Correct connection of the DRL lamp
A high-pressure mercury arc lamp is one of the types of electric lamps.
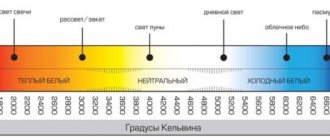
It is widely used to illuminate large objects, such as factories, factories, warehouses and even streets. It has a high light output, but does not have a high degree of quality and the light transmission is quite low. Such devices have a very wide power spectrum, from fifty to two thousand watts, and operate from a standard network of 220 volts, at a frequency of fifty hertz.
- Design and principle of operation of the lamp
- Throttle launch
- We check for functionality and malfunctions
- Connecting a lamp without a choke
Device
The shape of the product is oblong, reminiscent of ordinary incandescent light bulbs. But there are certain design differences between them.
The DRL includes the following elements:
- a glass bulb is something that almost all light sources have. Used to protect internal parts;
- metal base - used for screwing into the lampshade of an electrical appliance;
- a tube filled with mercury vapor. It is placed inside a glass flask and is made of quartz glass. Usually mercury is diluted with argon;
- lamps can be equipped with secondary electrodes and cathodes. This speeds up the ignition of the product, reaching the operating mode and increases stability;
- A carbon resistor is needed to connect the electrodes and cathodes.
Parameters and characteristics of the inductor
When choosing a ballast, you need to take into account its characteristics.
One of the main parameters is inductance, which is measured in H (Henry). The amount of reactance of the switched on ballast depends on its inductance. This value characterizes the magnetic properties of an electrical circuit. 1Gn passes 1A of current at a voltage of 1V. The main parameters of the inductive coil include:
- coil length in m;
- number of turns;
- permeability of the core material;
- cross-sectional size of the magnetic circuit;
- magnetic saturation.
The inductance of the ballast winding depends on all the characteristics described above.
The resistance of the coil winding turns depends on the cross-sectional area of the core. Therefore, when choosing ballasts for HPS, you need to take into account their power, on which the rated load current depends. Accordingly, the dimensions of the electric ballast depend on the power of the lamp.
Types of DRL lamps
DRL lamps have several modifications that have different technical characteristics and operating conditions.
- Classic DRL lamp. Standard modification. The disadvantages of the model include high heating during operation, sensitivity to voltage changes, and a long time to reach optimal performance characteristics. The most common are DRL 250 lamp and DRL 400. The luminous flux of DRL 250 allows the device to be used in home lighting.
- DRV or DRVED – tungsten mercury arc (erythemal tungsten) lamp. The product starts without using a choke and has improved light emission performance.
- DRLF - unlike a standard lamp, it has improved characteristics due to the coating of the bulb with reflective material.
Specifications
When calculating lighting systems for interior and exterior spaces, it is necessary to take into account the technical characteristics of lighting devices . The general meanings of these parameters are:
- Consume from 125 to 1000 W.
- For lighting devices up to 250 W, the E27 base is used, for more powerful devices - E40.
- Luminous flux - from 5900 lumens to 59000 lumens.
- The operating period is tens of thousands of hours.
- Possibility of operation at negative temperatures.
The technical characteristics of the DRL 250 lamp (luminous flux 13500 lm) make it possible to classify it as one of the most common lighting devices in this line.
This is a fairly powerful and economical device, capable of creating sufficient luminous flux for both outdoor conditions and industrial premises. The advantages of DRL lamps are low price , long service life and increased brightness.
What is a throttle for?
The choke for DRL lamps is used for starting; there are different types of lighting devices on the market in which it is used:
- Fluorescent and ultraviolet lamps.
Ultraviolet lamp Various types of mercury arc lighting devices: DRT, DRL, DRIZ, DRSh, DRI.
Arc mercury lamps Arc sodium lamps: DNaMT, DNaS, DNaT. Arc sodium lamp
All lighting devices have differences in the principle of obtaining light flux, there are other differences:
- different materials are used in their design;
- differ in the presence of chemical elements;
- inside the flasks there is pressure according to the own parameters of each lighting device;
- they differ in power and brightness of the light flux.
These types of lamps are united by the variable value of the starting current and resistance during the start-up process and further operation.
In order to limit the amount of operating current, different types of ballast are used in lighting devices of this type: electronic ballasts, ballasts and ballasts, which are inductor coils (chokes). At the moment of startup, each device of this type has a high resistance value; when the lighting device is ignited, a process of electrical breakdown occurs in the inert gas environment with which the lamp is filled (mercury or sodium vapor), and an arc discharge occurs.
During the process when the lamp is ignited, the ionized gas loses resistance from the arc discharge several tens of times, and for this reason the current increases and heat is released. If you do not limit the amount of current, it will instantly create a superheated gas environment, which will lead to breakdown of the lighting device and damage from the inside. To prevent this, a resistance (choke) is included in the lighting device circuit.
Physical parameters and connection diagram of the inductor
A DRL inductor connected in series has a reactance, the value of which depends on the inductor: one Henry passes one ampere of current when the voltage is one volt.
Throttle
The parameters of the inductor include:
- square of copper wire used;
- number of turns;
- what is the core and cross-sectional size of the magnetic circuit;
- what electromagnetic saturation.
The inductor has an active resistance, which is always taken into account when calculating the ballast for each type of lighting device of this type, taking into account its power; the overall dimensions of the inductor depend on this.
Let's consider a simple circuit for switching on the ballast, when the design of the DRL lamp provides (additional) electrodes for the process of occurrence of a glow discharge that turns into an electric arc.
DRL lamp connection diagram
In this case, inductance limits the amount of operating current in the lighting device.
Ballast for fluorescent lamps
Structurally, a fluorescent lighting device uses a ballast choke for starting; new types of this lighting device use electronic ballasts, this is an electronic type of ballast. The purpose of this device is to contain the increasing current value at one level, which maintains the required voltage on the electrodes inside the lighting fixture.
Technical properties of lamps of various types
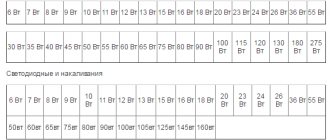
Before purchasing a lamp and lamp for it, you need to understand the features of the devices. Most designs are suitable for a DRL lamp, but the wrong choice of base size or power consumption will lead to poor lighting of the room. Here are the technical characteristics of various light bulbs in the table:
| Type | Light bulb model | Active power consumption | Burning duration | Light flow | Initial luminous flux (thousands of Lumens) |
| Mercury arc lamps | DRL 125 | 125 W | 140 hours | 12 thousand lm | 6 |
| 250 | 0.25 kilowatt | 280 h | 12 thousand lm | 13 | |
| 400 | 0.4 kW | 450 hours | 15 thousand Lumens | 24 | |
| DNAT | DNAT 100 | 0.1 kilowatt | 115 h | 6 thousand Lumens | 9,4 |
| DNAT 150 | 0.15 kW | 170 h | 10 thousand lm | 14 | |
| DNAT 250 | 0.25 kilowatt | 290 hours | 15 thousand Lumens | 24 | |
| DNAT 400 | 0.4 kW | 460 h | 15 thousand Lumens | 47,5 | |
| LED lights | analogue of DRL 125 | 40 Watt | 40 hours | up to 100 thousand lm | 2,5 |
| analogue of DRL 250 | 80 Watt | 80 hours | up to 100 thousand Lumens | 5 | |
| analogue of DRL 400 | 120 Watt | 120 hours | Up to 100 thousand lm | 10 |
As you can see, many lamps are interchangeable. DRL 125 and 400, as well as any other model, have an LED analogue that consumes less energy. The DRL lamp requires special starting equipment, but it lasts longer.
Source: cdelct.ru
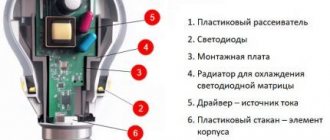
The main functional parts of a conventional DRL lamp
The main elements of a modern arc mercury fluorescent or phosphor lamp:
- plinth base connected to the lighting fixture socket;
- quartz burner, which is the central mechanism of the lighting device;
- a glass container that serves as the main protective shell of all internal elements.
Like most traditional lamps, the mercury fluorescent light source is a glass container with a threaded base installed at the bottom. The glow occurs due to the presence of a mercury-quartz burner, which has the shape of a tube and is filled with a mixture based on argon and mercury.
Four-electrode lamps are equipped with main and additional electrodes, which are connected to the main cathodes through opposite polarities with an additional carbon resistor. Additional electrodes not only stabilize the operation of the lighting device, but also significantly simplify the ignition process.
The main function of the base part is to receive mains electricity through a point and threaded element from the contacts of the socket, which is built into the lighting fixture.
At the next stage, electrical energy is transferred to the electrodes.
Connection diagrams
Most DRL devices have a choke in the circuit. However, there are methods that allow you to use DRL without a choke.
Throttle
The connection diagram for any DRL lamp is quite simple and includes connecting the loads in an electrical circuit in series. A 220 volt network is used, operating at a standard frequency. Due to this, even a high-power street lighting source can be connected to a regular home network.
Resistance stabilizes and corrects nutritional indicators. Due to it, a uniform glow is achieved without blinking and other undesirable factors. The luminous flux remains unchanged, which is important for any lighting source.
During startup, the system consumes significant voltage, which often reaches two or three input ratings. The resistance stabilizes this voltage and prevents the device from burning out.
The DRL lamp does not light up instantly. In some cases, it can take up to fifteen minutes to fully warm up and reach maximum light output.
The power of lighting devices can range from 50 to 2000 W. Specific power indicators do not affect the connection diagram and always require a single-phase 220 V network with a frequency of 50 Hz.
No throttle
If you need to connect a DRL 250 lamp without a choke, a simple solution would be to purchase a DRL that functions without additional components. The devices have a spiral installed inside, which is responsible for stabilizing the voltage.
You can also use a traditional incandescent lamp. It must be equivalent in power to the DRL used and have the required resistance rating. The incandescent lamp acts as a resistor, effectively lowering the output voltage.
The resistance element can be replaced with a capacitor or a set of capacitors. In this case, it is important to calculate the current supplied by the circuit as accurately as possible so that it corresponds to the operating voltage.
Comparison of DRL, DNAT and LED lamps
Table 1. Parameters of typical lamps and luminaires DRL and DNAT
| View | Type | Rated power, W | Active power consumption, W | Average burning time, hours | Lamp luminous flux, Lm (initial) | Average luminous flux taking into account the efficiency of the lamp diffuser, Lm (initial) | Average luminous flux of a luminaire with a lamp, Lm (after 3 months of operation) For selection of LED analogues * | Average luminous flux taking into account the efficiency of the lamp diffuser, Lm (after 1 year of operation) |
| DRL | DRL-125 | 125 | 140 | 12 000 | 6 000 | 4 400 | 3 100 | 2 600 |
| DRL-250 | 250 | 280 | 12 000 | 13 200 | 9 650 | 6 800 | 5 800 | |
| DRL-400 | 400 | 460 | 15 000 | 24 000 | 17 500 | 12 300 | 10 500 | |
| DRL-700 | 700 | 820 | 20 000 | 41 000 | 29 950 | 21 000 | 18 000 | |
| DNAT | ||||||||
| DNAT-50 | 50 | 55 | 6 000 | 3 700 | 2 800 | 2 400 | 2 200 | |
| DNAT-70 | 70 | 80 | 6 000 | 6 000 | 4 400 | 3 900 | 3 500 | |
| DNAT-100 | 100 | 115 | 6 000 | 9 400 | 6 850 | 6 000 | 5 500 | |
| DNAT-150 | 150 | 170 | 10 000 | 14 500 | 10 600 | 9 400 | 8 500 | |
| DNAT-250 | 250 | 300 | 15 000 | 26 000 | 19 000 | 16 700 | 15 200 | |
| DNAT-400 | 400 | 470 | 15 000 | 48 000 | 35 100 | 33 800 | 28 000 |
* Luminous flux taking into account losses in the lamp reflector and primary degradation of lamps (depending on their type) during initial operation.
Table 2. Comparative characteristics of luminaires with DRL, DNAT and LED lamps
| Lamp type | DRL | DNAT | LED lamp, modifications 2014 |
| Initial light output taking into account luminaire efficiency (lamp only) | 33 Lm/W (46 Lm/W) | 60 Lm/W (83 Lm/W) | 115 Lm/W (130 Lm/W, varies 90-135 Lm/W depending on the type of LED) |
| Decrease in luminous flux after 3 months (1 year of operation) | 30% ( 40% ) | 12% ( 20% ) | 2% ( 4% ) |
| Light output taking into account the efficiency of the lamp after 3 months / 1 year of operation | 23 Lm/W ( 20 Lm/W ) | 51 Lm/W ( 48 Lm/W ) | 112 LM/W ( 110 LM/W ) |
| Service life, hours | 12,000 (3 years*) | 10,000 (2.5 years*) | 80,000 (21 years*) |
| Contrast and color rendering | weak | very weak | high |
| Mechanical strength | average | average | excellent |
| Temperature stability | weak | very weak | excellent |
| Resistance to changes | weak | weak | excellent |
| Start-up time | 10-15 min | 10-15 min | 1-2 seconds |
| Heats up | strongly | strongly | moderately |
| Environmental Safety | the lamp contains up to 100 mg of mercury vapor | the lamp contains sodium-mercury amalgam and xenon | absolutely harmless |
* Average operating time of street lighting is 3800 hours per year (Mossvet, Lensvet)
MYTH No. 2.
The luminous flux of DRL and DNAT lamps is approximately equal to the reference data for DRL and DNAT
.
As a rule, luminous flux reference tables are given NOT for
DRL and DNAT
, but for
DRL and DNAT lamps.
Only part of the luminous flux of the lamp shines directly from the lamp; the rest of the luminous flux must be reflected from the light diffuser. The reflector-diffuser
of the lamp
has large losses
associated with the inability to collect and form the entire luminous flux due to optical-geometric difficulties in the manufacture of the reflector, as well as large losses of the reflective material, for which the key parameters are reliability and price, rather than optical properties.
Thus, losses due to the reflector are about 20-25%
.
If the lamps have protective glass
, it also introduces losses
of up to 10%
.
Conclusion: the real difference between the luminous flux of a DRL and DNAT lamp and a passport lamp is about 27% (25..35%)
MYTH No. 3. When making light calculations, you can focus on the nameplate luminous flux of the luminaire (luminous flux of DRL and DNaT lamps, taking into account the losses of the luminaire reflector).
DRL and HPS lamps have
severe degradation during initial operation
, which must be taken into account immediately when making light calculations!
After three months, DRL lamps lose about 30%
of the luminous flux, and after
1 year of operation, 40% of the luminous flux! After three months, HPS lamps lose about 15%
of the luminous flux, and after
1 year of operation, 20% of the luminous flux! Conclusion: to calculate illumination
for luminaires
with DRL and HPS lamps, it is necessary to take into account NOT the initial
(certificate)
luminous flux, but the luminous flux after initial operation, for example after 3 months, or better yet 1 year of operation! Note: In reality, LEDs
are not ideal either, and there are factors that also cause degradation of the luminous flux.
But for high-quality lamps with properly designed heat sinks and current stabilizers
, degradation is insignificant and can be neglected.
After three months, LEDs lose about 2%
of the luminous flux, and after
1 year of operation, 4% of the luminous flux!
MYTH No. 4.
The operation of DRL and DNAT lamps is more expensive than LED lamps in terms of the cost of lamps and the work required to replace them. The operation of DRL and HPS lamps
, of course, is mainly an expensive job of replacing burnt out and rapidly degrading lamps, where you need to take into account not only the purchase of the lamps themselves, but also mainly
the cost of expensive high-altitude work with a tower
.
It is also necessary to take into account significant additional work during operation to remove dust and dirt from the lenses and reflectors of the lamps. It is necessary to wipe the lamps quite often
, and carefully, given the fragility of the lamps.
This is quite expensive and NECESSARY maintenance
.
If you do not wipe the reflector and diffuser of the lamp in time, the loss of luminous flux can be up to 50%! Conclusion: LED lamps
also gather dust, but their design (due to flat glass and a sealed housing, as well as the absence of a reflector, which is subject to increased cleanliness requirements)
requires significantly less frequent and simpler maintenance
during operation.
LED lamps
Overvoltage and LEDs.
Voltage cannot be applied to the LED as such due to its current-voltage characteristic (volt-ampere characteristic). Either it won't light up or it will burn out, so the LED is controlled by current. The easiest way is through a resistor. The lamp provides a so-called driver to supply “edible” current to the LED circuit. The driver not only acts as a converter (adapter), but also protects the LEDs from overvoltage and power surges. In this case, it is the driver that takes the hit, which significantly reduces the cost of non-warranty repairs of the lamp.
Source: tdmegaprom.ru
Selection and characteristics of DRL
Among the suppliers that have proven themselves from a positive point of view, we can mention: GE, Philips, Osram, Sylvanya, Radium, DELUX, Lisma, Eurosvet, E.NEXT.
There are models with already built-in ballast. This way an external choke is not required.
In order to choose the required type of lighting fixture, you will need to answer the following questions:
- What service life is required?
- What brightness will be sufficient for the illuminated area?
- Which socket will be used?
- How much power will be required?
A special feature of this type of lamp is the requirement for their placement. They should be positioned high. For example, a 125 W illuminator should be raised to a height of 4 meters, and a 1 kW illuminator should be raised to a height of 8 meters.
Operating mode
According to technical regulations for cars, DRL should automatically turn on when the engine starts. When you turn on the low beams, they should turn off automatically so as not to dazzle at night.
There are also combined models with installed turn signals on sale. The turn signal duplication section is connected separately in parallel to the standard turn signals. Having a stable diet is also a must.
DRL with turn signal
For models with additional control, there is a follow-up backlight function that operates for 10 minutes after the engine is turned off. It illuminates your path to your home or dugout, depending on where you live. Osram DRL has a mode in which they do not turn off, but dim by 50%. I just don’t know how legal it is and whether it will cause blindness.