Cement M500 is a type of hydraulic binder, which is obtained by finely grinding clinker (which is a burnt mixture of clay and limestone), with the addition of gypsum and various minerals. Cement is used in a variety of areas of repair and construction work, internal and external.
Cement M 500 can be used for the preparation of masonry, plaster mortars, concrete for various structures (foundations, walls, screed, etc.), for laying tiles and a host of other tasks. Portland cement brand M500 is considered the most durable and high-quality, and therefore enjoys considerable popularity in the market.
M500 is a brand of binder capable of demonstrating an average compressive strength of around 500 kg/m3 after 28 days from the date of preparation. The mixture can be without additives or with various substances introduced into the composition in varying proportions.
The main advantages of cement M500 D0:
- Easy to prepare - just mix the components in the prescribed proportions and get a solution of the desired brand.
- Safety and environmental friendliness - the absence of toxins makes cement suitable for both external and internal work.
- Moderate consumption – reduces work costs.
- Chemical inertness - the frozen monolith is resistant to acids, alkalis, salts, etc.
- Excellent performance characteristics - PC 500 D0 demonstrates excellent strength, resistance to various influences, and durability.
The only disadvantage of the mixture is the rather high cost, but it fully corresponds to the quality and properties of the binder.
Application
M500 grade cement is used in the widest range of repair and construction work. Its characteristics and parameters make it possible to guarantee the quality and long service life of various structures, maximum strength and reliability.
The main areas of application of M500 cement:
- Creation of monolithic foundations, columns, slabs with reinforcement.
- Mixing various mortars - for plaster, bricklaying and blocks.
- Road, railway construction, bridge construction.
- Creation of runways in airfield conditions.
- Structures with special requirements - in an area of high groundwater flow, with the need for rapid solidification.
- Installation of power lines.
The material is considered universal - it all depends on what proportions were chosen for the solution. The proportion of cement and sand depends on the type of mortar: for super-strong structures 1:2, the classic version 1:3, for masonry mortars 1:4, other mortars allow a ratio of 1:5. Water is added in an amount sufficient to achieve a consistency for the solution that is comfortable to use.
Consumption rates
The grade of cement is the main parameter that determines the required amount of mixture used to create a cubic meter of concrete. The higher the grade, the less cement is required and, in general, using higher grades is more economical.
Thus, in terms of the amount of material consumed, M500 is one of the most profitable, since to obtain concrete of a certain strength, 15-20 percent more low-grade cement is required.
There are common proportions that are used to produce concrete from a cement-sand mixture.
These proportions vary depending on the purpose of the concrete being created. The main varieties include the following:
- for structures that require high strength , that is, foundations, floors and the like: 1 part cement to two parts sand;
- for masonry mortars: 1 part cement to 4 parts sand;
- For areas where significant load is not expected , such as floor screed, garden paths and plaster, use a ratio of 1 to 5 cement and sand, respectively.
When using mixtures that were created more than thirty days prior to mixing, a reduction in performance should be considered.
Every four weeks, the brand reduces about ten percent of activity, that is, for example, a fresh M500 after a couple of months in terms of functional characteristics is equal to M400 and the proportions for this brand should be used, that is, in quantities 15-20% more.
Compound
The characteristics of M500 cement largely depend on the components included in the composition and compliance with the preparation technology. To obtain Portland cement, slaked lime and clay are mixed to create clinker, to which gypsum or potassium sulfate, as well as various additives, are added.
The following additives are added to M500 cement (from higher to lower percentage): calcium and silicon oxides, aluminum and iron oxides, magnesium and potassium.
The clay rocks that make up cement are absolutely environmentally friendly, resistant to aggressive external environments, and are not afraid of corrosion. To improve certain properties, various additives can be added to the mixture - plasticizers, additives, etc.
Properties
Cement strength grade M500, manufactured according to GOST standards, has the basic properties:
- frost resistance,
- strength,
- water resistance;
- resistance to aggressive and saline solutions;
- reduced sulfate resistance;
- minimum indicators for deformation changes during shrinkage.
The use of modifying additives improves the basic properties of cement or gives it new ones. For example, hardening is accelerated, increased water resistance (hydrophobicity) is achieved, plasticity and tolerance to ultra-low temperatures are improved.
Peculiarities
Portland cement is distinguished from other brands of cement by its finer structure and white color. For its production, limestone is used (shell rock, limestone tuff, chalk, marble) as well as limestone marl or white clay (shale, loam),
Their percentage ratio in the finished mixture is 78%: 22% (acceptable ratio is 75%: 25%). M500 cement can be used for concreting work in low and ultra-low temperatures.
Production
Cement 500, like any other Portland cement, is produced according to the same principle. First, limestone and clay are sintered in a factory, thus producing clinker. Next, the clinker and gypsum are mixed and simultaneously ground finely. Lastly, various active additives can be introduced into the composition to increase resistance to moisture, strength, frost resistance, etc.
Mixtures prepared in this way are ready for mixing with water, are easy to use and guarantee the specified regulatory parameters in accordance with GOST. Cement without additives is marked M500 D0, with additives – M500 D20 (or more, depending on the volume of substances introduced into the composition).
Composition and types of building mixture
Portland cement M500 is an inorganic artificial material that, when liquid is added, first becomes plastic and then hardens to the state of stone. It consists of the following ingredients:
- clinker – calcium silicates;
- gypsum;
- plasticizing, hydrophobic, acid-resistant additives;
- blast furnace charge.
During production, the ingredients are ground to a powder state, after which they are mixed in prescribed proportions. The composition of the substance is dominated by calcium silicates - up to 80%.
Let's consider two types of products:
- Standard Portland cement M500 DO. Consists of pure clinker with the addition of gypsum. Does not contain additives or impurities.
- Modified Portland cement M500 D20. Includes 20% additives that give the mortar or concrete, among other things, anti-corrosion properties.
The manufacturer supplies both types of products packaged in multilayer paper bags of 45 and 50 kg, or without packaging.
Specifications
The M500 cement grade demonstrates high performance characteristics. The mixture is especially popular due to its strength, reliability and durability, as well as versatility.
Main properties of Portland cement M500:
- Start of setting – 45 minutes after mixing
- Complete hardening and strength gain - within 28 days
- Frost resistance – about 70 freeze/thaw cycles
- Bending load – up to 6.3 MPa (63 atmospheres)
- Grinding fineness – 92%
- Hygroscopic expansion – maximum 10 millimeters
- Compressive strength – 59.9 MPa (591 atmospheres)
- The shelf life of the dry mixture is about 1 year in its original, undamaged packaging (despite the fact that the packages usually indicate a shelf life of 12 months for M500 cement, after 3-6 months it gradually loses its properties)
- Radioactivity – up to 370 BC/kg (class 1)
- Density – up to 3200 kg/m3
Density
Density is an informative indicator that is responsible for the quality of the binder. It is the density that affects the reliability and strength of the hardened stone. The higher the bulk density indicator of Portland cement (PC) 500, the lower the porosity of the monolith will be and the worse it will absorb water and collapse under frost and various loads.
The bulk density of M500 cement can vary between 1100-1600 kg/m3. In calculations, an indicator of 1300 kg/m3 is usually used. The true density of the material is 3200 kg/m3.
Supplements
Various additives are introduced into Portland 500 cement, designed to improve certain of its properties and perform other tasks.
Main types of cement additives:
- To regulate properties - affect strength, setting time, plasticity, water absorption.
- Material – influence the processes of hydration and hardening. These can be active mineral additives or fillers.
- Technological - influence the grinding process, which can in a certain way affect the characteristics of the material, but is not at all necessary.
The volume of additives may vary, as indicated by the labeling. D0 is cement without additives, D5 or D20, for example, is cement that contains 5% and 20% of different substances, respectively. All additives are designed to improve the characteristics of the binder, to one degree or another.
Consumption rates
Portland cement M500 is supplied in bags of 25 kg, 50 kg (more in demand). And the question of how much binder is needed to prepare the solution is relevant for all craftsmen. Consumption rates depend on what kind of concrete needs to be prepared and why. Masonry and plaster mixtures are made from cement and sand in a ratio of 1:3, 1:2.
As a rule, the following components are used to fill and create durable structures: clean sand (without clay, silt, debris, small crushed stone), crushed stone with frost resistance F-65 and strength minimum M1000, Portland cement M500.
M500 cement consumption for different solutions:
- Concrete M200 – 250 kilograms
- M250 – 300 kilograms
- M300 – 350 kilograms
- M350 – 400 kilograms
- M400 – 450 kilograms
It is almost impossible to prepare concrete with a strength of M300 or higher at home, since it requires thorough mixing, which is extremely difficult to achieve without the use of technological equipment.
Packing and packing
Cement is produced and supplied in any volume. Standard packaging of M500 is in bags of 25, 50 kg (you can find M500 40 kg, but less often). After production, the cement is distributed into sealed towers, where a powerful ventilation system with a low level of air humidity is installed. Here the binder can be stored for up to 14 days.
Then the Portland cement is packaged in paper bags. The gross weight of the bag is no more than 51 kilograms. The bags must be made of several layers of polyethylene to prevent moisture from penetrating the powder. The packaging indicates the packaging date and markings with basic symbols that provide information about the material.
Under production conditions, the M500 should only be stored in its original container and for no more than a few months. If you plan to store it for a long time, the bags are placed on special pallets and turned over every 2 months.
Storage conditions: normal humidity level, air temperature up to +50 degrees. When in contact with air, cement absorbs moisture from it, which reduces its properties. Also, the binder loses parameters every few months, so the highest quality mortar can be obtained from fresh cement.
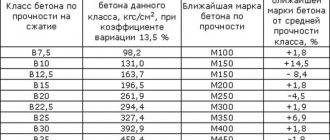
Main characteristics of cement M500
Scope of application of cement grade M500
Externally, cement M500 looks like a finely ground gray powder with a greenish tint. In the chemical composition of the material, which is a mineral powder in content and structure, a fairly large percentage is occupied by calcium silicates. Additives give concrete and mortars special strength. For the construction of bridge supports, power lines, and various hydraulic structures, cement of the highest quality is required, which has not only high strength characteristics, but also other, no less high indicators: viscosity, heat resistance, resistance to aggressive environments.
One of the main characteristics of the mixture is its frost resistance. Cement M500 has a frost resistance index of F70. The number after the letter “F” indicates how many cycles of complete freezing and thawing the concrete structure will withstand without changing its strength characteristics. In this case, concrete structures will withstand 70 cycles of complete freezing and thawing without deterioration in strength characteristics. After 70 cycles, the design strength of the structure will decrease by 10%. And in the future, such a decrease will occur every 70 cycles. This is a very high figure.
On the packaging the manufacturer indicates:
Technical characteristics of cement grade M500
- compressive strength 28 days after pouring – 50 MPa (500 kg/cm2);
- bending strength 28 days after pouring – 6.8 MPa (70 kg/cm2);
- setting of the solution - from three to four hours;
- complete hardening of the solution - 28 days;
- Shelf life in sealed packaging is one year;
- the weight of one cubic meter of concrete is from 3.0 to 3.2 tons;
- linear expansion upon hardening - up to one centimeter;
- mixture grinding fineness – 92%.
The speed of setting of the solution depends on the last indicator - the less time it takes for the solution to harden, the smaller the fraction of the mixture.
Marking
Regardless of whether M500 cement is purchased in 40 kg, 25 or 50 kg, all important information about the binder must be indicated on the bag. The marking is prescribed in GOST 10178-85. Designations must include the brand and volume of additives (Eurocement M500 D0 or D20, for example).
What do the letters in the markings mean:
- B – fast-hardening cement
- PC (ShPC) – Portland cement (or Portland slag cement)
- N – composition compliance with GOST standards
- PL – plasticized cement with a high level of frost resistance
On September 1, 2004, another GOST number 31108-2003 was adopted, which was replaced in December 2021 by GOST number 31108-2016.
It suggests the following classification:
- CEM I – Portland cement
- CEM II – PC with mineral additives
- CEM III - Portland slag cement
- CEM IV – pozzolanic cement
- CEM V – composite Portland cement
The introduction of additives into the binder (their type and volume) is regulated by GOST 24640-91.
Material parameters
Portland cement grade 500 has positive and negative technical characteristics:
1. Advantages of the building mixture:
- Frost resistance.
- Moisture-repellent properties.
- High flexural and compressive strength.
- Durability.
- Elasticity.
- Anti-corrosion resistance.
- Allowed for the production of critical structures on railways, airports, power lines, bridges.
The positive properties of the substance are preserved during operation if it is not mixed with other materials. The positive qualities of grade 500 are transferred to the mortar and concrete.
2. Disadvantages of the mixture:
- Low resistance to sulfates.
Technical characteristics of Portland cement M500 D20 have similar parameters to M500 DO:
- Compressive strength 59.9 MPa.
- Setting period: start - 45 minutes, end - no later than 10 hours.
- Flexural strength 6.4 MPa.
- Frost resistance F70.
- Grinding fineness 92%.
- Expansion when setting 10 mm.
- Bulk density 1100-1600 kg/m³.
- Actual density 3200 kg/m³.
Differences between M500 with additives and pure material
Cement grade 500 may require the presence of certain additives or be supplied without them. So, the difference between the composition D0 and D20 is that in the second case, 20% of the mixture are additives that in a certain way affect the properties and characteristics of cement, as well as hardened concrete.
Cement M500 D0 is created from pure clinker and gypsum, due to which it sets quickly, gives maximum service life, and makes it possible to pour reinforced concrete structures with a high level of water resistance and frost resistance. Additive-free cement guarantees long service life even in conditions of constantly high humidity, eliminating the risk of corrosion and deformation.
Thanks to the above advantages, cement M500 without additives is widely used in private and industrial construction, everywhere in the construction of power line supports, bridges, road and airfield pavements, as well as other important facilities.
M500 D20 cement contains about 75-80% clinker, which reduces the cost of the binder. It sets a little faster due to mineral additives. The general characteristics of cement with additives are slightly reduced, but this does not affect the strength.
Most often, Portland cement with additives is used to create repair and construction mortars. Facade plasters, self-leveling floors, durable masonry mortars are made from cement with additives, which is more comfortable to work with, costs less, but performs all the functions assigned to it perfectly.
White cement M500 is often used to create a colored solution - in this case, pigments act as additives.
Bulk density
The bulk density of M500 cement in dry form ranges from 1,100 to 1,600 kg/m3. This indicator depends on the mineral composition of the feedstock, the degree of compaction of the material, and the presence of additives. When making calculations, if there is no data on the exact characteristics of the substance, the specific gravity of the binder is taken at an average value of 1,300 kg/m3.
When transporting products or long-term storage, the density indicator increases due to compaction of the substance. Compaction of the binder also occurs at high humidity in the storage area. The density of cement mortar m500 is 3,000-3,200 kg/m3. Changing the degree of density of the binder affects the performance properties of the concrete mixture. The specific gravity also depends on the production technology, chemical composition, and particle size.
Preparation of concrete solution
To prepare a concrete solution according to the tables, you need to know some parameters - the weight of 1 m3 of cement, the specific gravity of other components, the required volume of the mixture, etc. But you can do it differently - measure all the components by volume (with a bucket, for example), which is much simpler.
The proportions of the components and the choice of fillers themselves directly depend on what kind of solution is being prepared and for what purpose. Below are tips and proportions for durable concrete used for pouring various structures.
Tips for preparing concrete:
- Sand – it’s better to take quarry sand, be sure to sift it.
- Large filler - granite crushed stone or crushed gravel of a fraction of 5-20 millimeters is suitable. If the foundation is being poured, it is better to take up to 40 millimeters. Lightweight concrete is created from slag, expanded clay, and other porous aggregates. Lean concrete is mixed without aggregates.
- Additives and additives may be included in the composition as needed. When adding them, be sure to take into account the volumetric weight of cement and other components - if there are a lot of additives, the properties may deteriorate.
- Tools for preparing concrete - a large trough, buckets, shovel, sieve, hammer, trowel.
- Before diluting M500 cement, you need to thoroughly mix all the dry ingredients. Water is added only after obtaining a homogeneous dry mass, preferably in portions, until the mixture reaches the desired consistency.
To obtain a concrete solution with average characteristics, make a classic batch: part cement, 1.9 parts sand and 3.8 parts filler. Water is taken in a volume equal to half the volume of cement (about 1.5-2 liters of water are used for 10 kilograms of dry mixture). Here it is not necessary to know the specific gravity of M500 cement and its density - everything is calculated by volume.
Tips for choosing
The building materials market is flooded with fakes. Let's look at how to avoid buying low-quality cement. We recommend paying attention to the following points:
- Date of manufacture and integrity of the bag. The shelf life of the binder is 2 months.
- Manufacturer country. Long-term transportation of goods reduces consumer properties.
- Low cost is a sign of inconsistency with quality.
- The actual weight is often less than required.
- Reviews from people about the seller reduce the risk of making a mistake.
- Buy building materials directly from the manufacturer or dealer.
Let's summarize. Russian cement M500 and structures made on its basis can withstand high loads, are durable, low in cost, and reduce the time required for work in civil, industrial and private construction.
- Assembly technology and types of foundation structures
- You can also build in a swamp!
Adviсe
Before you start working with cement, you need to carefully study its properties, find out the proportions, find out how much material is needed for 1m3 of mortar, etc.
Some tips from the experts:
- Cement is purchased in bags of 25/50 kilograms and as close as possible to the day of its use. The material should only be stored in its original container, without opening. If cement was purchased in bulk, it must be properly protected from precipitation and used as quickly as possible, since it will still “pull” moisture from the environment and lose its properties.
- It is better to buy cement right before work and in small quantities, purchasing the required volume. Stores in Moscow and the regions always have cement of all types in large quantities, so there is no point in purchasing material for future use.
- If you are planning a large purchase, it is better to purchase from wholesale suppliers or a manufacturer, bypassing intermediaries.
- Check the material’s compliance with GOSTs and the availability of certificates. It is also advisable to first check the reputation of the manufacturer, the quality of the equipment, and compliance with cement production technology.
- All additives included in the composition must be listed.
Cement M500 is a high-quality building material that is in demand on the modern market, which is used in a variety of fields, therefore it is considered universal. When choosing cement, you need to pay attention to the markings, and during the work process, follow the technology, which will make it possible to guarantee the highest quality of the result.
Scope of application
Portland cement for general construction purposes, grade 500 (without additives) is most in demand. It is used to impart frost resistance and high initial strength to concrete structures during emergency restoration work and in the construction of industrial facilities.
Cement M500 D20 is used for production in all areas of construction where high strength of the finished mortar or concrete mixture is not required.
The product is also used in landscape design for the manufacture of statues, cladding, columns, and decorative elements.