Testing electric motors after repair
Testing electric motors after repair
Electric motors are tested as follows:
The scope and standards of acceptance and preventive tests are given (point by point) below:
1) Measure the DC resistance of the stator and rotor windings. The resistance of the stator and rotor windings is measured during major repairs of motors with voltages of 2 kV and higher. The resistance values of the windings of various phases should not differ from previously measured values or factory data by more than 2%.
2) Measure the insulation resistance with a megometer for a voltage of 1000-2500 V. The insulation resistance value is not standardized.
3) Test the insulation of the stator winding with increased power frequency voltage.
The magnitude of the test voltage of industrial frequency during testing after a major overhaul (without changing the windings) must correspond to the data below:
Motors with voltages up to 500 V inclusive, after installation and insertion of the rotor, are tested with a voltage of 1000 V for 1 minute.
The magnitude of the test voltage when completely changing the windings of electric motors
(test duration 1 min)
5) Measure the clearances in the bearings and between the steel of the stator and rotor. The values of air gaps at diametrically opposite points should not differ by more than ± 10% from the average value.
6) Check the operation of the electric motors at idle for an hour. The amount of no-load current is not standardized.
7) Measure the vibration of the engines. During routine repairs, it is performed for smoke exhauster engines.
The magnitude of vibration should not exceed the following values:
 Measure the run-up in the axial direction. The amount of run-up should not be more than 4 mm. During a major overhaul, it is carried out by removing the rotor.
Measure the run-up in the axial direction. The amount of run-up should not be more than 4 mm. During a major overhaul, it is carried out by removing the rotor.
9) Check the engine operation under load.
Source
AC MOTOR TESTS
________________________________________________________________________________ (object, accession)
1. Passport details:
Connection diagram stat.
2. Resistance of motor windings to direct current at a temperature of ________ degrees. WITH.
3. The polarity of the winding terminals and terminal markings have been checked and correspond to the factory ones. 4. Testing the insulation of the motor windings with increased AC voltage for 1 minute.
Resistance insulation before test, MOhm
What are the types of electric motor tests?
What is the reason for testing for electric motors?
An asynchronous electric motor can operate without major repairs for about 20 years, but often this is not possible and major repairs must be carried out earlier. This mainly occurs due to poor quality of electricity from the supply voltage network. Wear and aging of insulation, regular overloads, poor operating conditions associated with high humidity and temperature changes - this is just a small list of troubles for a high-voltage motor.
Fig. No. 1. One of the testing laboratory departments
What are the types of high voltage tests?
To confirm compliance with GOST standards, the following are performed:
All types are characteristic of the electric motor after manufacture. However, after passing the inspection and after transporting the electric motor to the place of work, acceptance tests are performed. They are also made after major repairs.
Rice. No. 2. Two-level hierarchical scheme for logical assessment of the technical condition of an asynchronous motor
Electric motor insulation resistance measurement
Such measurements are made not only during repairs. For example, if during operation it is necessary to diagnose the electric motor and power cable in case of disconnection from protection. It is also necessary to measure this parameter before starting the device after a long period of inactivity, especially in unfavorable operating conditions.
For measurement, a megohmmeter is used, the voltage of which depends on the rated value of the electric motor under test. For devices up to 500 V, a 500 V . For a nominal value of 500 - 1000 V - 1000 V . For high-voltage electric motors, a megohmmeter is used that produces a voltage of 2500 V.
For stators of low-voltage motors, the standard is 1 MOhm, while the temperature of the test object is in the range of 10-30˚C. At a temperature of 60˚С, the permissible value is reduced to 0.5 MOhm.
Devices with voltages above 1000 V are divided into two categories. For stator winding powers of 1 - 5 MW, the limit values are indicated in the table.
For more powerful, over 5 MW, motors, the approach to the process is more responsible. Measurements are made in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
For asynchronous machines with a wound rotor, including synchronous machines with an excitation winding, the insulation of the rotor winding is also tested. But only for high-voltage engines with a power of over 1 MW. A 1000 V megohmmeter is used. The limit value is 0.2 MOhm.
To prevent the appearance of parasitic currents in the shafts closed on the mounting frame, powerful electric motors have insulated supports with bearings. The bearings are also isolated from the oil lines that lubricate them during operation. The condition of this type of insulation is checked with a 1000 V megohmmeter.
This parameter is monitored after major repairs associated with the removal of the rotor. The resistance should have a value different from zero and not decrease sharply relative to the previously obtained results. The rules do not provide for a more precise meaning.
Acceptance tests of the electric motor. What does it contain?
The importance of acceptance testing of an electric motor cannot be overestimated. They include the following actions:
Rice. No. 3. Methods for monitoring the quality state of insulation of electric motor windings, available in the arsenal of the electrical engineering laboratory
It is important to remember: Before testing, after transportation to the place of work, which was previously in reserve, or in open-air storage, the electric motor is checked for absorption coefficient with a megger. That is, the insulation must be dried. For the stator winding of an electric machine with a power of 5 MW and below, the absorption coefficient at a temperature from 10 to 30 ° C should not be more than 1.3. Otherwise, an insulation breakdown may occur.
Test Capabilities
The electrical engineering laboratory consists of various departments that conduct mechanical and climatic tests of electrical equipment. It also includes a vibroacoustic testing department. Due to its versatility, the laboratory can perform a full range of tests of electric motors, electric generators and pumps and installations combined with them.
The list includes vibroacoustic and aerodynamic tests of electromechanical installations with a power of up to 100 kW with a power frequency of up to 400 Hz. The scope of services of the electrical laboratory "Electrometer" includes research and testing of vibration of an electric motor with a power of up to 100 kW.
Our specialists have extensive experience in conducting various types of testing work and will perform tests of highly complex electric motors in the most difficult conditions.
Source
Testing an AC motor after repair
Introduction
In this report, I will talk about the work performed on the basics of technical operation and maintenance of electrical and electromechanical equipment.
During the internship I covered the following issues:
Instruction on safety regulations, rules and regulations of labor protection, industrial standardization and fire protection during industrial practice.
1. Installation of an alternating current electric motor with switching and protective devices.
2. Testing the AC motor after repair.
3.Assembling a circuit to reduce reactive power consumption and increase power factor.
4.Analysis of the need to dry the electric motor windings.
5. Detection of line fault location.
6. Familiarization with connecting electric motors and transformers in production.
Installation of an AC electric motor with switching and protective devices
Currently, switchgears are supplied by the electrical industry in a complete, fully assembled form with complete installation of all devices included in them, and their installation is reduced only to installation in the installation area in the design position. Electrical installation organizations do not install individual devices and devices, and therefore this book does not provide a description of their installation. If it is necessary to install individual devices, the description of which is given below, you should be guided by the technical documentation of the manufacturers, as well as reference books on the installation of electrical installations.
High voltage test
The test is carried out after the completion of a major overhaul of the engine, and for devices up to 1000 V it may not be carried out at all. The decision is made by the technical manager, which is confirmed by a corresponding order.
The test consists of applying increased power frequency voltage from an external source. For this purpose, portable or mobile testing units are used. One of the important requirements is that they must be designed for increased leakage currents. Therefore, not all of them suitable for testing the insulation of switchgear are suitable for electric motors. Test voltages are indicated in the table.
Voltage above the rated insulation voltage is stressful. It is lifted slowly and without jerking. The serviceability criterion is the absence of discharges inside the engine, the presence of which is monitored by the readings of a milliammeter connected in series with the test object. The instrument readings themselves are not standardized. Also, the installation protection should not trip.
During testing, the connection diagram of the windings is not disassembled; they are tested against the housing together. But in the event of a breakdown, in order to find the damaged area, you will have to not only disassemble the star or triangle circuit, but also disconnect all sections of the winding in the damaged phase. The faulty section is replaced with a new one.
Scope and standards of testing of asynchronous motors
All asynchronous engines put into operation must certainly be subjected to acceptance tests, according to the PUE, in the subsequent scope.
1. Determination of the ability to turn on asynchronous electric motors with voltages above 1000 V without drying.
2. Measuring the insulation resistance of electric motors:
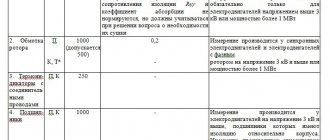
a) stator windings of an asynchronous electric motor with a voltage of up to 1000 V using a megohmmeter for a voltage of 1000 V (R 60 should be more than 0.5 MOhm at 10 - 30 °C),
b) rotor windings of asynchronous electric motors with a phase rotor megohmmeter for a voltage of 500 V (the insulation resistance must be more than 0.2 MOhm),
c) temperature sensors with a megohmmeter for a voltage of 250 V (insulation resistance is not standardized),
3. Power frequency overvoltage test
4. Constant current resistance measurement:
a) stator and rotor windings of asynchronous electric motors with a power of 300 kW or more (the difference between the measured resistances of windings of different phases or between measured and factory data is allowed less than 2%),
b) for rheostats and starting resistances, the total resistance is measured and the integrity of the taps is checked. The difference between the measured resistance and the passport data is allowed less than 10%.
See here: Measuring the insulation resistance of electric motor windings to constant current
5. Measuring the gaps between the steel of the rotor and stator. The difference between the air gaps at diametrically opposite points or points shifted relative to the rotor axis by 90° and the average air gap is allowed less than 10%.
6. Measuring clearances in plain bearings.
7. Vibration measurement of electric motor bearings.
See here: How to remove vibration from an electric motor
8. Measuring the rotor run-up in the axial direction for electric motors with plain bearings (a run-up value of 2 - 4 mm is acceptable).
9. Testing the air cooler with hydraulic pressure of 0.2 - 0.25 MPa (2 - 2.5 kgf/cm2). Test duration is 10 minutes.
10. Checking the operation of an asynchronous electric motor at idle or with an unloaded mechanism. The value of the no-load current of the electric motor is not standardized. The duration of the check is more than 1 hour.
11. Checking the operation of an asynchronous electric motor under load. This is done with the power consumed by the electric motor from the network provided by the process equipment at the time of commissioning. At the same time, control limits are determined for electric motors with variable speed.
When setting up electric motors, there is also often a need for additional tests and measurements.
Source
Testing an asynchronous squirrel-cage motor
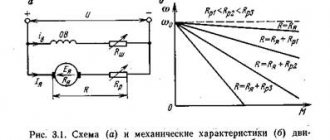
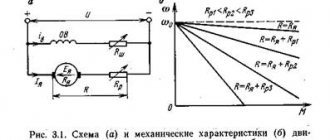
1. Study the structure and operating principle of a three-phase asynchronous motor.
2. Remove and build mechanical and performance characteristics.
3. Familiarize yourself with the features of starting and reversing, as well as with the operation of the engine in the event of a phase failure.
Directions for use
Using the recommended literature, familiarize yourself with the operating principle, design and purpose of the main parts of a three-phase asynchronous squirrel-cage motor. Pay attention to the design of the stator winding, which creates a rotating magnetic field. Understand the physical processes occurring in a short-circuited rotor winding. Pay attention to the starting features of an asynchronous motor and its operating properties.
An asynchronous motor is an alternating current motor whose rotor speed is less than the speed of rotation of the magnetic field and depends on the load on the shaft
Due to its simplicity of design, ease of operation and reliability, the induction motor has become the most common motor in industry.
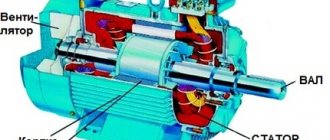
An asynchronous motor consists of two main parts:
a) stationary stator;
b) a rotating rotor.
The stator and rotor cores, separated by a small air gap (0.31.0 mm), make up the magnetic circuit of the machine. To reduce losses due to eddy currents, the stator and rotor cores are made of stamped sheets (Fig. 1) of electrical steel 0.5 mm thick, isolated from each other by a layer of varnish or scale.
A three-phase winding made of insulated copper wire is placed in the grooves located on the inner surface of the stator. Each winding phase occupies 1/3 of the stator slots. Thus, all three phases A, B, C of the stator winding are displaced in space at an angle of 120 one relative to the other (Fig. 2). The winding is connected according to the “star” or “triangle” circuit.
When such a system of windings is powered by three-phase alternating current, a rotating magnetic field is created in the stator.
According to the design of the rotor winding, asynchronous motors are divided into two types:
Rice. 1. Section of the stator and rotor cores
1. Stator plate. 4. Rotor groove.
2. Stator groove. 5. Hole for shaft attachment
3. Stator plate. 6. Air gap.
a) engines with squirrel-cage rotor;
b) motors with wound rotor (with slip rings).
Short-circuit winding The rotor is made of copper or aluminum rods pressed into the grooves of the rotor. At the ends, the rods are welded to rings made of the same material. In general, the winding forms a driving metal cage, reminiscent of a “squirrel wheel” (Fig. 3).
Reasons for testing
A prerequisite for positive test results is that the results obtained correspond to the passport indicators. However, in real life there are some deviations from the norm. This discrepancy in parameters is associated with poor supply voltage quality, operational failures, overloads for technological reasons, adverse weather conditions, insulation aging and deterioration of its quality due to changes in operating conditions. Therefore, the IM repeatedly fails much earlier than the predicted operating period. As a consequence, there is a need for control testing during operation, carrying out repairs, and performing various types of tests.
Electric motor testing: features
After a major overhaul of the electric motor (with rewinding of the stator windings), control (standard) electrical tests of the electric motors are carried out. If, as a result of repair work, the technical characteristics of the machine have been changed and they have become different from the passport data, then a standard test-check of the electric motor is performed. If the technical characteristics remain unchanged after repair (restoration), then control tests are carried out. Here the main technical characteristics include power, torque, rotor (armature, shaft) speed.
Typical post-repair tests of an electric motor include the following work (except for the main ones required for all types of testing):
Testing of AC electric motors (single-phase and three-phase) after routine repairs includes a smaller range of work.
In particular, using special equipment the following is carried out: