higher figure - are compared to an Arabian horse, traction batteries - to a draft horse.
The Pinsk enterprise is only on the way to creating a full cycle of production of rechargeable batteries, and now such plates are imported from Poznan, from another plant of the American corporation. “When we have our own space (we are renting it for now), we will be able to expand production. Now our limit is 380 thousand batteries per year. The market demand in Belarus is 700 thousand,” Anton Uminsky, head of the sales department, briefly briefs us on the matter.
The plates are wrapped in envelopes made of special tape; more precisely, this is done by a machine. Wraps - cuts, wraps - cuts... The goal is to eliminate contact between the positive and negative electrodes.
The separator tape made of porous polyethylene is somewhat reminiscent of rubber, but it is quite thin and has pores. The electrolyte must pass through them.
Everything at the enterprise is automated as much as possible. The equipment was set up by specialists working at the company’s European factories. And in case of a breakdown, technical support staff are always on duty. In an emergency, they are ready to immediately begin troubleshooting. Downtime of one of the two conveyor belts, even for an hour, can result in losses of hundreds of euros.
The conveyor forms a package from a set of plates - the machine alternates them: with a negative charge, then with a positive one, etc.
- The resulting pack is the battery - it can contain from 10 to 16 plates. In turn, each battery consists of six batteries. In total, there are from 60 to 96 plates in a battery, notes Alexander Matvienko, quality manager and one of the old-timers of the enterprise.
At this stage, human intervention is required—bad envelopes are rejected. It happens that the edges are unevenly cut and skewed. It's not a matter of aesthetics, of course. Remember above we talked about unwanted contact between negative and positive plates? It’s easier to remove the potential conflict now. The check, of course, will not be limited to this, but the details are below.
If you look more closely, you can see metal “bookmarks” or ears on both sides of the bag. The ears of the plus and minus plates are grouped on opposite sides of the package. Why, it will become clear a little later.
Now the packages are placed in another car.
The machine lubricates them with a special solution of organic acid, which removes the oxide film - so that the lead can be soldered better.
Before this, preparations were made to create an electrical circuit in the battery. And now the conveyor begins the main action - the “bookmarks”-ears are “dipped” into molten lead in a special mold (its temperature is 400 degrees Celsius) and the mold is immediately cooled with water. Therefore, the steam is clearly visible in the photo.
Lead ingots are stored nearby, which, in fact, are melted. They look impressive. Dropping one of these on your foot wouldn’t seem like much.
By the way, all employees of the enterprise wear special shoes (guests are given galoshes). When something heavy falls on your leg, it protects against injury, which can be quite serious. Goggles and a respirator are also required. It is prohibited to be in this workshop without a mask for more than four hours. All employees are tested monthly for lead levels in their bodies.
Now the future battery receives a plastic box divided into cells - a monoblock. They are also imported from abroad (from Poland and France, where several factories of the American corporation are located). An important point: there are holes in the inner walls. This is also not without reason. We'll remember about them a little later.
Another machine uses pliers to insert already soldered packages of plates into the monoblock: first the even ones, then the odd ones. Like cassettes in a tape recorder.
And here’s what the soldered “bookmark” ears look like. In the future, they will connect to the neighboring cell with a special bridge. Pins for “plus” and “minus” have also been added. At this stage, the electrical circuit of the battery is very clearly visible. Like on the pages of physics textbooks.
“The electromotive force of each cell is 2 V,” continues Alexander Matvienko. - When all six batteries are connected, you will get the desired 12 V battery. It will power both the radio and lighting devices, and, naturally, provide starting current to the starter.
It is difficult to measure the temperature of a metal from a photograph. But believe me, she is tall. Therefore, the future battery is sent to a buffer zone, where the bridges are cooled. At this time, a short circuit test is carried out under a voltage of 2 kV. Even potential contact between negative and positive plates is eliminated. At this stage, defective bags can still be removed and replaced. Opening the candy bar at later stages means incurring losses.
— How do you know that the equipment does not fail? — we ask. “There is a signal copy for this case,” Alexander puts the battery on the conveyor. The red light comes on, and the conveyor “spits out” the rejects into a special compartment.
The final stage of creating an electrical circuit. The plate packs are welded (attention!) through the same holes in the inner walls of the monoblock. Again, no human intervention! Hiss. Welding takes a couple of seconds. Ready!
Before welding
After welding. Pay attention to the indentations in the ears
Another short circuit test, at the same time checking the quality of welding of plate packages. This is the last moment when you can look inside the battery.
Occasionally the operator glances at the light board that hangs right in the workshop. On it, for each conveyor, the number of batteries planned for production and the number of manufactured ones are indicated. Yes, even in a practically American enterprise it will not be possible to get away from the plan.
Gradually, the battery takes on a more presentable appearance. The battery receives an internal cover with plus/minus terminals. Until recently, its design was different. Now it has been changed in favor of technology. Batteries in the same housing come off the assembly line at other Exide factories under the brands Centra, Exide, Tudor, etc.
And now the cover... is removed to finally weld it to the monoblock. She is pressed against the molten slab and pressed against a plastic box. Again, the process is as automated as possible.
The entire time we were at the plant, it seemed like someone was missing. The workshop is almost empty, but the work does not stop: there are only about a hundred people at the plant, a minority of whom are involved in production.
Soldering the plus and minus leads (the negative one is a little thinner). A metal pin (born) is connected to a “finger” familiar to motorists, onto which the terminals are attached.
“There are no other metals in the battery except lead alloy,” notes Alexander Matvienko. — Hand soldering is carried out in order to ensure full contact between the boron and the leads.
The battery is checked again. This time for tightness. The machine inserts tubes into the battery filler holes and supplies air under pressure.
— There are external and internal tightness. In the first case, we are talking about ensuring that the electrolyte does not spill and there are no microcracks on the body. In the second case, the reliability of the walls between the cells is checked. This is also important, because if the internal seal is broken, the battery will self-discharge faster,” explains Alexander.
They put an internal stamp - a brand.
In fact, this is needed more by the enterprise than by the buyer. The code encrypts the date, shift and some technical characteristics. For example, "1" means 55 amp-hours, "2" means 60 amp-hours.
We go up to the platform from which the main workshop is clearly visible. At the end of the day, managers hold a planning meeting here. You can feel the Western approach in everything. The speaker walks into a circle outlined on the floor. He is given no more than two minutes. The plant is headed by a Serbian of Australian origin, John Nikolic. He practically knows neither Russian nor Belarusian, so all communication takes place in English.
The “dry” battery is transported to the “wet” workshop. There are a lot of barrels and containers here, and the workers are dressed in special aprons, gloves, and oversleeves. An aggressive environment after all. You constantly have to deal with dilute sulfuric acid. Yes, this is where another important stage occurs - electrolyte is poured into the batteries. This is again done by a machine. The density of the electrolyte being poured is 1.26 g per 1 cubic meter. cm.
After this, the operator inserts plugs and connects the batteries with connector wires - an electrical circuit is obtained, which can contain up to 16 batteries. They settle for no more than an hour. At this time, the electrolyte is absorbed into the plates, and the batteries are cooled, because when filled, their temperature rises sharply.
The batteries are transported to the formation site. When you walk in, you immediately notice the characteristic smell of chemical reaction products; out of habit, we even started coughing. The batteries are still collected in one circuit. But now current is supplied there. For what?
- This is formation. If you fill in the electrolyte and do nothing, the process of sulfation, which is undesirable for batteries, will begin, the interaction of lead and acid, explains our guide. — As a result, crystals and lead sulfates are formed, which in the future will no longer be able to participate in chemical processes, and the battery will lose part of its capacity. By the way, a note to car enthusiasts: it is for this reason that a discharged battery cannot be stored for a long time. To prevent this, the battery is charged with current. Each type has its own programs and algorithms. Depending on the battery capacity, the process can take from 15 to 40 hours.
Already formed batteries are returned back to the “wet” workshop. Electrolyte is added there, the level of which, as a rule, decreases slightly. This is due to the fact that during the charging process the acid is absorbed into the plates, part of which goes to electrolysis. To top it off, the next automatic installation checks the level again.
All procedures with electrolyte are completed. A cover with special plugs is installed on the battery to prevent motorists from inadvertently being splashed with acid. Precautionary measures, of course, are not superfluous. The batteries produced here are maintenance-free. This means that for at least a year and a half, car enthusiasts should not look inside the battery on their own to measure the density and electrolyte level. Although it is possible to remove the cover.
All that remains is to clean up the mess. The battery falls into the washing tunnel. Here, drops of electrolyte are washed off.
Stripping the plus and minus terminals. They become beautiful and shiny - this is how the buyer will see them. But this is not only to give a presentable appearance - it is more difficult to remove current from oxidized terminals.
Another test - perhaps one of the most important and decisive. The battery is tested with a “high” current for performance. Within two seconds, an electric current of up to 1500 A is “taken” from the battery, while the voltage at the terminals is measured. The indicator should be at least 50% of the initial value, that is, from 6.0 to 6.5 V. If it is lower, then this is a defect, and the battery, no matter how offensive it may be, is sent to inspectors for analysis.
The controller must find out what is causing the problem. Then the research results are sent to the quality and technical support service to eliminate defective products in the future. Photos of defective items hang above the table.
The needle marker applies another coding. The first digit is the year of manufacture (“3” means 2013), the letter A is the month (in the Latin alphabet: A - January, B - February, C - March, etc.), F - the symbol of the plant (Pinsk enterprise Americans assigned the letter F), 18 - the day of the month, A1 - the shift designation. By the way, the warranty period starts from this moment.
Finishing touch. The worker puts the terminal cover on and places the stickers on the body. There is one trick here. There are several types of stickers, although there is no difference in batteries; they come off the same assembly line. The products of the Pinsk enterprise are known in Belarus under the Zubr brand, and in Russia the same batteries are sold under the Hagen brand. A well-known marketing ploy: when one product is sold under different names. Stickers are the last step. The batteries are then taken to a warehouse and from there to suppliers.
Source
Let's take a closer look at the battery design
The structure of a car battery is simple: a container for placing electrodes, plates, separators and a cover. The serviceable ones have necks for filling electrolyte and screw-on plugs in the lid. They allow you to add distilled water if necessary.
Battery cases are made of durable polypropylene.
The housing material is non-conductive and chemically resistant to sulfuric acid. There is a flange along the bottom edge of the case for rigid fastening in the car to prevent shocks and falls.
Ventilation (labyrinth) plugs are used in serviceable batteries. They protect against the electrolyte being carried out and splashing out, but ensure the free release of gas. Polyethylene granules can be used as a labyrinth filler.
To prevent incorrect connection of the battery to the vehicle's on-board network, the lead terminals differ in size, which is briefly described in the article about types of batteries.
Almost all types of lead-acid car batteries are irreparable.
How a car battery works
The operating principle of a car battery is based on two types of processes. When consumers are connected to the battery (starter, headlights, car control panel instruments, etc.), it discharges.
In this case, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy, which, in turn, can be converted into thermal, mechanical and light.
If you connect an electric motor to such a power source, then part of the electricity will turn into mechanical, and some into thermal.
When charging, the reverse process occurs - electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.
During charging, substances are formed on the cathode, anode and electrolyte plates that enter into an electrochemical reaction during discharge. Chemical reactions during charging occur in the opposite direction compared to chemical reactions during discharge. This explains why the battery is called a reversible current source; its operation is cyclical: discharge-charge.