Concrete is one of the most widely used materials in construction. Along with such properties as strength and durability, frost resistance is an important characteristic of concrete.
This quality is especially important in Russia, where many regions are characterized by harsh climatic conditions: changes in temperature and humidity, very low temperatures, due to which concrete can be saturated with water, salt solutions, and then subjected to repeated freezing and thawing.
Let's consider what frost resistance is, what methods are used to determine it, and whether it can be increased.
Why is frost resistance of concrete important?
Concrete, being a durable material, still has a porous structure; it always has pores and capillaries that can absorb moisture.
In autumn, as well as in winter, during thaws, concrete structures are saturated with water with minerals dissolved in it (upon contact with wet soil and precipitation, which may contain aggressive substances from man-made emissions). Then frosts occur, and all the moisture remaining in the pores of the concrete freezes, increasing in volume.
As a result, microcracks appear, and with each freeze-thaw cycle, these cracks become larger until the concrete begins to crumble.
What does it mean?
The expression “Concrete in salts” means testing a concrete solution for frost resistance. This is a method of testing concrete for frost resistance in a 5% aqueous solution of sodium chloride (NaCl). After testing, the concrete is assigned class F2 with a numerical designation, where the number indicates the number of freezing and thawing cycles. For example, F2 means that this concrete is able to withstand 100 freezing cycles in a state saturated with a salt solution without external signs of destruction (cracks, chips, peeling of the edges of the samples) and without a significant decrease in strength.
Typically, concrete that has been tested in salts and has shown a high frost resistance of at least 300 cycles also shows good water resistance. Such material does not require additional lining and painting to protect the structure from the external aggressive environment, which minimizes ongoing maintenance work.
What methods are used to test frost resistance?
The samples that are tested are concrete cubes with a side size of 10 or 15 cm. They are selected from each batch of concrete into standard forms in accordance with GOST 22685. Each series of samples is made from one batch of concrete.
GOST determines how concrete is selected and how samples are stored.
Important!
Determination of frost resistance begins only after the samples have reached their design strength.
The samples are kept for 24 hours in water or salt solution, immersed at 1/3 of the height. After 24 hours, the liquid level doubles, and the sample is again kept for 24 hours. For the next 48 hours, the cubes are left completely immersed in the solution or water.
Tests are ongoing continuously.
Test methods are divided into two groups:
- basic,
- accelerated.
First
The first method is used for any type of concrete, except for concrete for airfield and road surfaces, as well as concrete that will be used under conditions of exposure to mineral-rich water (these types of concrete are tested by the second basic method).
The first method involves freezing moisture-saturated samples in air and then thawing them in water (water temperature 20+/–2°C).
When using the second basic method, samples saturated with a solution of sodium chloride are frozen in air and thawed in a solution of NaCl (table salt).
After carrying out the planned number of tests, the change in the mass of the samples and their strength is measured and, using calculations using special formulas, the grade of concrete is determined by frost resistance.
Second
The second method is used for all types of concrete, except for those intended for airfields and road surfaces and lightweight concrete, which will be used under conditions of exposure to mineralized water.
Third
Used for all types of concrete, except lightweight concrete.
Accelerated methods use samples saturated with NaCl solution. They are frozen in air and thawed in a 5% salt solution.
The test results are then processed in the same way as when using basic methods.
The basic methods include the first and second, and the accelerated methods include the second and third.
Laboratory and alternative methods for determining the frost resistance of concrete
For laboratory research, basic (subject to repeated freezing and thawing) and control (new, absolute strength) samples of the concrete monolith are taken.
Control concrete samples before strength testing, and main samples before freezing are saturated with water/salt solution at a temperature of (18±2) °C.
To saturate, the samples are immersed in liquid to 1/3 of their height for 24 hours, then the liquid level is raised to 2/3 of the sample height and kept in this state for another 24 hours, after which the samples are completely immersed in liquid for 48 hours so that the level liquid was at least 20 mm above the top edge of the samples.
Samples are placed in the freezer. After this, the samples are thawed and their condition is assessed.
There are ways to determine the frost resistance of concrete using improvised means. To evaluate the indicator, the following are examined:
- Appearance of the material. A large granular structure, the presence of cracks, spotting, flaking and flaking areas - all this indicates low frost resistance of concrete.
- Water absorption level. When the indicator is in the range of 5 - 6%, we can talk about poor resistance to low temperatures.
Another express method for determining frost resistance is implemented according to the following scheme. Samples of the monolith under study are immersed in sodium sulfate and kept in it for 24 hours. After this time, they are dried for four hours at 100 ºС. The cycle of soaking and drying is repeated five times in the same way. At the end of the experiment, the material is examined for the presence of cracks, chips and other surface defects.
What types of frost-resistant concrete are there, and where are they used?
For effective construction, it is important to know exactly what the frost resistance of concrete is. That is why concrete is assigned a frost resistance grade. It is designated by the letter F and a numerical indicator in the range from 25 to 1000:
- Concrete with frost resistance up to F50 is used mainly for interior and preparatory work.
- F50–F150 shows average frost resistance values. Such concretes are suitable for the construction of facilities that will be operated in temperate climates.
- Concretes F150–F300 are intended for construction in cold regions.
- Grades above F300 are used for construction in extremely cold conditions, as well as for special-purpose facilities.
Conclusion
Frost resistance is one of the most important properties of concrete as a basic building material, characterizing its ability to long-term withstand temperature fluctuations from season to season. In temperate, and even more so arctic climates, when the annual temperature range reaches 80 degrees or more, the use of frost-resistant concrete has no alternative. However, there is no universal brand of concrete suitable for all cases. Frost-resistant concrete is purchased individually for each object, taking into account its purpose and local conditions.
What determines the frost resistance of concrete?
Obviously, the weak resistance of concrete to low temperatures is associated with its ability to become saturated with water, which will subsequently freeze. And the saturation with water is higher, the more pores and capillaries in the concrete.
Pores and capillaries also influence the water permeability and strength of concrete.
There is a direct relationship: the denser the concrete, the smaller and smaller the diameter of the pores and capillaries in it, the more durable, waterproof and frost-resistant it is. This means that dense and durable concrete will be the most frost-resistant.
How to increase the frost resistance of concrete
To obtain dense and durable concrete, the following conditions must be met:
- Use high-quality, high-grade cement. If concrete work is planned at low temperatures, or if increased requirements for frost resistance, strength, and water resistance are placed on concrete, a higher grade of cement is used.
- To increase the water resistance of concrete, use aluminous cements.
- Choose the correct water-cement ratio.
- Ensure that the concrete mixture is placed and compacted correctly so that there are no voids in the finished concrete.
- Provide concrete care and optimal hardening conditions so that the concrete gains high quality strength (air temperature +18–22°C, air humidity close to 100%).
- Use various additives for concrete.
What additives are used for concrete
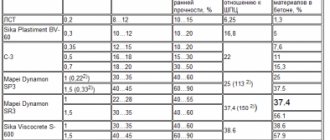
To obtain impeccable concrete, special chemical additives are developed to give the material certain desired properties. To increase the frost resistance of concrete, it is necessary to increase its density and water resistance. For this purpose, plasticizers and water repellents are used.
We advise you to study: Plasticizers for concrete
Plasticizers, such as Plastix from Cemmix, act as follows:
- They allow you to save up to 10–20% of cement without loss of strength or, without increasing the amount of cement, to obtain more durable concrete.
- They increase the mobility of the concrete mixture by 1–2 steps without increasing the amount of mixing water. The fact is that the amount of water required for hydration reactions to occur is much less than the amount of water required to mix a plastic and easy-to-lay concrete mixture. However, if you increase the water-cement ratio, there will be excess water in the mixture. It will not react with cement particles and will evaporate over time, but will leave extra pores in the concrete, which will negatively affect both its strength, water resistance and frost resistance. Adding a plasticizer completely solves this problem, because with it the concrete becomes more mobile and easier to work with without loss of strength.
- Concrete mixture with plasticizer, due to increased mobility, fits better. On the one hand, this allows you to save labor and energy costs for processing the laid concrete; on the other hand, the concrete is laid more densely, excess air is displaced, thereby reducing the number and diameter of pores and capillaries in the finished product.
- The concrete mixture with a plasticizer remains ready for work longer and does not delaminate, which increases the convenience of work.
In turn, additives intended for volumetric hydrophobization of concrete (hydrophobizers) increase the strength and frost resistance of concrete, protect reinforcement, and in some cases increase the mobility of concrete, making it possible to do without a plasticizer.
Important!
Plasticizers and water repellents are sometimes used together.
We advise you to study: Water repellents for concrete