What is it used for? Kinds
Road concrete is classified as heavy concrete. They are used for laying road surfaces and airfield pavements. It is distinguished by its ability to withstand constant heavy loads. In order to keep costs to a minimum, it is necessary to make concrete as durable as possible.
To produce the correct solution, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the recipe approved by GOST, depending on the place of use.
Road concrete is used for:
- Manufacturing a single-layer plane or a multi-layer top layer. The requirements for such a solution are as high as possible, since concrete will wear out not only from transport, but also from environmental influences.
- Laying the bottom layer of two-layer coatings. Manufacturing of this type is more economical due to lower requirements for its components, as well as the exclusion of the influence of the external environment.
- Filling the base for an improved type. The requirements for such concrete are low.
Impurities are added to the solution, which improve its resistance to low temperatures, the amount and type of which depend on climatic conditions. The components of concrete affect its wear resistance: the more mobile it is, the less stable the roadways will be. The route, in addition to loads from transport, can be influenced by water (snow, rain), temperature changes, so the road concrete for laying it must be of high quality and durable.
Return to contents
Types of road concrete
Road concrete can be classified into three groups based on the purpose of the material:
- solutions for constructing a single-layer pavement or creating the top layer of a road surface in multi-layer pavements (special requirements are put forward for the material, since it is subject to loads not only from vehicle traffic, but also from atmospheric factors);
- mixture for the base layer in two-layer road surfaces;
- products for foundation construction in permanent coatings (the performance indicators of the material are quite average, since significant loads on this layer are minimal).
Compound. Manufacturing Features
Fiber fiber is used in road concrete.
For durability and strength, a number of special additives are used that affect the quality characteristics. Polymer admixtures increase the strength of road concrete, including in aggressive environments. Fiber fiber affects resistance to dynamic impact; it provides additional reinforcement. Fiber increases wear resistance and is used for highways.
When preparing the solution, it is necessary to adhere to the proportions of cement, sand and additives (1: 2: 5). In order for road concrete to have all the necessary characteristics, it is necessary to maintain the correct ratio of water and cement in the solution: 0.6 for the lower layers; 0.5 for the top, 0.75 for laying the base. If there is too much water, it can affect the “work” of the additives in the solution.
Diameter of aggregate particles: up to 2 cm in the top layer; up to 4 cm at the bottom. Filler grains affect the solidity of the base; their quantity should not exceed 450 kg/m3, and for the top layer - 500 kg/m3. The mobility of concrete should not exceed 2 cm. Air-entraining additives are used for porosity. This parameter affects frost resistance and tolerance to chemical exposure.
To speed up the hardening of the plane, plasticizers are added during the mixing process. They are added before laying the concrete. Together with air-entraining admixtures and cement, they provide the highest possible properties of concrete.
All additives must be used according to manufacturers' instructions. If several admixtures are used simultaneously, their total amount should be less than 60 g/kg of cement. The solution is adapted in consistency to the installation devices and environmental conditions.
Return to contents
Composition of road concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete is often used as construction concrete. Concretes for road and airfield pavements are classified as heavy concrete, their density is 1800-2500 kg/m3, the content of binders in such concrete is reduced, which is why they are called lean.
Substances needed to produce road concrete: water, binder, fine and coarse aggregate. Sand acts as a fine aggregate, and basalt, less often limestone gravel or crushed stone is usually used as coarse aggregate.
The binder is hydrophobic and plasticized Portland cement. The content of C3A (trichalcium aluminate) in road concrete according to GOST should be less than 10%.
There is a special road Portland cement, it comes in two grades: M300 and M400, it has increased frost resistance, deformability, bending strength, resistance to impact loads, low shrinkage and abrasion.
According to standards, road concrete for highways must have frost resistance of F150, and for roads within the city - F100. Various modification additives provide the required frost resistance.
Gravel and crushed stone can be of different fractions. For the top layer of a multilayer structure, crushed stone or gravel with a diameter of 20 mm is used, for single-layer coatings - 40 mm. The grade of coarse aggregate should not be less than the values indicated in the table.
Sand can also be different. Typically fine to medium grain sand is used. To accelerate hardening, chemical additives – plasticizers – are added to concrete; the amount of additives should be less than 60 g/kg of cement.
Production
For laying roads, concrete is used, which is produced in factories.
The route is most often filled with solutions that are manufactured at the factory. This production has its own characteristics. The basis of such solutions are plasticizers or hydrophobic Portland cements. The final composition of the mixture depends on the desired result.
For two-layer automobile tracks, the top layer is made of Portland cement (grade M400 and higher), medium-sized and coarse sand, medium-sized crushed stone (compressive strength from 800 kg/m2). For the bottom layer, you can use material with strength from M300.
If the route is laid in conditions where critically low temperatures are possible, additives are used to increase frost resistance. This admixture is selected depending on the average monthly temperature in the area during cold times.
Return to contents
Main characteristics
An integral component of the possibility of comfortable movement by car are highways, roads and paths made of concrete. GOST indicates that the cement mortar for their construction must meet the following requirements:
- Minimum 150 grade for frost resistance - selected in accordance with the region in which the roadway will be built;
- Strength grade from M400 to create a top layer that bears the main impacts;
- Strength grade from M300 when using the mixture as a leveling ball.
When determining the characteristics of concrete for specific conditions of use, it is also worth paying attention to their mobility, abrasion and moisture resistance.
Compound
The quantity and quality indicators of the components are determined by the purposes of use and the level of load on the future coating. In most cases, the main components of the concrete mixture for creating road pavement are:
- Portland cement (hydrophobic or plasticized);
- Sand of medium and large fractions;
- Filler (granite, gravel) - its tensile strength should be 1200 kg/m2 and higher for the top ball, and for the leveling ball - 600-800.
Also, special plasticizers are added to ready-mixed concrete, with which you can adjust the performance of the mixture.
As for the proportions, the components listed in the list above are used in the same sequence with a ratio of 1:2:5.
Classification
Heavy traffic roads and concrete paths can be created. It is also used in the construction of transport and pedestrian routes for various purposes. That is why it is divided into 3 types.
To cover
It is used to create the top or only layer of the road surface. To prepare it, the most durable fillers and high grades of Portland cement must be used - the surface takes on enormous loads and must resist abrasion.
When creating a road surface for vehicle traffic, a prerequisite is the arrangement of a cushion. For these purposes, sand and crushed stone materials are used. The ball of each of them should be about 3-5 and be compacted using special equipment.
Characteristics of road concrete
- Microcracks. Construction often takes place in poor weather conditions, so the solution must ensure low levels of microcracks as the concrete cures.
- Resistance to external influences. Roadways are constantly subject to vibrations from traffic.
- Chemical resistance. In winter, roads are covered with substances that reduce slipping on ice.
- Stretching. A large load in road concrete falls not only in compression, but also in tension.
- Strength and frost resistance. The higher the performance in this category, the longer the service life will be, which means that the costs of repair work will be lower.
Return to contents
Brands of road concrete
Road and airfield concrete is characterized by a class of compressive strength, designated by the letter B. The number next to the letter shows what load in MPA the material can withstand without collapsing. The grade (M) of concrete also characterizes the properties; the numbers next to the letter indicate the compressive strength in kgf/m2.
Most often, concrete B20 M250 and road concrete B15 M200 are used for constructing roads. In the manufacture of concrete slabs for the construction of airfield pavements, viaducts and bridges, road concrete grade B30 M400 is used, which is endowed with great strength, frost resistance, durability and wear resistance.
Laying
Dosage
Laying road concrete.
Granular aggregates are dosed separately each. Cement, aggregates and additives are added by weight. Road concrete is made in a forced-action concrete mixer. After adding all the components, they need to be mixed for about another minute. In order for the coating to be uniform, each layer is poured from only one mixer.
Return to contents
Working with the site
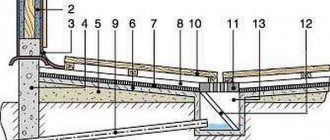
In order to minimize the influence of water, the area under it is raised and the slope is adjusted.
Return to contents
Reconstruction
If the purpose of the work is not to lay a new route, but to apply concrete to an existing road surface, the task is greatly simplified, since there is no need to wait for the concrete to be compacted. The work area is cleared. The area is leveled so that there are no bumps or holes. The area is covered with coarse sand (30-50 mm), and then with the same layer of crushed stone. They make formwork. There is no need to fill the entire area with concrete at once. Gaps must be left at short distances.
Return to contents
Samples
Before you start laying the mortar, you need to check the constituent materials. This is done in order to check whether certain additives will give the necessary qualities to the material. The result of the study must be recorded in the protocol for each parameter separately. Such a document is part of the construction contract.
If the construction of another facility is carried out in the same area and environmental conditions, it is allowed to use previous data, but they should not be older than 24 months. Samples may be requested by the customer. If materials are supplied from production, factory quality control is also required.
Return to contents
Laying road concrete
The materials are laid on a clean, not over-moistened base, taking into account the requirements of SP 78.13330.2012. Coatings are made from mixtures:
- movable in sliding forms;
- rigid, compacted by rolling.
For laying using the first method, concrete is prepared with workability grade P-1, with a volume of entrained air of at least 5%. The speed of movement of the concrete paver is set according to standard values, but not more than 3 m/min with a maximum mobility of the mixture of 4 cm. The pins are placed in the joints of the coating before concreting or sunk into the finished structure using vibratory hammers.
In the second method of laying, concrete with hardness grade Zh4 is used. Before concreting begins, the base is moistened. The mixture is distributed by a tracked asphalt paver, profiler, or motor grader with elevation control. Rigid mixtures are compacted with rollers in one layer up to 25 cm thick.
To care for the concrete surface, bitumen and film-forming compounds and wet sand are used.
Technical advantages
Accordingly, to be able to resist this kind of load, road concrete must have a whole list of strengths, among which there are many interesting ones. For example, despite the fact that this material really does not cost a lot of money and can be used in huge volumes, it boasts record mechanical strength. Dynamic loads for this concrete do not pose any problem.
It is also necessary to note the increased wear resistance, because road concrete is laid not for a couple of years, but for a whole century. This is not a joke - some companies that lay road concrete give a guarantee of exactly 100 years, regardless of the load. Road concrete boasts excellent frost resistance, chemical inertness and many other useful qualities.