What it is?
The internal resistance of the battery varies within different limits, based on the porosity, design and geometry of the grid, the type of electrodes used, the presence of alloying substances, the quality of the coating and the quality of the electrical contact. The resistance between the sponge lead and the array of negative electrodes is at approximately the same level. But at the same time, lead peroxide deposited on the surface of the positive electrode array has approximately ten thousand times greater resistance.
In general, the internal resistance of a battery is the amount of polarization that is applied to the voltage flowing internally. It makes no difference what kind of current we are talking about - discharge or charging. The indicator varies within different limits, depending on the name of the element inside the battery. The electrolyte, separators and electrode grids always have their own significance.
Important! The above elements are influenced by a number of factors, as a result of which the internal resistance of the battery varies, depending on the type of battery. Therefore, it will never be a bad idea to carefully familiarize yourself with the current indicators.
What can cause internal resistance to increase?
Reasons for increased resistance of LiPo and other batteries may include the following:
- Many charge-discharge cycles inevitably lead to an increase in internal resistance.
- Battery age. The higher it is, the greater the resistance. Plus, the battery drains even if you don't use it.
- Storing a battery in a fully discharged and fully charged state causes the internal resistance to rapidly increase.
- Deep discharging or severe overcharging greatly increases the battery resistance, be careful with this.
- Overheat. If the battery overheats, this will lead to chemical changes inside it, which in turn will lead to swelling and increased resistance.
What determines the internal resistance of a battery?
When a lead-acid battery discharges, lead sulfate begins to form on the electrodes. Its appearance negatively affects the conductivity of the plates, as a result of which they are more resistant to current transmission. It is also worth noting that lead sulfate tends to be deposited in the pores where the plates are coated. The diffusion of sulfuric acid from the electrolyte is worse. When a lead-acid battery reaches the end of its discharge, the resistance level immediately increases to two to three times the rated value. When the power source is replenished with energy, the lead sulfate dissolves. Result - the parameters are restored to their original level.
Attention! In car batteries, the indicator depends on the resistance value of the electrolyte used. This increases the dependence on the temperature of the liquid inside the battery and its concentration. When the ambient temperature drops to the minimum permissible level, the electrolyte resistance automatically increases. And when the electrolyte freezes completely, the resistance reaches an infinite value.
The minimum resistance value is achieved if the battery:
- contains inside an electrolyte whose density is 1.225 grams per cubic centimeter;
- operates at a temperature of 15 degrees Celsius.
By increasing or decreasing the density, the resistance level automatically increases. Consequently, the internal resistance of a car battery is steadily increasing.
Important! The resistance level of separators can vary based on porosity and thickness.
Do not forget that the current flowing through the various elements of the battery affects the level of polarization resistance. The latter, in turn, appears for a number of reasons.
- The surface of the electrode and the electrolyte itself are battery elements that tend to change the electrode potential.
- When current passes through the system, the electrolyte changes its concentration. The closer it is to the electrodes, the more intense this process occurs. The result is a change in the electrode potentials. When the circuit is opened and the current disappears, the level of electrode potentials is restored to the primary value.
Lead-acid batteries are characterized by minimal internal resistance when compared with other popular types of batteries. Due to this, they easily deliver huge current for a short period of time (up to 2000 A). It is therefore not surprising that they are used to power car engine starters, given the load placed on the system at the time of start-up.
It would not be superfluous to recall that the internal resistance of the battery varies depending on the frequency. What kind of current is constant or alternating does not matter. In a series of studies initiated by enthusiasts and scientists, it was noticed that a lead-acid battery had a pronounced resistance when a current of 200-300 Hz was applied to it.
How can you estimate the internal resistance of a battery?
As an example, consider a 55 Ah car lead-acid battery with a nominal voltage of 12 volts. A fully charged battery has a voltage of 12.6-12.9 volts. Let's assume that a resistor with a resistance of 1 ohm is connected to the battery. Let the voltage of the open battery be 12.9 volts. Then the current should theoretically be 12.9 V / 1 Ohm = 12.9 amperes. But in reality it will be below 12.5 volts. Why is this happening? This is explained by the fact that in an electrolyte the rate of diffusion of ions is not infinitely large.
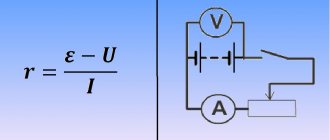
Battery diagram with a connected resistor
In the image, the battery is shown as a 2-pole power source.
It has an electromotive force (EMF), which corresponds to the open circuit voltage, and internal resistance. In the diagram they are designated E and Rin. When the circuit is closed, the emf of the battery partially drops across the resistor, as well as through the internal resistance itself. That is, what happens in the circuit can be described by the following formula. E = (R + Rin) * I.
In the images below you can see the values of the EMF of a car battery in an open circuit and the voltage when connecting a load in the form of two car light bulbs connected in parallel.
battery emf
Voltage under load
As already mentioned, the internal resistance of the battery is a conventional value. A lead-acid battery is a nonlinear device, the internal resistance of which varies depending on temperature, load, state of charge, electrolyte concentration and other above-mentioned parameters. So, to carry out accurate calculations of the battery, discharge curves are used, and not the value of internal resistance.
In this case, the value of internal resistance can be used in calculations of electrical circuits with batteries. Naturally, the value of internal resistance is always taken taking into account the factors on which it depends (charge or discharge, direct or alternating current, current frequency, etc.). So, based on the formula above, you can calculate the internal resistance of a battery with an emf of 12.6 volts when discharged with a constant current of 2 amperes.
r = (E ─ U) / I = (12.9 V – 12.5 V) / 2 A = 0.2 Ohm.
By the way, some chargers allow you to measure the internal resistance of the battery. For example, below you can see the value of the internal resistance of a charged car battery, measured by charging the SkyRC iMax B6 mini. True, it is unknown on what principle the device calculates this value.
Internal resistance of a car battery according to SkyRC iMax B6 mini
Principle and rules of verification
Let's take as a basis a regular lead-acid battery for a passenger car, the capacity of which is 55 ampere/hour and the voltage is 12 V. When it is charged to its full value, the battery is capable of delivering a voltage of up to 13 volts. Now imagine that the owner decided to connect a one-ohm resistor to the power source. When open, the battery is capable of delivering 13 volts. From a theoretical point of view, the current should be at 13 A. But in practice, the figure is lower - usually less than 12.5 V. What is the reason for this behavior? The thing is that the rate of ion diffusion inside the electrolyte is not infinite.
Many motorists often do not know how to measure the internal resistance of a battery. It has long been possible to purchase special devices on the market that allow you to check the current value of internal resistance. The principle of interaction between internal resistance and battery capacity is taken as the basis. When using a load fork and other similar equipment, testing occurs only when the power source is under load. This is reminiscent of checking the battery resistance at a constant current value. Other meters that are used in practice show data based on the current state of the battery. There is also a third type of equipment - a spectrum meter. Here it becomes possible to compare the resistance spectra of a battery that produces alternating current of different frequencies. Depending on the obtained indicator, after the measurement, the owner can draw conclusions regarding the state of the power source at the time of diagnosis.
In general, checking the internal resistance contributes to a qualitative assessment of the current condition of the battery. To prevent owners from making gross mistakes during diagnostics, manufacturers indicate the permissible frequency at which it is allowed to check conductivity. The label indicates in parallel the current value that allows testing. When you determine the EMF and internal resistance of the battery, you will know for sure that the final indicators are affected by the strength and frequency of the voltage. Accordingly, after measuring the conductivity, it will not be possible to obtain quantitative data through which the user would understand how long the battery will last after successive discharge cycles to the load. The main reason for this is the lack of logical relationship between the internal resistance and the capacitance of the power source.
The innovative internal battery resistance meter works by evaluating the waveform obtained by testing the battery response using a special waveform. The result is the ability to quickly assess the residual capacity of the power source. In turn, based on the assessment, the aging and wear of the battery, the duration of discharge taking into account the current state, as well as the remaining resource are determined.
In addition, the owner can measure the current battery resistance with a multimeter. But the device will not be able to give a detailed assessment of the residual life.
Additional Information
It is recommended to measure the internal resistance of a car battery constantly and in a timely manner. High-quality diagnostics simplify replacement planning. Every year the figure increases by about six percent. If it increases by more than eight percent, the workshop specialists begin to analyze the load and operating conditions under which the power supply operates. The accuracy of determining violations and defects depends on the diagnostic method.
The simplest method in terms of implementation is to supply alternating voltage. For this, a transformer, a limiting resistor, a voltmeter and a capacitor are used. The duration of the check varies from one to two hours. During this period of time, the equipment sets the current voltage value. The purpose of the voltmeter is to increase the accuracy of the result obtained.
The AC conductivity test produces a value consisting of an active and a reactive value. To derive the required result, you need to prepare a frequency dependence. The implementation of the presented method is accompanied by a number of difficulties due to electrochemical processes. Therefore, supplying alternating voltage through the wires is suitable if you need to make a general assessment of the current state of the battery.
Automotive workshops and garage cooperatives use the constant load method. The peculiarity is that during the testing process the battery, which is under constant voltage, is rapidly discharged. Using a voltmeter, specialists check the voltage without and with load. The calculation is based on Ohm's law. The method is suitable if the test object is a large-sized battery. The analysis uses high-precision equipment that can check the conductivity of the battery and a number of other indicators. It is possible to use testers with a film-carbon resistor.
It is important to understand that as part of the implementation of this technique, the capacitor does not pay any attention to the measuring device. Therefore, when receiving the results, the active component of the battery is subject to evaluation. To test an old battery for conductivity and other parameters, this method will not work. The reason lies in the difficulty of establishing the true state. On the other hand, no one forbids checking the resistance of the car battery and the EMF at the correct voltage.
Based on the information presented above, the following conclusions can be drawn. Checking internal resistance falls into the category of mandatory diagnostic procedures, which, if performed in a timely manner, will allow the motorist to assess the current condition of the power source. As part of its implementation, various methods can be used, based on the purpose and characteristics of the battery.
You may also be interested
.
Batteries 0