Features of operation of network protection circuit breakers
Whatever class the circuit breaker belongs to, its main task is always the same - to quickly detect the occurrence of excessive current and de-energize the network before the cable and devices connected to the line are damaged.
Currents that may pose a danger to the network are divided into two types:
- Overload currents. Their appearance most often occurs due to the inclusion of devices in the network, the total power of which exceeds what the line can withstand. Another cause of overload is a malfunction of one or more devices.
- Overcurrents caused by short circuit. A short circuit occurs when the phase and neutral conductors are connected to each other. In normal condition they are connected to the load separately.
The design and principle of operation of the circuit breaker is on video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=9bTw3wtgOWY
Overload currents
Their value most often slightly exceeds the rating of the machine, so the passage of such an electric current through the circuit, if it does not drag on for too long, does not cause damage to the line. In this case, instantaneous de-energization is not required in this case; moreover, the electron flow often quickly returns to normal. Each AV is designed for a certain excess of electric current at which it is triggered.
A thermal release, the basis of which is a bimetallic plate, is responsible for turning off the power under the influence of a powerful load.
This element heats up under the influence of a powerful current, becomes plastic, bends and triggers the machine.
Short circuit currents
The flow of electrons caused by a short circuit significantly exceeds the rating of the protective device, causing the latter to immediately trip, cutting off the power. An electromagnetic release, which is a solenoid with a core, is responsible for detecting a short circuit and immediate response of the device. The latter, under the influence of overcurrent, instantly affects the circuit breaker, causing it to trip. This process takes a split second.
However, there is one caveat. Sometimes the overload current can also be very large, but not caused by a short circuit. How is the device supposed to determine the difference between them?
In the video about the selectivity of circuit breakers:
Here we smoothly move on to the main issue that our material is devoted to. There are, as we have already said, several classes of AB, differing in time-current characteristics. The most common of them, which are used in household electrical networks, are devices of classes B, C and D. Circuit breakers belonging to category A are much less common. They are the most sensitive and are used to protect high-precision devices.
These devices differ from each other in terms of instantaneous tripping current. Its value is determined by the multiple of the current passing through the circuit to the rating of the machine.
Selecting a machine based on load power
To select a circuit breaker based on load power, it is necessary to calculate the load current and select the rating of the circuit breaker greater than or equal to the obtained value. The current value expressed in amperes in a single-phase 220 V network usually exceeds the load power value expressed in kilowatts by 5 times, i.e. if the power of the electrical receiver (washing machine, light bulb, refrigerator) is 1.2 kW, then the current that will flow in the wire or cable is 6.0 A (1.2 kW * 5 = 6.0 A). Calculated at 380 V, in three-phase networks, everything is similar, only the current value exceeds the load power by 2 times.
You can calculate more accurately and calculate the current according to Ohm's law I=P/U - I=1200 W/220V =5.45A. For three phases the voltage will be 380V.
Possible
How to choose a circuit breaker according to the power of a 380 engine
The automatic circuit breaker (AB) is selected according to the rated current I of the circuit breaker and the rated current I of the release. I rast =I dl/K t
, where I dl =I n.dv – long-term current in the line, I n.dv – rated motor current, K t – thermal coefficient, taking into account the installation conditions of the motor.
K t =1
- for installation in an open version;
K t =0.85
– for installation in closed cabinets.
Idl=Iн= Рн/(Un·√3·ηн·cosφ), (1)
where Рн is engine power, kW; Un – rated voltage of the electric motor, kV; ηн – engine efficiency (without percent), cosφ – engine power factor. Rated current of an asynchronous motor with short circuit. the rotor will be approximately equal to its double power, taken in kilowatts: In≈ 2Рн(kW)
Select AB: Type – In.off – Irast –
It is necessary that the following condition be fulfilled: Imm.sr ≥ KIcr, where Iinst.sr is the instantaneous operation current, Icr is the maximum short-term current, K is a coefficient that takes into account the inaccuracy of determining Icr in the line. K = 1.25
– for AB with In > 100A;
K = 1.4
– for AB with In ≤ 100A.
Icr = Istart = Ki In, where Ki is the multiplicity of the starting torque Ki = Istart/In
. Ki values are taken from tables. If the condition is met, then the AV is selected correctly; if it is not met, then the AV with a large value of the release current is selected.
Let's give an example.
AB installation condition:
Based on the engine type, we write out its nominal data from the table:
Since the machine is installed in a cabinet, Kt = 0.85, therefore:
Based on the current of the release we select the machine: VA 51-25; In = 25 A Irast = 16 A;
Imgn.av = 10∙Irast = 10∙16 = 160 A
The inequality is satisfied, which means the machine was chosen correctly.
Source
How to choose a machine for electrical wiring
In order to choose the right circuit breaker, you need to estimate the maximum permissible current load of the network (sum up all devices). The denomination of the machine (the number after the letter) should not exceed this value.
For an ordinary apartment where there are no “serious” power consumers such as an air conditioner or water heater, a class B machine is suitable. Such a network is considered lightly loaded. It is dangerous to install a high-load circuit breaker (class D) for a network that powers light bulbs. He will not perceive voltage surges in it as harmful and can even miss a short circuit.
A lightly loaded device in a network with a heavy load in normal mode, on the contrary, will operate inappropriately and often.
Yes, we almost missed it: machines differ in the number of phases (poles). The number of poles of the machine indicates which type of network it can work with. You can also install one class C input switch and one single-phase switch in the apartment to provide separate areas (kitchen, room, separately for air conditioning, if provided). If you don’t want to complicate things, in a two-room apartment you can get by with one circuit breaker B with a rating of 16.
We have almost figured out how to choose a circuit breaker based on current and power. But if you consider only the load of consumers, you can run into trouble. The choice of machine directly depends on the type of wiring and cable. If the wiring is weak, a powerful automatic machine will not cope with its tasks when overloaded.
That is, you always need to take into account the cross-section of the wire and its throughput
In houses before 2001-2003, there will most likely be aluminum wiring in single-layer insulation. Most likely, it has already served its purpose (nominally it can withstand 20 years under ideal conditions, without overload). It is categorically not recommended to install a new machine on it, taking into account only the total power of consumers. The automatic machine will stop working frequently, but the problem of overheating will remain.
There are essentially two options:
- Change the wiring to copper.
- For powerful consumers (washing machine, boiler, air conditioner), draw a separate line from the panel and install a separate machine on it.
Copper wire carries more current than aluminum
But here, in addition to the material, it is important to take into account its cross-section. It makes it clear how many amps can be passed through the cable without fear of damage and overheating
- Aluminum wire with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2 safely operates with currents up to 16-24 A.
- Copper wire with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2 safely operates with currents of 21-30 A.
This means that with a load of 23 A, a machine rated at 16 A will de-energize the wiring in a minute. It is enough to prevent the copper wire from overheating. If you install a 25 A circuit breaker, before disconnecting the cable will carry current beyond its normal load, it will overheat, the insulation will wear out faster, and the socket will burn out over time. For aluminum wiring, accordingly, these values are lower.
For ease of understanding, we offer a table for selecting a circuit breaker based on the cable cross-section.
Last piece of advice: you shouldn’t skimp on your safety. It is better to buy machines from specialized stores and choose manufacturers with a proven reputation. On-site managers will answer questions that we may have missed in this article.
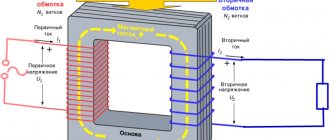
Automatic switch for protecting an electric motor - how to choose the right one?
When selecting circuit breakers that can protect electric motors from damage as a result of short circuits or excessively high loads, it is necessary to take into account the large value of the starting current, often 5-7 times higher than the nominal value. Asynchronous power units with a squirrel-cage rotor are subject to the most powerful starting overloads. Since this equipment is widely used for work in industrial and domestic conditions, the issue of protecting both the device itself and the power cable is very relevant. This article will discuss how to correctly calculate and select a motor protection circuit breaker.
Tasks of devices for protecting electric motors
Household electrical equipment is usually protected from large inrush currents in networks using three-phase circuit breakers that operate some time after the current exceeds the rated value. Thus, the motor shaft has time to spin up to the desired rotation speed, after which the force of the electron flow decreases. But the protective devices used in everyday life do not have precise settings. Therefore, the choice of a circuit breaker that allows you to protect an asynchronous motor from overloads and short-circuit overcurrents is more complicated.
Modern motor protection circuit breakers are often installed in a common housing with starters (the so-called motor starting switching devices). They are designed to perform the following tasks:
- Protecting the device from overcurrent occurring inside the motor or in the power supply circuit.
- Protection of the power unit from phase conductor breakage, as well as phase imbalance.
- Providing a time delay that is necessary so that the motor, which is forced to stop as a result of overheating, has time to cool down.
Control and protective automation for the engine on video:
- Shutting down the installation if the load is no longer supplied to the shaft.
- Protection of the power unit from long overloads.
- Protection of the electric motor from overheating (to perform this function, additional temperature sensors are mounted inside the unit or on its body).
- Indication of operating modes, as well as notification of emergency conditions.
It is also necessary to take into account that the circuit breaker for protecting the electric motor must be compatible with control and control mechanisms.
Calculation of an automatic machine for an electric motor
Until recently, the following scheme was used to protect electric motors: a thermal regulator was installed inside the starter, connected in series with the contactor. This mechanism worked like this. When a large current passed through the relay for a long time, the bimetallic plate installed in it was heated, which, bending, interrupted the contactor circuit. If the excess of the set load was short-term (as happens when starting the engine), the plate did not have time to heat up and trigger the machine.
Internal structure of the motor protection circuit breaker in the video:
The main disadvantage of this scheme was that it did not save the unit from voltage surges, as well as phase imbalance. Nowadays, the protection of electric power plants is provided by more accurate and modern devices, which we will talk about a little later. Now let’s move on to the question of how to calculate the machine that needs to be installed in the electric motor circuit.
To select a protective circuit breaker for an electrical installation, you need to know its time-current characteristics, as well as its category. The time-current characteristic does not depend on the rated current for which the AV is designed.
To prevent the circuit breaker from tripping every time the motor is started, the value of the starting current should not be greater than that which causes the device to immediately operate (cut-off). The ratio of the starting current and the nominal value is specified in the equipment passport, the maximum allowable is 7/1.
When calculating the machine practically, you should use the reliability coefficient, denoted by the symbol Kn. If the rated current of the device does not exceed 100A, then the value of Kn is 1.4; for larger values it is 1.25. Based on this, the value of the cut-off current is determined by the formula Iots ≥ Kn x Istart. We select the circuit breaker in accordance with the calculated parameters.
Another value that must be taken into account when selecting when the machine is mounted in an electrical panel or a special cabinet is the temperature coefficient (CT). This value is 0.85, and the rated current of the protective device should be multiplied by it when selecting (In/Kt).
Modern electrical protection devices for power units
Modular automatic motors, which are universal devices that successfully cope with all the functions described above, are very popular.
In addition, they can be used to adjust shutdown parameters with high accuracy.
Modern automatic motors come in many varieties, differing from each other in appearance, characteristics and control method. As when selecting a conventional device, you need to know the value of the starting current, as well as the rated current. In addition, it is necessary to decide what functions the protective device should perform. Having made the necessary calculations, you can buy an automatic motor. The price of these devices directly depends on their capabilities and the power of the electric motor.
Information about the company
Tekhprivod Company, LLC
has been operating in the drive equipment market since 1997. Our goal is to build impeccable communication in the “manufacturer-dealer-customer” chain. Our main goal is customer satisfaction with the quality of products and service.
represented in several regions of Russia: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Nizhny Novgorod, Kazan, Rostov-on-Don. We also have a partner company in Minsk (Belarus).
Advantages: – Our warehouses stock a wide range of equipment, which guarantees prompt delivery. – Individual terms of cooperation, flexible pricing policy, working with regular clients without prepayment. – Possibility of completing drive equipment with additional options. – Sale of gearboxes and geared motors both in basic configuration and in individual configuration in accordance with customer technical requirements. – Delivery of equipment to all regions of Russia and CIS countries. – Technical consultations regarding the selection, installation and commissioning of equipment. – Warranty and post-warranty service.
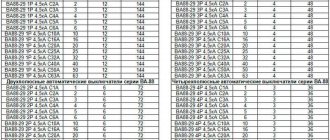
Current ratings of circuit breakers
The limit value of the nominal value is determined by the formula Ir ≤ Ipr/1.45, where Ipr is the permissible current in long-term mode for a certain wiring. If you plan to install a network, proceed as follows:
- clarify the consumer connection diagram;
- collect passport data of equipment, measure voltage;
- according to the presented diagram, they are calculated separately, the currents in individual circuits are summed up;
- for each group it is necessary to select a machine that will withstand the appropriate load;
- determine cable products with a suitable conductor cross-section.
Rules for choosing denomination
An example of choosing the machine's nominal value for each line
For correct conclusions, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the connected equipment. If the total current is calculated to be 19 amperes, users prefer to buy a 25A device. This solution assumes the possibility of applying additional loads without significant restrictions.
However, in some situations it is better to choose a 20A circuit breaker. This ensures a relatively shorter time for power outages when the current increases (temperature increases) with a bimetallic disconnector
This precaution will help maintain the integrity of the electric motor windings when the rotor rotation is blocked by a jammed drive.
Different response times are useful to ensure selective operation of protective equipment. Devices with lower latency are installed on the lines. In an emergency, only the damaged part is disconnected from electricity. The input machine will not have time to turn off. Power supply through other circuits is useful for maintaining lighting, alarms, and other engineering systems in working order.
Selecting a 0.4 kV circuit breaker: calculation of protection, settings for networks and motors
The circuit breaker is selected based on the following conditions:
1. Correspondence of the rated voltage of the switch Un to the rated network voltage Uс: Un, Uс. (6.1)
2. Correspondence of the rated current of the release In.rast to the rated load current Idn: In.rast, Idn. (6.2) 3. Correspondence of the rated current of the release Iin.rast to the maximum operating current Ioper.max of the group of electrical receivers (for input power switches of assemblies and panels) in long-term mode: In.rast, Ioper.max. (6.3).
Climatic versions of electric motors
When choosing an electric motor, not only its technical characteristics are taken into account, but also the environmental conditions in which it will be operated.
Modern electric drives are available in different climatic versions. Categories are marked with corresponding letters and numbers:
- U - models for use in temperate climates;
- HL - electric motors adapted to cold climates;
- TS - versions for dry tropical climates;
- TV - versions for humid tropical climates;
- T - universal versions for tropical climates;
- О - electric motors for operation on land;
- M - engines for operation in marine climates (cold and temperate);
- B - models that can be used in any area on land and at sea.
The numbers in the model nomenclature indicate the type of its placement:
- 1 — possibility of operation in open areas;
- 2 - installation in rooms with free access of air;
- 3 — operation in closed workshops and premises;
- 4 - use in industrial and other premises with the ability to regulate climatic conditions (availability of ventilation, heating);
- 5 - versions designed for operation in areas of high humidity, with high condensation formation.
Circuit breakers
Anyone who has dealt with electrical wiring has heard about circuit breakers or circuit breakers.
First of all, a competent electrician will always advise you to treat the choice of such an important part of the electrical network with particular scrupulousness. Since later this simple device can save you from many troubles
It doesn’t matter at all what type of electrical installation work is being carried out - whether new wiring is being installed in a newly built house, the old one is being replaced, the panel is being modernized, or a separate branch is being laid for too energy-intensive devices - in any case, special attention must be paid to the selection of the machine according to power and other parameters
Purpose of the device
Any modern machine has two degrees of protection. This means that he will be able to help in the two most common situations.
- The first implies overheating of the wiring as a result of the passage of currents through it that are greater than the rated ones. It’s easy to guess what this can lead to: a cable burnout, and ultimately a short circuit or even a fire.
- The second situation that a circuit breaker can prevent is a short circuit, as a result of which the current strength in the circuit can increase by enormous values, and this can, at best, lead to the failure of all electrical equipment. At worst, it could result in a fire of electrical equipment, and from it the entire room. There is no need to talk about the integrity of the wiring at all.
Thus, the machine is capable of protecting not only personal property, but in some cases, life. Although for this it is necessary to carry out a competent calculation of the circuit breaker in terms of power and a number of other parameters. And also, you should not take the machine “with a reserve”, since at critical values of currents in the network it may simply not work, which is equivalent to its absence.
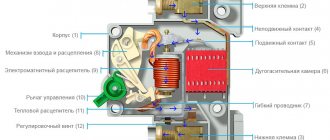
Principle of operation
The main task of the safety switch is to cut off the supply of electric current from the supply cable to the consumer's network. This happens thanks to the releases located in the body of the machine. Moreover, there are two types of such parts:
- Electromagnetic, which consists of a coil, a spring and a core, which, when the rated currents are exceeded, is retracted and through the spring disconnects the contacts. This happens almost instantly - from 0.01 to 0.001 seconds, which can provide reliable protection.
- Bimetallic thermal - triggered by the passage of currents exceeding the limit values. In this case, the bimetallic plate, which is the basis of such a release, bends and the contacts break.
Types of ABs and their features
Given the variety of electrical networks and certain situations, machines can be of different types. The principle of their operation is no different in any significant way - the same releases are triggered, but depending on the situation and a number of other nuances, different variations are used.
Thus, for a standard single-phase network with a voltage of 220 volts, single-pole and two-pole AVs are produced. The former are capable of breaking only one wire - a phase. The latter can work with both phase and zero. Of course, it is preferable to use the second option. Especially when it comes to rooms with high humidity. Of course, a single-pole circuit breaker will cope with its task, but situations may arise when burnt-out wires are short-circuited. In this case, naturally, the phase will be cut off, but the neutral wire will be energized, which can be extremely dangerous.
For three-phase networks with a voltage of 380 volts, three- or four-pole circuit breakers are used. They must be installed both at the entrance and directly in front of the consumer. As is clear, such machines cut off all three phases connected to them. In rare cases, it is possible to use one- or two-pole protective devices to cut off one or two phases, respectively.
Selection of circuit breakers for electric motors
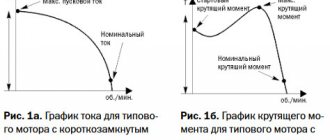
When choosing circuit breakers to protect motors, we must take into account that when starting an electric motor, a starting current arises that exceeds 5 - 7 times the rated value.
Circuit breakers are selected according to the following conditions:
- Unom. – rated voltage, V;
- Unom.net – rated mains voltage, V.
- Inom.rast. – rated current of the circuit breaker release, A;
- Inom.motor – rated current of the electric motor, A.
The setting current of the electromagnetic and semiconductor release is selected according to the formula [L1, p. 106]:
For an approximate calculation of the current setting of the electromagnetic and semiconductor release, it can be taken from Table 6.1 [L1, p. 107].
Table 6.1 – Values of coefficients for calculating the cut-off current of circuit breakers installed in electric motor circuits
The reliability of operation of the machine during a two-phase and single-phase short circuit during a short circuit at the motor terminals is determined by the sensitivity coefficient and is calculated using the formula [L1, p. 107]:
If there are no values for the dispersion coefficient kp, it is recommended to take the sensitivity coefficient in the range of 1.4-1.5.
If the sensitivity of protection against phase-to-phase short circuits is insufficient, the following measures should be taken:
- clarify the value of Iс.о taking into account the influence of the external network resistance on the starting current of the electric motor;
- choose another type of AB;
- increase the cable cross-section by one or two steps, but no more;
- apply remote relay protection.
If the sensitivity of protection against single-phase short circuits is insufficient, the following measures should be taken:
- use a cable of a different design with a zero core, aluminum sheath;
- lay additional neutral metal connections;
- use AV with built-in protection against single-phase short circuits;
- apply remote relay protection against single-phase short circuits, the operation current of this protection is assumed to be 0.5-1*Inom.motor. Sensitivity coefficient kch > 1.5, according to PUE 7th edition;
Briefly the principle of operation and purpose of circuit breakers
In the event of a short circuit, the circuit breaker is triggered almost instantly thanks to the electromagnetic splitter. At a certain excess of the rated current value, the heating bimetallic plate will turn off the voltage after some time, which can be found out from the current characteristic time graph.
This safety device protects the wiring from short circuits and overcurrents exceeding the calculated value for a given wire cross-section, which can heat the conductors to the melting point and cause the insulation to ignite. To prevent this from happening, you need not only to choose the right protective switch that matches the power of the connected devices, but also to check whether the existing network can withstand such loads.
Appearance of a three-pole circuit breaker
Wires must match the load
It often happens that in an old house a new electric meter, automatic machines, and RCDs are installed, but the wiring remains old. A lot of household appliances are bought, the power is summed up and an automatic machine is selected for it, which regularly holds the load of all switched on electrical appliances.
Everything seems to be correct, but suddenly the wire insulation begins to emit a characteristic odor and smoke, a flame appears, and the protection does not work. This can happen if the wiring parameters are not designed for such current.
Let's say the cross-section of the old cable core is 1.5mm², with a maximum permissible current limit of 19A. We assume that several electrical appliances were connected to it at the same time, making up a total load of 5 kW, which in current equivalent is approximately 22.7 A; it corresponds to a 25 A circuit breaker.
The wire will heat up, but this machine will remain on all the time until the insulation melts, which will lead to a short circuit, and the fire can already flare up in full swing.
NYM power cable
Protect the weakest link in the electrical wiring
Therefore, before choosing a machine according to the load being protected, you need to make sure that the wiring will withstand this load.
According to PUE 3.1.4, the machine must protect the weakest section of the electrical circuit from overloads, or be selected with a rated current corresponding to the currents of the connected electrical installations, which again implies their connection with conductors with the required cross-section.
If you ignore this rule, you should not blame an incorrectly designed machine and curse its manufacturer if a weak link in the electrical wiring causes a fire.
Melted wire insulation
Calculation of the machine's nominal value
We assume that the wiring is new, reliable, correctly calculated, and meets all requirements. In this case, the selection of a circuit breaker comes down to determining a suitable rating from a typical range of values, based on the calculated load current, which is calculated by the formula:
where P is the total power of electrical appliances.
This means active load (lighting, electric heating elements, household appliances). This calculation is completely suitable for a home electrical network in an apartment.
Let's say the power calculation is made: P = 7.2 kW. I=P/U=7200/220=32.72 A. Select a suitable 32A machine from a range of values: 1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80, 100.
This rating is slightly less than the calculated value, but it is practically impossible for all electrical appliances in the apartment to be turned on at the same time. It is also worth considering that in practice, the operation of the machine begins with a value 1.13 times greater than the nominal value, due to its time-current characteristics, that is, 32 * 1.13 = 36.16 A.
To simplify the selection of a circuit breaker, there is a table where the ratings of the circuit breakers correspond to the power of single-phase and three-phase loads:
Current circuit breaker selection table
The denomination found using the formula in the above example is closest in terms of power value, which is indicated in the red highlighted cell. Also, if you want to calculate the current for a three-phase network, when choosing a machine, read the article about calculating and choosing the wire cross-section
The selection of circuit breakers for electrical installations (electric motors, transformers) with reactive loads, as a rule, is not made based on power. The rating and type of current characteristics of the circuit breaker are selected according to the operating and starting current specified in the passport of this device.
Table for selecting wire cross-section by power
What wire cross-section is needed for 3 kW
Formula for finding current power
Smooth start of an asynchronous electric motor with a squirrel-cage rotor
New Year's greetings with humor
Selecting a circuit breaker for an electric motor
Nowadays, circuit breakers (CBs) have experienced a huge leap in their development. Nobody uses fuses or anything similar due to their very significant disadvantages, unlike AB.
At the same time, the number and variety of devices has grown to the extent that very often you need to know how to select a circuit breaker for an electric motor. In order not to make a mistake in choosing a circuit breaker, you need to have an idea of its main characteristics and, of course, parameters.
The first is the rated current of the machine. This is the value for which the machine is designed for normal operation. Increasingly, machines come with regulators for the range of the specified rated current. But if you specify a value greater than what is allowed on the machine, the protection will work and it will not work.
The second is the type of machine. It determines the short-term current value at which the machine will operate. If your circuit breaker is connected to the necessary equipment, then the currents that arise when it is turned on can be tens of times greater than the short-term current value indicated on the switch.
Electric motors are an excellent example. When they are started, the short-term current increases exactly 10 times.
There are three main types of automatic switches based on short-term current strength:
- Type B – short-term increase in current value by 3-5 times;
- Type C – 5-10 times magnification;
- Type D (D) – 10-50 times;
The next parameter is the response time. The period of time starting from the moment when the controlled parameter exceeded the limit value and until the moment the contacts are open. Based on response time, circuit breakers are divided into:
- Selective – response time – 1 second;
- Normal – time from 0.02 to 0.1 seconds;
- High-speed - 0.005 seconds.
Selective AVs are used in circuit breakers because they have a contact with an opening delay. Such ABs are placed at the beginning of the chain of machines, followed by less powerful ones. If an emergency occurs, thanks to selectivity, they will turn off only some of the equipment that is at risk, while the rest is in working order.
And the last thing is the breaking capacity. For automatic switches, this is the maximum value that is briefly present in the circuit to ensure the operation of the switch (welding contacts at currents higher than normal). It can be a hundred times the normal operating current. Occurs when there is a short circuit.
We must not forget about the release mechanisms. There are only two types of them:
- Thermal cutoff. In this embodiment, a plate is used that is made of two different metals with thermal conductivity indicators that differ from each other. The operating current of the circuit flows through it. If the value of this current is nominal or slightly less, the plate is in the closed position. But if, over a long period of time, the current value exceeds the rated value, the plate will heat up, become deformed and the circuit will open. The important fact here is that the current has a long-term effect and can exceed the norm by at least 10%.
- If you need protection from large and sudden current surges, then you should pay attention to electromagnetic tripping. Here the mechanism is built on the basis of a solenoid. The maximum value at which the circuit should open is set. As soon as it is reached within a certain period of time (jump), the solenoid is “retracted” and opens the contact - the protection has worked.
Our online store presents different versions of AB2M circuit breakers with different drives.
Select and calculate an automatic machine for an electric motor
There are two common ways to select a switch for an engine.
So, the first way is to calculate the total power of the devices that will be powered by this switch. We calculate what kind of devices (TV, refrigerator, computer, washing machine, etc.) will be connected to this electric current circuit, add up the power of all these devices and, based on this, calculate the current of the outlet group. When making such calculations, you should take into account how many phases there are in your grown electric motor. For example, in three-phase, with a power of 4 kW, 4 ∙ 3 = 12A, which means 12A is the operating current. This means that a 16A automatic machine will fit such an electric motor.
The second way to calculate the maximum power of devices connected to the machine is to calculate the total power through the passports of each device. The power ratings of the devices indicate the power, so we add it up and determine the total power. As an example, 2kW + 600W + 2100W = 4700W. Now we simply substitute the value into the generally accepted formula: I=W/U, where I is power, W is voltage and U is current in the network; I = 4700 divided by 220, so we get 21.36A. But do not forget that washing machines and some other appliances have their own motors, and they have a so-called starting current, which, when started, is much greater than the indicated power of the appliance. But manufacturers of automatic machines know this very well and therefore there is a current setting on the switches.
Selecting a machine is not so difficult, guided by the following rules:
Motor protection by automatic switch. Practical calculations
A special feature of protecting the electric motor from overloads and short circuits is the increased starting current, which can be seven times the rated value.
The strongest overloads at the start are characteristic of asynchronous motors with a squirrel-cage rotor, which are most used in everyday life and in production, therefore their proper protection, as well as the protection of the electrical wiring of the power supply circuits of electric motors, are especially relevant. In household electrical engineering, the problem with large starting currents of electric motors is solved with the help of automatic switches, in which the shutdown (cutoff) does not occur immediately after exceeding the rated current, but after some time.
This period of time, which depends on the time-current characteristics of the circuit breaker, should be enough for the motor shaft to spin up to operating speed and the current consumption to drop to the nominal level. But circuit breakers do not have the flexibility of precise adjustment, so special protective devices are used to protect electric motors.
Conventional three-phase circuit breaker is often used to protect electric motors