Why do you need an electrical equipment logbook?
To avoid accidents when working with electrical equipment, it is important to comply with established safety and operating standards:
- do not allow unqualified personnel to work with electrical equipment;
- carry out tool testing in a timely manner;
- register all tools and electrical equipment, dates and results of their tests in a special journal.
The need for organizations to maintain special log books for electrical equipment is indicated by the order of the Ministry of Energy of Russia dated January 13, 2003 N 6 “On approval of the Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations.” Energy consumers, according to the rules, are citizens, entrepreneurs and organizations, regardless of ownership and organizational and legal forms, that own electrical installations with voltages from 1000 volts to 220,000 volts.
The head of the organization is obliged to ensure:
- proper maintenance, operation and maintenance of the tool;
- testing electrical equipment;
- selection of electrical technical personnel, timely medical examinations;
- training and testing the knowledge of such personnel;
- appointment of a person responsible for electrical facilities (if necessary in each department), who will deal with electrical safety issues.
The rules say that each structural unit must create a list of technical documentation approved by the technical manager. This list, among other things, includes electrical equipment log books, which should list all the main tools, indicating the characteristics and inventory numbers. The magazines are accompanied by instructions, technical passports, certificates, test reports, measurements, repairs and maintenance. The word “magazines” is used in the plural. So how many electrical forms should a company have?
How many power tool logs should an organization have?
Unified forms of documents are not attached to the rules, from which we can conclude that the form of maintaining such records is arbitrary.
There is a recommended form for recording, checking and testing power tools and auxiliary equipment, which is given in the appendix to the safety rules when working with tools and devices (RD 34.03.204). These standards were approved by the USSR Ministry of Energy on April 30, 1985. They are not registered by the Ministry of Justice, and therefore are not a normative act.
Since January 2021, the operation of power tools is regulated by the Labor Safety Rules when working with tools and devices, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated August 17, 2015 N 552n. This is an official legal act, which, however, does not contain any recommended forms for accounting forms.
In the letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated August 16, 2016 N 15-2/ОOG-2956, officials explain that the rules RD 34.03.204 approved in the USSR can still be applied today to the extent that they do not contradict modern Rules. This means that the usual sample of the recommended form for checking electrical equipment can be used to record the tool. It is worth remembering that this is not a mandatory form and equipment can be taken into account differently.
In practice, several accounting documents relating to electrical appliances and equipment are often created:
- for registration of electrical equipment and power tools;
- accounting, inspection and testing of power tools and auxiliary equipment;
- a separate logbook for checking the grounding of electrical equipment.
They also separate inspections of various types of equipment.
For convenience, you can have 2 or 3 different documents, but during inspections it is enough if you have one log, which will list the characteristics of electrical equipment, inventory numbers and, most importantly, the results and dates of inspections. The old form, recommended by the rules of the USSR Ministry of Energy, reflects this information quite fully.
Rules for filling out and maintaining a journal
The document is maintained by an employee specially appointed by order of the manager - responsible for electrical equipment. A responsible person is appointed in each structural unit and a separate journal is opened. The assigned electrical safety group of the person in charge must be at least third.
The general rules for maintaining primary accounting documents apply to the design of the form: the pages must be numbered, bound, certified with the seal of the organization and the signature of a manager or authorized person. The seal is placed on a strip of paper, which is used to glue the ends of the lacing, so that part of it falls on the certification inscription, and part of it falls on the last page.
The standard journal form contains the following information:
- serial number of the record;
- full name of the instrument;
- inventory number;
- date of last test;
- reason for the inspection (scheduled periodic - once every six months; unscheduled - after repair);
- date and result of the high voltage insulation test;
- date and result of insulation resistance measurement;
- date and result of the grounding test;
- date and result of external inspection of electrical equipment and no-load testing;
- time of the next scheduled inspection;
- Full name and signature of the employee who conducted the inspection.
Here is a sample of a completed document.
Testing of electrical equipment must be carried out using special instruments in an electrical laboratory. If there is no such laboratory at the enterprise, then the instrument is checked in licensed organizations that have the necessary equipment.
Let's take a closer look at the columns of the log, figuring out what exactly should be written and after what check:
- the name of the electric tool is copied from its technical passport - we enter it in detail indicating the brand and model;
- the inventory number must be assigned and painted on the body; it is important to enter it without errors;
- if the test is the first, then in the “date of last test” column we indicate the date of the factory inspection from the technical passport. If not the first, look at the date in the magazine;
- The reason for the test is either planned or after repair. Scheduled checks are carried out at least once every 6 months; the technical manager may determine the need for more frequent tests depending on the intensity of equipment operation;
- During an external inspection of the instrument, we look for chips, check the plug fastenings, and the wire for flexibility, creases, and insulation damage. When testing operation at idle, turn on the tool, press “start”, checking the smoothness of the press, the presence of extraneous noise, burning smell, and sparking. Based on the result, we write down whether it is satisfactory or unsatisfactory;
- The insulation resistance is checked with a device called a megohmmeter. The test is carried out by 2 people, one of them must have an electrical safety group of at least third. The device is connected to the tool, the handle is rotated (or the button is pressed) until the megger arrow approaches zero. The readings are recorded and then measured in two more ways. The reading value must exceed 0.5 Mohm. If all three measurements showed a normal result, write it in the column - satisfactory;
- The serviceability of the grounding circuit of tools with grounding contacts on the plug is checked with an ohmmeter. The device readings should tend to zero. The device is attached to the grounding contacts and metal parts of the housing. The check is carried out by 1 person. Based on the results, we write down whether it is satisfactory or not;
- We carefully check the date of the next test when making an entry, especially if the employee responsible for electrical equipment has set test dates more often than once every six months;
- The worker conducting the test, finishing making entries in the electrical equipment logbook, puts his last name, initials and signature.
Frequency of testing power tools
We bought several drills and four grinders for work; we have a small construction and repair business. And then someone advised us to carry out some kind of testing of this power tool, and the phrase also sounded like, the frequency of testing the power tool. But of course, it never occurred to anyone to ask again, but now we are asking ourselves whether it is necessary to carry out some tests on the power tool we purchased, and if so, what is this based on?
Of course, there are rules that cannot be ignored, these are inter-industry rules on labor protection (safety rules) when operating electrical installations, here is a copy of an excerpt from this rule, which relates specifically to your topic. read carefully.
pot r m-016-2001 rd 153-34.0-03.150-00
10.7. hand-held electrical machines, portable power tools and lamps, auxiliary equipment issued and used in work must be checked and tested within the time limits and volumes established by the guest, technical specifications for products, current scope and standards for testing electrical equipment and electrical installation devices. To maintain good condition, conduct periodic tests and inspections of hand-held electrical machines, portable power tools and lamps, auxiliary equipment, a responsible employee with group iii must be appointed by order of the head of the organization.
rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations (approved by order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2003 No. 6)
3.5.10. to maintain good condition, conduct periodic checks of portable and mobile electrical receivers, and auxiliary equipment for them, a responsible employee or employees with group iii must be appointed by order of the consumer’s manager. These employees are required to keep a log of inventory records, periodic inspection and repair of portable and mobile electrical receivers, and auxiliary equipment for them. 3.5.11. Portable and mobile electrical receivers and auxiliary equipment for them must be subject to periodic inspection at least once every 6 months. the results of the inspection are reflected by the workers specified in clause 3.5.10 in the inventory log, periodic inspection and repair of portable and mobile electrical receivers and auxiliary equipment for them. 3.5.12. The scope of periodic inspection of portable and mobile electrical receivers and auxiliary equipment includes: external inspection; check idle operation for at least 5 minutes; insulation resistance measurement; checking the serviceability of the grounding circuit of electrical receivers and auxiliary equipment of classes 01 and 1. 3.5.13. During operation, portable and mobile electrical receivers and auxiliary equipment for them must be subject to maintenance, testing and measurements, and scheduled preventive maintenance in accordance with the instructions of the manufacturers given in the documentation for these electrical receivers and auxiliary equipment for them.
labor safety in construction
part 1. general requirements
7.4.38. tools used in construction, the building materials industry and the construction industry must be inspected at least once every 10 days, as well as immediately before use. a faulty tool that does not meet safety requirements must be removed.
I don’t know about the rules, but I firmly understood for myself in my deep youth (I myself work in the same field with power tools) that all the tools you work on, no matter whether they are new or old, must be carefully inspected at least once in 8 days. I just witnessed a faulty tool almost lead to the death of a person. And before work, in the intervals between major inspections, it doesn’t hurt to at least simply inspect your working power tool. You shouldn't joke with life.
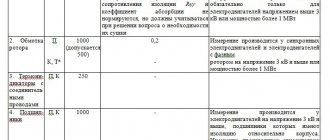
According to ch. 3.6. PTEEP “Guidelines for testing electrical equipment and devices of electrical installations of Consumers”, the timing of tests and measurements of parameters of electrical equipment of electrical installations is determined by the technical manager of the Consumer on the basis of Appendix 3 of the Rules, taking into account the recommendations of factory instructions, the state of electrical installations and local conditions. The frequency of tests indicated for certain types of electrical equipment is recommended and can be changed by the decision of the technical manager of the Consumer.
The acceptance test standards must comply with the requirements of Section 1 “General Rules” of Chapter 1.8. “Acceptance Test Standards” of Electrical Installation Rules (seventh edition).
Read also: Rules for installing an air conditioner in an apartment
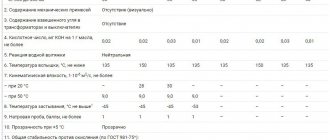
In accordance with PTEEP (Appendix 3), measurements of the insulation resistance of electrical network elements are carried out at the following times: - electrical wiring, including lighting networks, in particularly hazardous rooms and outdoor installations - once a year, in other cases - once every 3 years ; — cranes and elevators — once a year; - stationary electric stoves - once a year when the stove is heated.
In other cases, tests and measurements are carried out at intervals determined in the system of scheduled preventive maintenance (PPR), approved by the technical manager of the Consumer (clause 3.6.2. PTEEP).
Responsibility
In accordance with Article 9.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, violations in the field of operation of electrical equipment are punishable by fines:
- for individuals - from 1000 to 2000 rubles;
- for officials - from 2000 to 4000 rubles;
- for individual entrepreneurs - from 2000 to 4000 rubles or suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
- for legal entities - from 20,000 to 40,000 rubles or suspension similar to individual entrepreneurs.
The lack of mandatory documentation is one of the violations, and the manager needs to decide: download the electrical equipment logbook (filling sample) for free and use it, thereby fulfilling the requirements of the Rules for the Technical Operation of Electrical Installations, or risk being fined a large amount.
PTEEP and POT R M are written in blood... It sounds terrible, but that's how it is. Behind every line there are human victims. Neglect of safety rules
leads to tragedy.
According to statistics, most often the victims of accidents in electrical installations are experienced electricians with extensive work experience and a high electrical safety group.
A person believes in his professionalism so much that he stops being afraid - and this is the sad result.
At any enterprise, electrical safety issues should be dealt with by a specially trained person—responsible for electrical equipment
. This is not a position, but an “honorable duty,” as Rostechnadzor inspectors joke.
Let's quote PTEEP
: "1.2.3. To directly fulfill the responsibilities for organizing the operation of electrical installations, the head of the Consumer (except for citizens who are owners of electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V) appoints with the appropriate document the person responsible for the electrical equipment of the organization (hereinafter referred to as the person responsible for the electrical equipment) ... The person responsible for the electrical equipment and his deputy are appointed from among the managers and specialists of the Consumer.” .
It is this specialist who is assigned the responsibilities
on conducting special and organizing measurements and testing of power tools.
What is a portable power tool?
Electric impact wrenches, electric drills, electric planers, grinders and polishers and other electrified machinery not secured to a permanent foundation, as well as electric extension cords and portable lights are all portable power tools.
.
Before entering into the results of measurements and tests, it is necessary to carry out these actions
.
You need to start by assigning each power tool and portable lamp a serial number
(according to the new rules, an inventory number), which is written on the body with paint or a permanent marker in the place that is least exposed to mechanical stress.
Who has the right to carry out measurements and tests?
To carry out testing and measurement work, special instruments are required
, instruments are an integral part of the electrical laboratory, therefore, the enterprise must have such a laboratory in order to carry out the work on its own.
If, due to various circumstances, an enterprise cannot afford such luxury, it should contact an organization that owns a licensed electrical laboratory and qualified personnel.
The electrical safety group for persons carrying out testing and measurement work must be at least III
.
Logbook for recording and testing electrical equipment.
Posted information
Contains the following columns
:
- name of the power tool;
- inventory number;
- date of last test;
- reason for testing, inspection (after repair or periodic);
- insulation resistance measurement;
- checking the serviceability of the grounding circuit;
- external inspection and check of idle operation;
- date of the next test, inspection;
- the person who carried out the inspection, test (full name, signature).
We will consider the order of filling out each of the columns separately and in great detail.
Name
It must exactly match the name of the instrument indicated in the passport.
For example, you cannot simply write “drill”; you must indicate: “Makita HP 207 network impact drill.”
Inventory number
The procedure for assigning and applying an inventory number to the instrument body was discussed above.
At this stage, the inventory number is recorded without errors in the appropriate column.
Date of last test
Everything is very simple here: we write the date of the last test of a portable power tool, recorded. If the tool is new, enter the factory test date indicated in the passport in this column.
Reason for testing
There are only two such reasons: the instrument has been repaired and requires additional testing, or the next inspection is due (6 months have passed since the date of the previous test).
How an electrified tool is tested
Periodic inspections and tests of power tools are carried out at least once every 6 months . If the tool is used intensively at an enterprise or department, then this period is reduced. The new test period is fixed by issuing a corresponding order for the enterprise.
After repairing the tool, an additional (extraordinary) inspection and test is carried out.
The test results are recorded in a log. The scope of the check is as follows:
- visual inspection;
- operating the tool at idle speed for at least 5 minutes;
- insulation resistance measurement;
- checking the grounding circuit.
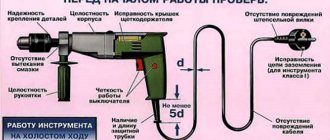
External inspection and checking idle speed
Checking a power tool should begin with an external inspection. Procedure
:
- carefully inspect the body of the instrument, make sure there are no cracks, chips or dirt;
- carefully examine the plug, paying attention to how tightly the pins are fastened in the body; if the plug body is dismountable, check the fastening screws, use a screwdriver to tighten all screw connections, and make sure the body is intact;
- Check the supply wire for flexibility, the absence of twists, breaks and cracks on the surface of the wire, inspect the attachment points to the plug and the body of the tool (double insulation must not be broken).
Checking idle speed
carried out by connecting the tool to the electrical network and pressing the “Start” button. The power tool is tested without load. What to pay attention to:
Based on the results of the inspection and testing at idle speed, an entry is made in the log, including the date of the test and its result.
(satisfactory or unsatisfactory).
Inspection and testing of hand-held power tools
Inspection and testing of hand-held power tools must be carried out at enterprises in accordance with labor protection rules.
However, if you often use a tool at home or in the country, checking the power tool periodically is extremely important to avoid possible problems. Construction tools that are used intensively should be checked every 6 months.
In general, you should accustom yourself to conduct a visual inspection of the tools for the current job before starting work.
The most dangerous thing for a person when working with a power tool is the possibility of electric shock. To avoid this, check before each time you use a portable power tool:
- Cable integrity
- The presence and integrity of the protective tube located at the junction of the cable and the instrument body. The length of the tube must be at least 5 times longer than the thickness of the power cable.
- Integrity of the grounding circuit (this applies to instruments of electrical safety class 1);
- No damage to the plug;
We recommend reading: Orthopedic group in Sanpin kindergartens
Let's move on to the body of the power tool:
- The brush holder covers must be in good working order and free from mechanical damage;
- Conduct a visual inspection of the entire area of the instrument, especially the joints: nothing should come off anywhere, no cracks or broken areas;
- If there is a handle, it must also be securely fixed and intact;
- All moving parts (for example, a chuck in a drill, hammer drill or screwdriver) must be securely fastened;
Insulation resistance measurement
This procedure is performed using a megohmmeter. Device requirements
:
- output voltage – 1000 V;
The measurement is carried out by a team of two people, the electrical safety group of one of them should not be lower than III
.
Before starting work, you need to check the megohmmeter
.
To do this, you need to short-circuit the terminals of the device
, rotate the handle until the arrow on the scale approaches 0. Then you need to
disconnect the leads and rotate the handle again
. The instrument needle should deflect towards ∞.
Measurement procedure:
- The terminals of the device are connected to the plug pins of the power tool being tested. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the terminal tips of the device do not touch each other
. Depending on the type of megohmmeter, you need to rotate the handle of the device or press the button for 1 minute. Record the megohmmeter readings, stop measuring, disconnect the leads. - Fix one of the device terminals on the pin of the tool plug, the second - on a metal part of the tool body. Carry out the measurement within 1 minute
, record the instrument reading, and stop the measurement. - Connect the terminal of the device to another pin of the tool plug; do not touch the terminal of the device previously connected to the metal part of the tool body
. Carry out the measurement for 1 minute, record the instrument reading, stop the measurement, disconnect the leads.
Insulation resistance is considered normal
, if the measured value exceeds 0.5 MΩ.
In the event that at least one of the measurements showed a lower insulation resistance value
, the tested power tool is rejected (entry “Unsatisfactory” in the corresponding column of the journal).
If all three instrument insulation resistance measurements are satisfactory
, an entry is made in the appropriate column of the journal, recording the date of the test and its result (satisfactory).
Insulation resistance test
The measurement is carried out with a special measuring device - a megohmmeter, for a voltage of 500 V. The duration of application of the test voltage from the megohmmeter is 1 minute.
Before using the device, make sure it is in working order. To do this, they perform two control measurements:
| Measuring circuit | Measured value |
| The probes of the device are open and held in the air | Maximum possible readings of the device |
| The probes of the device are closed to each other | 0 MOhm |
Insulation resistance measurements are performed while the “On” button of the power tool is pressed. The test voltage is applied between the product body and any power conductor. The measured value should not be lower than 0.5 MOhm .
To test extension cords, three measurements are taken by connecting the megohmmeter probes between:
- zero and phase conductors;
- zero and grounding conductor;
- phase and grounding conductor.
For a step-down transformer, the insulation resistance of the primary and secondary windings relative to the housing and to each other is measured.
Testing voltage converters with a megohmmeter is carried out according to the manufacturer's instructions, since they contain semiconductor devices.
Checking the serviceability of the grounding circuit
The test is performed on a power tool that has grounding pins on the plug. The purpose of this check is to ensure the integrity of the grounding circuit
, therefore, the closer the device reading is to 0, the better. Requirements for the device:
- the date of the next verification has not expired (indicated on the label attached to the device body, after the words “Best before...”);
- absence of dirt and visible mechanical damage (cracks, chips) on the device body.
The check can be carried out by one person. You should start by testing the performance of the ohmmeter:
turn on the device and short-circuit the terminals. The arrow on the scale should point to 0. After opening the terminals, a working device will show ∞.
Actually checking the continuity of the circuit
occurs as follows: one of the terminals of the device is attached to the grounding contact of the instrument plug, the second - to the metal parts of the case.
When the device is turned on, its readings are recorded, the result is entered in the appropriate column of the log with the date indicated.
Ground circuit is faulty
, if the instrument readings tend to ∞ (record “Unsatisfactory”).
In this case, the power tool cannot be used
.
Test labels on power tools
For each of them, a clear algorithm has been developed, which we will discuss below. Verification is an event that is carried out by special certified laboratories.
The methodology for this process is approved in the current instructions “Standards for testing power tools up to 1000V”.
Important The periodic verification of electrical equipment includes the following steps: Determining the presence and serviceability of the grounding circuit using an ohmmeter.
One end of the device is connected to the output on the plug, while the other is connected to ground on the instrument itself.
If the ohmmeter reading exceeds 0.5 Ohm, the electrical equipment is considered unsuitable for further use. Insulation integrity analysis. Determination of a violation of its integrity is carried out using a megger, as well as a power source.
For an electric instrument with a maximum voltage of 50V, the analysis should be carried out up to 550 V, with a maximum voltage of 220 V up to 900 V, and higher up to 1350 V. The device readings during the test should not be lower than 500 kOhm. If the readings drop below, the electrical device is considered unfit for use.
The length of the tube must be at least 5 times longer than the thickness of the power cable. Let's move on to the body of the power tool: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire area of the tool, especially the joints: nothing should come off anywhere, no cracks or broken areas; All moving parts (for example, a chuck in a drill, hammer drill or screwdriver) must be securely fastened; The brush holder covers must be in good working order and free from mechanical damage;
Date of next test, inspection
The frequency of inspections was mentioned above. It is worth dwelling in more detail on those cases where tests are carried out more often than once every six months
. This becomes necessary under the condition of active use of a portable power tool; the timing is determined by the person responsible for the electrical equipment.
How to determine the date of the next test: add 6 months to the current date
(or the quantity determined by the person responsible for electrical equipment) and make an entry in the appropriate column of the journal.
The person who carried out the inspection or test
The data of the person who carried out the inspection is entered in this column.
(surname, initials) and his signature is placed.
This completes the filling out of the electrical tool inspection and testing log, so that in six months (or earlier) the entire procedure can be repeated
.
It may seem to some that all of the above activities are redundant and that it is not at all necessary to carry them out.
Let's try to convince a hypothetical opponent of the opposite.
Rostekhnadzor statistics tell us that the majority of accidents (more than 60%) occur at consumer electrical installations. The reason is failure to comply with mandatory measures aimed at maintaining the safe condition of electrical equipment, including portable power tools.
It is worth thinking about the fact that reluctance to follow the rules
leads to human casualties and draw appropriate conclusions.
Where any power tool is used, a log of its inspections and tests must be kept. Compliance with safety precautions when working with power tools makes it possible not only to avoid injuries, but also to preserve the life and health of employees. Moreover, sad as it may be, even experienced electricians sometimes neglect safety rules when working with power tools.
At the enterprise, safety issues and the inspection and testing of electrical tools should be dealt with by a specialist who has special training and permission for such work. Usually this is an employee who has a technical education, and he also deals with all issues related to electricity and maintaining special accounting logs.
The benefits of tool checks
A properly functioning power tool is not dangerous.
- Safety;
- Extending tool life;
- Prevention of tool breakdowns: sometimes a small “jamb” in the operation of the tool leads to failure of the entire device, and after that it is not always suitable for repair, or the cost of spare parts will make this repair unprofitable. So take a closer look and listen to your electrical assistants - vigilance will save you nerves, time and money.
General information about the logbook of accounting, inspection, maintenance and testing of power tools
When operating various power tools and devices, they require periodic testing and inspection. The data obtained from the results of tests and inspections must be recorded in a logbook.
The employee responsible for filling out the log must know that before entering the test results, they must be produced.
To check a power tool, you may need certain instruments that should be located in special laboratories. If your company does not have it, you should contact a laboratory that has experienced workers to conduct tests. Only after their conclusion is all data recorded in the inspection and testing log of the power tool.
Magazine cover design example
Who has the right to periodically inspect power tools?
The question of who has the right to periodically inspect power tools has a simple answer. This task is carried out by a specially trained employee (or specialists) - with professional training and approval for electrical safety.
Among the activities of such a person may also be related issues on electrical equipment and maintaining other accounting records. The main requirement for such a person is specialized technical or higher education.
At the beginning of the inspection, a log is filled out - a document recording all the necessary information:
- type and name of the device, its inventory number or other unique features;
- previously known data on the condition, identified defects;
- personal data of the inspector (repairman), date of completion of work and signature;
- recommended date for next inspection.
All information on measurements obtained using instruments is entered into the log. The document is bound, all its pages are numbered - the design is carried out according to all document management rules.
Sample logbook for checking power tools
After the actual work, a protocol or act is drawn up, which includes the above and other necessary information. It includes the general purpose of the test and its methodology.
As for household electrical appliances, it is recommended to contact a special organization. Their services can be found in any city and even with a focus on certain types of appliances.
How to maintain such a document
Requirements
Like any other magazine in an enterprise, it must be correctly and competently designed.
- All sheets must be numbered, the magazine must be laced and glued on the back with a strip of paper, that is, sealed.
- The seal must bear the date, the signature of the person in charge and the seal of the company.
Power tools should be checked at least once every six months. In the event that any power tool has been repaired, an unscheduled inspection must be carried out afterwards. All data should be recorded in a log each time.
Form
This form of journal usually has the following sections:
- Name of the power tool (as in the passport);
- Inventory number assigned to the instrument when it was added to the balance sheet;
- Date of tests that were carried out;
- A test carried out without load. Appearance upon inspection;
- Condition monitoring via grounding circuit;
- Insulation condition monitoring;
- In this connection, the test of the power tool is carried out, as well as the reason for the tests;
- Day, month and year when the next equipment inspection is required;
Before filling out this log, you should start by inspecting the appearance of the device, checking the idle speed and operating the device for 5 minutes at idle speed. After this, all received data is entered into a log.
Logging data
Important! The time of the previous test should always be indicated. If it was carried out at the manufacturer’s factory, then the test data is taken from the power tool passport.
Filling
First you need to sign the magazine cover. Here it is written either the owner, his, the full name of the document, the start and end dates of the journal.
The magazine should then be numbered, laced and secured with a paper seal. The seal must indicate
- The position of the person responsible for filling out the journal, his last name, first name and patronymic;
- Journal opening date;
- Number of numbered pages;
All this must be endorsed with the seal of your organization.
- The next step is to start making entries in the journal. Here on the first page you must indicate the full name of the power tool. It is written out from the product passport and must fully comply with it.
- The next entry will be the inventory number of the device. It must be applied to the device with indelible paint by the responsible person of the enterprise.
- The date of the last test must be indicated, even if the instrument is new. In this case, indicate data on tests carried out by the manufacturer.
The data in the next four sections is filled in from the instrument’s passport when it is new. In subsequent cases in the lines
- High voltage insulation tests
- Does the insulation material meet the requirements?
- Detection of ground circuit defects
Laboratory data is recorded. They can be obtained as a result of testing and monitoring of instruments in a laboratory that has a special license to carry out this work.
- Then records are made of the results of checking the operation of the power tool at idle speed and data on the appearance of the device.
- The following column is highlighted to indicate the time for subsequent inspection and examination of the instrument.
- And the last line is allocated for the signature of the employee who tested and controlled the power tool.
A form for registering and maintaining power tools is available.
Sample of filling out a logbook and checking a power tool
Any construction and repair cannot be done without hand tools; this simplifies and speeds up its implementation. In this case, portable power tools are most often used as the most reliable and mobile. Electrical energy is one of the most widespread around the world; it is used both in domestic and industrial environments. However, not every master knows that electric tools must be checked regularly so that they do not cause an accident involving electric shock or an explosion (fire) when working in hazardous fire conditions. In this article we will tell you how to check a power tool, how often it should be done and who should do this type of work.
Insulation resistance of power tools standard - Fire safety
Any construction and repair cannot be done without hand tools; this simplifies and speeds up its implementation. In this case, portable power tools are most often used as the most reliable and mobile. Electrical energy is one of the most widespread around the world; it is used both in domestic and industrial environments.
However, not every master knows that electric tools must be checked regularly so that they do not cause an accident involving electric shock or an explosion (fire) when working in hazardous fire conditions.
In this article we will tell you how to check a power tool, how often it should be done and who should do this type of work.
Electrical safety classification of power tools
When operating an electric tool, you should know that, according to the current GOST, it is divided into several protection classes. The inspection of portable power tools, its frequency and methodology directly depend on this.
- 0 – has only working insulation without grounding devices and connections;
- 01 - there is working insulation and a grounding element, but the cord itself with which the tool is equipped does not have a grounding wire;
- 1 – has working insulation and a grounding element, which is connected through a cable having a corresponding terminal;
- 2 – equipped with double insulation, that is, electrical wiring and live parts are insulated, and the housing is made of dielectric material;
- 3 - this class of power tools is connected to a low safe voltage - no more than 42 Volts, and the devices are not subject to grounding.
Most often, in everyday life and at the enterprise, workers use class 2 power tools, since they have sufficient insulation so that a person is not injured.
Tool checking method
It is allowed to use household and industrial power tools that have passed the test. For this, a clear algorithm has been developed that must be followed by everyone who wants to work with it. In this case, you need to clearly understand the difference between verification and verification.
Verification
- these are tests that are carried out in special laboratories located at every large enterprise. The tests include:
- Determining the presence and serviceability of the grounding circuit by using a special ohmmeter - one end of the device is connected to the terminal on the plug, and the other to the ground located on the tool itself. Measurements should show no more than 0.5 Ohm, which satisfies the safety conditions for using the tool.
- Measurement for the integrity and quality of insulation is checked with a megohmmeter at a voltage of no more than 500 V for a power tool designed for an operating voltage of 220 V. You don’t have to turn it quickly, this will be enough to see the insulation resistance of the tool. In this case, be sure to remember to press the button that turns on the electric tool. The device must show an insulation resistance of more than 500 kOhm; if this value is less, working with it is prohibited.
- Next, a trial test is carried out while idling for 5–7 minutes.
Power tools can also be tested with increased voltage. In this case, a tool with a voltage of up to 50 Volts is tested with a test voltage of 550 V. If the tool is designed for a voltage above 50 V, but with a power of up to 1 kW, the test voltage should be 900 V, above 1 kW - 1350 V. Tests are carried out within 1 minutes.
Examination
– carried out through visual control and inspection. You need to check not only the housing, but also the cord connecting it to the power source. You need to pay attention to:
- The integrity of the body, there may be cracks and breaks.
- The power cable should not show any visible drying out, damage, chafing, or signs of burning or heating. Particular attention should be paid and checked at the points where the electrical cord enters the housing and the plug.
- The plug and its contact part, which will be connected to the network, are inspected and checked for integrity.
The check must be performed before starting work, and before turning it on after moving to another workplace. Naturally, professional laboratory verification is carried out only at large enterprises and firms; in everyday conditions, a worker should at least carefully inspect the power tool he picks up before work.
If we talk about the timing of the verification of power tools, then according to existing regulatory rules, periodic verification of the tool should be no less than every year, and it is necessary to check the power tool, as indicated earlier, before each use. If manual electrical equipment is used in extreme climatic and production conditions, it is recommended to check it with a megohmmeter at least once every 10 days.
Important point!
When checking a tool at a factory, the first thing you need to look at is the date of the test. If the date has expired or there is no testing tag on the power tool at all, then it is prohibited to operate it - it must be removed and submitted for testing.
Verification and testing of electric tools
There are occupational safety rules that describe algorithms for preparing for work and using various devices and devices powered from the electrical network. For the entire existing list of such mechanisms, the most serious danger to users is their live parts, which can, if touched, give a person an electric shock. In order to avoid the possibility of such dangerous touches, modern electrically driven tools are produced with double electrical insulation, protecting the current-carrying elements of the devices. In addition, such devices are produced with grounding conductors built into the power supply cable, brought out to the corresponding contact of the electrical plug.
Read also: Do-it-yourself plow for a heavy walk-behind tractor
Parameters for checking the power tool before starting work.
Nevertheless, even when working with modern electrical equipment, it is necessary to comply with the developed conditions for safe operation, which include their verification and testing.
The essence of these terms is as follows:
- Checks of a power tool include a visual inspection of the entire device with an examination of the integrity of its body, fixation of chips, breaks and cracks, as well as an inspection of the cable supplying the device for the detection of abrasions and damage to the integrity of the insulation of the cores. At the same time, the integrity of the electrical cord plug and the quality of its contacts are checked.
- Checking manual electrical equipment is a more extensive, in-depth check with a certain frequency. The size of the maximum possible interval between the previous and subsequent checks is strictly fixed for it.
Verification includes:
- Determining the integrity of the grounding conductor of the power cable by measuring it with an ohmmeter connected to the “ground” contact of the electrical plug of the cable and the “ground” point in the device itself.
- Measuring the insulation of the electrically conductive cores of the power cable with a high-voltage device - a megohmmeter (output voltage up to 500 V) - relative to the “ground” contact on the plug when the device power button is pressed.
- Monitor the operation of the device at idle for several minutes (at least 5). The insulation resistance is measured with a megger for 1 minute, and the resulting value should not be less than 0.5 MOhm. During verification, all actions must be carried out in accordance with the algorithm for routine checking of power tools.
Timing for checking power tools
Schematic diagram of a stand for checking and testing power tools.
Existing regulatory documents define the longest interval between regular inspections of power tools as 6 months. For industries (construction enterprises) where the conditions for using power tools are complicated by external factors (temperature changes, dust, exposure to aggressive environments), the interval between scheduled inspections is reduced to 10 days.
You need to understand that the expression “no less often than” only means that it is possible to check more often, but it is prohibited to increase the established inter-check interval.
Checking power tools for professional use
At enterprises, organizations and various types of structures that use power tools for professional purposes, clear records of the availability, issue, inspection and repair of such devices must be organized. As a rule, the management of a structural unit officially appoints an employee who is entrusted with full responsibility for accounting, storage, issuance and inspection (both routine and scheduled) of available power tools. All necessary information on them is entered by the responsible employee in a journal of the established form.
The current check of such devices issued for the relevant work is carried out jointly by the issuing and receiving employees. When returning the tool after completion of work, inspection actions are carried out in a similar manner. Damages identified by the inspection are officially recorded for subsequent measures to eliminate them.
Read also: Set of wood cutters for a lathe
Rules for using power tools.
If such devices are few in number and are assigned to specific specialists without organizing centralized storage, a mandatory check of the tool before use must be carried out by the employee assigned to perform the task using a power tool.
If any irregularities are detected in the fastening of the housing or in its integrity, as well as in the case of damage to the power cable or its plug, as well as if the tool operates abnormally at idle (sparking of the brushes of the electric motor of the device), the tool is not allowed to be used. If it is not possible to eliminate the identified defect on your own (having the appropriate permission to do so), then the device must be removed from service, which should be promptly reported to the employee responsible for accounting and checking electrical tools for the structural unit.
The words about admission are far from idle, since not every employee is allowed to work with electrical appliances and their parts based on labor protection rules and electrical safety requirements. It follows that carrying out a routine check of a power tool, during which the insulation resistance is monitored on its exposed live parts using high-voltage measuring instruments, cannot be entrusted to any free employee of the department. Such a check can be carried out either by specialists who have the appropriate electrical safety clearance group and the necessary practical skills for such work, or by special units designed for such purposes.
Checks of household power tools
Of course, the above standards and testing algorithms were developed in relation to the professional use of electrical equipment and are mandatory for implementation in a professional environment, which is monitored by the relevant labor protection specialists. In everyday life, all issues of checking power tools and responsibility for negative consequences arising from non-compliance with established rules and regulations fall on the owner of such devices.
In home devices, it is recommended, along with the relevant regulatory documentation, to be guided by common sense, which suggests that using a faulty power tool is fraught with serious trouble. Therefore, just like in production, at home, power tools must be checked every time before using them.
The inspection process should be carried out completely in accordance with the regulations established for power tools: control the reliability of fastening of parts of the device, the integrity of the elements of its body, the absence of damage to the cable powering the device and its electrical plug, as well as the normal operation of the tool without load. After use, the device should be prepared for further storage, for which it must be carefully cleaned of work residues, dust and dirt. If a power tool is mostly stored in the house rather than used, it is recommended to turn it on for a few minutes without load at least once a quarter.
Smooth start of power tools.
It is recommended to check household power tools using an algorithm developed for professional devices. However, the time interval between periodic inspections may be longer than the standard six-month interval. If such a tool is rarely used, it can be calibrated once a year. The aging of the materials from which such a device is made and their physical wear cause a decrease in the original quality of the product, including a decrease in the insulation resistance of the power tool. Therefore, by carrying out the specified periodic check, the device owner has the opportunity to promptly detect this decrease.
However, both for professional structures and for home conditions, the same requirement applies to people who are involved in checking household power tools: they must be specialists who have the appropriate clearance for the specified work. The optimal solution in this case may be to contact a specialized organization or company that verifies its power tools.
Read also: How to unscrew a stuck screw
Owners of household power tools are strongly advised to carry out the established types of checks without abandoning them. It is quite possible that deviations in the operation of the device identified during the inspection and corrected in a timely manner will save the user of the power tool’s health, not to mention his life.
Inspection of power tools at the enterprise must be carried out in accordance with the safety regulations in force at the enterprise. It is difficult to assess the importance of this event, because any malfunction can lead to injuries of varying severity.
Registration and accounting of inspection
Power tools used in enterprises for professional purposes must be numbered and entered into a logbook. The management of the enterprise and structural unit must organize clear records of the storage, operation and testing of manual electrical equipment. All necessary information is recorded in a specially prepared journal, and based on the results of the inspection and verification, a corresponding protocol is issued. And also a mandatory measure to ensure the safe operation of this equipment is qualified instruction of personnel with a knowledge test, in which the verification methods, as well as the rules for using it, are announced under signature. One of the important criteria for inspection and safe operation is the use of auxiliary equipment, such as carriers and extension cords. They also need to be checked once a year, and ensuring this is the direct responsibility of the person responsible for electrical equipment.