Concrete floors: description
Concrete floors are a mixture of cement, fillers (sand, crushed stone, expanded clay, broken brick, etc.), and water. The proportions of the mixture vary depending on the different needs for the grade of concrete. Concrete grades, in turn, differ in strength and degree of frost resistance.
It is believed that concrete is the most practical material for subfloors. Concrete floors can withstand enormous mechanical loads and pressure, therefore they are often used in technical premises, such as production workshops, automobile service stations, various hangars, warehouses, etc.
Concrete floors are also laid in residential areas. In private housing construction, for example, concrete floors strengthen the entire foundation and give strength to the entire area of the room.
Concrete mix composition
Benefits of concrete floors
- Fireproof.
- High strength.
- Do not require special care.
- Easy to install.
- Not afraid of mechanical and chemical influences.
- Very long service life.
- Not prone to the growth of fungus and mold.
- Ideal base for ceramic tiles, parquet, laminate, carpet, etc.
- High moisture resistance.
- Over time it does not lose its properties.
Disadvantages of concrete floors
- Large energy costs for installation and dismantling of the coating.
- In residential premises it is necessary to lay additional covering on a concrete base.
- Concrete floors are quite cold due to the high thermal conductivity of the material.
- It is necessary to take into account the strength of load-bearing structures when installing a concrete floor in multi-story buildings due to the large weight of concrete.
- Preparing to lay a concrete floor takes a lot of time.
- It takes a long time for the concrete mixture to completely harden. The hardening time of standard concrete mixtures is about one month, but can vary significantly depending on the additives introduced.
Proportional mass composition of concrete for the floor
The concrete mixture includes a binder, fine-grained and coarse-grained fillers, water and additives if necessary. Their proportions for the material in our case depend on the brand of cement:
When using M400 cement – 1 part cement, 2.8 parts sand and 4.8 parts crushed stone. When using M500 cement – 1 part cement, 3.5 parts sand and 5.6 parts crushed stone.
To prepare one cubic meter of concrete solution ready for pouring, you need:
320-340 kilograms of cement; 590-610 kilograms of sand; 1200-1300 kilograms of crushed stone; 170-190 liters of water; 2-5 kilograms of additives.
Floor screed type
The floor screed can be monolithic, sectional or floating.
- Monolithic floor screed . Filled with one layer without the use of sound, heat, or waterproofing materials.
- Sectional filling method. The concrete screed must be poured in a single layer, but there are situations when this is not possible due to the large volume. In such cases, the floor area is divided into sections and poured sectionally.
- Floating floor screed. This type of screed does not come into contact with the walls and subfloors. A small distance between the screed and the walls serves as an expansion joint and is filled with any insulating tapes. Between the floating and rough screed, as a rule, sound, heat, and waterproofing materials are laid.
Floor screed thickness
There are several options for the thickness of the floor screed.
- Screed up to 2 cm . This is basically a self-leveling mixture, or concrete for final leveling of the surface. Poured without the use of reinforcing materials.
- Not less than 4 cm. It is believed that the minimum thickness of the rough screed should be no thinner than 4 cm, regardless of whether reinforcing material is used or not.
- Screed up to 7 cm. In this version of the screed, reinforcement or reinforcing mesh must be provided.
- Screed up to 30 cm. This screed thickness is used in production workshops and industrial premises. Pouring more than 30 cm of screed is not economically profitable; there will be no benefit from a thickness of more than 30 cm, but the material consumption and cost of work will increase significantly. It is advisable to use bedding to reach a screed thickness of up to 30 cm.
Concrete screed for heated floors
Warm floors can be electric or water.
Water heated floor.
For a water heated floor, the thickness of the screed should be at least 30-35 mm above the upper edge of the pipe, optimally 40-45 mm. It is advisable to use the grade of concrete M 300 and class B 22.5. This thickness of concrete is recommended for use in residential premises using water-heated floors.
Electric heated floor.
It is poured with a layer of at least 30-35 mm , up to 40-45 mm, concrete grade M 300 and class B 22.5. For water and electric heated floors, a plasticizer is added to make the concrete elastic.
Application of the main grades of concrete by strength
- M-100
is used for carrying out preparatory procedures before pouring monolithic foundation strips and slabs. This concrete is laid in a thin layer on a sand bed. After this, reinforcement for the future structure is installed. - M-150
is used when performing preparatory operations before pouring the foundation. It is also used for screeding and pouring floors, building foundations for small structures, and concreting paths. - M-200
is used for pouring paths, for blind areas, foundations, concrete floor screed in residential premises and for garage floors. - M-250 and M-300
are used to create a monolithic foundation, fences, stairs, supports, floor slabs with a small or medium load, respectively, and concrete blind areas. - M-350
is used for the manufacture of a variety of critical structures, for example, monolithic foundations, floor slabs, crossbars, columns, swimming pool bowls, and so on. - M-400
is used in the construction of bridges, cash storage facilities, hydraulic facilities and structures with special requirements. - M-450, M-500, M-550
are used for the same purposes as M-400, as well as in the construction of subways, dams and dams. - M-600
is used in the construction of facilities that are resistant to aggressive environmental factors and have maximum strength. Such objects include reinforced concrete bridge structures, reinforced concrete structures for special purposes, and hydraulic engineering facilities.
Types of concrete mixtures
A concrete mixture is a finished product manufactured primarily at a factory in compliance with technology. This mixture is called BSG , which means ready-mixed concrete. BSG includes various types of concrete, which differ in volumetric weight.
'RK Beton' ready-mixed concrete plant (BSG) with delivery 24x7 Moscow
Concrete production in Moscow and the Moscow region. 8 concrete plants in the region. Delivery and services of a concrete pump truck . Concrete plant website.
- BST . The concrete mixture is heavy. Gravel, crushed stone, and granite serve as fillers for the mixture. It is used in the construction of industrial facilities, for the installation of rough screed. Density 1800-2500 kg/m3.
- BSM . The concrete mixture is fine-grained. Heavy concrete using fine filler fractions up to 5 mm. The maximum density of the mixture is ensured by cement containing alite. Used for the construction of thin-walled structures and rough screeds. Unlike BST, it has better filling of cavities. Density 1800-2500 kg/m3.
- BSL . The concrete mixture is light. This type of concrete is lightweight due to the low weight of the fillers. Mostly, the filler is expanded clay or some other porous filler. Such concrete has good sound and heat insulation properties. Density 500-1800 kg/m3.
Differences between floor screeds
Types of floor screeds
Single layer concrete for floor
The simplest type of concreting floors. The most common in private households and apartments. Mounted up to 250 mm thick in one layer. After complete hardening, a durable base with high mechanical properties is obtained.
Multilayer concrete for floor
It is used for the restoration of concrete floors with a concrete layer thickness of at least 250 mm , when reconstructing an existing rough foundation to add a hydro- or thermal insulation layer.
Reinforced concrete for floor
Reinforced concrete is poured in industrial premises with a minimum layer of 40 mm ; this type of concrete has the highest strength and resistance to high loads. Due to reinforcing materials, it is possible to slightly reduce the thickness of the concrete floor, reduce the weight of the entire structure, thereby reducing the load on the foundation, this is especially true when it comes to multi-story buildings. Metal or plastic reinforcement, metal or plastic mesh, and finely dispersed components are used as reinforcing materials.
The diameter of the mesh rods and reinforcement should be calculated based on the load on the concrete base. Thus, the diameter of the mesh rods ranges from 0.5-5 mm, the reinforcement 8-12 mm .
Non-reinforced concrete for floor
Non-reinforced concrete is used in technical rooms with not very high mechanical load on the subfloor. These are mainly small workshops, mini boiler houses. The minimum thickness of the screed is at least 40 mm.
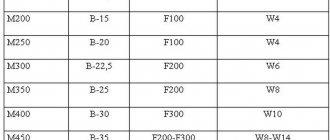
Concrete grades for floor screed
Table of ratios of classes and grades of concrete for floors
The grade of concrete (indicated by the letter M) is the strength of the product, indicating the load in kgf/cm2, a numerical value from 50 to 1000 units; concrete up to grade M 350 is used for pouring floors . Relatively speaking, the grade of concrete is the declared strength indicator based on production technology.
For the installation of concrete floors, the most often used brands are M 100, M 150, M 200, M 250. The brand is selected depending on the operating conditions.
Often several brands of concrete mix are used. For example, grade M 100 is used for a leveling pad, grade M 100 is used on hardened concrete, a reinforcing frame is mounted, then grade M 150-M 350 is used.
For concrete floors with increased mechanical load, it is necessary to use a concrete mixture of at least M 250 grade.
- M 50. The weakest concrete available . M 50 is mainly used to prepare a preparatory layer before pouring the foundation and installing curbs.
- M 100 . It is used as an underlying cushion for screeds and foundations. For filling cavities that do not experience stress.
- M 150 . Concrete of this brand is used for rough screed in a house or apartment , pedestrian path on a personal plot.
- M 200-250 . Sufficiently strong concrete for pouring strip foundations, blind areas, and open terraces. Stable under conditions of low mechanical load. Suitable for installing screeds in the garage.
- M 300 . It is used for the manufacture of stairs both indoors and outdoors, for monolithic foundations and outdoor areas. Has good moisture resistance.
- M 350 . It is used for the construction of monolithic houses, including floor slabs, for the foundation of multi-storey buildings supporting columns.
Floor concrete class
It is designated by the letter B and numbers from 1 to 60, and is measured in MPa. The class of concrete, this is the actual strength of ready-made concrete, has an approximate ratio to the grade of concrete in terms of strength of 13.5%. Tests are carried out after the material has completely hardened.
SNiP concrete for flooring
Building codes and regulations ( SNiP ), simply put, are the norms and rules that construction organizations must follow when performing construction work and calculations.
- SNiP 31-06 . For residential and public buildings (repaired, reconstructed) up to 55 m high.
- SNiP 10.03 . Standards for the construction of premises for keeping animals.
- SNiP 2.03.11 . The standards are aimed at designing corrosion protection for concrete and reinforced concrete structures.
- SNiP 31-05 . Design work in public buildings and sports facilities must also be carried out according to special rules.
- SNiP 11.02 . Special requirements for concrete floors in refrigerated rooms.
- SNiP 3.04.01 . Special requirements also apply to the ambient temperature during the installation of concrete floors.
Why is it important to maintain the required ratio?
Depending on the brand of cement, the following proportion of cement and sand for the screed is selected:
- Mortar grade 300 and cement grade 600, proportion 3:1.
- Mortar grade 200 and cement grade 600, proportion 4:1.
- Mortar grade 300 and cement grade 500, proportion 2:1.
- Mortar grade 200 and cement grade 500, proportion 3:1.
- Mortar grade 300 and cement grade 400, proportion 1:1.
- Mortar grade 200 and cement grade 400, proportion 2:1.
- Mortar grade 150 and cement grade 400, proportion 3:1.
- Mortar grade 200 and cement grade 300, proportion 1:1.
- Mortar grade 150 and cement grade 300, proportion 2:1.
- Mortar grade 100 and cement grade 300, proportion 3:1.
To create a screed in an apartment, as a rule, a solution of grade 200 or 150 is used.
Today, various materials are used as floor coverings: tiles, putty, plaster, etc. For their durable and reliable installation, strict proportions of the main components of the mixture on concrete must be observed. You can visually determine the correctness of the ratios of the components by the thickness of the solution.
If you overdo it with water, the ratio of the components will be incorrect, therefore, the mixture will lie worse, and the floor will crack over time.
To properly mix all the ingredients in the required quantities, you must strictly follow the manufacturer's recommendations. This applies to ready-made dry mixtures. If you use home-made solutions, it is recommended to select the ratios according to the brand of cement and the selected aggregate. The ratio of ingredients in the sand-cement mixture determines not only the final quality of the coating, but also sound-, heat- and moisture-resistant parameters, and the possibility of laying communications.
The grade of cement determines the ratio of the main ingredients in the mixture, such as cement, sand filler, and water.
Ingredient ratio table.
It is recommended to knead the screed from a grade of mortar greater than M150 with a compressive strength of 10 MPa. The optimal grade is M200. To select the ratio, sand should be taken with a minimum clay content. Impurities reduce the adhesive properties of the mixture, therefore, the strength characteristics of the floor decrease. If clay cannot be avoided, the proportion of cement in the total mass should be increased by 20%.
The brand of cement-sand mortar for the screed is selected based on the floor covering being laid.
There are other reasons why a higher grade of mortar is used. First. No one is sure of the quality of cement, so they prefer to play it safe than to redo it all over again. Secondly, modern coatings require a flat, solid base and the screed mortar must be durable. And thirdly, you simply cannot install a low grade under self-leveling compounds or modern tile adhesives with polymer additives.
READ MORE: Fiberboard on a wooden floor
If you decide to mix the screed mortar yourself, you need to decide on the amount of cement you will need. It can be calculated based on the found volume of solution. There are tables that show the consumption of cement for screed depending on the brand of mortar and binder.
The amount of cement in one cubic meter of screed mortar
Let's calculate the amount of cement for one cube of M150 sand concrete screed. If we use M400 cement, 400 kilograms of cement will be needed per cube (according to the table). To find how much cement will be needed for the example described above, you need to multiply the found volume of solution by the norm: 0.6 m³ * 400 kg = 240 kg. That is, for this room you will need 240 kilograms of cement. To determine the number of bags, divide this figure by the mass of cement in the bag.
- If there are 50 kg of cement in a bag, you will need: 240 kg / 50 kg = 4.8 bags.
- When packed in 25 kg: 240 kg / 25 kg = 9.6 bags.
Other packaging also exists, but is rare. Once you decide on the brand and manufacturer, you can accurately calculate the number of bags of cement for the floor screed.
How to calculate the amount of cement per cubic meter of sand
You can also calculate the cement consumption based on the available amount of sand. You never know. Maybe someone will buy sand and so that there are no leftovers, it must all be used up.
How to calculate the amount of concrete for floor screed
Calculating the volume of the required amount of concrete for pouring floors is not so difficult. To do this you need:
- Measure the area of the room (length and width).
- Recapture the horizon.
- Find the lowest point and the highest point.
- Measure both points.
- Take the average value of the formation height.
- Multiply all obtained values.
Example: room area is 10 x 10 m, the thickness of the future layer at the lowest point is 7 cm, at the highest point 3 cm, on average it will be 5 cm (0.05 m).
Multiply: 10 x 10 x 0.05 = 5 cubic meters. The required volume of concrete mixture is 5 cubic meters.
Concrete floor technology
- Find the lowest point. Before starting work with concrete floors, it is first necessary to carry out geodetic work, find and mark the zero (horizon).
- Prepare the base. On the ground. Before installing a concrete screed, it is necessary to prepare the base for the concrete floor; to do this, you need to compact the soil and make a cushion in the form of a sand bedding.
On a monolithic base. Concrete floors are installed after the foundation has been repaired, if required. Cracks and potholes are filled with a mixture of cement and sand, i.e. brand 50. - Installation of waterproofing. Concrete takes a long time to gain strength; while the mixture is hardening, it should not be allowed to dry out. Therefore, waterproofing is used; it prevents liquid from escaping from the concrete.
- Installation of formwork. Formwork is wooden, metal, plastic panels, with the help of which you need to give the necessary shape to the future layer.
- Formation reinforcement. If technology requires it, the base is reinforced before pouring concrete floors. This is done to increase the strength of the concrete base.
- Installation of concrete floors. Before carrying out work with concrete, you need to objectively evaluate the entire scope of work. The fact is that concrete should be poured in one layer; pouring floors in 2-3 stages with large intervals of several hours or more is a gross violation of the technological process. Therefore, situations often arise when it makes sense to order ready-made concrete from a concrete mixer. If the object is located at a height or in a place that is difficult for a concrete mixer to reach, there is a concrete pump.
- Actions during concrete work. To perform the job efficiently, the mixture must be leveled and compacted. For this, various tools are used, such as a vibrating screed and a vibrator. Using a vibrator, air is expelled from the concrete mixture, and using a vibrating screed, the concrete mixture is evenly distributed over the surface.
Vibrating screed.
Concrete vibrator.
- Grouting concrete floors. After 6-8 hours after completion of work, the concrete base should be cleaned with a special trowel (if the area is not large, you can rub the screed manually using a polyurethane float). It is recommended to repeat the procedure every few hours.
- Hardening of the concrete floor. After cleaning the surface, you need to let the base get stronger for several days. All this time, the concrete floor must be irrigated with water.
- Expansion joint. No later than 72 hours after finishing work, it is necessary to cut the expansion joint with an angle grinder. This must be done if a large load on the floors is expected, for large areas. Any base makes a movement invisible to the human eye. This happens due to the acting load from the mass of the structure itself, the equipment on it, thermal expansion during heating or contraction during cooling, and seismic movements. An expansion joint will avoid destruction of the concrete floor. The depth of the expansion joint is usually 1/3 of the total layer thickness.
- Treatment of expansion joints. After the seams have been cut, they must be treated with any sealing material. This will prevent water and debris from getting into the seams.
The article was written for the site.
Tags: Concrete, Self-leveling floor
Use of additives
More often, classic material without specific additives is used for interior concrete work. However, in a number of cases their use is justified, especially if the object is in an unfinished stage of construction and is exposed to external environmental factors.
Currently reading: Monolithic concrete construction
Typical Additives:
Plasticizers. They give the product additional elasticity, compact the structure of the plastic mass, increase frost resistance and moisture resistance after the product hardens. Antifreeze. They are added to the material when it is laid in the autumn-winter or early spring period, when the average daily temperature drops below 0 degrees Celsius. The substances prevent the liquid in the solution from freezing. Hardening accelerators. Used as an auxiliary component to speed up the hardening process of the concrete mixture and gain its critical strength. Hardening retarders. Used for quickly setting concrete used in conditions of low humidity and high temperature. Expanders. Prevents shrinkage of products after pouring. Other types. Waterproofing additives, anti-corrosion additives, coloring pigments, biocidal extractors, polarizers, air-entraining compounds, porosizers and much more.