Voltage and frequency of current, dangerous or not?
Voltage and frequency are much safer than current.
For example, a car ignition coil at the output generates an electrical impulse with a voltage of 20-24 thousand V, but due to the very low current strength, such an impulse is not dangerous to humans, the maximum that it causes is an unpleasant sensation.
But if the current in the coil was much greater, this impulse would be fatal to a person. That’s why it is said that “current kills.”
The effect of current on the human body depends on many parameters, and first of all, its strength and type (constant, variable).
The impact also depends on the time of human contact with the source of electricity.
A person’s susceptibility to the effects, his physical and emotional state also influences.
If one person may practically not feel the effect of a current of a certain strength, then the second may already feel this value, and strongly.
The path of electrical discharge through the body is also important.
The most dangerous route is through the central nervous system, respiratory organs and heart.
Light and mechanical effects of current (8 grades, on the day of physics)
Light and mechanical effects of current (8 grades, on the day of physics)
Light effect of electric current
In its simplest form, the luminous effect of electric current can be observed in an incandescent lamp, the spiral of which is heated by the current passing through it to white heat and emits light.
For an incandescent lamp, light energy accounts for about 5% of the supplied electricity, the remaining 95% of which is converted into heat.
Fluorescent lamps more efficiently convert current energy into light - up to 20% of the electricity is converted into visible light thanks to a phosphor that receives ultraviolet radiation from an electrical discharge in mercury vapor or in an inert gas such as neon.
The luminous effect of electric current is realized more efficiently in LEDs. When electric current is passed through a pn junction in the forward direction, charge carriers - electrons and holes - recombine with the emission of photons (due to the transition of electrons from one energy level to another).
The best light emitters are direct-gap semiconductors (that is, those that allow direct optical band-band transitions), such as GaAs, InP, ZnSe or CdTe. By varying the composition of semiconductors, it is possible to create LEDs for various wavelengths from ultraviolet (GaN) to mid-infrared (PbS). The efficiency of an LED as a light source reaches an average of 50%.
Mechanical action of electric current
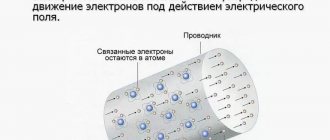
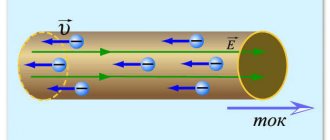
As noted above, each conductor through which electric current flows forms a magnetic field around itself. Magnetic actions are converted into motion, for example, in electric motors, magnetic lifting devices, magnetic valves, relays, etc.
The mechanical action of one current on another is described by Ampere's law. This law was first established by André Marie Ampère in 1820 for direct current. From Ampere's law it follows that parallel conductors with electric currents flowing in one direction attract, and in opposite directions they repel.
Ampere's law is also the law that determines the force with which a magnetic field acts on a small segment of a conductor carrying current. The force with which the magnetic field acts on an element of a current-carrying conductor located in a magnetic field is directly proportional to the current in the conductor and the vector product of the element of the length of the conductor and the magnetic induction.
The operation of electric motors is based on this principle, where the rotor plays the role of a frame with current, oriented in the external magnetic field of the stator with a torque M.
The effect of current of different magnitudes on the body
The minimum current value that can be felt by a person is 1 mA. But again this value depends on susceptibility.
When this parameter increases, unpleasant pain sensations appear and the muscles begin to contract involuntarily.
Up to 12-15 mA, the current strength is called tear-off. A person is able to independently break contact with the source, although as the parameter approaches the specified values, it becomes increasingly difficult to break contact.
Over 15 mA, the current is considered unbreakable; a person is not able to break the contact himself; outside help is required.
When the parameter increases to 25 mA, the muscles at the point of contact are completely paralyzed, and this is accompanied by very severe pain, and the person’s breathing becomes more difficult.
A current of up to 50 mA, in addition to very severe pain and muscle paralysis, is accompanied by respiratory paralysis and decreased heart activity, the person loses consciousness.
A current value of up to 80 mA leads to respiratory paralysis within a few seconds of exposure; with longer contact, cardiac fibrillation is possible.
100 mA very quickly leads to fibrillation and then to cardiac paralysis.
A current of 5A instantly leads to respiratory paralysis, the heart stops while a person is in contact with the source, and burns form at the site of contact.
How to provide first aid
The electrolytic effect of current can manifest itself in any form, but everyone should be able to provide first aid in such cases. Help can save a person's life.
You might be interested in: Features of using rosin
Dressing for minor injuries
Algorithm of preliminary actions:
- Call an ambulance.
- If possible, de-energize the electrical installation - you need to stop the effect of electric current on a person as quickly as possible.
- The installation can be de-energized by cutting the cable.
- Pull the victim away from the place where the electrical installation is still working.
- It is recommended to place a dry board or plywood base under the fallen victim (external conditions must be taken into account).
- Check if there is a pulse. Take measurements on the wrist and neck.
- Look at the condition of the pupils: too large pupils will definitely indicate a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain.
Precautionary measures
How to help a person in such a way as to save a life and not aggravate the situation:
- Provide peace. It is advisable to choose a body position that is comfortable for the person. In this case, it is worth taking into account the specific location of the injuries.
- It is imperative to check the airway patency. Mucus or blood may accumulate in the mouth. It is necessary to remove the foreign liquid.
- It is necessary to monitor respiratory function and pulse at regular intervals. If necessary (there are no signs of vital activity, breathing has stopped), artificial respiration and chest compressions should be performed.
- If there is mechanical damage to the body and its covering, it is necessary to stop the bleeding and apply a bandage or splint.
Providing first aid
Continue to apply until the ambulance arrives.
Types of impact
There are several types of effects that electric current can have on the human body.
Thermal.
The first type is thermal effects. With such exposure, burns appear on the skin, it can affect tissues, blood vessels overheat, and the functioning of organs is disrupted along the path of the current.
Chemical.
The second is chemical exposure. It is accompanied by the occurrence of electrolysis of fluids inside a person; blood and lymph are broken down, which leads to a change in their physicochemical composition.
Mechanical.
The third impact is mechanical. When it occurs, human tissue ruptures, and cracks may appear in the bones.
Biological.
The last type of impact is biological. Exposure to current leads to cramps of muscles and organs, disruption of organ activity, up to the complete cessation of their functioning.
Biological and mechanical effects
The degree of damage can vary and leaves its mark on living tissue. Current can leave thermal, electrolytic, mechanical and biological “imprints”. Usually it is the last 2 categories that are distinguished.
You may be interested in this Designation wat
The mechanical, or as it is also called dynamic, effect of electric current is determined by the delamination and rupture of various tissues. This affects mainly muscle and lung tissue, and the walls of blood vessels in the circulatory system. This happens under the influence of an electrodynamic effect, as well as the instantaneous explosive formation of steam from superheated tissue fluid and blood.
Mechanical manifestation of electric shock
The biological effect of electric current on the human body can be understood by the activation of living tissues and a change in their functionality. Additionally, there is a disruption of internal bioelectric processes, which up to this point were proceeding normally. This work directly affects viable functions. The biological effects of current in this interpretation are considered to be of a very dangerous type.
Additional Information ! Determining the type of exposure can help guide the treatment process.
Thermal - gives itself away as burns in certain areas of the body. Blood vessels, nerve endings, heart, brain and other organs are heated to very high temperatures. Such overheating causes serious disorders of tissue functions. Organic fluid decomposes, namely lymph, blood, and cellular fluid.
Thermal damage
This is accompanied by significant disturbances in body fluids and its physical properties. Many changes occur in the chemical composition.
Types of Electrical Injuries
Electrical injuries that electric current can cause to the body are divided into external and internal.
There are several external electrical injuries. The most common herbal is burn. Most electrical injuries result in burns.
However, there are also other types of electrical injuries.:
- The signs are oval in shape and appear on the skin as pale yellow or gray spots. Since the skin at the point of contact dies upon exposure, the marks are not painful, the area of skin hardens somewhat and fades over time;
- Metallization is the transfer of wire metal particles to the skin as a result of an electric arc appearing between the wire and human skin. The area of skin where metallization occurred is painful, the affected area takes on a metallic tint;
- Ophthalmia is the effect of ultraviolet rays of an electric arc on the membrane of the eye, causing it to become inflamed. Accompanied by the appearance over time of severe pain in the eyes and lacrimation. After a while, the unpleasant sensations pass;
- Mechanical damage - when exposed, muscle cramps that appear can lead to rupture of tissues, blood vessels, and skin.
Internal damage when struck occurs due to electrical shock.
When current passes through internal organs, their tissues are excited, which is accompanied by dysfunction.
Electric shock is the most dangerous type of injury.
The degree of influence of current on the body
The effect of electric current on the human body has a certain classification, which is divided into 4 degrees.
The first degree is the impact on a person of a source of electricity with a low current strength, during which involuntary muscle contraction occurs, but the person is conscious.
Second degree - the source of electricity has an average current strength, is accompanied by muscle contraction, the person loses consciousness, but breathing and pulse are present.
The third degree is a person’s contact with an energy source with a high current intensity, due to which paralysis of the respiratory system occurs and it is absent, as well as the functioning of the heart is impaired.
The fourth degree is the impact on a person of electricity with a very high current strength, at which breathing and heart function are absent, clinical death occurs.
Actions of electric current
Details The effects of electric current are those phenomena that electric current causes.
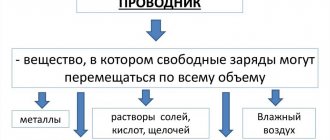
Based on these phenomena, one can judge whether there is an electric current in the circuit or not. Thermal effect of current.
- electric current causes metal conductors to heat up until they glow.
Chemical effect of current.
— when an electric current passes through an electrolyte, substances contained in the solution may be released on the electrodes. - observed in liquid conductors.
Magnetic effect of current.
- a conductor carrying current acquires magnetic properties. - observed in the presence of electric current in any conductors (solid, liquid, gaseous).
CAN YOU UNDERSTAND
The discovery of the physicist Arago in 1820 was as follows: when a thin copper wire connected to a current source was immersed in iron filings, they stuck to it. Explain this phenomenon. There are copper screws and iron screws mixed in the box. How can you quickly sort them out if you have a battery, a long enough copper insulated wire and an iron rod?
BOOKSHELF
Stars of the Dioscuri. A miracle of nature - ball lightning.
EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ON THE HUMAN BODY.
The physiological effect of current at the early stage of development of the science of electricity was the only one that was known to scientists, and was based on the experimenters’ own sensations.
One of the first who felt the effect of current was the Dutch physicist P. Muschenbroek, who lived in the 18th century. Having received an electric shock, he stated that “he would not agree to undergo such a test again even for the royal throne of France.”
negative action:
Electric current causes changes in the nervous system, resulting in irritation or paralysis. When exposed to electric current, convulsive muscle spasms occur. It is customary to say that a person’s electric current “holds”: the victim is unable to let go of the object - the source of electricity ___
When struck by a sufficiently strong electric current, a convulsive spasm of the diaphragm—the main respiratory muscle in the body—and the heart occurs. This causes immediate cessation of breathing and cardiac activity. The effect of electric current on the brain causes loss of consciousness. In contact with the human body, the electric current also has a thermal effect, and third-degree burns occur at the point of contact. ___
Direct current is less dangerous than alternating current in the electrical network, which even at 220V can cause very serious damage to the body. The effect of electric current on a person is enhanced by the presence of wet shoes and wet hands, which are characterized by increased electrical conductivity. ___
When struck by lightning, a tree-like pattern of bluish color appears on the victim’s body. It is commonly said that lightning left its image. In fact, when struck by lightning, paralysis of the subcutaneous vessels occurs.
positive action:
Electroshock is an electrical stimulation of the brain that is used to treat some mental illnesses. Defibrillators are electrical medical devices used to restore cardiac arrhythmias by exposing the body to short-term high-voltage electrical discharges. Galvanization is the passage of a weak direct current through the body, which has an analgesic effect and improves blood circulation.
When working with electrical appliances, be careful!
Next page “Entertaining tricks for 8th grade”
Back to section "8th grade"
Safety precautions
To prevent possible electric shock to a person, there are a number of rules prescribed in the safety and labor protection instructions.
Thus, work with electrical devices should be carried out only with tools with protected handles that do not allow current to pass through.
Repairs to electrical appliances should only be carried out after de-energizing them and removing the plug from the socket.
Repairs to electrical networks must be carried out after a power outage. At the same time, corresponding signs are hung on the switches that were used to de-energize.
When working with powerful devices, dielectric mats, shoes, and gloves are additionally used.
And for children there are special electrical safety rules.