What is a filament lamp
In simple words, a filament lamp is a combination of two types of light bulbs: LED and incandescent. The principle of operation is taken from the first, and the design features from the second.
Inside the glass bulb there is an LED strip connected, which is why the lamp got its name. The word "filament" is translated from English as "thread".
In terms of glow, a filament light source is almost no different from an incandescent lamp (it has a yellowish tint), but in design and functionality it is ahead of its competitor.
Disadvantages of filament lamps
- In addition to many advantages, filament LED lamps are not without disadvantages. So:
- The presence of a special driver increases the price of the device;
- The flask in which the filaments are located is quite fragile and must be handled very carefully.
- LED filament lamps must be coated exclusively with high-quality phosphor, otherwise blue light leakage may occur, which is harmful to the eyes. This means that you can only purchase such goods from trusted and reliable manufacturers. That is why we are so careful about the products we offer. Our website presents only high-quality filament LED lamps, which you can buy at the best prices in Moscow.
Thus, LED filament lamps can easily be considered one of the best achievements of modern LED technology. They are the future, in which all efforts will be aimed at offering consumers more advanced and practical devices.
Design, design features of the Tomich filament lamp
Structurally, the emitter of such a lamp consists of three elements:
- Glass or sapphire base.
- Blue/red LEDs in the amount of 28 pieces.
- Phosphor coating providing white light with a special color temperature.
If we consider the design as a whole, the filament light source consists of the following elements:
- Base for E14 or E27.
- Transparent bulb with high light transmittance.
- Glass leg with elements that provide voltage supply to the LED strip.
- Filament parts.
- Driver (electronics) located in the base casing.
The driver takes up minimal dimensions and easily fits on the board. The latter, in turn, is mounted in the base of the light bulb.
This design allows the use of high-quality circuits with varying levels of complexity to reduce ripple.
Design
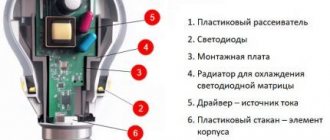
The filament lamp design combines old and proven incandescent lamp assembly technology with new, more modern materials. The standard lamp design consists of:
- LED filament;
- a gas flask made of glass;
- leg made of glass;
- base;
- driver.
The structure of a filament lamp.
The main elements should be examined in more detail.
Base
The base is the main part of the lamp, which serves to hold all the wires and the bulb together. This is the only place where there can be a driver that is responsible for serviceability. The most common types of bases are E27 and E14.
The saturation and brightness of the light determines the atmosphere of the establishment
Glass flask
The bulb is the main element of the lamp, without which it will not be able to work properly and fully illuminate the room. This is a completely transparent bulb and can be of different shapes, depending on the use of the lamp. There are certain types of flasks with a special white or cream coating to make the color richer and brighter.
Variety of filament lamps
The flask contains a special gas and also contains a structure made of LED filament. When LEDs are heated, the gas allows the heat to quickly disperse light along the walls of the bulb to illuminate the entire room.
In addition, the gas controls the heating process of the filament. The heat is distributed over the entire surface of the flask, and since it exceeds 3 times the amount of heat, the temperature does not exceed 60 degrees Celsius, which is absolutely safe for use.
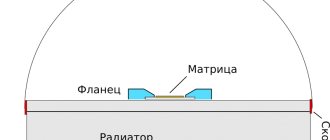
Glass leg and conductors
The glass leg is designed to attach the base of the filament threads to it. It serves as a support to stabilize the lamp during power surges. There are also conductors in the leg. They transfer an electrical charge from the socket to the filaments so that the lamp starts to burn.
Leg - support for filament light bulb
LEDs
The peculiarity of filament thread is that it is produced using the same technology as display modules for phones and tablets. The technology is called Chip-on-Glass. The filament thread consists of several parts: glass substrate, LEDs, phosphor.
The filament thread is a small glass substrate 2-3 cm in length made of sapphire glass, which does not melt or crack at high temperatures. LED crystals (7-10 pieces) are laid out in one line inside the substrate.
You may be interested in this Features of fluorescent lamps
Original light bulb design
Conductors are attached to the ends of the substrate, which supply a charge of current to the LEDs. The top of the substrate is coated with a phosphor, which provides the required color and temperature of light. The threads are connected into one structure, and its bases are attached to the leg.
Driver
The driver is the most important part, responsible for its performance, energy efficiency, etc. The driver is a small electronic chip that is assembled on a printed circuit board. It is responsible for the duration of operation of the diodes when temperature and voltage change. It is this that ensures the absence of flicker and glare of light.
Interesting! Modern models of filament lamps are equipped with advanced drivers that cover large electrical networks and operate with a huge voltage spectrum.
Saving energy is the main goal of filament lamp manufacturers
Before purchasing a lamp, its color can be determined visually, even without turning it on. It all depends on the color of the filament thread. For example, if the thread is bright yellow or orange, the light will be warmer, with a yellowish or creamy tint. If the thread is lemon-colored, the light will be white, daylight. In addition, the angle of illumination can be determined by the shape and length of the thread. The more LEDs and the longer their substrates, the more light crystals they contain, which means the light will be brighter and the spray angle will be greater.
What power does it produce?
The average filament power is about 1 W, and the voltage is 60 V. In general, the light bulb consumes from four to eight W and has the following parameters:
- luminous efficiency: 120 - 140 Lm/W;
- light temperature: up to 4500 K depending on the level of performance;
- service life 30,000 hours;
- ratio of output power with incandescent lamp, filament/LC: 2 – 25 W, 4 – 40 W, 6 – 60 W, 8 – 75 W.
For comparison, incandescent, LED and fluorescent lamps have power in the ranges: 10 - 500 W, 3 - 30 and 15 - 80 watts, respectively.
Conventional light sources show the lowest light temperature - 2700 K with a service life of 1000 hours.
As for fluorescent and LED lamps, they show the best characteristics: light temperature up to 6500 or 6400 K, and service life - 40 and 50 thousand hours, respectively.
Tomich filament light bulb driver
Using the LED principle requires installing a driver located inside the base. The purpose of the device is to reduce the current from the network to a value that is safe for LED elements.
The driver consists of the following elements:
- Fuse.
- Diode bridge rectifier.
- Smoothing capacitors.
- Pulse current regulator microcircuit with additional components. The circuit includes a diode, a choke, and an RF resistance capacitor.
The driver circuit deserves special interest. A fuse F1 is installed in the phase wire, instead of which you can put a resistance of up to 20 Ohms up to 1 W of power.
The elements of the scheme also include:
- diode bridge for rectifying current to a voltage of 400 - 1000 V, DB1;
- capacitor for smoothing ripples at the output DB1, E2;
- additional capacitance for supplying voltage to the circuit, E1;
- device driver, thanks to which the entire circuit works, SM7315P;
- capacity for filtering ripples at the output, E3;
- current sensor for adjusting the current in the light source circuit, R1 (the higher the resistance, the lower the current);
- resistance to reduce the current on the converter, R2;
- diode ensuring the operation of the converter, D1;
- storage inductance for voltage conversion, L
In fact, elements D1, L1 and a transistor switch form a typical pulse converter circuit.
How the scheme works
The principle of operation of the circuit is simple. The voltage supplied to the input is rectified using a diode bridge. Further, thanks to the action of the capacitance and capacitor, the current is smoothed.
On approaching the microcircuit, the current is converted into RF pulses, smoothed using a capacitor. Subsequently, power is supplied to the filament LED and returned to the network.
As for the driver, it includes a PWM controller and additional devices (comparators, multiplexers, etc.). They compare the real and nominal currents, and then send a signal to the PWM controller to make changes to the pulse duty cycle.
Cooling
There is a false misconception that LEDs do not get hot. On the contrary, they get very hot, and some microcircuits do not work for even several minutes without cooling.
For small LEDs housed in SMD-type housings, heat is transferred to the contact pads installed through them.
We already know that one filament consumes an average of 1 W. For comparison, SMD diodes for 1 W of power are designed to provide about 25-30 kW. see cooling device. And here the question arises about cooling the lamps.
Please note the following:
- The filament is a matrix.
- Structurally, diodes are soldered behind the matrix part, which emit a small amount of heat due to low power. For example, if you divide 1 Watt by 28 light bulbs, you get an average of 0.036 Watts per LED.
Helium or a special gas is used to remove heat, providing minimal heating to 55-60 degrees Celsius. This allows them to be used in luminaires with fabric, paper and plastic lamps. In this case, the filament lamp thread heats up to 100 degrees Celsius.
Advantages and disadvantages of filament lamps
Before switching to filament light sources, it is necessary to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages:
- Economical.
- Uniform glow in all directions, an excellent solution for lighting a summer house.
- Stylish appearance, which allows them to be used in open lamps.
- Wear resistance.
- Long service life.
- Versatility of use and the possibility of installation in many models of lighting devices.
- Excellent color rendition.
- Minimal heating due to gas pumped inside.
- High degree of brightness.
- Easy to dispose of as household waste.
Disadvantages of filament products:
- High price.
- A fragile flask that requires careful handling.
- When the voltage is unstable, flickering appears and the quality of light deteriorates.
- Impossibility of repair.
- Designed only for 220-volt networks.
- The presence of two types of socles - on E14 and E27.
- Variation in quality.
- Complaints about short service life.
- The presence of a dead zone under the light source when the bulb is positioned vertically (details below).
Filament lamp design
The main advantage of new energy-saving LED lamps is a simplified light distribution system that does not have large energy losses. Therefore, filament, in comparison with other lamps of this class, is a very effective means of lighting, including as a ceiling lamp. And all because heat removal in a filament LED lamp is carried out due to a special gas with which the glass bulb is filled. This gas (what substances are included in its composition is still unknown) has a high degree of thermal conductivity. Therefore, due to this gas and the thin walls of the glass flask, the heating temperature of the lamp is no more than 60 0C.
Filament lamp design
Filament LED lamps use DC voltage, thanks to a special driver mounted in the base in the form of a plastic ring. It is due to this driver that voltage conversion occurs, which allows saving a large amount of electrical energy. The sockets are made in both E14 and E27 standards, that is, they use any type of lighting fixture sockets: chandeliers, ceiling lamps, sconces, and so on. In addition, the filament turns on instantly, which cannot be noted with incandescent lamps, which require time to heat up the filament.
Distribution of filaments, what the market offers, selection criteria
With the advent of filament light sources, more and more people began to switch to new products. The reason was the original design and a larger luminescence angle without the use of additional optical systems. In standard LEDs, located in a plastic case, the angle is 170 degrees, but here it is 300.
As for manufacturers, products from Maxus, Videx, Philips, Osram, Lisma and Tomich lamp are popular.
Criterias of choice
When purchasing filament light bulbs, it is important to pay attention not only to the power and type of base, but also to other criteria.
Below we consider the main parameters:
- Product type: decorative lamp, lighting, special, etc.
- Base type - E27, E14 or E40.
- Voltage: 170 - 240 V.
- Power: from 2 - 12 W.
- Analogue of an incandescent lamp: 16 - 560 W.
- Brightness: from 9 - 1521 Lumens.
- Minimum lighting area.
- Light color - white (warm, neutral, cool), red, yellow, blue, amber.
- Color temperature: 1800 - 6500 K.
- Shape - ball, sphere, pear, candle, circle, spiral, oval, pencil, decorative figurine and others.
- Flask finish: matte, transparent, golden, amber, tinted, white, silver.
- Material: blown glass/metal, plastic, glass, frosted glass.
- Height: 7 - 435 mm.
- Diameter: 4 - 225 mm.
- Device control - switch, wall switch, rotary-push dimmer.
- The glow angle is 300, 320 or 360 degrees.
- Color rendering index: 77 - 90.
- Brand - Uniel, Elgo, Lexman, Osram, Gauss, Elektrostandart and others.
Additionally, take into account other parameters - useful luminous flux, availability of compatible applications, service life, maximum number of starts, energy consumption class. Pay attention to the country of origin and type of packaging.
Popular models
The market offers a large selection of filament lamps that are in demand and have received positive user reviews.
Below we highlight several popular options.
Gauss LED Filament E14 candle
Chinese product with an E14 base and a power of 11 W. The product shines like an 80 W incandescent light bulb. The lighting color is neutral white, and the maximum area is 7 square meters. m.
The convergence angle is 360 degrees, and the useful luminous flux is 750 lm. The model is designed for 50,000 starts and stops, and the average service life is 35,000 hours.
LED filament lamp Lexman
Device made in China. The model is equipped with an E14 base and has a power of 4.5 W. The declared parameters allow you to shine as well as a 40-watt incandescent lamp.
The illumination light is warm white (closer to yellow), the illumination area is about two square meters, and the illumination angle is 360 degrees.
The useful luminous flux is at the level of 470 Lm. The light bulb has a resource of 25,000 on and off, as well as a service life of 25,000 hours.
Advantages and disadvantages
Filament LED lamps are known to a small circle of consumers because they are produced in limited quantities. Their development is still ongoing in order to eliminate all shortcomings and present to the whole world the global release of new generation lamps. At the moment, those who use filament lamps highlight several pros and cons.
Advantages:
- Large lighting angle. Compared to conventional and LED models, the illumination angle of a filament lamp is 3 times greater, almost 360 degrees. A similar effect was achieved by combining completely transparent and durable glass and LED construction into one structure. Thus, one lamp can illuminate a room of 20-35 sq.m.
- Completely transparent flask. Due to this, the level of energy efficiency of the lamp increases.
Advantages of using a filament device
Please note! Incandescent and LED versions use translucent bulbs. They absorb some of the light, causing the light to become dimmer.
You may be interested in: Reasons for blinking light bulbs and their elimination
- During long-term operation, the temperature in the bulb increases to a maximum level, which prevents the light diodes from being distributed normally over the entire surface of the bulb. The result is poor lighting or “flashing.” In filament lamps this point is provided. Thanks to the special design of the LEDs, the temperature spreads evenly along the filament, heating each light crystal to the optimal temperature. This allows the light to spread better across the overall surface of the bulb and make the light brighter. In addition, the gas contained in the bulb and diodes regulates the temperature in the lamp, preventing overheating.
- Performance and performance. A regular lamp lasts no more than 1000 hours, while filament models last 30,000 hours.
- Practicality. On the market you can see a huge number of filament lamps of different colors, shapes, and types. They can be installed in lamps, mounted in suspended ceilings, floors, and so on.
- Comfort. These lamps do not flicker, the color is pleasant to the eye, and can be used as a constant light source. They are not afraid of temperature changes or power surges.
Properties of a glass bulb filament light bulb
Disadvantages:
- Small power models are available on the market. The lamps began to be produced in 2008, so their perfection is still in progress.
- Not compatible with low voltage networks.
- They cost more than regular lamps.
- The flask is made only of glass. This reduces the practicality of the model. At the moment, lamps from other materials are being designed.
- The filament cannot be repaired. If one diode from the structure fails, it can no longer be repaired like a regular lamp.
What is a meter zone
When a filament lamp glows, if the bulb is positioned strictly vertically, a so-called zone of less illumination is formed under it, which can be called “dead”. The lighting level in it is two times less than in the main lighting zone.
At a distance of one and a half meters, the spot reaches a size of 50 cm. Accordingly, it increases as it moves away from the light source.
The shape of this spot, depending on the model of the llama, the number and location of the spirals, is different.
Check pulsation when purchasing
When purchasing a filament lamp, it is important to check the ripple. Ignoring this requirement may lead to disappointment when using the device as the main lighting in a bedroom, living room or other room.
According to the laws of the Russian Federation (PP No. 1356 of October 10, 2017 “On approval of requirements for lighting devices”), the sale of light sources with a pulsation of more than 10% and a CRI of less than 80 is prohibited.
The driver is responsible for pulsation and in high-quality products this figure does not exceed 1%.
And you need to remember that inside even light bulbs of the same shape there can be two different drivers. One with normal pulsation and high-quality parts, and the second one made using cheap elements.
Scope of use
Modern models are very relevant, as they are suitable for any area.
- The light distribution angle is 360 degrees, which increases the brightness and illumination of the room. Such characteristics are necessary for the operation of plants and factories.
- Due to its small size, as well as the variety of shapes and colors of the lamp, it can be used as a decorative element in construction and interior design.
Where are filament lamps used?
- Due to its resistance to temperature changes and power surges, it is suitable for lighting market and shopping areas, large centers, cafes, and restaurants.
- Due to the operating time (30,000 hours), it can be used for home use. It is economical and reliable.
You might be interested in: Features of connecting IZU for DNAT
A significant advantage here is versatility - practicality of application.
Determining the temperature of the glow
Few people know that the glow temperature can be easily determined by the shade of the phosphor even without screwing the lamp into the socket.
Here it stands out:
- Lemon shade - 4500 K (neutral white).
- Yellow - 3000 K (warm white).
- Orange - 2500 K (with an even warmer tint).
One glance is enough to determine the oriented temperature.
Results
Filament lamps are an alternative to LED products that offer better performance and a stylish look. Such models are characterized by versatility, high light output, a huge selection and the absence of a dead zone around the perimeter.
Thanks to their long service life, the devices quickly pay for themselves and provide high-quality lighting.
We must not forget about the shortcomings that prevent such products from “exploiting”.
Today this is the fragility of the flask, high price and pulsations with low quality of the product and electricity.
Advantages and disadvantages
Filament lamps are a product of innovative technology, but they have their advantages and disadvantages. Benefits include:
- full compatibility with lighting devices designed for incandescent lamps;
- energy saving;
- familiar design;
- large angle of light propagation, compared to LED lamps that have a large radiator and unidirectional diodes;
- long service life;
- high level of light output due to the transparency of the design and small radiator;
- light weight – 20-40 g.
The disadvantages include:
- fragility of the body, since the flask is made of glass;
- there are no models designed for low-voltage networks;
- high price.