What is a battery called?
A battery in the most general sense of this concept is a technical device that is used to accumulate any type of energy for the purpose of its subsequent uniform release over a fairly long period of time (in contrast to a capacitor, which releases the accumulated charge instantly).
A capacitor directly stores electrical charge, unlike a battery, which, when charging, converts electrical energy into the energy of a chemical reaction, and when operating under load, converts the accumulated chemical energy into electrical energy. The principle of operation of a rechargeable battery is that a chemical reaction constantly occurs between the electrolyte liquid and the metal electrode plates. Single batteries are very weak and cannot provide enough current to operate most devices. Therefore, most often they are combined into batteries, which use a series or parallel connection of individual batteries.
How does the battery work?
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to your car's battery and electrical system. In fact, if the engine is the heart of our car, then the battery is its central nervous system (and maybe even its soul) - it stores and produces electricity, and also controls the current strength of the electrical network. The last thing you want is to be left on a deserted highway with a dead battery. The more you know about the battery and the electrical system in general, the less likely you are to get into this situation.
How does a car battery work?
The car battery provides the entire electrical system of the car with the necessary amount of electricity to power all the electrical components in your car. And we are talking about a rather huge responsibility here. Without a battery, a car, as you probably already understood, will not go anywhere. Let's take a look at how this powerful little box works!
A chemical reaction is the main operating principle of a battery: it simply converts chemical energy into electrical energy needed to power your car, provide voltage to the starter and many other electrical components of the car, and electrical energy back to chemical energy. Another important function of the battery is that it provides a constant current - it also stabilizes the voltage to keep the engine running.
In a simple way, the principle of operation of a battery can be characterized as follows: chemical processes in it lead to the appearance of an electric current that powers the car - such current is especially useful, and most of it is consumed when you spin the engine with the starter, starting it; when the car is started, the engine turns the generator - and here we see the process of converting mechanical energy (torsion of the generator) into electrical energy - in turn, the generator transfers the current it produces to the battery, and it converts the electricity into chemical energy - accumulates it, stores it, so that later again “feed” it that starter or any other electrical systems of the car when the generator does not work or when the electricity produced by the generator is not enough to power all the car’s systems.
A car battery has two poles: one positive and the other negative, and you probably already know this if you have at least once seen or disconnected/attached the battery terminals. These poles are connected to the car and are responsible for powering a number of very important mechanisms in the car, including:
- Engine starting
- Air conditioner
- Audio system playback
- All lighting mechanisms (headlights, taillights, various types of lighting, etc.)
- Windscreen wipers
- Much, much more.
We have selected something even more interesting for you: How often should you change the battery?
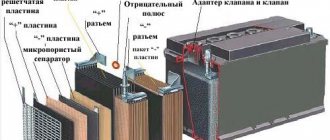
In the vast majority of cases, the battery consists of six cells. Each cell contains two electrodes, which are made from eight overlapping metal plates. These eight overlapping metal plates form what is known as a "voltaic cell". Thus, in total, each cell includes 2 electrodes and 16 plates. It is through these plates that the car is powered by electricity. But how does it work?
In fact, everything is quite simple - let's summarize the above:
- The battery consists of six cells
- Each cell consists of two sets of plates
- Each plate set includes eight overlapping metal plates
And now a little chemistry...
The first set of plates in the cell is positive, and the second is negative. The positive grid is coated with lead oxide and brings electrons into the cell. The negative set is directly coated with lead, and it, on the contrary, releases electrons. The metal plates - remember, eight of them in each grid, 16 in each cell - are in a mixture of water and sulfuric acid (in fact, this concentration is only about 35 percent sulfuric acid, but this is more than enough to burn through clothes, for example and severely burn the skin.This mixture acts as an electrolyte - a substance that conducts electricity well.
When the battery is charged (from a generator or other means), a chemical reaction of lead oxidation occurs on a positive charge, as a result of which the electrolyte is saturated with sulfuric acid and the specific gravity of the electrolyte increases. When the battery, on the contrary, is discharged, feeding any electrical systems of the car (we remember that the main consumer is the starter), then due to the restoration of lead on another - negative set of plates, as a result of which more water is formed, and, consequently, the specific the weight of the electrolyte decreases. At the same time, the chemical process in each of the plates is so insignificant that very little energy is released, but at the exit from the car battery, when all these reactions take place in all 6 cells, we already receive the innermost 12 Volts.
Possible battery problems
The battery becomes unusable over time - this is its natural wear and, in addition, various kinds of harmful processes in it and impacts on it can significantly shorten its life. And the first symptoms that there is a problem with the battery are the inability to start the car (especially in frosty weather).
So, what problems can there be with the battery?
- Low fluid level in the battery: Car batteries usually have a small part of the case in the form of a translucent strip - so that you can always monitor the fluid level of your battery. If the fluid level is below the lead plates (the conductor of electricity) inside the battery, then this is the time to either top it up or replace the battery.
- Battery swelling is when your battery case looks like it has eaten a lot and is swollen. This may indicate an urgent battery replacement. Excessive heat can be blamed as the cause of battery swelling and, as a result, reduced battery life.
- Rotten egg smell from your battery: You may notice a strong rotten egg smell (actually a sulfur smell) around your battery. Reason: battery leak. This leak, in addition to the smell, also causes corrosion around the terminals.
Battery low
The design of such power supplies requires the presence of two terminals: plus and minus. Their operation occurs in this way: when there is no load, the electrical circuit is open, and when connected to the poles of any device, the circuit is closed and the battery begins to discharge. The discharge current flowing through the battery under such conditions occurs due to the movement of ions between the electrodes: anions and cations.
It is most convenient to consider the process of discharging the battery in more detail using a specific example. The cathode (positive electrode in the current source) consists of nickel oxide hydrate, to which graphite powder is added to improve conductivity.
To make the anode (negative electrode) in batteries of this type, iron grids with cadmium sponge are used. The electrolyte in such a device will be a mixture of potassium and lithium hydroxides. Nickel oxide-hydroxide in such an alkaline power source enters into a chemical interaction with cadmium atoms and water molecules. As a result of this reaction, cadmium and lithium hydroxides are formed, and electricity is also released.
Battery charge cycle
To start charging from the battery terminals, you must disconnect the load.
A direct current with a voltage value greater than the output voltage of the device being charged is supplied to the free terminals of the battery. When charging, polarity must be strictly observed, that is, the positive and negative contacts of the battery and charger must match. It is important to consider that the charging device must be selected with greater power than the battery itself in order to overcome the resistance of the energy remaining in it and produce an electric current in the direction opposite to the discharge current. As a result, reversible chemical reactions occurring in the battery will change their direction.
We recommend: How to choose the right battery for a motorcycle
To consider an example, you can also take a nickel-cadmium battery. The reaction involves cadmium and nickel hydroxides formed during the discharge cycle. The products of this reaction will be nickel oxide-hydroxide, water and reduced cadmium.
From all of the above it follows that during the operating cycle only the chemical composition of the electrodes changes. The electrolyte only creates the environment required for reactions to occur. Over time, it may evaporate, which will not have the best effect on the battery life. The considered principle of operation is true for any type of battery; only the chemical composition of the electrodes and electrolyte will change.
Modern innovations in battery design
Attempts to eliminate the main flaws in the design of the car battery have led to the creation of new lead alloys that are more resistant to the aggressive effects of acid. The use of alloying additives of calcium, tin, and nickel made it possible to reduce self-discharge and water loss to the lowest possible level. At the bottom of the device body, traps began to be used to accumulate particles of the active mass of the electrodes, which significantly reduced the risk of short-circuiting the anode and cathode in the bottom part.
The design of the car's battery has changed and it has received maintenance-free status. Now, according to the manufacturer, the device does not require monitoring the water level in the battery banks and the density of the electrolyte, as was the case in older models. The battery device now has devices in the form of a float eye indicator that changes color depending on the state of charge.
Promising solutions
Among the innovations that appeared in the device relatively recently and designed to improve the characteristics of a car’s lead-acid battery are:
- the use of gel-like types of battery electrolyte based on silicon compounds. Zero water loss and good performance allow the use of such devices even in car interiors;
- the use of electronic diagnostic chips that allow subtle and dosed intervention in the operation of each device bank;
- the use of graphite and carbon to form the basis of the positive and negative electrodes, which will make the car battery lighter and more compact.
Advice! Despite the widely advertised lack of need to maintain modern battery models, the basis for longevity will be a modern charging and diagnostic system that allows it to be charged under optimal conditions.
Lamellar-nickel-iron batteries with alkaline electrolyte
The idea of starter batteries based on alkaline electrolyte and electrodes made of pressed nickel and iron powder was developed and implemented. The model of the SZHN -50 series is well known, produced in the Soviet Union in limited quantities for military equipment. The battery device had good characteristics:
- high service life, the number of charge-discharge cycles reached 1000, which exceeded the service life of acid;
- low sensitivity to operating conditions;
- long-term recharging or storage in a discharged state did not have such a detrimental effect on the condition of the device.
The device used a large amount of scarce nickel, making the battery difficult and unprofitable.
Interesting! The practice of operating Soviet alkaline batteries for cars has shown the possibility of using such batteries for 15-20 years with an estimated 10-year period, subject to careful compliance with operating rules.
Modern lithium ion car batteries
The widespread use of lithium batteries in cars is associated with modern electric vehicles, where such a device is widely used due to its high capacity parameters and low weight. Lithium ion auxiliary batteries are available on the market to quickly charge the main battery. There are a number of devices equipped with an ionistor unit that allows you to start engines with a displacement of no more than 500 cm3.
Important! The lithium ion battery is incredibly sensitive to overcharging and requires precise operation of the electronic control unit. If the chip is faulty, it may catch fire. Video of the battery device:
Battery device video:
- How to increase the electrolyte density in a battery
- How to test a car battery with a multimeter
- Average car battery life
- What should the car battery voltage be?
Battery connection types
Separate storage elements make it possible to obtain low voltage and current. For example, most often the voltage value will be in the range of 1-2 volts. For the operation of most devices, such values are clearly insufficient. To increase the resulting voltage or current, you need to connect the batteries into a battery. It is necessary to dwell in more detail on the description of these methods.
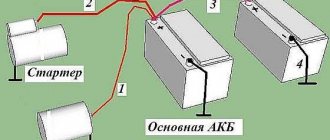
Parallel connection
To connect storage elements into a battery or several batteries, you need to connect their positive terminals to positive ones, and negative terminals to negative ones. The connected terminals of all elements are connected to the load. With this connection method, the voltage in the circuit will be the same as that of each battery separately (if you use batteries with the same voltage). And the capacity will become equal to the sum of the capacities of all elements included in the battery. Accordingly, the current strength that such a device will be able to provide for a certain period before complete discharge will also increase.
Sequential method
When using the serial method of connecting batteries, oppositely polarized contacts should be connected.
The positive terminal of one device is connected to the negative terminal of the other, and the electrical circuit is connected to the free contacts of the first and last batteries. The final output voltage when using this type of connection will be equal to the sum of the output voltages of all involved electric current sources. For example, to obtain a battery with an output voltage of twelve volts, you should connect in series four sources with a voltage of three volts or a dozen batteries with an output voltage of 1.2 volts. The total capacity of the batteries collected using a series connection will be equal to the capacity of each battery separately, that is, it will not change.
Car battery device
You know, the first lead battery appeared back in 1859 (invented by the Frenchman Gaston Plante). And in its fifteen hundred years it has changed little. True, a car battery uses several cells connected in series.
SO : A car battery usually consists of 6 elements connected in series. Each element is considered independent, that is, if it is turned off, it will work autonomously - producing approximately 2.1 - 2.2V. If you imagine one cell in cross-section, it will be a flat and rectangular, sealed “jar” - that’s what it’s called. As you guessed, if you multiply 2.1V by “6”, you get 6 X 2.1 = 12.6V, this is the normal total voltage in the charged state.
Lead plates are placed in each “jar” and a special electrolyte (based on sulfuric acid) is filled. The plates are divided into separate groups - positive and negative. They are not adjacent to each other, although they are located nearby; dielectric elements are laid between them - usually plastic or rubberized sheets. If the negative and positive plates touch, the battery will not work - the bank will close. Lead plates are made:
Negative - usually made of pure but porous lead (Pb)
Plus ones - made from lead dioxide (PbO2)
The sulfuric acid in which they are immersed is a very good conductor - scientifically an electrolyte, it promotes the accumulation of energy.
The idea is simple - if you apply electric current to the battery, it will begin to accumulate it. Then after some time ( be sure to read this article ), he will give it away.
There is also such a thing as battery capacity - it depends on the amount of lead used in production - the more, the more energy can be accumulated. Measured in Ampere/hour (Am/h) - this is the number of Amperes that the battery will deliver per hour. Now the most common options are 55 - 60 Am/h, which are used on most passenger cars.
As you can see, the device is banal and simple, lead + acid, enclosed in a sealed plastic case (plastic because it does not react with acid). If you really want, you can do it at home - if you have lead and acid.
Well, let's move on to working on a car.
Types of current sources
Batteries differ in their purpose, characteristics, how the battery is designed and the materials used in their manufacture. Today, more than three dozen types of different batteries are produced in the world, the main difference between them is the chemical composition of the electrodes, as well as the type of electrolyte used. So, for example, the group of lithium-ion batteries includes twelve different models. The most popular of all those produced are the following types:
- lead-acid;
- lithium;
- nickel-cadmium.
We recommend: Starting and traction battery for electric boat motor
They account for a significant part of the battery market. To get a better idea of what materials modern batteries can be made from, here is a complete list of them:
- iron;
- lead;
- titanium;
- lithium;
- cadmium;
- cobalt;
- nickel;
- zinc;
- vanadium;
- silver;
- aluminum;
- a number of other metals, which, however, are used extremely rarely.
The use of various materials in production has a significant impact on the final performance indicators and, as a consequence, on the area of possible use. For example, lithium-ion batteries are often installed in mobile computers and other gadgets.
While nickel-cadmium batteries are mainly used as an alternative to simple disposable batteries. In theory, any type of battery can be combined with any device. It's just a matter of feasibility and production costs.
Main characteristics
Above we discussed the materials used in the manufacture of rechargeable batteries, the basic principles of their operation and connection methods. Now we can move on to their performance characteristics. The most important performance characteristics are:
- Battery energy density This indicator is equal to the ratio of the total amount of electricity that the battery is capable of delivering to its mass or volume.
- Capacity is the maximum charge delivered by the battery during the discharge cycle, until the minimum voltage value at the terminals is reached. In the metric system, this value is expressed in coulombs (C), but in everyday life the non-system unit ampere-hour (Ah) or, for weak batteries, milliamp-hour is much more often used. Also in some cases, an indicator called energy capacity can be used. It is expressed in joules (SI system) or watt-hours. The capacity shows the power of the device and for how long it can be powered by a specific battery.
- Temperature range - the range of ambient temperatures in which the manufacturer recommends using this battery. If there is a significant deviation from the manufacturer's recommended operating temperature range, the likelihood that the power source will become unusable greatly increases. This can be explained by the influence of low and high temperatures on the rate of chemical reactions, as well as on changes in pressure inside the battery.
- self-discharge is the loss of charge that occurs in a charged battery when there is no load connected to the contacts. The value of this indicator is determined mainly by the design of the battery. It can increase over time due to disruption of the insulation between the electrodes for a number of reasons.
All these battery parameters are of greatest interest to the end user.
Battery parameters
The need to know the basic parameters of the battery is important not only at the stage of its purchase, but also during the maintenance process. One of the key characteristics is the capacity of this equipment, which will provide information about the duration of its uninterrupted operation. For measurement, a unit such as ampere-hours is used, which shows the period during which the product can operate without recharging, using up its capacity. The value of the capacitance itself is influenced by external factors: ambient temperature, current strength and design features.
Another important criterion is called the starting current of the battery. In order to find out, they measure the value that the battery provides at a temperature of 18 Celsius. It is the starting current indicator that is taken into account when they want to determine the serviceability of the equipment. Normal voltage is usually around 12.6 V, but can fluctuate between 13-14 V, depending on the model.
Each bank should produce a voltage of about 2V, and it can be measured using a special load fork. It sets the resistance that falls on each of the cans, also taking into account their capacity.
It is important to remember: overcharging is also undesirable for the battery, as is a weak charge. If you do not turn off the charger in time, this may cause the electrolyte to boil.
The battery charging power can be obtained by multiplying the voltage and the starting current. However, to talk about power, you should also take into account the air temperature outside the car window. Too cold weather has a negative effect on power. More current will be required to start, and therefore more power is needed in winter than in the warm season.
To find out detailed characteristics, it is better to refer to the markings - as a rule, they are applied to the body of the product. On it you can find the manufacturer and year of manufacture, trademark and type of battery, weight, number of cans and other necessary standards. The main material can be ebonite, thermoplastic or plastic that has undergone special processing. The weight of the battery does not refer to the basic characteristics and may even differ from the value stated by the manufacturer. This can happen because the lead plates interact with the electrolyte and gradually deteriorate.
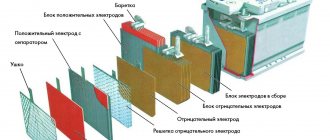
Electrode device
A lead-acid battery can be used as an example. Each cell of such a battery contains a pair of electrodes and separating plates, which are made of porous material that does not react chemically with acid. Such plates are designed to prevent short circuits of electrodes immersed in the electrolyte, and are called separators.
We recommend: Types of batteries and their differences from each other
The electrodes in such batteries are made in the form of flat lead grids. Powdered lead dioxide (in anode plates) and metal lead in powder form (in cathode plates) are pressed into the cells of such gratings. The use of powders is driven by the desire to increase the interface area at the electrolyte-electrode interface, which significantly increases the capacity of such a current source.
There are experimental samples of batteries in which lead grids are replaced with electrodes consisting of woven carbon fiber threads, which are coated with the finest lead coating. This technology allows you to use significantly less lead due to its distribution over a large area, which makes the battery not only smaller and lighter, but also increases its efficiency. The efficiency is higher than traditional ones, and the charging time is greatly reduced.
Main types of car batteries
Antimony batteries
This is an older type of car battery that contains more than 5 percent antimony in its lead plates. Models of modern batteries contain significantly less antimony (Sb) in their plates. The role of antimony in battery plates is to increase their strength. Pure lead is very soft and not in its pure form is suitable for use in batteries. Antimony causes a sharp activation of the electrolysis process, which begins in the battery at a voltage of 12 volts. In this case, hydrogen and oxygen are released. This looks like electrolyte boiling.
In antimony batteries there is a large consumption of water from the electrolyte. As a result of a decrease in the electrolyte level, the electrode plates are exposed. To prevent this from happening, you need to periodically add distilled water to the jars. The resulting antimony appearance of car batteries is often referred to as serviceable. Although modern types of car batteries also have structural elements necessary for maintenance.
Now antimony batteries are no longer used as starter batteries. They were replaced by other, more progressive battery modifications. This type of battery is still preserved in various stationary power sources, where the unpretentiousness of the battery is required. And modern car batteries are produced with significantly less antimony content.
Low antimony batteries
Plates with a reduced antimony content began to be used in order to reduce the rate of evaporation of water from the electrolyte. Low-antimony types of batteries include those that have less than 5 percent antimony in their plates. As a result of their use, it was possible to avoid the problem of frequent topping up with distilled water. But this does not mean that such batteries do not require maintenance at all.
Another advantage of this type of car battery is the lower degree of self-discharge of the battery during storage than that of older antimony models. These batteries are often called maintenance-free, but it would be more correct to call them low-maintenance. After all, the statement that they do not require maintenance is an advertising slogan. Water losses from the electrolyte are still present. Therefore, you still need to check the level and add distilled water. The advantages of low-antimony batteries include their tolerance to the electrical parameters of the vehicle's on-board network. If voltage surges occur in the network, the battery parameters do not suffer much from this. This cannot be said about more modern types of car batteries: calcium, AGM, gel. Experts believe that low-antimony batteries are best suited for use in domestically produced passenger cars. This is due to the fact that not all Russian cars yet provide voltage stability in the on-board network. Moreover, this type of battery has an affordable price.
Calcium batteries
Adding calcium to lead grids instead of antimony was a solution to reduce water evaporation in the battery. Often on batteries of this type you can find Ca/Ca type markings. This designation indicates that calcium is contained in the arrays of positive and negative electrodes. Some manufacturers also add small amounts of silver. This allows you to reduce the internal resistance of the battery, increase efficiency and capacity. But the main feature of calcium batteries was a decrease in the intensity of electrolysis and, accordingly, a drop in the electrolyte level.
Calcium battery models are now being produced in which there is virtually no evaporation of water over the entire service life. As a result, the car owner does not need to check the electrolyte level and its density. And in this case, the name maintenance-free batteries will be true. In addition to low water consumption, calcium-type batteries have a low degree of self-discharge. Compared to antimony batteries, self-discharge is approximately 70 percent less. As a result, Ca/Ca batteries can retain their performance characteristics during storage significantly longer. Essentially, replacing antimony with calcium increased the voltage required to start the electrolysis process from 12 to 16 volts. Therefore, recharging became less critical.
But any device has both advantages and disadvantages. Calcium batteries are much more sensitive to strong discharge than other types of car batteries. It takes 3-4 strong discharges and the battery capacity drops irreversibly. This means that the amount of current stored by the battery is greatly reduced. In this case, the battery will have to be replaced.
It is also worth noting that the calcium type of batteries is sensitive to the stability of the electrical characteristics of the vehicle’s on-board network. They do not like strong voltage fluctuations. Therefore, before installing such a battery, make sure that the generator, voltage regulator and other devices in the car network are in good working order. In addition, the price of calcium-type batteries is slightly higher than low-antimony batteries. Typically, Ca/Ca batteries are installed on foreign cars with a standard set of options. Such cars are equipped with high-quality electrical equipment and the stability of electrical characteristics is guaranteed. When choosing this type of battery, do not forget that during their operation you should not allow the battery to be deeply discharged.
Hybrid batteries
On the body of such batteries you can find the designation Ca+ or Ca/Sb. The electrode grids in such batteries are produced using various technologies. Positive ones are made with the addition of antimony, negative ones using calcium technology. Hybrid car batteries are an attempt to combine the advantages of these types of batteries. As a result, the characteristics turned out to be average.
Water consumption in hybrid batteries is less than in low-antimony batteries, but higher than Ca/Ca. But this type of battery is more resistant to deep discharge and voltage surges in the vehicle’s electrical subsystem. Read more about hybrid car batteries in a separate article.
AGM and gel batteries
Batteries produced using AMG and GEL technology (commonly referred to as gel) have a bound electrolyte. This type of battery was an attempt to solve the problem of safe operation of batteries. After all, in classic batteries, the electrolyte can leak if the case is turned over or the case is damaged. Sulfuric acid is an aggressive substance and poses a danger to the human body. Therefore, the problem was solved by placing the electrolyte in a bound state and reducing its fluidity. In addition to increasing safety in gel batteries, it was possible to reduce the shedding of the active mass of the plates.
The differences between AMG and GEL technologies lie in the method of binding the electrolyte. In an AGM battery, porous glass fiber, which is located between the plates, is impregnated with electrolyte. AGM stands for Absorbent Glass Mat or translated into Russian as “absorbent glass material”. According to GEL technology, the electrolyte is converted into a gel state using additives of silicon compounds. Often batteries made using these technologies are collectively called gel batteries. You can see prices for gel batteries in the review at the link. Since this type of battery does not contain liquid electrolyte, they are not afraid of installation in an inclined position. But, despite the statements of marketers, these batteries should not be used in an upside-down position. The advantages of both types of gel batteries include low self-discharge and high resistance to vibration. The advantages of gel batteries include one more property. They can produce a high starting current regardless of the battery charge and until the battery is almost completely discharged. After a deep discharge, they completely restore their capacity and can withstand a large number of charge-discharge cycles (about 200).
But gel batteries are very sensitive to the battery charging process. This type of battery is charged at lower current values than in the case of classic lead-acid models. They require the use of a charger with special capabilities.
Sellers today offer universal charger models, but you need to be careful when choosing them. Here is an article about charger requirements for gel batteries. We also recommend reading the material on how to charge a gel battery. In addition, gel-type batteries are demanding on the stability of electrical parameters in the vehicle’s on-board network. In the cold, gel batteries, as well as batteries with liquid electrolyte, can act up. At negative temperatures, the conductivity of the gel-like electrolyte decreases. The ideal lifespan of this type of battery is ten years. But in practice, you should count on 6-7 years. In some cases, such batteries can be restored. For information on how to restore a gel battery, read the article at the link. They are used less in cars than other types of batteries. Their distribution is limited by their high cost. Much more often they can be found in UPS (uninterruptible power supplies), motorcycles, and water vehicles. Gel batteries in cars can be found on expensive premium foreign cars and SUVs, where there are a large number of electrical consumers. Read more about gel batteries.
Alkaline batteries
This type of battery uses alkali as the electrolyte rather than acid. There are quite a lot of alkaline batteries, but only two types are intended for use as starter batteries in cars. It is worth noting that alkaline batteries are very rarely found in cars. Much more often they are used in warehouse equipment as traction batteries.
Ni─Cd batteries have positive electrodes coated with NiO(OH) (Ni hydroxide or Ni metahydroxide or Ni III oxide hydrate). Negative electrodes are coated with a mixture of iron and cadmium. The positive electrodes in a nickel-iron battery are similarly coated with Ni hydroxide. But the negative electrode is made of iron. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used as an electrolyte in these types of batteries. The plates here, as in lead-acid batteries, are in “envelopes”. But they are made of perforated metal plates. The active mass is pressed into these envelopes, which significantly increases the battery's resistance to vibration.
It is worth noting that in alkaline batteries the number of positive and negative electrodes differs. In the nickel-cadmium type there is 1 more positive plate than negative plate. The plates themselves are located at the edges and connected to the battery body. In the nickel-iron type there is one more negative plate than positive plates. Alkaline batteries require significantly less electrolyte than acid batteries, since it is not consumed during the reaction.
Advantages of alkaline batteries over lead-acid batteries:
- Easily tolerate overdischarge. This type of battery is stored with virtually no loss of performance;
- Alkaline batteries perform much better at low temperatures;
- Alkaline batteries have a self-discharge lower than acid batteries;
- There are no harmful fumes;
- Accumulate a large capacity per unit of your mass. As a result, when used as traction devices, they can supply current for a longer period of time.
Disadvantages of alkaline batteries:
- Alkaline batteries have a lower voltage than lead-acid batteries. As a result, to achieve the required voltage, it is necessary to combine a larger number of cans, which means the dimensions increase;
- The price of alkaline batteries is significantly higher than acid ones.
Currently, alkaline starter batteries are only available for some trucks. The main area of application for alkaline batteries is traction batteries (for example, for warehouse equipment). As for using them on passenger cars, for now it looks impractical.
Lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are currently very promising in terms of additional sources of electric current. In this case, the current carriers are lithium ions. At the same time, the material of the electrodes very often changes along with the improvement of this technology. At the initial stage of development, lithium metal was used as a negative electrode. Due to its high explosiveness, it was replaced with graphite. Various lithium oxides were used as the positive electrode, which added manganese or cobalt. In modern samples of lithium-ion batteries, they are replaced by lithium-ferro-phosphate alloys, since they cost less, have less toxicity and are easier to recycle.
The main advantages of lithium-ion batteries:
- Large specific electrical capacity (that is, capacity per unit mass of the battery);
- The individual cell voltage is greater than standard lead-acid. 4 volts versus 2 volts for the classic element.
- Low degree of self-discharge.
The Li─ion type also has disadvantages. Moreover, they are quite serious and prevent the widespread use of such batteries in cars.
Disadvantages of lithium-ion batteries:
- Sensitive to negative temperatures. As the temperature decreases, the current supplied by the Li─ion battery decreases;
- The number of charge-discharge cycles is currently small (approximately 500);
- Aging of lithium-ion batteries. That is, during storage their capacity decreases. Over two years, capacity decreases by about 20 percent;
- Sensitivity to deep discharge;
- The power of Li-ion batteries is insufficient to use them as starter batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are mainly used to power various mobile electronics. If developers get rid of the shortcomings of lithium-ion batteries, they can replace acid batteries.
Conductive substance
The electrode and separator plates are immersed in an electrolyte, which is used in lead-acid batteries as sulfuric acid diluted with distilled water.
This water is used to prepare the solution because it does not affect the acidity of the medium. The conductivity of the solution obtained in this way depends only on the concentration of sulfuric acid and at room conditions will be maximum when the density of the electrolyte liquid is 1.23 grams per cubic centimeter. The conductivity of the electrolyte is inversely proportional to the internal resistance of the power source, and, accordingly, increasing the conductivity reduces energy losses and increases efficiency. It is worth noting that in cold climates, sulfuric acid concentrations increased to 1.29−1.31 grams per cubic centimeter are often used. This is done to prevent the electrolyte from freezing. After all, the ice that forms can damage the battery case.
In batteries that are installed in household uninterruptible power supplies, alarm systems and other household appliances, the liquid electrolyte is sometimes thickened to a paste with a sodium silicate solution. But the principle of operation of the battery remains the same.
Areas of battery application
Rechargeable batteries are widely used in all types of technical devices.
Not a single portable electronic device can do without them: from wristwatches to laptops. Even in simple electric flashlights, manufacturers prefer to use built-in batteries instead of replaceable batteries. Cars were no exception. In cars of conventional designs, a car battery is used to start the engine and provide uninterrupted power to on-board electrical and electronics. In increasingly popular hybrid and electric vehicles, batteries play an even more important role. Moreover, in this case, the requirements for the design of the car battery are even higher.
The following parameters are extremely important: starting current, discharge depth and the maximum number of recharge cycles that the battery can withstand. We can safely say that modern lifestyle would be impossible without batteries.