Are there any advantages to winter concrete work?
In general, working with concrete in harsh conditions of low temperatures entails additional difficulties, but it is impossible to stop construction for six months every time autumn comes, and besides, winter work also has significant advantages:
- Winter discounts on building materials and the decline in demand for labor make it possible to save money.
- In winter, foundations can be concreted on weak or brittle soil.
- Frozen access roads make it possible to easily deliver heavy equipment and materials to a construction site.
Antifreeze additives in concrete: features, application, characteristics
Winter concreting
Monolithic structures created in warm weather, after drying, are strong and reliable structures.
Note! The high strength of reinforced concrete products means that if it is necessary to create a hole in a given structure or shorten it, it is necessary to use methods such as cutting reinforced concrete with diamond wheels and diamond drilling of holes in concrete.
But in order to ensure the same level of strength for concrete structures created in the cold season, measures should be taken to keep water in the building mass in a liquid state.
Antifreeze additives, which are also called concrete setting and hardening accelerators, can help in this matter. They make it possible to reduce the freezing point of moisture, thereby helping to normalize the hardening process of the concrete monolith structure.
Antifreeze components
- Compositions that prevent the crystallization of liquids in building mixtures by lowering the freezing point of the building mass. They are also called retarders or weak cement set accelerators. These substances include two types of electrolytes:
- Strong - table or technical salt for concrete (sodium chloride), sodium nitride;
- Weak - ammonia solution, substances of limited origin (urea, polyhydric alcohols);
- Antifreeze compounds that accelerate the hardening process and have high antifreeze properties. Such additives include potash, mixtures based on calcium chloride with sodium nitrite, with sodium chloride, etc.
- Salt, introduced into the solution with your own hands, allows you to lower the freezing point of water, which will avoid destruction of the structure of the product and the formation of cavities in a monolithic structure filled in in winter;
- The price of this supplement is low;
- NaCl does not affect the rate of hardening of the solution, so concrete can be mixed with salt in winter long before it is poured. Thus, mixing the building mass with this additive can be done, for example, at the factory long before its transportation to the construction site without loss of basic properties;
- Such an additive increases the mobility of solution particles, which facilitates the process of forming products of the required shape from a given mass;
- It does not change the structure of the cement mass.
In the photo - additive in bags
NaCl – sodium chloride (CN) or ordinary commercial salt. Concrete with technical salt is an excellent substance for construction work in winter in conditions of negative temperatures.
Technical salt is added to the concrete solution in order to provide it with anti-frost characteristics.
This additive has the following properties and characteristics:
Note! This component for concrete is the cheapest antifreeze additive.
Advice. It is recommended to use calcium chloride together with sodium chloride.
The availability of this kind of antifreeze additive and its low price is often the reason that most builders resort to using completely different, more expensive means.
In addition to the many advantages of such an additive, it also has one significant drawback, which often becomes the reason for the impossibility of using it for concrete. The fact is that salt has a high level of corrosive activity.
This means that the use of metal reinforcement simultaneously with a cement mixture with the addition of sodium chloride will lead to the process of rusting and peeling of this structure from the concrete.
Thus, the reinforced concrete structure loses its integrity, which qualitatively reduces the level of strength of the entire product.
Antifreeze additive
Advice. The proportions of salt in concrete also suggest the addition of calcium chloride in the first case in the amount of 0.5% by weight of the solution, and in the second 2%.
Having decided to make a plasticizer for concrete with your own hands, you should know that anti-frost additives are distinguished by the type of chemical that is added to the solution for the purpose of preparing a concrete solution intended for use in frost. So, in particular, these can be the following chemical elements:
- chloride salts, namely sodium chloride (table salt) and calcium chloride;
- sodium nitrite;
- potassium carbonate or potash.
By using these substances as special additives in the building mixture, during construction you can do without heating the mortar poured into the formwork. It is worth knowing that the same chloride salts significantly increase the corrosion of metal fittings. In this regard, if you decide to prepare concrete with your own hands, add such salts to it only when you are going to concrete unreinforced structures.
When preparing an anti-frost solution for concrete with your own hands, it is necessary to take into account the fact that different types of plasticizers have different properties and characteristics. It is they who will subsequently influence the characteristics of the concrete itself and structures made from it.
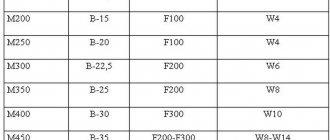
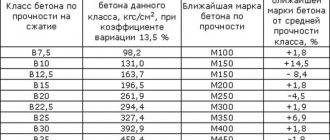
So, for example, chloride salts added to the solution should not account for more than 7.5% of the cement mass. Potassium nitrite in such a mixture should occupy 10%, and potash - 15% of the specific gravity of cement. Moreover, if you use chloride salts as an anti-freeze additive, then by the time the water-salt solution freezes, the strength of the concrete cannot be less than 5.0 MPa. Such concrete must be cured under cover until the stripping strength level is reached.
We suggest you read: How to insulate a room
The use of anti-frost plasticizers makes it possible to avoid heating a concrete structure only when the temperature at the construction site is not lower than the design temperature. If the maximum permissible concentration of chloride salts and sodium nitrite is introduced into the solution, the poured concrete can withstand a temperature of 15°C in the open air without heating.
In any case, if the temperature drops below the specified threshold, it will be necessary to take measures to insulate the formwork and cover the poured structure using the “thermos” method, as well as ensure their heating using steam or electricity.
Concrete solutions with a high level of salt plasticizers are good because they can tolerate negative temperatures when leaving the mixer. At the same time, to mix the mixture itself, you can take cold materials such as sand, crushed stone and gravel. At the same time, their temperature should not be lower than 15°C.
If you want to avoid early setting of the concrete mixture due to the presence of too many chloride plasticizers in it, it is prepared using a separate method. To do this, sand, cement and crushed stone are first mixed together with water, to which an anti-frost plasticizer with 70% mixing water has been added.
When building a house or fence, every site owner wants the structure to have not only an attractive appearance, but also good technical characteristics. To improve these indicators, special substances – plasticizers – are added to the concrete solution. However, a more experienced builder, for economic purposes, often creates a plasticizer for concrete with his own hands. In this way, it is possible to significantly reduce the cost of the component and achieve better performance for the future building.
Monolithic structures created in warm weather, after drying, are durable and high-quality structures.
But in order to ensure the same level of strength for cement structures created in winter, it is necessary to use measures that allow water to be retained in the building mass in a liquid state.
Antifreeze additives, which are also called concrete setting and hardening accelerators, can help in this matter. They make it possible to reduce the freezing point of the liquid, thereby helping to normalize the hardening process of the cement monolith structure.
Means for this type on the modern market are presented in two main types:
- Compositions that interfere with the crystallization processes of liquids in building mixtures by lowering the freezing point of the building mass. They are also called retarders or mild cement set accelerators. These substances include two types of electrolytes:
- Strong - table or technical salt for concrete (sodium chloride), sodium nitride;
- not strong - ammonia solution, substances of limited origin (urea, polyhydric alcohols);
- Antifreeze compounds that help accelerate the hardening process and have high antifreeze properties. Such additives include potash, mixtures based on calcium chloride with sodium nitrite, with sodium chloride, etc.
Types of antifreeze additives
Having decided to make a plasticizer for concrete with your own hands, you should know that anti-frost additives are distinguished by the type of chemical that is added to the solution for the purpose of preparing a concrete solution intended for use in frost. So, in particular, these can be the following chemical elements:
- chloride salts, namely sodium chloride (table salt) and calcium chloride;
- sodium nitrite;
- potassium carbonate or potash.
By using these substances as special additives in the building mixture, during construction you can do without heating the mortar poured into the formwork. It is worth knowing that the same chloride salts significantly increase the corrosion of metal fittings. In this regard, if you decide to prepare concrete with your own hands, add such salts to it only when you are going to concrete unreinforced structures. Some of these salts can also be used for concreting reinforced concrete products with the restrictions established in the relevant construction and technical documentation.
When making an anti-freeze plasticizer for concrete with your own hands, remember that the principle of operation of such additives is that the chemicals listed above, added to water and then to the solution, lower the freezing point of the aqueous solution contained in the concrete. As a result, it acquires the ability to harden at sub-zero temperatures.
Antifreeze additives in concrete: features, application, characteristics
In winter, the main enemy of high-quality concreting is low temperatures, which have a negative impact on the processes occurring both during concreting and during concrete hardening.
The formation of a solid substance - concrete - occurs as a result of the hydration reaction of the minerals that make up Portland cement. For this reaction to take place, a temperature above 0°C is necessary, since at negative temperatures water freezes and the hydration reaction stops.
Already at temperatures below 5°C, the reaction rate sharply slows down, and the strength gain of concrete slows down.
Low temperatures cause the following problems:
- cessation of the hydration reaction;
- increase in internal pressure due to freezing and associated expansion of the material;
- the formation of ice crystals around the reinforcement, which leads to poor adhesion to concrete;
- obtaining low-strength concrete.
The main task in winter is to ensure that the concrete reaches critical strength (30–50% of the design strength), after which negative temperatures no longer have a negative impact on concrete. Typically, under optimal conditions, critical strength is achieved 4–6 days after installation.
Therefore, in winter, temperature becomes of primary importance.
The temperature of the concrete mixture is measured before, during and after placement.
Antifreeze additives for concrete in different containers
General provisions
Let's take a closer look at what happens if antifreeze additives are not applied to concrete, but simply continue construction work.
The fact is that this solution contains a certain proportion of water, therefore:
Thus, concrete must be protected from freezing until it reaches a certain critical mass, after which the hardening process cannot be stopped.
Concrete with antifreeze additives hardens efficiently even at sub-zero temperatures
Description
What is concrete with antifreeze additives?
An antifreeze additive is a substance that lowers the freezing point of water in the substances to which the additive is added
Advantages
Cement mortars benefit from an antifreeze additive due to a number of advantages:
Flaws
Disadvantages of PMD:
- lead to the formation of salt stains on top of the material, they are extremely difficult to remove;
- The strength of the material is significantly reduced if the preparation technology is violated: add an excessive or insufficient amount of anti-freeze additive to the concrete or ignore caring for it until it sets;
- Some components are toxic and unsuitable for use in residential areas.
Each antifreeze additive for concrete affects the physical and chemical properties of the solution in a different way.
This property allows concrete and various mixtures to harden at temperatures below zero.
Modern compounds are manufactured taking into account one of three mechanisms:
The listed groups are further divided into subgroups. Without knowing their properties it is impossible to make the right choice.
Plasticizers
After using an anti-frost additive, concrete is easier to lay and level. It is easier to fill any form with the mixture and remove voids from it. Cement retains moisture longer. PMDs reduce energy and water costs.
Strengthening
Corrosion resistant
Antifreeze, corrosion-resistant additives are used to protect reinforced concrete structures from frost and oxidation. They have a positive effect on the service life of the product, improving durability. With such additives, concrete is more resistant to aggressive substances.
Mobility regulators
In warm air conditions at a construction site, the cement mortar sets quickly, and substances of this group prolong the possibility of using the mixture.
They are chemical additives and come in two types:
- Additives that are introduced into the mixture in small quantities (0.1–2% by weight of cement) and regulate the properties of concrete.
- Finely ground ligatures (5–20%) are used to reduce cement consumption without changing the quality of products.
Frost-resistant
Frost-resistant additives are antifreezes that allow construction work to be carried out at negative thermometer values.
You can determine the composition of the product by labeling:
Complex
Construction of houses, baths, saunas and swimming pools in the cold season requires several of the listed effects simultaneously. Complex additives accelerate the hardening of concrete and cement mortars, strengthen reinforced concrete structures and protect the metal from destruction.
Kawabanga! How to choose insulation for a concrete floor under linoleum and install it in one day
When used correctly, builders get the expected results.
Winter concrete at home
As part of the work project, activities are developed that ensure:
- Preventing concrete mortar from freezing during transportation, laying and compaction.
- Prevention of freezing of freshly laid concrete until critical strength is achieved.
- Favorable heat and humidity conditions for strengthening of hardening concrete.
The finished concrete mixture supplied to the construction site must have a temperature of at least 5°C. To do this, mixing is carried out in warm (up to 70°C) water, and the filling materials are heated.
Surfaces for concreting and reinforcement must be heated close to the temperature of the concrete solution, for which warm or hot air is used, but not steam or water.
When transporting the finished concrete mixture for a long time and it is impossible to use heating, antifreeze additives are used.
There are two main methods of winter concreting:
- warm concrete;
- cold concrete.
Cold concrete is concrete that will harden without heating. To ensure its hardening, special antifreeze additives are designed to reduce the freezing point of water and at the same time accelerate hydration reactions so that the amount of unbound water in the solution decreases as quickly as possible.
Widespread antifreeze additives are electrolytes, Na and K salts, but their use has some limitations:
- sodium salts are not used in reinforced concrete, as they lead to corrosion of the reinforcement;
- some types of Portland cement (for example, highly alkaline or made from clinker with a high content of aluminosilicates) are not used in conjunction with electrolytes;
- sodium and potassium salts are not used in mixtures with potentially reactive rock filler;
- electrolyte salts should be tested experimentally for the formation of efflorescence.
Modern complex antifreeze additives do not have the disadvantages of electrolyte salts, provide the ability to carry out concrete work at low temperatures and have a complex effect (not only antifreeze, but also plasticizing and others).
Warm concrete is concrete that, after laying, is subjected to various heating and heating procedures.
During home construction, concreting in conditions of negative temperatures is acceptable for objects of low importance.
For independent work, use kneading in heated (not higher than 70°C) water.
The order of laying the components of the concrete mixture is changed: first, coarse aggregate is poured into the water, then sand and cement.
At home, the use of heating concrete or installing greenhouses is not profitable; special anti-frost additives come to the fore, which make it possible to successfully carry out concrete work in winter.
In winter, to lower the freezing point of free water, salt (sodium chloride) or other sodium and potassium salts, which act as electrolytes, are added to the concrete solution.
The use of salts can lead to corrosion of reinforcement and the appearance of efflorescence on finished concrete. The best option is to use complex antifreeze additives and plasticizers.
Making winter supplements at home
You can prepare PMD for concrete with your own hands by choosing chloride compounds (salt) for mixing. This additive reduces the freezing point of the concrete mixture, shortens the setting time, reduces the consumption of the main components (cement), and preserves the structure without changing the properties of water and concrete. This composition is best used when pouring unreinforced structural elements. You should know that various additives determine the technical properties of concrete (density, mobility, water resistance, viscosity), conditions of use and are strictly regulated by GOST 22266-94.
Proper application of PMD allows you to increase the mobility of concrete, the freezing point of the liquid, increase the setting time period, reduce the thickness of the concrete monolith without loss of strength, and reduce the cost of construction work by adding low grade cement to the mortar.
Antifreeze additives in concrete meet safety requirements and meet environmental standards, therefore the use of chemical compounds is permitted as the most optimal way to solve problems during concreting in winter.
Do-it-yourself antifreeze additives for concrete
Sometimes it is not possible to purchase a ready-made product, but you don’t want to stop construction. In this situation, you have to make such a plasticizer additive for concrete with your own hands.
The simplest and most affordable way is to add regular table salt to the concrete solution.
In scientific language it is called sodium chloride. Salts, if you remember your school chemistry course, generally help lower the freezing point of solutions.
What to do if you need to protect metal parts? In such a situation, so-called corrosion inhibitors will come to the rescue. These are substances that significantly slow down the rusting of metal elements. This role is most often played by potassium nitrate nitrate (NPN), an intermediate product in the production of potassium nitrate.
To prepare a non-freezing plasticizer for concrete with your own hands, add 3-4% of the volume of dry cement, table salt or potassium chloride and NNC, to the solution along with water. The ratio of NaCl or KCl and potassium nitrite nitrate should be 1:1. To improve the plasticity of concrete, urea is also added to the solution in a volume of 7-10%.
You can make your own anti-frost plasticizer for concrete using ammonia water. This is perhaps the most cost-effective way to make concrete mortar more plastic and not lose strength characteristics in cold weather.
Ammonia water has a significantly lower expansion coefficient than, for example, an aqueous solution of salts. In addition, this substance not only does not contribute to metal corrosion, but, on the contrary, slows it down. Another advantage of this additive is that efflorescence on the masonry appears much less frequently or is absent altogether.
The concentration of ammonia water directly depends on the temperature at which concrete work is carried out. It can range from 5 to 20%. The lower the air temperature, the more concentrated the ammonia water should be.
When making plasticizing antifreeze additives for concrete with your own hands, it is worth remembering that different concrete works require different additives in different quantities. There are special tables for this. They present calculations of additives at different temperature operating conditions.
However, construction industry experts say that for an independent developer it is better to purchase ready-made antifreeze plasticizing mixtures and add them, strictly following the instructions.
Hardening of the concrete solution slows down significantly as the temperature decreases. If the temperature reaches sub-zero levels, even not very low (- 3-5◦ C), the water in the solution begins to freeze. As a result, the concrete practically stops hardening. Instead, it just freezes. When defrosted, it still hardens, but becomes friable and significantly loses its strength characteristics.
To preserve the ability of concrete to gain strength, it is necessary to ensure the presence of a liquid component in it. Antifreeze additives contribute to this.
There are a number of plasticizer additives for concrete solutions on sale. They improve the dispersion of solid components of the solution. This means that the friability of cement, sand, gravel and the transformation of the solution into a suspension increases. At the same time, the solution’s resistance to freezing increases to -15◦ C, and the hardening process of the concrete solution is also accelerated.
Antifreeze additives (antifreeze) and plasticizers are produced by both domestic enterprises and foreign companies. Russian products include Relamix, Poliplast and others. You can also find many Chinese-made products on the market.
The problem with antifreeze additives in most cases is that they contain chlorides, which promote corrosion of reinforcing parts. For example, when laying a foundation or screed with reinforcing mesh.
Some manufacturers, such as the Swiss company Sika, offer chloride-free antifreeze additives.
Hardening of the concrete solution slows down significantly as the temperature decreases. If the temperature reaches minus values, even not very low (- 3-5 ◦ C), the water in the solution begins to freeze. As a result, the concrete practically stops hardening. Instead, it just freezes. When defrosted, it still hardens, but becomes friable and significantly loses its strength characteristics.
We suggest you read: How to properly pour concrete into a foundation
There are a number of plasticizer additives for concrete solutions on sale. They improve the dispersion of solid components of the solution. This means that the friability of cement, sand, gravel and the transformation of the solution into a suspension increases. In this case, the resistance of the solution to freezing increases to -15 ◦ C, and the hardening process of the concrete solution is also accelerated.
It is worth noting that the best solution would be to buy a ready-made complex concrete additive at any hardware store. They are not so expensive, the consumption is small and at the same time they provide significant improvements in the properties of the solution in winter with minimal negative consequences. If the volume of work is not very large, the air temperature according to the forecast will not fall below -10°C and there is access to retail outlets, then this method will be the most optimal.
But there are times when you need to create an antifreeze additive yourself and calculate the required amount. In this case, you should pay attention to salts (chlorides), they are the most accessible in our country. Chloride salts significantly lower the freezing point of solutions, reduce their setting time, and reduce cement consumption.
Chlorides have one significant drawback - they greatly contribute to the corrosion of reinforcing elements. So if the structure is reinforced, and the decision is made to work with salts, then it is necessary to take care of adding corrosion inhibitors to the concrete.
Everything is clear in theory, but what happens in practice? It is better to use Calcium Chloride as the main additive - this is rightfully the cheapest and most effective PMD today. It can be combined with sodium chloride (commercial salt). To protect against corrosion, add NNK to the mixture in a 1:1 ratio with salts.
The following compositions are also acceptable: a mixture of 2% CaCl2 1% NaNO2 (sodium nitrite or sodium nitrite), CaNO2 (calcium nitrite) can be used in the same ratio. NNK urea and NNKhK urea are also available complexes.
Selected additives are added directly when mixing the solution along with the mixing water. For more detailed information about each of the additives, go to the Antifreeze Additives section of our website.
Pouring concrete in winter using technically difficult methods
Plasticizers for concrete are components based on polymer components and liquid concrete mortar. They are used to ensure the elasticity of the masonry mixture, achieving the desired flow properties and optimal degree of moisture absorption. The additive contains reagents that react with concrete elements, forming a plastic mass. This improves adhesion, increases the density and strength of the mixture.
Certain types of plasticizers give concrete the following properties: increased fluidity, increased frost resistance, increased waterproofing properties
During the hardening process, the solution does not break up into separate fragments and no water is released. And although the hardening time noticeably increases, this is rather a plus, since it becomes possible to correct mistakes made during pouring in a timely manner.
The main condition for a high-quality composition is full compatibility with the elements included in the mixture, a low level of volatility and a high degree of resistance to solvents.
Concrete mortar is one of the most popular building materials. But when the temperature drops below zero, its hardening becomes problematic. This is often encountered when pouring foundations in the fall and winter. Experts say that pouring concrete at sub-zero temperatures is possible without heating, but for this, certain requirements are met to ensure proper hardening of the concrete mixture.
Concrete is a mixture of fillers - sand and crushed stone, bonded together with hardened cement laitance. When it reacts with water, it hydrates, after which it hardens with the simultaneous evaporation of water. Critical strength at normal temperatures is achieved within one or one and a half days, depending on the humidity of the surrounding air.
The optimal temperature for the reaction to occur is about 20⁰C; the solution gains design strength within 28 days. To prevent water from evaporating too quickly in the first days, the concrete is covered with waterproofing.
At 5⁰C, the solidification of the composition slows down by 2 times, and at zero temperature, hydration stops. If the critical strength of concrete has already been achieved before this, nothing will happen to it; it will gain strength after warming. If critical strength has not been gained before freezing, the material will not gain the required indicators and will crumble after defrosting. In this case, it is impossible to pour any brand of concrete at sub-zero temperatures.
The main condition for the correct pouring of concrete at subzero temperatures is the preservation of heat sufficient to ensure the development of critical strength. Popular methods for laying mortars in winter:
- Preheating of the mixture being prepared;
- Installation of reliable thermal insulation and maintenance of the solution;
- Electric heating of concrete poured into formwork;
- Addition of special additives that reduce the freezing point of water and accelerate hardening.
Thus, it is possible to pour concrete outdoors even in winter without loss of strength indicators, but for this you need to adhere to the selected methods. In terms of cost, the use of heat guns is the most unprofitable option; the cheapest method is the addition of additives. Electric heating and high-quality thermal insulation are intermediate options.
It is advisable to use technically complex methods of winter concreting using insulated formwork, heating electrodes, laying a heating cable, etc. These methods require careful preliminary calculations.
Features of national concrete pouring. How to pour concrete at low temperatures
Frost protection is not only required when pouring in winter. Concrete hardening occurs within at least 1 month, and the first frosts in central Russia are possible as early as October. Therefore, when pouring in autumn, precautions are also necessary.
According to SNiP 3.03.01-87 “Load-bearing and enclosing structures”, the following rules for pouring concrete in the cold season must be observed:
Mix the solution in heated devices or in a warm room.
Kawabanga! Primer Concrete-contact Prospectors
Use heated water and mixture components (except cement). Water should be heated to a temperature of no more than 70° C.
Do not use frozen materials.
Preheat the fittings.
Increase the duration of the vibration formation process by 25%.
Make sure that before freezing the concrete gains a strength of at least 5 MPa.
During winter mixing, the order of laying the components of the mixture changes: water is poured in first, then the PGS is laid in and several turns are made, and the cement is laid in last. Mixing time increases by 20-50%.
Before starting concreting, it is necessary to clear snow and ice from the formwork and warm it up, as well as provide shelter from possible precipitation. For heating, use portable braziers or heat guns.
Winter concreting is carried out continuously. Each layer is poured before a film has formed on the surface of the previous one, while it is wet. The filled parts are immediately covered with heat-insulating materials.
Labor-intensive and expensive work on heating concrete during the hardening period can be replaced by using antifreeze additives.
Concrete products made at low temperatures using anti-frost additives gain strength on the 28th day to about 30% of the design value. After thawing, strength gain will continue, so in winter the products cannot be fully loaded.
Video: features of winter concreting
Curing
The main goal of caring for concrete during the period of gaining critical strength is to ensure optimal temperature and humidity. In summer, this is achieved by pouring water over the concrete.
At subzero temperatures, water freezes.
Therefore, the main measures for caring for concrete include:
use of antifreeze additives (or heating);
covering the surface with heat-insulating materials.
Video: proper care of concrete after pouring
Possible consequences of winter concreting
Failure to comply with concrete laying technologies in winter results in concrete products of reduced strength, with cracks, efflorescence and other defects, as well as poor adhesion to reinforcement. The products are short-lived in use.
Concrete work in winter is most often a necessary measure, but even in this case there are advantages. When choosing a technology for winter work, many factors are taken into account: the type of structures, the composition of the concrete mixture, the availability of equipment and the economic effect of their use. Antifreeze additives are desirable for use when choosing any method of conducting concrete work in winter.
Tags: concrete, subzero, how much, salt, temperature
« Previous entry
What is concrete with antifreeze additives?
Advantages
Advantages of antifreeze additives:
The advantages of antifreeze additives can be judged from the following video:
Flaws
Disadvantages of special additives:
Kawabanga! Choosing adhesive for aerated concrete blocks - features, brands
Existing additives have different effects on the physical and chemical properties of concrete. In total, three mechanisms of their antifreeze action can be distinguished:
How winter concreting with the use of anti-frost additives occurs/works, whether such concrete needs to be heated - we will talk about all this further.