What is geotextile
Woven geotextiles
Geotextiles are one of the most popular effective materials used for waterproofing building elements located in the ground. Geotextiles for foundations are made from polymeric materials such as polyester, polyester and polypropylene.
Geotextiles are made in two types: woven fabric and heat-treated non-woven film. Both types are produced either from one material or in a combination of several polymers.
The woven base gives the fabric a special plasticity. Thanks to this property, the material can be laid in the most complex places. The fabric base is better than thermotextiles and withstands fracture deformation well.
Thermally treated fabric has a higher density. It must be laid on soils with high humidity and high groundwater levels. Textile fabric, in addition to its insulating qualities, has reinforcing properties.
Main functions of geotextiles
Polymer sheets are used as:
- reinforcement of the foundation base;
- a drainage layer that ensures moisture removal from the soil;
- separating layer between the soil and the sand cushion, crushed stone layer.
Reinforcement
Geotextile under the cushion
Before laying the sand cushion, a layer of canvas is laid on the ground. This creates an elastic layer that evenly distributes the load over the entire surface of the foundation base. The reinforcing properties of geotextiles significantly increase the bearing capacity of weak soils.
Geotextiles with a density of 350-600 g/m2 are used to uniformly distribute the load on the soil base.
Drainage layer
Geotextiles are a reliable barrier to the penetration of moisture and groundwater into the structure of foundation structures of buildings and structures. The geotextile layer is a kind of drainage system from the foundation structures. For this purpose, material with a density of 200 g/m2 is used.
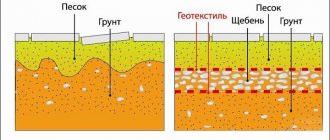
Geotextile separating layers
A layer of geotextile laid between the soil and the sandy base of the foundation prevents the process of siltation of the sand layer from developing. Laying sheets of polymer fabric between the bulk layers of the foundation cushion will prevent them from mixing. This will not reduce the load-bearing capacity of the pillow and will preserve the drainage properties of the foundation base.
Technology for laying waterproofing from geotextiles
Let's consider the technology of laying geotextiles for various types of foundations:
Strip monolithic foundation
Design of laying textiles in a strip base
A layer of polymer film with a density of 350 to 6oo g/m2 is laid along the entire length at the bottom of the dug trenches. Such material will create a reliable barrier against the passage of moisture from the soil to the building structures. At the same time, dense textiles will provide strong reinforcement for the underlying layer of the foundation. After installing the formwork, waterproofing is attached to its walls, extending its edges beyond the upper edges of the fences.
After dismantling the formwork, check the integrity of the waterproofing coating. The question arises: what type of geotextile should I choose for laying on the upper surface of the monolithic tape? Of course, it is better to use heat-pressed fabric with a density of 250 g/m2. It doesn’t make sense to use thicker fabric because it won’t do anything other than increase the cost of construction.
Precast concrete strip foundation
It differs from the waterproofing device of a monolithic tape in that the polymer film is attached to the side surface of a prefabricated reinforced concrete foundation using bitumen mastic or other adhesive.
The edges of the film coating must extend beyond the perimeter of the foundation slab by 100-150 mm.
Pile foundation
Covering the soil base on a pile field with geotextile makes sense when constructing a basement floor. Before installing the grillage, the soil surface between the tops of the piles is carefully covered with a textile polymer film. Then they choose what kind of waterproofing coating to make. They make either sand, crushed stone preparation, or a concrete screed. Then the plinth fencing is installed.
Slab foundation
Geotextiles under a monolithic foundation
A “carpet” of geotextiles is laid over the entire area of the excavated pit for a monolithic foundation concrete slab. Which geofabric is better to choose? Since the surface of the soil base has practically no bends, thermo-pressed film with a high density is chosen for waterproofing and reinforcing the base of the slab.
After installing the underlying slab cushion, a layer of textile for drainage purposes is laid on it. The density of such a film is sufficient within the range of 200-250 g/m2.
Blind area
The blind area is a closed surface covering around the house. A durable protective belt protects the base and foundation of the house from the penetration of natural precipitation (rain, melted snow) into the structure of underground structures. A protective belt around the building reduces possible swelling of the soil due to freezing. The blind area around the house should be made with a continuous strip.
Geotextiles are laid on a prepared cushion around the base. The edge of the film adjacent to the house is brought out just above the marked line of the blind area surface. The places where the waterproofing meets the walls are coated with hot bitumen and an expansion joint is formed.
What geotextiles are needed for the foundation: choice of density
The main criteria are operating conditions and expected loads, which are completely determined by soil parameters and the weight of the structure. The main characteristics of the fabric depend on them: surface density, tensile strength, water permeability, filtration coefficient. There is simply no prescribed method for choosing geotextiles; in each case a different brand is required; laying the first one available is the wrong approach.
If it is impossible to consult specialists, they start from such characteristics as surface density (g/m2). The lower recommended limit for strengthening the soil under the foundation depends on the method of manufacturing geotextiles: it varies from 350 to 600 g/m2 for needle-punched non-woven fabric and is at least 200 for thermally bonded fabric. If there is a risk of flooding and high groundwater level, it is recommended to choose denser types; if there is a possible displacement of soils, lay fabrics that are as resistant to tearing as possible. If there is a significant content of fine and clay particles, the use of high-density thermally bonded material in drainage systems, on the contrary, is impractical.
The manufacturers deserve special mention. High-quality geotextiles for foundations are offered by both foreign and domestic factories; among the first are the brands Terram, Typar and Polyfelt. Russian products with equal characteristics are cheaper; Dornit, Geospan, Stabitex, Lavsan Geo have the best reviews. When calculating the amount of material, it is important to take into account the amount of overlap. The geotextile is sold in rolls up to 6 m wide; choosing the appropriate option is quite simple.
During the installation process, it is important to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations; standard step-by-step instructions for laying geotextiles include the following steps:
- Preparatory: leveling the soil, removing tree roots, filling large cracks and voids, compaction. If necessary, a little sand is added and compacted to certain areas. The smoother the surface, the better.
- Unfolding the canvas. It is important to lay geotextiles correctly - with an overlap of 30 cm on a flat base, and within 40-50 cm on a poorly prepared surface or the risk of ground failures. At this stage, material displacement is avoided; a new layer can only be laid on a well-leveled lower one.
- Connecting joints: stitching with staples or welding. In order to save money, many builders advise choosing the second method; it allows for a reduction in the amount of overlap of adjacent sheets to 10 cm with good strength of the seams. But the process becomes more complicated: all edges are heated with a special burner, the joint is pressed down and held for some time. Another option is to use a bag sewing machine.
- Laying the next layer: earth in drainage systems, sand or crushed stone. When forming the layer using special equipment, it is important to keep the geotextiles and joints intact and without displacement.
At the end, the edges are wrapped under the blind area of the building or covered with crushed stone or sand. The side walls of the tape or slab are not wrapped with geotextiles; other building materials are provided for their waterproofing. The main purpose of a margin of 1-2 m is to ensure correct connection of the foundation structure with the ground and dampen loads.
In some cases, geotextiles are advised to be laid in several layers and even to combine materials, but due to the inevitable increase in costs (the minimum price per m2 for brands with a suitable density is 20 rubles), it is better to check this point with specialists. The latter also applies to the chosen joining method and the amount of overlap.
All types of geotextiles belong to the group of materials that can simultaneously isolate individual technological layers from each other, reinforce the structure and allow moisture to pass in only one direction. Geotextile fabric is one of the most popular insulation materials in modern construction. Why geotextiles are needed in the foundation, how to choose and use it is described in this article.
The most popular types of geotextiles
Among geotextiles from domestic manufacturers, 3 brands can be distinguished:
- Stabilex consists of 100% polyamide. It has high tensile strength. Laying of this material provides reliable reinforcement of the soil base;
- Geospan has excellent characteristics and low cost;
- Dornit has high elasticity and resistance to mechanical damage.
We recommend watching a video about choosing the thickness of textiles depending on the base used.
All domestic geotextiles have good characteristics and low prices compared to foreign analogues.
How to lay geotextiles under the foundation
Preparatory work
Before laying geotextiles, it is necessary to dig a trench under the foundation, level it and compact its bottom well.
Laying the material
Geotextile rolls are rolled out along the length of the foundation. This is done manually. It is recommended to lay the canvas as wide as possible, with a margin of 1.5 ± 0.5 m. This will allow it to better absorb soil loads. On very weak soils, the material can be laid in several layers.
Geotextile bonding
When using geotextiles in foundations on dense soils, the material can be joined by stitching. To do this, use a bag sewing machine, or, less often, a household machine. Another way of joining is to overlap the fabric.
Backfill
The remaining layers of the base are laid on top of the geotextile.
Geotextiles are rolled polymer-based building materials designed to strengthen the soil, provide drainage and separate building layers. Its use protects the foundation of buildings and extends their service life; the maximum effect is observed when laying it on clayey, floating or weak soils, soils with a high organic content. Installation is not difficult, but requires following a number of rules: it is important to choose the brand of the desired density, unfold it on a flat surface with overlap and fix the seams. The geotextile must be laid at the stage of excavation and preparation for concreting.
Description of material, purpose and functions
The basis is polyester, polyester and propylene fibers and their combinations. Depending on the manufacturing method, woven and non-woven fabrics are distinguished, the latter, in turn, are divided into needle-punched and heat-treated. Thermally bonded geotextiles are considered the most durable; with the same density as other brands, they will last longer. All types are united by:
- Ability to withstand high mechanical loads without rupture or deformation. It is this that allows geotextiles to protect the base from plant roots.
- Good elasticity without loss of strength properties.
- High resistance to biological threats, alkalis, acids, and other active substances.
- Environmentally safe, free of toxins.
- Moisture resistance, moisture transmission without accumulation. Due to this property, geotextiles are recommended to be installed in drainage systems around or under the building: they protect pipes from silting without impeding the movement of water.
The material simultaneously performs several functions; it is recommended to buy it when building foundations on any type of soil with the exception of rocky ones. In particular, it is recommended to lay it for the purpose of:
1. Soil reinforcement. If it is necessary to strengthen the bearing capacity of soil layers and reduce the load on the foundation, geotextiles are recommended to be laid along the entire bottom of the construction pit. In this case, the area of the laid material exceeds the size of the building (from 1 m and above in each direction). Taking into account the last condition, it is extremely important to choose an option not only with the required density, but also to correctly calculate its quantity; end-to-end flooring does not fulfill the task of reinforcement.
2. Additional protection from groundwater and arrangement of drainage. The geotextile fabric freely allows moisture to pass through, trapping small particles of silt; its covering around crushed stone with pipes placed inside protects them and increases the efficiency of drainage. The horizontally deployed canvas along the bottom interrupts the movement of moisture through the capillaries, that is, it reduces the volume flowing to the foundation. You should not expect that geotextiles can replace full-fledged roll waterproofing; their functions are different, but they provide protection for sand cushions or concrete from direct flows of groundwater. The higher the density of the brand, the stronger it will be.