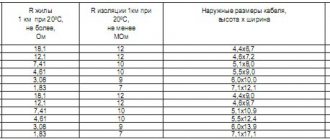
The material is a type of inorganic substance. It is used in the construction of floors, steps, the creation of glass-magnesium sheets and decorative elements. The material was first used in construction at the end of the last millennium for the manufacture of xylolite floors, facing tiles and small architectural structures.
Features of the material
Interest in magnesium cement either increased or waned for a while. This was due to a lack of information about the substance. The main advantage of the material is its high environmental characteristics, including protection from electromagnetic radiation, electrostatic influences, intrinsic safety and non-flammability.
The substance itself and materials made from it have high strength, close to natural materials. But, unlike the latter, magnesium binder has high tensile and bending strength (up to 20 mPa). This property is contributed by magnesium oxychloride fibers that crystallize in the hard cement. In addition, magnesium fibers perform a reinforcing function.
Compared to other binders, magnesium substance has very high adhesion to mineral and organic substances. High density, low alkalinity, as well as the presence of bischofite mineral, provide protection against rotting of organic fillers in cement. Thanks to this property, products made from magnesium binder are highly resistant to mold and mildew. The mixture forms a dense, pore-free material that is wear-resistant, waterproof, oil- and gasoline-resistant.
The maximum strength of the mixture and concrete is gained quickly: within 24 hours the figure reaches 30-50% of the maximum, and within a week - 60-90%.
Magnesia cement MAGcement
Stromex LLC produces and regularly supplies composite magnesia dry building mixtures under the MAGcement® brand.
The presence of a well-equipped production base with modern equipment and qualified personnel ensure the production of high-quality dry construction mixtures with a wide range of applications: from self-leveling floors and plaster to the production of decorative and high-precision fire-resistant products from artificial stone, as well as magnesium cement mortars. The developed original recipe for magnesium cement has no analogues in the territory of the Customs Union (Russian Federation, Republic of Belarus, Republic of Kazakhstan).
Composite magnesia dry building mixture MAGcement® (hereinafter referred to as KMSSS MAGcement® ), TU 5745-001-91580724-2016, is a two-component set of dry materials intended for the independent production of magnesia cement and concrete, as well as products from artificial magnesia stone using various fillers .
Scope of application of KMSSS MAGcement®:
- production of magnesium concrete with a compressive strength grade of up to M800 (class B60);
- installation of self-leveling magnesium self-leveling floors;
- performing plastering and putty work, incl. when working with LSU (magnesium glass sheets);
- used as magnesium tile adhesive, incl. for ceramic tiles and salt blocks;
- used as magnesia cement for cementing, repairing and killing oil and gas wells, incl. for fastening and sealing the annulus of a well during drilling operations;
- used as magnesium cement in road repairs;
- production of LSU, magnesium building boards, panels, blocks, bricks;
- production of fiberboard and xylolite;
- production of refractory products;
- production of high-precision and decorative products from artificial stone;
- production of products for radio electronics;
- used as materials for children's creativity;
- special construction.
Finished products obtained from KMSSS MAGcement® have the following properties: rapid setting after mixing with water (from 20 minutes to 5 hours), high strength, high adhesion to other materials (concrete, ceramics, metal, wood, etc.), non-shrinkage, environmental safety for humans, antistatic protection, protection from electromagnetic radiation, chemical resistance and oil and petrol resistance, low abrasion and dustlessness, non-flammability (classification “NG” according to SNiP 21-01-97), resistance against rodents, insects, bacteria, mold, fungus.
Finished products made from KMSSS MAGcement® are amenable to mechanical processing: drilling, milling, grinding, polishing, painting.
Composite magnesia dry building mixture MAGcement® is magnesia cement (Sorel cement) in its classic form. More details about magnesia cement and magnesia concrete and their application are described in the article Magnesia building materials.
MAGcement® is a new word in construction!
certificate of conformity for KMSSS MAGcement®.
You can get the current price list for KMSSS MAGcement®
For questions regarding the purchase of these products, as well as cooperation in the field of sales of dry construction mixtures, please contact us by contact numbers.
You may also be interested in:
- soil stabilization in road construction
- dust suppression on roads and in the mining industry
General characteristics
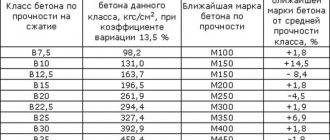
Magnesia cement gives the product high strength along with resistance to aggressive environments. Material marking - 500 and above.
The solution is made not using water, as with traditional cement, but using a special aqueous solution of magnesium salts. It is called a shutter. This fact allows magnesia cement to achieve maximum hardness in a short period of time.
Its characteristics are as follows:
- resistance to oils, salts, alkalis, organic solvents;
- Fire safety;
- low thermal conductivity;
- durability and wear resistance;
- flexural and compressive strength during hardening;
- high adhesion rates with organic and inorganic sealers;
- bactericidal properties.
Among the disadvantages of the material:
- low water resistance;
- instability to corrosion.
Another serious drawback that complicates the use of magnesium cement is the impossibility of transportation: it is possible to create a binder only in the place where the building, object or product will be recreated. Otherwise, the substance will quickly harden and will not be available for deformation.
To summarize, we can say that the advantages of magnesium cement outweigh its disadvantages, provided all conditions and dosages for creating the mixture are met.
Do you use magnesium cement in construction?
Yes
No
Application of magnesium cement for plaster mortar
The binder in magnesium cement plasters is caustic magnesite with an activity of 600-1000 kg/cm2. Instead of caustic magnesite from normal firing, waste from the so-called dead firing of magnesite can be used.
The main requirement for caustic magnesite, whether normally fired or in the form of waste, is high grinding fineness. The finer the grind, the higher the astringent properties of caustic-fired magnesite and its ductility. Magnesium chloride or magnesium sulfate can be used as a sealer. The latter gives slightly less strength, but at the same time less hygroscopic plaster.
All types of inert materials used in stone and lime-sand plasters can be used as a filler in magnesium plasters. The addition of low grade microasbestos is also used. In order to increase sound and heat insulation properties, organic fillers in the form of wood flour and sawdust can also be introduced. The dyes for magnesia binder are the same mineral pigments as for coloring Portland cement, with the exception of ultramarine.
Compound
- Magnesium oxide. This substance is obtained from magnesite MgCO3 or dolomite as a result of calcination at high temperatures. After this process it is milled. Depending on the type of raw material used and the purpose of the substance, caustic magnesite or caustic dolomite is used.
- Magnesium chloride acts as a separator.
- Magnesium sulfate is also used as a sealer. It increases the water resistance of cement, while reducing the strength indicators.
Cement production undergoes several stages. Magnesium oxide is calcined to 804 degrees Celsius and mixed with a 30% solution of magnesium chloride in a 2:1 ratio. As a result, a structural formation is formed of magnesium atoms bonded to each other by hydroxyl groups, water molecules and chlorine ions. Within a few hours the mixture turns into a strong, hard, white, easily polished mass.
In this case, the composition of the binder is not uniform. A number of studies have found that some areas contain a high concentration of magnesium oxide, while others contain magnesium binder. The remaining mineral components are present in quantities of no more than 10%. What does this depend on? First of all, it depends on the conditions of production of the substance, as well as on the speed of solidification. Therefore, during the production of the composition, fairly strict limits must be observed in the relationship between the sealer and magnesite (or dolomite).
Pros of coverage
Magnesia floors have a number of advantages:
Floor filling ALFAPOL
- No shrinkage even under high loads.
- Magnesia concrete is wear-resistant - there is no dust during operation, which is typical for Portland cement. This is a layer of monolithic acrylic stone.
Attention! This screed is rigid throughout its entire thickness - its stability is more than 5 times higher than cement screed.
- The coating will immediately withstand a pressure of 70 MPa, and after the completion of the formation of cement stone (after three months) - 100 MPa. This coating is used in rooms where machine tools vibrate.
- High adhesion to substrates: metal, asphalt, which allows for a not very thick layer.
- High speed of hardening and strength gain, which allows you to walk on the surface in 2-3 hours, and fully use it in 2-3 days.
- Oil and petrol resistance of the coating, as the magnesium mixture closes the pores.
- The surface reinforced with crystals of bischofite and magnesite substances resists stretching/compression and bending.
- The floor is non-slip and will withstand contact with liquid perfectly.
- The coating lasts at least 50 years.
Based on magnesite with the use of additives, new dry mixtures for construction work have been developed, for example ALFAPOL, which have additional good positive characteristics:
- Intrinsically safe;
- Anti-electrostatic;
- Protection from electromagnetic fields and non-ionizing radiation, which helps prevent radio-electronic interference and unauthorized information leaks.
Magnesian
concrete is used all the time, but traditions limit the scope of application.
Areas of application
With an ever-increasing shortage of cement and the unpredictability of its price at the height of the construction season, it seems relevant to look for ways to intelligently replace cement-containing structural elements. Let's consider the possibility of replacing the classic cement-sand floor screed in residential premises. Typically, a cement-sand screed is laid with a thickness of 50 mm. Magnesia-sand semi-dry screed can be laid in a layer of only 20 mm. The material itself “sticks” tightly to the concrete slab, and due to the absolute non-shrinkability of the magnesium binder, we get a completely finished, “on the horizon” screed that does not require further finishing leveling for linoleum, parquet, tiles, etc. The maturation period of magnesia-sand semi-dry screed is 7 hours - for the passage of people, for operation - 5 days. Thus, in an alternative application of magnesium screed we get:
- significant reduction in finishing work time;
- comprehensive cost reduction, because there will be no need to use expensive finishing floor levelers;
- reduction by approximately 2.5 times of the weight load on the foundation and structure of the building, compared to CFRP (with almost the same density of the material, the thickness is less);
- completely hygienic, dust-free (unlike cement compositions) material; is not destroyed by micromycete fungi that cause diseases in humans;
- durability due to increased strength and lack of tendency to crack.
Today, the construction market offers both magnesium mixtures, which are laid using a method similar to traditional concrete (with the exception of a number of operations, such as compaction), and self-leveling compounds, which are the most convenient to use.
Thin-layer industrial floors last more than 20 years - this is a fairly good period compared to other solutions, which allows you to further reduce the cost of operating floors and direct funds to business development, which will never stop due to forced repairs of the floor covering.
What is magnesium flooring?
This is a monolith, the construction of which uses a multicomponent magnesium mixture, which includes environmental materials: magnesite, bischofite. The latter is a natural antiseptic, found in sea salt.
Magnesite is a powdery substance of magnesium oxide. This is a unique material that is successfully combined with various fillers of synthetic or natural origin.
Magnesia floors are made from sand, crushed stone (marble, gravel), pigment and two of these natural substances. The reinforcing component is polypropylene fiber. In its composition, instead of Portland cement, magnesite cement is used, which is used in the manufacture of concrete grades 500 and more.
The term “cement” is used unjustifiably in relation to this mixture - it is a multicomponent solution of magnesium salts. Moreover, when the proportion changes, the material acquires new qualities. For example, increasing the amount of stone flour leads to increased strength, adding sawdust leads to improved thermal insulation, etc.