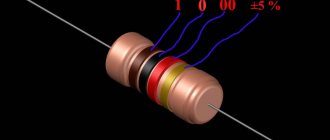
Marking according to GOST
Today, in our country, cement is labeled according to the requirements of the new GOST 31108, developed in 2003 and revised in 2021. Both versions of this regulatory document are valid, do not contradict each other and are consistent with the labeling requirements adopted in European countries.
However, the old markings according to GOST 10178-85 are still found in construction documentation and on cement packages. For the average person, it is more understandable and familiar, but does not reflect many important characteristics, such as the composition of the material, the type and amount of additives. Which often leads to a “blind” purchase, without taking into account many nuances that may affect the quality of the structures being built.
Example of marking according to the new standard Source stroyportal.ru
This means that those who are starting construction need to study new grades of cement, their application and interpretation. Tables and photo examples will make this task easier.
Old markings
According to previous requirements, cement was labeled briefly, indicating the composition of the material, its strength, percentage of additives and special properties.
The composition of cement is indicated by a group of capital letters. For example, Portland cement is PC, white Portland cement is PCB, slag Portland cement is ShPC.
Immediately following them are numbers indicating the compressive strength of the finished concrete (in kg/cm²), which it reaches 28 days after production: 300, 400 or 500. Often the marking of cement that goes on retail sale looks even simpler: on the bag indicate the full name of the binder type and strength grade.
Strength grade is the main criterion for choosing cement Source posudachimodache.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in finishing materials and related work
The letter D with numbers following the strength indicates that the material contains a certain amount of additives - from 0 to 20%. And the last letters indicate its special properties:
- N – normally hardening;
- B – fast-hardening;
- PL – plastic;
- GF – has hydrophobic properties.
Marking according to the old GOST Source skachat-kartinki.ru
For example, SSPTs 400-D0 B stands for sulfate-resistant Portland cement with strength grade M400, fast-hardening, with zero additive content.
New marking
The main change that can mislead the average buyer concerns the strength grade of cement. Now it is not the brand that is indicated, but the strength class in MPa, so we see different values. To avoid confusion, you need to remember that:
- 22,5 corresponds to M300;
- 32,5 – M400;
- 42,5 – M500;
- 52,5 – M600.
The first letters in the marking are CEM, followed by Roman numerals indicating the type of material:
- I – pure Portland cement without mineral additives;
- II – Portland cement with additives;
- III – Portland slag cement;
- IV – pozzolanic Portland cement;
- V – composite Portland cement.
The type and amount of additives are also indicated in the cement marking; deciphering this information is not as difficult as it seems.
Example of new marking Source 24aul.ru
What is cement marking?
There are several brands of cement, according to which the material differs in compressive strength, setting time, frost resistance, etc. The marking is indicated on the product packaging, and it can be difficult to decipher (at least for a beginner). Due to the difference in existing standards, one of which is used by one or another manufacturer, confusion may arise. Let's figure it out together!
In our country there are 3 types of cement markings:
- GOST 10178 (1985);
- GOST 31108 (2003);
- European standard EN 197-1.
Thus, bags of cement may contain a designation according to both the new and the old standard.
Selecting a brand by application
In private construction, cement IV and V are not used, and they are rarely found on sale, since they have special properties and are used for the construction of structures under difficult operating conditions.
For the same reason, and also because of the high cost, CEM I class 42.5 and 52.5 is not in demand.
The most popular grades of cement in terms of strength are CEM I and CEM II 32.5. Higher grades are used for critical structures - load-bearing or under load. And 22.5 is used for the production of plaster, installation of concrete footings, decorative and load-free elements.
CEM III is an excellent option for the manufacture of concrete blocks, curbs, well rings and other products in contact with water or wet soil.
Old-fashioned markings
Cement marking in the usual form for Russia is a designation in accordance with GOST 10178-85 “Portland cement and Portland slag cement”. It includes information on the strength, composition and types of additives used in the production of the binder.
The main component always comes first in the designation:
- PC – Portland cement in pure form, not less than 80%;
- ShPC is a combined binder consisting of Portland cement clinker and slag, the amount of which is at least 20%;
- PPC – pozzolanic Portland cement;
- WRC – waterproof expanding.
Next, the cement compressive strength grade at the age of 28 days is set: 300, 400, 500, 550, 600 (according to GOST). Please note that the letter “M” is not placed before the digital designation.
The amount of additives is marked with the letter “D”, followed by the amount of additives from 0 to 20% (D0...D20).
After the additives, the rate of hardening of the stone is indicated - “B” - fast-hardening or “N” - normal-hardening. This is a peculiar reflection of the nature of additives and additives to the cement binder. In addition, if there are additional properties, they are indicated by letter abbreviations:
- SS – sulfate-resistant;
- PL – plasticized to increase the workability of the solution;
- GF – hydrophobized to improve the stone’s resistance to water.
An example of decoding cement markings according to GOST 10178-85:
Portland cement 500-D15-B - PL GOST 10178-85
Portland cement (or PC) is a clinker binder in its pure form; 500 – grade of cement in terms of compressive strength 28 days after molding the samples; D15 – the presence of additives that improve properties in an amount of no more than 15%; B – fast-hardening cement (starts setting no later than 10-15 minutes); PL – plasticized binder; GOST 10178-85 is the regulation on which the labeling is based.
Briefly about the main thing
Understanding the markings of cement is not at all difficult if you remember the basic designations regarding its composition and strength. In addition, not many of its varieties are used in individual construction. For example, if you are used to buying PC400 D20 cement, but don’t see it on sale, then look for CEM I 32.5 or CEM II/A 32.5. These materials are similar in composition and characteristics. And additional letters in the labeling will help you find out exactly what additives are included in the composition.
Ratings 0
Cement marking according to the new GOST
In the new standard, in addition to the number of additives, there is a designation of cement by type, and then a letter designation of mineral additives by composition. The designations are deciphered as follows: • CEM I – pure Portland cement; • CEM II/A – Portland cement in a mixture of subtype “A”, maybe “B”; • CEM III/A – Portland slag cement of various subtypes; • CEM IV/A – cement with the addition of pozzolan of various subtypes; • CEM V/A – composite cement of various subtypes.
new designations according to GOST for cement
Types of cement and their applications
Types of cement and their purpose:
- Portland cement (PC) is a monolithic structure made of concrete and reinforced concrete. This is the most common type. It got its name from the Isle of Portland in Great Britain. It was there that natural stone for this variety was first mined.
- Slag Portland cement (SPC) – monolithic underground and underwater structures.
- Pozzolanic – for prefabricated and monolithic structures.
- Alumina - for repair work.
- Gypsum-alumina - for concrete that should not shrink, expand or allow water to pass through.
- White or colored - for exterior and interior decoration of the building.
Other varieties according to the old standards are presented below.
The brand of the mixture and its characteristics affect the scope of application.
Concrete calculator: composition calculation
| Brand | Where is it used? | Peculiarities |
| M400 | It is used for plastering surfaces, brickwork, concreting underground, above-ground, underwater objects, and producing reinforced concrete structures. | The fastest-hardening mixture is M400 D0, which does not contain any additives. |
| M500 | Used in industrial construction: foundations for communications and buildings, beams, floor slabs, precast reinforced concrete. | The brand is waterproof, strong and durable. |
| M600 | Used in the production of concrete class B40 (with very high strength) for high-quality prefabricated structures. | It is not used in the construction of ordinary buildings, since the mixture hardens very quickly. |
GRANDS AND CLASSES OF PORTLAND CEMENT
GRANDS AND CLASSES OF PORTLAND CEMENT
Portland cements according to GOST 10178-85
| Name of cement | Designation | Stamps |
| Portland cement | PC-D0 PC-D5 PC-D20 | 300, 400, 500, 550, |
| Rapid hardening Portland cement * | PC-D20-B | 400, 500 |
| Sulfate resistant Portland cement | SSPTs-D0, SSPTs-D20 | 400, 500 |
| Slag Portland cement | ShPC | 300, 400, 500 |
| Rapid-hardening Portland slag cement * | ShPTs-B | |
| Sulfate-resistant Portland slag cement | SSSHPTs | 300, 400 |
| Pozzolanic Portland cement | PPC | 300, 400 |
Mineralogical composition of Portland cement clinker
| Name of mineral | Formula | Abbreviation | Approximate content in clinker, % |
| Tricalcium silicate (alite) | 3CaO∙SiO2 | C3S | 40…-65 |
| Dicalcium silicate (belite) | 2CaO∙SiO2 | C2S | 15-…40 |
| Tricalcium aluminate | ZCaO∙Al2O3 | C3A | 5…-15 |
| Tetracalcium aluminum ferrite | 4CaO∙Al2O3∙Fe2O3 | C4AF | 10…-20 |
Strength requirements for Portland cement grades according to GOST 10178-85
| Brand → | 300 | 400 | 500 | 550 | 600 |
| R28 under compression, kgf/cm2 (MPa), not less | (29,4) | (39,2) | (49,0) | (53,9) | (58,8) |
| R28 at bending, kgf/cm2 (MPa), not less | (4,4) | (5,4) | (5,9) | (6,1) | (6,4) |
Actual result. ultimate compressive strength after 28 days of hardening is an indicator of cement activity , for example: compressive strength after 28 days of hardening was 435 kgf/cm2 (
42.6 MPa)
.
This is his activity.
Depending on the composition and purpose, various types of Portland cement are produced, without mineral additives (DO) and with mineral additives (D5 and D20 - up to 5 and 20% additives, respectively).
Strength requirements for fast-hardening cements
| Cement designation | Brand | Tensile strength at the age of 3 days , MPa (kgf/cm2 ), not less |
| when bending | when compressed | |
| PC-D20-B | 3,9 (40) 4,4 (45) | 24,5 (250) 27,5 (280) |
| ShPTs-B | 5,4 (55) | 21,5 (220) |
Designation of cement. For example, Portland cement grade 400 with additives up to 20%, quick-hardening, plasticized, is designated as follows:
Portland cement 400-D20-B-PL or PC 400-D20-B-PL.
Granular blast furnace additives are used as additives for road concrete.
Ordinary Portland cement
Ordinary Portland cement is available in two types:
Portland cement without mineral additives,
·Portland cement with additives (with active mineral additives no more than 20%).
Granulated blast furnace and electrothermophosphorus slags, rocks of sedimentary origin (diatomites, tripoli, opoka), gliezhes (naturally fired clays), etc. are used as additives. Additives are introduced to increase the water resistance of cement (to bind the released calcium oxide hydrate into poorly soluble calcium hydrosilicates); their use leads to savings in expensive clinker. Using mineral additives, you can regulate a number of other properties of Portland cement: heat generation during hardening, density of cement stone, etc. The types and content of additives in Portland cement are presented in Table. 12.
Symbol for cement
The symbol for cement should consist of:
· names of the type of cement - Portland cement, slag Portland cement, sulfate-resistant Portland cement, pozzolanic Portland cement. It is allowed to use the abbreviated designation of the name - respectively PTs, ShPTs, SSPTs and PuzzPTs;
· cement grades - 500, 400, 500, 550, 600;
· designations of the maximum content of additives in Portland cement - DO, D5, D20 (0%, 5%, 20%);
· designation of fast-hardening cement - B;
· designation of plasticization or hydrophobization of cement - PL, GF;
· designation of cement obtained from clinker of standardized composition - N.
For example, Portland cement grade 400, with additives up to 20%, quick-hardening, plasticized is designated:
Portland cement 400-D20-B-PL or PC 400-D20-B-PL.
Table 12
| Cement designation | Active mineral additives,% by weight | |||
| Total | Including | |||
| Blast furnace granulated slag | Sedimentary origin other than gliège | Other actives, including gliage | ||
| PC-DO | not allowed | |||
| PC-D5 | up to 5 | up to 5 | up to 5 | up to 5 |
| Pts-D20,PTs-D20-B | >5 to 20 | up to 20 | to 10 | up to 20 |
| ShPTs, ShPTs-B | >20 to 80 | >20 to 80 | to 10 | to 10 |
| SSPTs-DO | not allowed | |||
| SSPTs-D20 | >10 to 20 | >10 to 20 | >5 to 10 | — |
| ssshpts | >20 to 80 | >20 to 80 | — | — |
| PuzzPC | >20 to 40 | — | >20 to 30 | >25 to 40 |
For classes 22.5; 32.5; 42.5; 52.5.
By compressive strength at the age of 2 (7) days
(hardening speed) (except for class 22.5) cements are divided into:
· normally hardening – N;
· quick-hardening - B
Requirements for the physical and mechanical properties of cements
| Cement strength class | Compressive strength, MPa, aged | Beginning of setting, min, not earlier | Uniformity of volume change (expansion) mm, no more |
| 2 days, no less | days, no less | 28 days | |
| no less | no more | ||
| 22.5N | — | 22,5 | 42,5 |
| 32.5N | — | 32,5 | 52,5 |
| 32.5B | — | ||
| 42.5N | — | 42,5 | 62,5 |
| 42.5B | — | ||
| 52.5N 52.5B | — — | 52,5 | — |
Examples of symbols.
1. Portland cement class 42.5, quick-hardening:
GRANDS AND CLASSES OF PORTLAND CEMENT