Subscribe to the newsletter
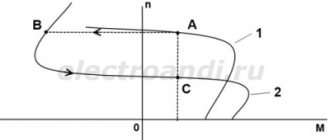
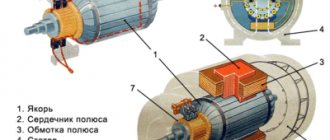
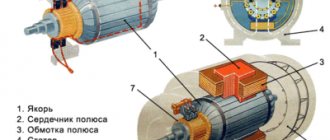
Production processes involving the operation of equipment equipped with AC or DC electric motors require periodic shutdowns. However, after disconnecting the supply voltage from the electric motors, their rotors continue to rotate by inertia and stop only after a certain period of time. This stopping of the electric motor is called freewheeling.
For electric motors that operate with frequent starts and stops, free coasting is not suitable. To reduce the time required to completely stop rotor rotation, forced braking is applied. Electric motor braking methods are divided into mechanical and electrical.
Mechanical braking
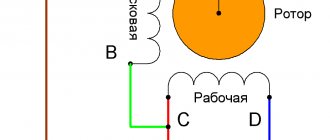
Stopping engines with this method of braking is carried out thanks to special pads on the brake pulley. After turning off the supply voltage, the brake pads are pressed against the pulley under the influence of springs. As a result of the friction between the pads and the pulley, the kinetic energy of the rotating shaft is converted into thermal energy, which leads to its complete stop. After applying voltage, the electromagnet (YB) releases the brake pads, and operation of the electric motor continues in normal mode.
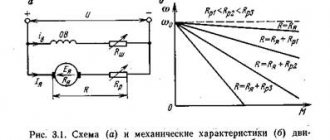
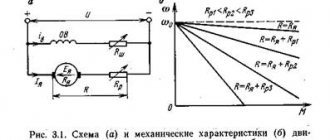
Depending on the electrical braking circuit, the kinetic energy of the rotating rotor can be transferred to the network or to a battery of capacitors, and also converted into heat, which is absorbed by the windings of the electric motor or special rheostats.
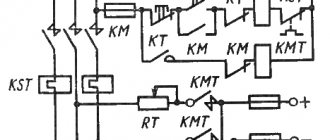
Dynamic motor braking
This stopping circuit is suitable for three-phase electric motors with both squirrel cage and wound rotor types.