During road construction, various innovative materials are used, each of which has its own unique properties. Laying the geotextile is necessary to create a dividing layer when performing road work, as well as to create drainage systems. Geotextile laying technology improves the performance capabilities of the surface and allows you to: strengthen slopes, embankments and other coverings; create waterproofing that prevents the appearance of moisture; protect the surface from mechanical damage; qualitatively separate layers of bulk structures; increase the strength of the coating. The installation technology of the geofabric is not complicated, but it requires compliance with the sequence and quality of the stages. The work on creating geotextile surfaces can be divided into 6 stages.
Selection of geotextiles
There are two types of geotextile material:
- woven;
- non-woven, for the production of which different formation methods are used.
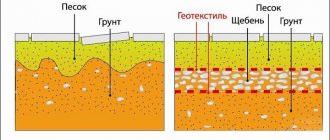
The picture above shows a woven, white geotextile.
Non-woven geotextiles are made by mass weaving synthetic fibers, which improves the strength of the material, and heating and pressing with rollers is carried out to secure the shape of the fabric. This structure has the property of a filter membrane and is the best layer for separating soil.
The method of producing woven fabric is similar to the method of producing non-woven fabric, but due to the different structure of the threads, woven-type geotextiles have better warp strength. Woven geotextiles are prone to diagonal deformation under physical load, so they are used in places where high strength is needed, but minor deformation is allowed. Due to the matted fibrous structure, the non-woven type performs the function of a filter membrane perfectly.
Which side to lay geotextiles
There is no clear answer to this question. Some craftsmen believe that the material can be laid on either side, because its characteristics will not change.
In the attached instructions, some manufacturers advise their consumers to lay geotextiles with the smooth side down.
Other experts say that a rough surface will promote greater traction on the soil. However, it is best to simply read the manufacturer's recommendations and act according to their instructions.
Transportation and storage of geotextiles
Geotextile fabrics should be stored on a dry and flat surface so that they do not lose their shape. For a compact arrangement of rolls, it is permissible to arrange them in a layer, which should not exceed 5 rows.
Geotextiles are wound on a rigid core, which can break under physical stress, so placing the rolls crosswise is strictly prohibited. Manufacturers of canvases advise removing the original packaging only before directly laying the material on the surface.
Where is geotextile used and what are its features?
We list the main areas of construction and industry where geotextiles are indispensable:
- for the construction of industrial buildings, as well as residential buildings;
- when installing a sewer system. Geotextiles do not allow sand and soil particles to pass through, so they sort of filter water;
- during the construction of all types of roads and even runways. Laying geotextiles increases the wear resistance of materials and also does not allow the coating layers to mix with each other;
- geotextiles are increasingly being used for laying underground gas pipelines;
- gardeners use the material to prevent weeds from germinating, as well as to insulate garden trees in winter. Country paths will become much stronger if geotextiles are laid under them;
- to strengthen the foundation.
As you can see, the material is almost universal in use. Its moisture resistance depends on the density of the fabric and the method of its manufacture. Geotextiles are stored in rolls. You can purchase the material at construction markets, in large specialized stores, as well as online with delivery. When choosing geotextiles, pay attention to its density, manufacturer (give preference to well-known brands), as well as the type of material (it can be needle-punched or thermally bonded).
Preparatory work
The technology of laying geotextiles is carried out on the surface, which in turn requires high-quality preparation of the base. Before laying the canvas, it is necessary to get rid of soil defects: holes, depressions, cracks, vegetation, etc. In order to identify all defects, you can perform preliminary rolling of the blade, which will determine the existing irregularities.
Read on topic: Classification of road surfaces
All holes and depressions must be filled with soil or sand, the layer compacted using a vibrating plate or vibrating rammer and leveled. Shrubs and roots should be uprooted or cut down, and surface water should be compensated with an additional layer of sand. If the object does not pose a threat to damage to the geotextile, then preparation of the base is not necessary.
Which geofabric to use for drainage: features of choice
Consumers are offered a range of geotextiles for drainage; the price per m2 depends on the characteristics of a particular material. It is not recommended to use canvases made from mixed fabrics, as over time they are washed out, and at the same time the ability to filter liquids is reduced.
The geotextile for the drainage system is selected with a reserve, so that the raw materials are placed with the outlet
It is worth considering the filtration rate indicated by the company. The optimal filtration coefficient varies from 125-140 m/day. If groundwater is located high, then the value should be even higher.
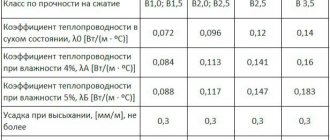
The cost of the product depends on the manufacturer and density value. Material from specific manufacturers and its price can be viewed in the table.
Variety for foundation protection
The durability of the building depends on the quality of the foundation. To protect the building from being washed away by groundwater, you need to properly arrange the drainage system. Before work, you need to determine the depth of groundwater. This will help you choose crushed stone, pipes and geotextiles.
The use of high-quality materials for blind areas prevents moisture from melting inside the house
A trench is dug along the contour of the foundation. It is done with an inclination. The width of the notch is calculated taking into account the diameter of the pipes.
If there is a blind area, then the recess is located along it. Sand is poured to the bottom, and then geotextiles are laid, which are sprinkled with crushed stone. Pipes and crushed stone are placed on top. The layers are covered with geofabric, which is fixed with wire.
Dornit: non-woven geotextile for various uses
Dornite is considered one of the popular materials. It is a sheet of polymer substance. Before purchasing a product, you need to familiarize yourself with the technical characteristics of dornite geotextiles. This heat-treated and needle-punched geofabric is designed to withstand stress.
The production technology allows the products to be used in the construction of highways, for laying pipelines, as a base for paving slabs and for parking lots. Dornite is intended for separating layers of a drainage structure, to increase the strength properties and to protect against the processes of leaching of soil rocks.
Dornit geofabric is distinguished by its density and quality indicators
Drainage structure for a garden plot
The passage of groundwater harms the plants that grow in the garden.
Geotextile is used for certain types of seedlings. It protects the plant from weeds
To drain water from the territory, trenches are dug along the perimeter into which narrow pipes are placed. They are divided into separate elements and fixed on the spreads using tees. In this case, each section of the highway is wrapped with geofabric. Then crushed stone, geotextiles, crushed stone and a layer of soil are laid out.
With the help of this material beautiful paths in the garden are arranged.
Price for geotextiles per sq.m.
The average cost of geotextiles is about 10-20 rubles per square meter. Products from domestic manufacturers have a low price. Before purchasing, you need to study the properties of the product. It is worth finding out the cost of installation in advance. The price for such a service starts from 35 rubles per square meter.
Laying the canvas
After preparing the soil, the process of laying the sheet occurs, during which the geotextile must be straightened and laid along the length of the construction site. Before rolling out the rolls in the finished areas, you need to install a deck and only then lay the geotextile rolls so that its edges extend beyond the embankment for better fixation outside the road.
Longitudinal laying relative to the axis of the embankment is simpler, while transverse laying ensures the strength of the layers along the width of the embankment. To manually roll out rolls of canvas, several people will be required to secure the material step by step. Laying can also be done using attachments, the main thing is that there are no folds on the surface of the laid coating.
All rolls must be evenly aligned, fastened together and fixed to the ground using anchors. Each subsequent layer must be laid on the previous one with an overlap of 0.3-0.7 meters in order to ensure the performance of certain functions assigned to it and to minimize the possibility of divergence of the fixed layers after the load is applied.
During installation, the movement of equipment or workers on laid geotextile sheets is prohibited.
Geotextile laying technology – Flat road
During road construction, various innovative materials are used, each of which has its own unique properties. Laying the geotextile is necessary to create a dividing layer when performing road work, as well as to create drainage systems. Geotextile laying technology improves the performance capabilities of the surface and allows you to: strengthen slopes, embankments and other coverings; create waterproofing that prevents the appearance of moisture; protect the surface from mechanical damage; qualitatively separate layers of bulk structures; increase the strength of the coating. The installation technology of the geofabric is not complicated, but it requires compliance with the sequence and quality of the stages. The work on creating geotextile surfaces can be divided into 6 stages.
Selection of geotextiles
There are two types of geotextile material:
- woven;
- non-woven, for the production of which different formation methods are used.
The picture above shows a woven, white geotextile.
Non-woven geotextiles are made by mass weaving synthetic fibers, which improves the strength of the material, and heating and pressing with rollers is carried out to secure the shape of the fabric. This structure has the property of a filter membrane and is the best layer for separating soil.
The method of producing woven fabric is similar to the method of producing non-woven fabric, but due to the different structure of the threads, woven-type geotextiles have better warp strength. Woven geotextiles are prone to diagonal deformation under physical load, so they are used in places where high strength is needed, but minor deformation is allowed. Due to the matted fibrous structure, the non-woven type performs the function of a filter membrane perfectly.
Transportation and storage of geotextiles
Geotextile fabrics should be stored on a dry and flat surface so that they do not lose their shape. For a compact arrangement of rolls, it is permissible to arrange them in a layer, which should not exceed 5 rows.
Geotextiles are wound on a rigid core, which can break under physical stress, so placing the rolls crosswise is strictly prohibited. Manufacturers of canvases advise removing the original packaging only before directly laying the material on the surface.
Preparatory work
The technology of laying geotextiles is carried out on the surface, which in turn requires high-quality preparation of the base. Before laying the canvas, it is necessary to get rid of soil defects: holes, depressions, cracks, vegetation, etc. In order to identify all defects, you can perform preliminary rolling of the blade, which will determine the existing irregularities.
All holes and depressions must be filled with soil or sand, the layer compacted using a vibrating plate or vibrating rammer and leveled. Shrubs and roots should be uprooted or cut down, and surface water should be compensated with an additional layer of sand. If the object does not pose a threat to damage to the geotextile, then preparation of the base is not necessary.
Laying the canvas
After preparing the soil, the process of laying the sheet occurs, during which the geotextile must be straightened and laid along the length of the construction site. Before rolling out the rolls in the finished areas, you need to install a deck and only then lay the geotextile rolls so that its edges extend beyond the embankment for better fixation outside the road.
Longitudinal laying relative to the axis of the embankment is simpler, while transverse laying ensures the strength of the layers along the width of the embankment. To manually roll out rolls of canvas, several people will be required to secure the material step by step. Laying can also be done using attachments, the main thing is that there are no folds on the surface of the laid coating.
All rolls must be evenly aligned, fastened together and fixed to the ground using anchors. Each subsequent layer must be laid on the previous one with an overlap of 0.3-0.7 meters in order to ensure the performance of certain functions assigned to it and to minimize the possibility of divergence of the fixed layers after the load is applied.
During installation, the movement of equipment or workers on laid geotextile sheets is prohibited.
Fastening the canvases
To minimize the length of the overlap, the laid geotextile sheets must be fastened together. The connection of geotextiles can be carried out using the welded method or the end-to-end stitching method. Welding a connection with a low-temperature torch will save material and carry out installation in a shorter time, and the stitching method does not require complex operations or any knowledge of instruments.
In the stitching method, anchors are used to secure the materials to the ground, which must be installed every 1.5-2 meters to ensure resistance to wind and maintain the tension of the material.
Backfilling and compaction
The next step after fixing the canvases is backfilling with a structural layer from a height of no more than 1.2-1.5 meters, because if the material falls, it can destroy the integrity of the geotextile. At the same time, interaction with heavy vehicles on uncovered surfaces should not be allowed. Based on the characteristics of the base soil and bulk materials, the soil layer is compacted, which can be done either manually or using machinery.
Until the last layer is completely compacted, the geotextile should not be subjected to heavy loads; therefore, movement of equipment around the work area is allowed only if the backfill thickness is at least 200 mm. If the soil's ability to withstand large loads is insufficient, small-sized equipment with low pressure per unit area should be used.
To achieve best results, compaction should be done in layers. During the installation of geotextiles, it is recommended to constantly monitor the quality of the work performed in order to eliminate errors in a timely manner. If any sections of the fabric have been damaged, it is necessary to replace them or apply patches with an overlap of 50 centimeters to ensure their stability on the surface of the geotextile.
Laying asphalt
When laying asphalt, using a level, you need to determine the direction of the slope in the direction where the bulk of rainwater will collect and the storm drain will be located. The slope should not exceed 10 mm per 1 meter.
To select the thickness of the asphalt pavement, it is necessary to determine the degree of load on the surface. Depending on the loads imposed in the future, it is necessary to select a suitable layer thickness. So, for the adjacent area, a layer of fine-grained asphalt of 4-5 centimeters is quite sufficient. For more intensive use, an additional base layer of coarse asphalt is required. Laying asphalt should not be carried out in the rain, because the properties of the product are lost and the road will not be strong enough and stable enough.
If the established rules for using geotextiles are strictly followed, the asphalt concrete pavement will last quite a long time and will have to be replaced no less than after 10 years.
Similar articles
rovnayadoroga.ru
Fastening the canvases
To minimize the length of the overlap, the laid geotextile sheets must be fastened together. The connection of geotextiles can be carried out using the welded method or the end-to-end stitching method. Welding a connection with a low-temperature torch will save material and carry out installation in a shorter time, and the stitching method does not require complex operations or any knowledge of instruments.
In the stitching method, anchors are used to secure the materials to the ground, which must be installed every 1.5-2 meters to ensure resistance to wind and maintain the tension of the material.
Read on topic: New cars up to 1 million rubles
Preparing the soil surface
Geotextiles are laid on prepared underlying soil; the surface must be leveled and cleared of vegetation, stones, and tree roots. The final operation before laying the geofabric should be soil compaction using a 7.5-ton soil roller. A durable woven geo-fabric 3-5 m wide with a density of 0.6-0.8 kg/m2 is laid on the prepared area of soil, the magnitude of the breaking loads is at least 80 kN/m. The canvas is treated with stabilizing and antiseptic impregnations. When working on wet and swampy soils, a geotextile with anti-filtration properties is used. The material is unpacked on a surface area prepared for flooring. The canvas is laid along or across the road strip. When laying longitudinally, the roll is rolled out to its full length. The canvas is leveled and, at maximum tension, secured with anchors. Anchors are installed along the edge of the strip every 2-3 meters. The next strip is laid overlapping, with an overlap of 20-40 cm.
Backfilling and compaction
The next step after fixing the canvases is backfilling with a structural layer from a height of no more than 1.2-1.5 meters, because if the material falls, it can destroy the integrity of the geotextile. At the same time, interaction with heavy vehicles on uncovered surfaces should not be allowed. Based on the characteristics of the base soil and bulk materials, the soil layer is compacted, which can be done either manually or using machinery.
Until the last layer is completely compacted, the geotextile should not be subjected to heavy loads; therefore, movement of equipment around the work area is allowed only if the backfill thickness is at least 200 mm. If the soil's ability to withstand large loads is insufficient, small-sized equipment with low pressure per unit area should be used.
To achieve best results, compaction should be done in layers. During the installation of geotextiles, it is recommended to constantly monitor the quality of the work performed in order to eliminate errors in a timely manner. If any sections of the fabric have been damaged, it is necessary to replace them or apply patches with an overlap of 50 centimeters to ensure their stability on the surface of the geotextile.
Laying geotextiles during the construction of foundations
The level of effectiveness of using protective geological sheets for building foundations largely depends on the exact adherence to the technology of laying the material. For each type of foundation, it has certain features. But before laying geotextiles under the foundation, you should study the basic principles:
- the surface of the soil or bulk material must be well compacted and horizontally leveled as much as possible;
- the overlap of adjacent canvases when laying is a strip of at least 200 mm, if there is a slope - twice as much;
- If possible, it is recommended to use a thermal method of joining the panels; otherwise, plastic or metal staples should be used.
A gas torch or blowtorch is used to weld the sheets. After sufficient heating, adjacent edges are placed on top of each other and pressed tightly. Concrete is not poured onto geotextiles. Before concreting, the canvas is covered with a layer of compacted sand 50-100 mm thick.
Monolithic strip foundation
A geological fabric with a density of 300 g/m2 or more is laid at the bottom of the trench before backfilling the underlying cushion. If a layer of gravel and sand is poured separately, and not as a mixture, then they should also be separated with geotextiles under a strip foundation with a density of 200-300 g/m2. This will prevent the sand from gradually washing out into the gravel layer.
The bottom layer of textile should be connected to the vertical fabric on the outside of the tape and only after that should the assembly of the formwork structure begin. With permanent formwork made of polystyrene foam, a vertical strip of rolled insulation is not needed, since the foam itself will provide sufficient protection.
After pouring the concrete mixture and setting it, the upper plane of the monolithic tape should also be covered with a cloth with a density of 150-250 g/m2. A higher density is not required in this case.
Precast concrete strip foundation
The difference between the protection and the monolithic structure is that the side wall of the tape is protected with geotextile, gluing it to the concrete surface using bitumen mastic. In this case, the edges of the side panel should extend beyond the edges of the wall and connect with other layers.
Slab bases
Strips of canvas are spread along the entire bottom of the pit so that they extend beyond the perimeter of the foundation by 150-200 mm. Then the formwork is installed, the reinforcement frame is assembled and concrete is poured.
After removing the formwork panels, the film is wrapped on the side ends and glued using bitumen mastic. The upper plane of the monolithic slab is not insulated, since it will be closed from external influences.
What geotextile should I use for a monolithic slab foundation? It is recommended to choose non-woven material with a density of 150-200 g/m2 as the material. Or tightly woven with a density of 200-250 g/m2. It will provide good protection for the structure and improve its stability.
Columnar and pile foundations
The pillars and piles themselves do not need to be waterproofed with geotextiles. But, if there is a basement floor, before installing the grillage, it is recommended to cover the leveled ground with a cloth and pour sand, gravel on top or fill the surface with concrete. After this, you can proceed to the installation of the grillage and basement walls.
As a protective material, you can choose non-woven film material with a density of 150-200 g/m2.
Laying asphalt
When laying asphalt, using a level, you need to determine the direction of the slope in the direction where the bulk of rainwater will collect and the storm drain will be located. The slope should not exceed 10 mm per 1 meter.
To select the thickness of the asphalt pavement, it is necessary to determine the degree of load on the surface. Depending on the loads imposed in the future, it is necessary to select a suitable layer thickness. So, for the adjacent area, a layer of fine-grained asphalt of 4-5 centimeters is quite sufficient. For more intensive use, an additional base layer of coarse asphalt is required. Laying asphalt should not be carried out in the rain, because the properties of the product are lost and the road will not be strong enough and stable enough.
If the established rules for using geotextiles are strictly followed, the asphalt concrete pavement will last quite a long time and will have to be replaced no less than after 10 years.
Read on topic: Construction of stone coverings
Geotextile consumption
In order to immediately process the entire area, you need to determine immediately before laying exactly how much material you will need. The rate of consumption must also be determined. The calculations are not difficult to perform, but you must first familiarize yourself with several important points.
So, initially you must characterize the conditions in which geotextiles will be used. After all, it can be used not only for soil reinforcement, but also to improve the quality of pipeline insulation. It is also often used during the preparation of drainage and filtration systems.
If you plan to use geotextiles during the preparation of water drainage, then in this case the size of the overlap should be 15 cm for each circle. Do not forget that during calculations the length of the pipe must be taken into account.
Installation of geotextiles on the base is performed a little differently. Therefore, other parameters are taken into account here. Depending on how flat and prepared the work area is, the margin can be about 20-30 centimeters. In addition, it is necessary to add a few more centimeters if the coating will be additionally reinforced with anchors.