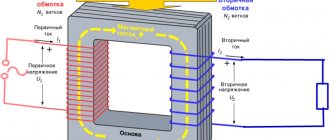
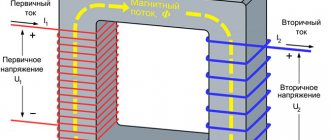
Types of differential current
The whole variety of differential currents that can arise in the main circuit of a residual current device is reduced in GOST R 51326.1 and GOST R 51327.1 to the following two types: sinusoidal differential current and pulsating direct differential current.
- Sinusoidal differential current occurs if rectifiers, dimmers, adjustable electric drives and similar devices that significantly change the shape of the sinusoidal current are not used in the alternating current electrical circuits that are connected to the residual current device. The leakage current and ground fault current in such electrical circuits have a shape close to a sinusoid. The differential current has the same sinusoidal shape. When using the instruments and devices listed above in electrical installations of buildings, the shape of the sinusoidal current in electrical circuits can change significantly. If, for example, in any electrical receiver a diode is used as a discrete regulator of the power it consumes, then in the event of damage to the main insulation of the current-carrying part connected after the diode, a ground fault current may occur, which will flow only for half a period - so called pulsating direct current. The differential current in the main circuit of the residual current device will also be a pulsating direct current. It significantly changes the characteristics of the RCD compared to sinusoidal differential current. In electrical installations of residential buildings, a large number of electrical receivers with built-in rectifiers are used. They are all characterized by small dc leakage currents, which can create a total (background) dc leakage current flowing through the main circuit of the residual current device. The flow of even a small direct current through the primary winding of a differential transformer significantly changes (degrades) its characteristics. Therefore, GOST R 51326.1 and GOST R 51327.1 take into account the possibility of a small direct current flowing through the main circuit of the residual current device.
- Pulsating direct current is defined in the standards as wave-like pulses of electric current with a duration (in angular measure) of at least 150 o per one pulsation period, following periodically with a nominal frequency and separated by time intervals during which the electric current takes a zero value or a value not exceeding 0.006 And direct current. Pulsating direct current is also characterized by the current delay angle, which is understood as the period of time in angular value during which the phase control device delays the flow of electric current in the electrical circuit. The appearance of a pulsating direct current in the main circuit of a residual current device significantly changes the characteristics of those RCDs that are designed to work only with sinusoidal current. Therefore, modern type A residual current devices have differential transformers and residual current releases made of special materials. They function equally well when a sinusoidal differential current occurs and when a pulsating direct differential current appears.
The article used materials from the Book of Protective Modular Equipment produced by ABB
Source: www.elektro-portal.com
What are differential currents in an electrical circuit?
To understand what differential current is, let’s answer another question: why don’t we get electric shocks? The answer seems simple, because all wire cores are coated with insulating materials. This one is true, but if you stand on an insulating mat and touch a live wire, will you get an electric shock? No, it won't hit. Why? Because the mat does not allow the electrical circuit to close from the current-carrying conductor through you to the ground.
Differential current is not a physical process, but the value of the vector sum of currents in a circuit in an rms value. Often, differential current is called fault current. The physical process that leads to the appearance of differential current in a circuit is called current leakage.
When leakage current appears, differential current may not appear. For example, for some reason, a leakage current appears on the metal body of the washing machine, but the machine body is not grounded and electrically isolated, which means there is no differential current in the circuit. A person touches the body of the washing machine and with his body closes an electrical circuit through which a differential current will flow, which is a manifestation of the leakage current. If the body of the washing machine was initially grounded, then immediately after the leakage current appeared, a differential current appeared through the body to the ground, and the RCD disconnected the circuit from the power supply.
Rated residual current
| Home // Our library // Directory // RCD // Rated differential current |
RATED DIFFERENTIAL BREAKING CURRENT IΔn
The rated residual current IΔn is the value of the residual current specified by the manufacturer at which the RCD must trip under specified conditions. In domestic electrical engineering practice and, in particular, in relay protection, the term “setpoint” has been used for many years. In relation to RCDs, the rated residual current is the setting.
Breaking and non-breaking differential currents
The operating current (or tripping current) is understood as such a differential current, the flow of which leads to the disconnection of the RCCB in the event of leaks in the circuit.
The current, the flow of which is permissible in the circuit of a residual current device (RCD) and does not trigger it, is called differential non-tripping current.
In a loaded circuit where pulse-type devices operate: rectifiers, discrete digital devices for power regulation - all these are modern household appliances, differential background currents are present. But such currents are not damage currents, and the electrical circuit cannot be disconnected in this case. Therefore, the RCD response threshold was chosen so as not to react to the operating value of the background, but to turn off the leakage current that exceeds this value.
What is a differential automatic machine (difavtomat)?
A device designed to turn off the power supply to the network when disturbances occur in it that can lead to failure of the wiring and equipment connected to it, in electrical engineering it is called a circuit breaker (AB). This device is usually called more simply - an automatic machine. One of its varieties is a residual current device, which de-energizes the line when a current leak is detected, thereby preventing people from being electrocuted when touching the cable. The peculiarity of the RCD is that it cannot be installed without an AV that protects the line from short circuits and overvoltage. In order not to connect two protective devices to the line, a differential circuit breaker was created - a device that combines the functions of an RCD and a circuit breaker.
Residual current protection
You can protect yourself from overvoltage and all the unpleasant signs of damaged electrical wiring and networks using a differential circuit breaker or residual current device. Both are designed to protect users from electric shock. Can be triggered by a short circuit. As a rule, the work of the first devices is aimed at eliminating the consequences of direct contact, and the work of the second is aimed at eliminating unpleasant situations with indirect contact of electricity.
That is, in the first case, the devices directly protect a person from electric shock, and in the second case, the devices protect electrical equipment and, thereby, the person himself. Both devices pass voltage through themselves and produce a normal current value at the output. They work with both alternating and direct current. There are both single-phase, two- and three-phase.
Note! It is worth pointing out that you can protect yourself differently by doing the wiring correctly and carefully monitoring the operation of the network.
In general, differential current is energy that enters the ground or other conductive elements in an electrical circuit that is not damaged. The operating principle is based on the presence of an electrical conductor. It constantly appears as a result of electrical breakdown of the cable insulating dielectric. You can protect yourself from it by using differential protection devices.
Features and purpose of the difavtomat
If almost everyone knows about ordinary electric automatic machines, then when they hear the word “difa-automatic”, many will ask: “What is this?” In simple terms, a differential circuit breaker is a circuit protection device that cuts off the power in the event of any fault that could result in damage to the line or electric shock to people.
The device consists of several main parts:
- Plastic body, resistant to melting and fire.
- One or two power supply and power off levers.
- Labeled terminals to which incoming and outgoing cables are connected.
- “Test” button, designed to check the serviceability of the device.
In the latest models of these machines, a signal indicator is also installed, which allows you to differentiate the reasons for the operation. Thanks to it, you can determine why the device turned off - due to a current leak or due to a line overload. This feature makes troubleshooting easier.
Visually about the device of the difavtomat in the video:
Automatic residual current protective switches can be installed in both single-phase and three-phase lines. They are intended for:
- Protection of the electrical network from short-circuit overcurrents and excessive voltage.
- Prevent electrical leakage that could cause fire or electrocution to people and pets.
The residual current switch for household lines with one phase and operating voltage 220V has two poles. In industrial networks at 380V, a three-phase, four-pole differential circuit breaker is installed. Quadrupoles take up more space in the distribution panel, since a differential protection unit is installed with them.
What is the rated breaking current
The rated breaking current is the current value that can be turned off by the circuit breaker if it is equal to the highest operating voltage. This is the value for a mains short circuit that trips the fuse. As a rule, this figure is indicated on the packaging of the differential circuit breaker.
You might be interested in Features of calculating power by current and voltage
Rated electric current
Appearance of the difavtomat
When looking at the RCD and differential AV, you will notice that they are very similar in design and size. There is even a “Test” button on both devices. But this does not mean that they are completely the same. The residual current device is not an independent device and, as mentioned above, should not be installed in a circuit without a protective circuit breaker. The difavtomat combines an RCD and an AV, so it does not require the installation of additional devices.
In order not to confuse the RCD and the differential protective switch, most domestic manufacturers mark their products with the corresponding abbreviation - RCD or RCBO. Imported devices can be distinguished by other characteristics. For example, the current rating of a residual current device is indicated by a number and the letter “A” (Ampere) after it - for example, 16A. The current rating of the difavtomat is written differently: a Latin letter is placed in front, corresponding to the characteristics of the built-in releases. After it comes a number indicating the value of the rated current - for example, C16.
Overload and short circuit protection
Now let's talk about how a differential circuit breaker works when a short circuit occurs in the circuit and when the voltage increases significantly. In these cases, its operating principle is similar to that of a conventional circuit breaker.
The RCBO contains two releases that operate independently of each other. Each of them is designed to de-energize the network when various disturbances occur.
The video shows the internal structure of the difavtomat:
Protection against line overloads is provided by a thermal release, the role of which is performed by a plate of two metals with different expansion coefficients (bimetallic).
When the voltage in the circuit exceeds the nominal value, the plate begins to heat up, which leads to its bending towards the disconnecting element. By touching it, she triggers the AB.
The network is protected from short circuit overcurrents by an electromagnetic release, which is a solenoid with a core. With a sharp increase in current strength, characteristic of a short circuit, an electromagnetic pulse occurs. Under its influence, within a fraction of a second, the release causes the switch to operate and stop the supply of electricity to the line.
When the fault has been resolved, the device can be turned on manually again. However, it should be remembered that if the network parameters returned to normal very quickly after turning off the AV, the device should be given a little time to cool completely. If you turn on a heated device, this will negatively affect its service life.
Installation procedure
The RCBO is mounted on a DIN rail. When connecting, you need to be very careful not to confuse the order of connecting the cables. In household single-phase lines, the input conductor is connected to terminal number 1, and the output conductor is inserted into terminal number 2. The neutral wire is connected to the terminal marked with the letter N. Input cables are connected to the top of the device, and output cables to the bottom.
You can connect the outputs to the line directly. If the network parameters are not stable, or you want to ensure the highest level of protection, you should install additional AVs.
The neutral wires from the machines must be connected to an isolated neutral bus. To avoid failure of the device or its incorrect operation, it is necessary to ensure that the output neutral cable does not come into contact with other conductors or with the body of the electrical panel.
You can see how to connect the difavtomat in the video:
Grounding of RCBOs
The neutral cable should be grounded only in front of the differential protection device. An incorrect connection will lead to the fact that the difavtomat will turn off even when a small load is applied.
If several differential circuit breakers are connected in parallel, then it is impossible to swap the neutral conductors at their outputs or connect them to a common zero bus. This will also cause the devices to malfunction.
The neutral point of the RCBO should be connected in pairs with its own phase. It cannot be used as a neutral conductor for devices with a different phase source.
To avoid mixing up the zeros, it is recommended to use marked cables.
For jumpers and connections, it is necessary to use a conductor whose cross-section corresponds to the network load.
If the machine is equipped with a malfunction indicator, the reason for the operation will be immediately clear. In the absence of a “beacon”, the cause of the failure will have to be found using the “scientific poke” method. If the RCBO starts to trip after connecting an additional load to the network, then most likely the device is faulty or an error was made when connecting it.