Application benefits
- the liquid present in the mixture freezes at lower temperatures than normal, allowing the solution to set;
- the solution becomes more plastic - it is easier to form individual parts of the structure;
- reinforcement in reinforced concrete structures does not oxidize due to corrosion inhibitors present in the additives;
- the water resistance of reinforced concrete increases;
- the mixture becomes strong in a shorter time.
Concrete hardens faster in cold weather - one of the advantages.
After adding the additive to the solution, the mixture becomes more dense due to the saturation of micropores in the concrete with carbonated calcium hydroxide, and it becomes easier to pour it into the mold. The strength of the structure is doubled. 18 hours are enough for the concrete structure to fully harden. Extraction takes place without damaging the integrity of the concrete. High-quality PMDs do not allow the appearance of “salt” on the surface.
The use of antifreeze additives allows you to:
- mix the solution with low-grade concrete, reducing material costs;
- make thinner layers of concrete without risking the quality of the structure (due to increased strength) - the solution is saved;
- concrete will not need treatment with waterproofing agents.
Return to contents
Bricklaying in winter with the construction of a greenhouse
The heater is a kind of thermos for preserving the heat generated during the hardening of mortar compositions. Usually it is a wooden frame covered with tarpaulin or thick plastic film. To maintain the required temperature around the clock, heating devices (heat guns, stoves and various types of heaters) are installed inside.
A favorable moisture-thermal regime is created by additional water humidification of the structures. The method provides guaranteed strength of the masonry, but is expensive to implement. Therefore, it is usually used in the construction of small buildings.
In general, working with concrete in harsh conditions of low temperatures entails additional difficulties, but it is impossible to stop construction for six months every time autumn comes, and besides, winter work also has significant advantages:
- Winter discounts on building materials and the decline in demand for labor make it possible to save money.
- In winter, foundations can be concreted on weak or brittle soil.
- Frozen access roads make it possible to easily deliver heavy equipment and materials to a construction site.
In order not to be disappointed in the results of construction activities that are carried out at negative air temperatures, it is enough to pay attention to the following recommendations:
- It is prohibited to use building materials covered with snow, frost or ice for masonry.
- All components of the future solution, including antifreeze additives and plasticizers, should be stored in dry, ventilated areas at room temperature.
- Regardless of the composition of the mortar and temperature conditions, it is recommended to carry out masonry work as quickly as possible in winter. The lack of delay allows the substances to set faster.
- When going on a break, the rows of masonry must be insulated with plastic film or other suitable material suitable for the role of an effective temporary insulator.
- As a basis for preparing the solution, you should use cement of a grade not lower than M-50. Mixing the components, even if “antifreeze” is used, should be carried out in a warm room.
- If it is necessary to work at low temperatures, it is better to give preference to purchasing ready-made solutions to which antifreeze substances are added in optimal proportions at the production stage.
When a house is being built, of course, you want the process to go faster, without stopping even in winter. In order to justify working at sub-zero temperatures and understand how brickwork reacts to frost, we will consider the physical and technical nuances of masonry and ways to “bypass” the climate.
In the construction of brick walls, in the classic version it is supposed to use mortar. In order not to discover America, you can use ordinary cement mortar:
- Sand (quarry; river - expensive option).
- Cement (grade 400 - for any work).
- Water.
Among the three components of cement, only water prevents winter construction. This happens because the bricks in the masonry are not bonded with mortar at subzero temperatures.
When the temperature drops below freezing, water turns to ice. As a result, the desired physical reaction does not occur between the ingredients of the solution.
Theoretically, it is possible to lay the mortar, but in this case it will freeze to its natural state of hardness, and therefore there will be neither the strength of the masonry nor the binding of the mortar.
Thus, when the temperature drops, it is impossible to lay bricks according to standard work patterns. However, there are other options for the composition of solutions and winter work.
Properties of the solution
In addition to various methods, chemical additives are also required. Basically these are special anti-cold products.
During construction, special nests are created in the seams, plugged with plugs, and temperature measurements are constantly taken. It should be taken into account that a brick, for example, is solid, conducts cold quite slowly, so there is time for the mortar to set.
While the exothermic reaction is taking place, adding heat, the solution is “pressed” by the brick from below and above.
As a result, we obtain a table in which the temperature of the solution corresponds to the air measurement indicators.
- 5 degrees - minus 10 degrees;
- 10 degrees – minus 10-20 degrees;
- 15 degrees – minus 20 degrees.
Freezing method
In this case, even despite the negative temperature, brick laying is carried out in the open air, while the mortar has a fairly high temperature.
This method is based on the fact that the mortar in the seams is frozen and gradually hardens in the spring (partly directly during the laying process). Thus, thermal energy is constantly released during the chemical interaction of cement and water.
Important! This method allows you to build walls with a height of no more than 15 m. Given the technical safety standard, the strength can be calculated in accordance with the spring period of hardening of the cement mortar.
Chemical additives
Another way is chemical additives. They perform several functions:
- The freezing rate of water decreases several times at sub-zero temperatures.
- The solution sets and hardens faster, but does not lose its qualities.
Basic additives that can be used if given instructions:
- Potash (reduces the hardening time of the solution at temperatures below minus 25 degrees). When the solution sets quickly, it loses some of its properties, so you can add yeast mash - 1%.
- Sodium nitrate (not less than 15 degrees).
Important! Most modern additives are poisonous, and therefore you need to follow safety rules and work exclusively in protective clothing.
Thermos method
Using this method, it is possible to carry out work at sub-zero temperatures. If using the standard method it is possible to carry out work at temperatures down to minus 5 degrees, then when it is further reduced, either chemical additives or other working methods are required.
The thermos method is that the cement mortar releases heat during laying, sufficient to maintain the process of good hardening. In addition, two conditions must be taken into account:
- Before installation, the brick is heated. For this you need an ordinary blowtorch. Both solid brick and double silicate M 150 are subject to heating.
- The masonry is covered with a layer of thermal insulation every few square meters or rows.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to tighten windows for the winter
This method is quite simple, so if you need to continue construction when cold weather sets in, then even a beginner will not have any difficulty using it. The main thing is that you can do everything yourself, conveniently and quickly.
Electric heating
The essence of the electric heating method is to attach sewn-on electrodes on the side of the outer wall. An electric current is passed through the cement mortar, thereby heating it.
When the building mixture warms up, the brick receives heat, resulting in a warm island being formed on the wall. Thus, without changing the physical properties of the solution, the masonry gradually hardens.
Advice! When it is necessary to use electric current during construction, it is important not only to provide insulation, but also to have a heated base.
The question of what temperature is optimal for laying bricks becomes relevant in cases where it is impossible to conduct electricity or when there are no chemical additives. But at the same time, construction often stops altogether in winter.
This is especially important in the private sector, since engineering networks and communications need to be installed there. The optimal temperature for work is up to minus 5-7 degrees; if it is further reduced, the above methods should be used.
However, the question of temperature for masonry will cease to be acute when there is ordinary salt. If you use it, work continues at any negative temperature. Moreover, this effective method is cost-effective because it is inexpensive.
On the other hand, in the future, excess salt may protrude from the wall. In this case, the facade will need to be repainted several times.
All these methods help in construction virtually all year round. Supporting information can be found in the video posted for this article (also on how to prepare a solution during construction in winter).
Experts do not recommend performing external finishing work on a newly erected wall in winter. It is better to postpone this process to the spring, and at a time when the constructed structure has completely thawed. At the same time, it is possible to plaster finished facades built in summer or autumn (for example, from aerated blocks or ceramic bricks).
Before plastering, the surface must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt, snow, ice and frost. All layers of plaster should be applied within one day, performing the next one immediately after the previous one has thickened slightly. The main thing is not to forget to add anti-frost additives to the composition. It is necessary to introduce “antifreeze” even if the outside air temperature drops below 5 °C.
Where is it used?
Antifreeze additives are used in the construction of structures:
- monolithic reinforced concrete;
- with off-design reinforcement, a layer of mortar of more than half a meter;
- prestressed reinforced concrete;
- lightweight concrete;
- plaster mixture;
- paths;
- bridges;
- oil and gas production platforms;
- dams, dikes.
Before adding antifreeze, a test is carried out to determine:
- oxidizing effect on concrete;
- formation of “salts”;
- speed of setting;
- strength.
Return to contents
Concreting technology in winter conditions
The first condition when building walls in the cold period is that before laying, the brick or block must be cleared of snow, ice or frost. The second important rule is that cement and the finished mixture must be stored in insulated containers. Moreover, it is impossible to warm up a slightly set solution. Therefore, it is very important to ensure high laying speed and rapid compaction of the underlying rows with the upper ones.
The solution is prepared at subzero temperatures in heated rooms, using cement grade M50 or more. Large lumps (more than 1 cm) and pieces of ice are not allowed in the sand.
Finally, in the spring, during the thawing period, it is necessary to monitor the strength and stability of the wall made in winter. Indeed, as the temperature rises, the masonry also thaws, and small sedimentary phenomena and microcracks may occur. Therefore, as during masonry, you should check the verticality of the structures every 2-3 days, and if a minimal deviation is detected, you should immediately install struts and supports made of wooden logs or metal pipes, which will prevent further displacement.
Another way to combat uneven settlement is the preliminary installation of supporting elements and forced thawing of the wall during early spring using air heaters, electric heaters or heat guns located inside the building. To do this, it is necessary to raise the room temperature to 30°C and maintain it for several days.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Sauna stoves with a heat exchanger for heating
When laying in winter, it is especially important to maintain the thickness of the mortar and maintain the level
Failure to follow the rules for preparing mortars and masonry will, at a minimum, lead to the formation of efflorescence, and at a maximum, to the appearance of cracks
During breaks between work, you need to cover fresh masonry
As part of the work project, activities are developed that ensure:
- Preventing concrete mortar from freezing during transportation, laying and compaction.
- Prevention of freezing of freshly laid concrete until critical strength is achieved.
- Favorable heat and humidity conditions for strengthening of hardening concrete.
The finished concrete mixture supplied to the construction site must have a temperature of at least 5°C. To do this, mixing is carried out in warm (up to 70°C) water, and the filling materials are heated.
Surfaces for concreting and reinforcement must be heated close to the temperature of the concrete solution, for which warm or hot air is used, but not steam or water.
When transporting the finished concrete mixture for a long time and it is impossible to use heating, antifreeze additives are used.
There are two main methods of winter concreting:
- warm concrete;
- cold concrete.
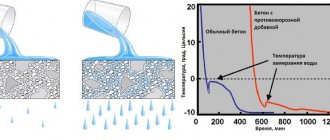
Cold concrete is concrete that will harden without heating. To ensure its hardening, special antifreeze additives are designed to reduce the freezing point of water and at the same time accelerate hydration reactions so that the amount of unbound water in the solution decreases as quickly as possible.
Widespread antifreeze additives are electrolytes, Na and K salts, but their use has some limitations:
- sodium salts are not used in reinforced concrete, as they lead to corrosion of the reinforcement;
- some types of Portland cement (for example, highly alkaline or made from clinker with a high content of aluminosilicates) are not used in conjunction with electrolytes;
- sodium and potassium salts are not used in mixtures with potentially reactive rock filler;
- electrolyte salts should be tested experimentally for the formation of efflorescence.
Modern complex antifreeze additives do not have the disadvantages of electrolyte salts, provide the ability to carry out concrete work at low temperatures and have a complex effect (not only antifreeze, but also plasticizing and others).
Warm concrete is concrete that, after laying, is subjected to various heating and heating procedures.
During home construction, concreting in conditions of negative temperatures is acceptable for objects of low importance.
For independent work, use kneading in heated (not higher than 70°C) water.
The order of laying the components of the concrete mixture is changed: first, coarse aggregate is poured into the water, then sand and cement.
At home, the use of heating concrete or installing greenhouses is not profitable; special anti-frost additives come to the fore, which make it possible to successfully carry out concrete work in winter.
In winter, to lower the freezing point of free water, salt (sodium chloride) or other sodium and potassium salts, which act as electrolytes, are added to the concrete solution.
The use of salts can lead to corrosion of reinforcement and the appearance of efflorescence on finished concrete. The best option is to use complex antifreeze additives and plasticizers.
Types of additives
High-quality additives for concrete mortar allow it to harden in severe frosts up to 35 degrees. Additives are divided (by chemical effect): superplasticizers, accelerators, mobility regulators that increase frost resistance, modifiers, complex ones.
Return to contents
Plasticizers
Plasticizers - naphthalene sulfate, melamine resin sulfate, organic polyacrylates. They have a plasticizing effect on the solution. Does not require large water consumption. Makes the solution more durable, moisture-proof, concentrated. The mixture is easier to apply - it can be poured in an even layer. Saves energy costs and water. The use of plasticizers allows the mixture to be placed in a mold with high quality, without the formation of voids. Microparticles of concrete solution retain moisture better.
Return to contents
Strengthening
Hardening accelerators - aluminum sulfate, iron sulfate, calcium nitrate, calcium chloride. They act by reducing the hardening time of the solution. When concrete sets, it loses its plasticity, and when it hardens, it gains strength. Their effect is designed for the first three days of drying. During this period, the supplement has the highest level of effectiveness. The class strength of concrete also increases.
Return to contents
Mobility regulators
Substances that allow you to extend the period of use of the finished solution in conditions of increased air temperature and transportation.
Return to contents
Frost-resistant
Frost-resistant additives allow construction work to be carried out at sub-zero temperatures.
Types of antifreeze:
- P – calcium carbonate increases the rate of hardening at thirty degrees below zero;
- NC – calcium nitrate;
- M – urea;
- M NK – a mixture of calcium nitrate with urea;
- CA is the result of a combination of hydrochloric acid and calcium. Causes metal oxidation and is not used to create reinforced concrete structures.
Return to contents
Corrosion resistant
Modifiers are used to protect concrete structures from oxidation and frost. Thanks to additives, they last longer.
Return to contents
Complex
Concrete can be improved in different directions by several additives at once. PMD of complex action increases operational characteristics, has a positive effect on reinforcement, and strengthens reinforced concrete structures.
Return to contents
We use antifreeze additives
The problem of solutions being ready for use in frosty weather is solved in several ways. But most often, antifreeze additives are added to construction mixtures - special salts that reduce the freezing point of water and prevent it from turning into ice. This is done directly on the construction site. As a result, the mortar joint has time to gain sufficient strength before the water freezes. For this purpose, additives such as potassium carbonate (potash), sodium nitrate (sodium nitrite), calcium chloride, sodium chloride, sodium formate, etc. are used.
When building a cottage for work at temperatures down to -15 ° C, experts advise choosing sodium nitrite or sodium formate as an additive. If it gets even colder, you need to use potash (up to -30 ° C). The advantage of all options is the absence of corrosion during the construction of reinforced structures. Efflorescence does not appear on the surface of the hardened solution. But it is better not to use chlorine-containing substances - they accelerate corrosion processes, which leads to the destruction of reinforcing parts.
It is true that potash and sodium nitrite are dangerous and poisonous materials. The final cement or concrete solutions do not harm human health, but when using these additives, safety precautions must be observed: store the substances in a dry and locked room in the original packaging, and prepare the solutions wearing goggles, rubber gloves, boots and construction overalls. Sodium formate is easier to work with because it is not toxic.
It is very important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended proportions when preparing the composition.
They usually depend on the ambient temperature. The average figures are shown in the table. Number of antifreeze additives
| Air temperature, °C | Consumption of additives,% by weight of cement in the mixture | ||
| Potash | Sodium nitrite | Sodium formate | |
| -5°C | 5-6 | 4-6 | 2-3 |
| -10°С | 6-8 | 6-8 | 3-4 |
| -15°С | 8-10 | 8-10 | 4-5 |
In addition to antifreeze additives (relatively speaking, “antifreeze”), there are plasticizers (or superplasticizers). They increase the plasticity of the mortar mixture and thereby make it possible to reduce the amount of water required for mixing. Plasticizers improve the frost resistance of the solution and increase its density. In this regard, for at least several days after installation, no physical changes occur in the solution, and it has time to set.
The use of these additives is useful in the manufacture of mortars for masonry, concrete work, and installation of self-leveling floors. Plasticizing substances are introduced along with water; their minimum amount should be 5-10% of the weight of cement. This proportion is sufficient for masonry. If concreting is necessary, you need to increase the plasticizer consumption to 10-15%. This will further increase the plasticity of the mixture during laying and at the same time the moisture resistance of the finished concrete.
Finally, there are winter additives such as special compounds that accelerate the hardening process of the solution (strength gain). Thanks to them, it turns into a strong stone before it has time to freeze. Such additives are useful, first of all, for creating monolithic structures (concrete floors, walls using permanent formwork technology). Their consumption is usually 2-5% by weight of cement.
But it is most optimal to use two or more types of additives at the same time. The exception is plaster mixtures. It is better to introduce only “antifreeze” into them. And plasticizers for such compositions are completely contraindicated, otherwise they will simply flow down the wall after application, without having time to set properly. But it is better to add anti-frost additives and plasticizers at the same time to the mortar for laying walls made of bricks or large blocks. Hardening accelerators in combination with plasticizers are useful for concrete. You can combine all three types of additives. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the fundamental possibility of their joint use without loss of quality. Information about this can be found in the manufacturer's instructions.
There are also ready-made combination supplements on sale that combine two or more qualities.
Tips for choosing
When choosing antifreeze additives, they take into account the method, circumstances of operation of the concrete structure, ambient temperature, brand, composition of cement, and quality of the additive. The PMDs used by specialists the most are considered optimal:
- potash (7% concentration) is suitable for Portland cement;
- sodium nitrite;
- sodium chloride is used for rapid hardening modifications.
When choosing PMD, you need to pay attention to the experience, image of the manufacturer, reviews in order to avoid purchasing a low-quality product.