New materials are constantly appearing on the construction market, but traditional solutions do not lose their popularity and continue to be used to solve various problems. These include heavy concrete, which is used in a wide variety of cases. On their basis, floor slabs, trusses, lintels, reinforced belts, huge blocks and other structures are created.
Advantages and disadvantages
Understanding the question of what heavy concrete is, you need to familiarize yourself with the advantages of its use.
These include:
- Easy to serve and install.
- Long service life.
- Increased strength properties after drying.
- Affordable price.
- High density.
- Compliance with fire safety requirements.
Positive qualities include resistance to moisture and negative temperatures.
The list of minuses includes the following items:
- The need to install additional thermal insulation coating.
- The need for regular wetting with water to obtain optimal strength properties.
- The need for finishing work.
- A number of difficulties in organizing communications.
Areas of application
The specific properties of heavy concrete make it possible to use it to solve large construction problems, including:
- Arrangement of reinforced concrete structures. To increase strength properties and reduce hardening time, special mineral fillers are introduced into the composition and subjected to heat treatment.
- Construction of hydraulic structures. This area requires special attention and responsibility, so high demands are placed on the class of material. To equip an industrial facility with an increased degree of stability, especially hard concrete is used. It is characterized by a long service life and resistance to external factors.
- Coating of highways and airport roads. Heavy concrete, the density of which is quite high, can withstand heavy loads from massive equipment, and its resistance to negative temperatures contributes to the construction of a reliable and durable coating.
- Pouring foundations for industrial facilities. Due to its improved strength properties, the material can be used to construct foundations for large buildings.
- Laying walls and ceilings of premises that have high requirements in terms of reliability. These include bank vaults, government facilities, chemical plants and factories.
Heavy-duty concrete is required for all structures that face heavy loads. Due to its special properties and characteristics, its popularity remains high, despite the emergence of new materials and solutions.
Types of concrete
Heavy concrete, the composition of which is based on higher grades of Portland cement, can be intended for different purposes.
Depending on the scope of application, there is the following classification of material:
- Highly durable. During the mixing process, the best cement mixture, clean sand and coarse crushed stone are added. Production is carried out using vibration equipment, which gives the concrete the increased density of heavy concrete. In order to increase strength, additional components - plasticizers - are added to the composition.
- Reinforced concrete. Used for the construction of reinforced concrete blocks, floors and other reinforced concrete structures.
- Fast setting. It contains a quick-hardening cement mixture and additional elements, including hydrogen chloride. The presence of additives helps reduce the hardening time without losing the quality of the final product.
- For hydraulic structures. It is a special type of concrete that is used for the construction of structures in damp environments. The material is not affected by water, and it retains its original appearance even after several years of intensive use.
- Road. It is used to cover highways and is resistant to heavy technical loads.
- Cast. It is created on the basis of fast-hardening cement with plasticizers and a high liquid content in the composition.
- Fine grained. It is created on the basis of cement stones without the presence of large and heavy components. It is in demand when constructing buildings with thin walls.
- Acid resistant. It is resistant to aggressive substances and acids, therefore it is used for the construction of chemical-type premises.
- Heat resistant. Not afraid of prolonged exposure to high temperature environments. Industrial furnaces operating at temperatures up to 12000°C are built on the basis of heat-resistant concrete.
- Polymer varieties. During the production process, raw materials are impregnated with special resins and polymer additives. This provides an increased degree of strength and reliability.
- Decorative. It is produced using dyes and special fillers, such as natural-colored marble stone. The material is in demand for the construction of alleys and parks, decorating garden paths and borders, designing facades, etc.
There are also special types of concrete, which differ in different composition and class.
Types of composition
Road view
Used for rebuilding, repairing and reconstructing roadway surfaces. There are different types of road concrete:
- Compositions for coatings that have one layer. They are used to create a top layer and when laying multi-layer canvases.
- Material for laying the bottom layer. Used for two-layer coatings.
- Hardened. It is used to cover improved roads, sports routes, and airstrips.
Plasticized Portland cement will be able to provide the finished material with the desired properties.
Road concrete is characterized by different compositions and technical characteristics, it all depends on the intended use. The basis of the mixture is plasticized or hydrophobic Portland cement. An important criterion is the brand of the mixture used; it should be no lower than M400, in rare cases - M300.
High strength
This type includes mixtures under the brands M600 to M1000. The minimum strength indicators are not less than B70. It is used for construction in various directions. Qualities and characteristics depend on the following indicators:
- Binder. Particularly active Portland cement. The density of the mixture is 22-27%, resistance is 400-600.
- Sand. Coarse or fine quartz feldspathic sands are used.
- Large filler. Crushed stone is used, the grade of which is selected depending on the specifics of the operation.
- Silicate additives. Silica dust is added. Concrete with strength C54/66, C60/75 does not require such additional substances.
Refractory
Often this material is made with a cellular structure.
Heat-resistant compounds are the most popular in the construction of industrial structures. They are characterized by maintaining operational and technical parameters even in close contact with high temperatures. Refractory concrete is divided into the following subtypes:
- heavy;
- easy;
- cellular.
Concrete varies according to the influence of temperature according to the following criteria:
- shutter speed up to 1590 degrees;
- resistance up to 1790;
- stability more than 1800 degrees.
There is a difference in use between structural and heat-insulating refractory concrete.
Reinforced concrete
A material that contains a concrete-cement mixture with metal elements inside. It is distinguished by its interaction: concrete remains resistant to the moment of compression, and steel reinforcement to the effect of tension. Determining factors:
- strong adhesion of concrete and metal parts;
- the same coefficient of resistance to temperature changes;
- resistance of the material to corrosion.
Fast-hardening
Pozzolanic cement may also have a place in such materials.
The composition is characterized by increased strength even without a pre-stabilization stage. The qualities and properties of the mixture are achieved thanks to the quick-hardening cement included in the composition and various additives that accelerate the hardening process. The most commonly used are pozzolanic cements, Portland slag cements or Portland cements with the addition of calcium chloride. For a concrete mixture, the percentage of the auxiliary substance should not exceed 4% of the total composition, and for reinforced concrete - 2.5%.
Hydraulic
It is used for the construction of dams, hydroelectric power stations, piers, breakwaters, sewage treatment plants and bridges. Divided into three main types:
The construction of dams is impossible without this material.
- Underwater. Location: under the water column.
- Periodic. It is located in an ever-changing environment where the water level and interaction with moisture are not stable.
- External. Located above the water level.
Polymer concrete
A new type of concrete, the basis of which is resins, which replace silicates and cement in production, namely:
- phenol-formaldehyde;
- epoxy;
- urea-formaldehyde;
- furanic
The material intake can be supplemented with gravel.
Included components:
- mineral chips;
- crushed stone or gravel;
- sawdust;
- other processed products.
Characteristics
The properties of heavy concrete directly depend on the raw materials used in the process of mixing the mixture and the scope of application of the material.
Modern classification is based on the following characteristics:
- By class.
- By concrete grade.
- According to GOST.
- By cost.
By class
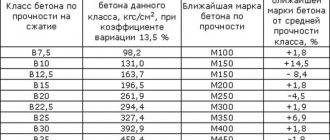
Existing classes of concrete differ in both performance characteristics and quality. According to GOST standards, a whole line of materials with different grades is distinguished. It includes solutions such as B3.5, B5, B7.5, B10, B12.5, B25, B30, B70, B90, B100, etc. GOST standards also allow the production of intermediate classes, such as 27.5.
The listed varieties are characterized by special properties that need to be paid attention to when choosing or creating a concrete solution. The main characteristics are specified in the standard.
Concrete grades
Brand identification is determined by compressive strength and axial tensile strength. Depending on these properties, the following brands are distinguished:
- M50 and M100 are characterized by low compressive strength, which does not allow them to be used for a wide range of construction works. The main area of application is landscaping.
- M150 - the brand is in demand in the production of screeds and blind areas.
- M200 is considered the most popular material for the restoration of foundations, platforms and stairs.
- M250 and M350 are used for the construction of monolithic buildings and other concrete structures.
- M350 demonstrates an increased degree of strength and is used in the manufacture of airfield slabs.
- M400 is used to create secure bank vaults, hydraulic structures and bridges.
- M500-M600 are used in the construction of the subway.
There are also particularly strong compounds with grades up to M800, but their use is quite rare.
GOST
Each composition of heavy concrete must meet certain GOST requirements. Any deviations from the given rules are unacceptable. When producing this building material, you need to take into account the GOST 26633-2012 standard, which provides for the following values:
- Frost resistance - F500.
- Water resistance - W6-W12.
- Shrinkage during setting is 0.15 mm per 1 m.
- Tensile strength - Bt10-Bt40.
Price
The cost of the solution is determined by a number of factors, including the price of all components. While water, crushed stone and clean sand are quite easy to find, purchasing plasticizers and other additives will require some effort and financial investment. The price tag also depends on the brand of the mixture. Production of 1 m³ of solution under the M100 brand will cost 2,400 rubles.
The use of super-heavy concrete in private construction is not justified, which is due to the high cost of all components. The solution provides for the presence of rare elements.
Types of heavy concrete
Heavy concrete, starting from grade M250, has a density of more than 1800 kg/m3. If the compressive strength of the composition is 262 kg/cm2, then the closest grade can be determined, namely M250. According to GOST 25192-2012, the index is indicated in an extensive list of building material grades, starting from M50 and ending with M1000. It is more convenient to designate the material’s compression resistance number 262 as 250, therefore, in accordance with GOST, the concrete packaging will conventionally indicate the M250 grade.
The scope of application of heavy concrete according to GOST 25192-2012 is large-scale construction of objects, including multi-storey buildings, floor slabs, fences, stairs, swimming pool bowls, airport runways. Concrete grades of different strengths in accordance with GOST 25192-2012 are suitable for construction in conditions of high humidity and for the construction of foundations for industrial buildings. Heavy concrete is characterized by the following properties:
- high strength;
- frost resistance;
- fire safety;
- waterproof;
- chemical resistance.
READ ALSO: Preparation of concrete - with a hand mixer, in a concrete mixer and concrete delivered from the plant.
Proportions per 1m³. The composition of reinforced concrete, its grade and strength are regulated by GOST 13015-2012. The monolith includes steel reinforcement and the mortar itself. Heavy concrete includes steel concrete, which according to GOST has increased strength and contains Portland cement M500, steel shavings and quartz sand.
Basic properties
The main properties of concrete include:
- Strength.
- Water resistance.
- Porosity.
- Frost resistance.
- Thermal conductivity.
- Fire resistance.
Strength
A key indicator of high quality concrete is its strength. Heavy varieties must cope with intense loads, so high demands are placed on strength properties.
They must be observed both at the stage of mixing the mixture and when solving all construction problems. Since concrete is considered a non-uniform material, fluctuations in strength are considered normal.
Water resistance
Concrete is considered a waterproof material that does not lose its initial characteristics after prolonged exposure to a humid environment. Water resistance indicators depend on the ratio of components in the composition and are depicted under the letter W. The value range varies from W2 to W20.
Porosity
Even the most durable brands of concrete have small cells, which determine a property such as porosity. The intensity of porosity is determined by the type and volume of filler, as well as the ratio of water and cement. The degree of vibration treatment and a host of other factors are also taken into account. The base value varies from 6 to 15%.
Frost resistance
The degree of frost resistance indicates the material’s resistance to the destructive effects of negative temperatures or loads when moisture thaws after a long winter. Frost resistance refers to the number of freezing and defrosting cycles. The more such cycles, the higher the indicator. Commercially available brands have values from 50 to 300 cycles.
Thermal conductivity
The weak point of concrete is its thermal conductivity. Despite the improved strength properties and long service life, the material is subject to severe freezing and cannot retain heat inside itself. As density increases, thermal conductivity increases.
Fire resistance
Fire resistance is considered the most important property of a material, which determines its resistance to ignition. When exposed to temperatures up to 200ºС, strength characteristics are reduced by 30%. When the temperature rises to 500ºС, the structure deforms.
Heavy concrete.
Concrete with high grades, starting from M500 and higher, is used for the production of reinforced concrete structures that will initially be stressed, since heavy concrete on large dense aggregate has low creep and shrinkage and therefore the loss of initial stress in steel reinforcement is less. Consequently, the safety margin in such a structure is much greater than that of any cellular concrete or concrete with porous aggregate.
In addition, heavy concrete has high strength and therefore protects steel reinforcement well from corrosion, and this is very important if the reinforced concrete structure operates in an aggressive environment and under prestress.
For some special types of heavy concrete , special requirements for tensile strength are imposed. Design grades for the tensile strength of concrete can be: 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40. At the same time, high grades are applied to such concrete as: road, airfield, technical and others.
Due to their high density and strength, heavy concretes have excellent resistance to surface wear; this property is especially important for road concrete and for concrete used to pour the floors of industrial buildings.
In addition, heavy concrete has good protective properties against radioactive radiation, and therefore they are widely used in biological protection against radiation in nuclear reactors.
Heavy concrete has one big drawback: high thermal conductivity.
Calculation of composition and batching
When making calculations for the future mixture, it is necessary to adhere to the recommended values and requirements, since they determine the strength and reliability of the structure. Experts offer ready-made proportions that allow you to correctly calculate the ratio of all components:
| Concrete grade | Quantity of concrete from 10 liters of cement (l) | Composition of volume per 10 l (P/Sh) | Total mass composition (C/P/Shch) (kg) |
| 450 | 29 | 10/22 | 1/1, 1/2,5 |
| 400 | 31 | 11/24 | 1/1,2/2,7 |
| 300 | 41 | 17/32 | 1/1,9/3,7 |
| 350 | 43 | 19/34 | ½,1/3,9 |
| 200 | 54 | 25/42 | ½,8/4,8 |
| 150 | 64 | 32/50 | 1/3,5/5,7 |
| 100 | 78 | 41/60 | ¼,6/7 |
When kneading with your own hands, you must follow the following instructions:
- We prepare a container where the mixture will be mixed.
- We place water in the container (in the case of other types of concrete, filler is initially placed).
- We add cement, sand and filler to the composition, continuing to mix the solution.
- Next we add additional components and plasticizers, if necessary.
- The solution is mixed until a homogeneous consistency free of lumps is obtained.
By following this guide, you can make a high-quality concrete solution that will meet all requirements and standards.