Change in physical properties
The physical characteristics of the operating oil directly determine how reliably the electrical equipment will function. Therefore, during the testing process, close attention is paid to the following properties of transformer oil:
- Acceptable value of density (specific gravity) . It is important that this parameter is inferior to ice. This is due to the fact that when ice formed in an idle installation (in winter), it formed at the bottom of the tank, without creating obstacles to free circulation in the oil cooling system. The norm is considered to be a density in the range of 860-880 kg/m 3 at a temperature of 20.0°C. According to the laws of physics, specific gravity indicators change depending on temperature (when heated, they increase, and when cooled, they decrease).
- Critical heating of the oil to the ignition temperature (flash point ). This parameter must be high enough to prevent fire when the transformer, operating in overload mode, is subjected to extreme heat. The normal temperature is considered to be between 125-135°C. Over time, under the influence of frequent overheating, the oil begins to decompose, which leads to a sharp decrease in the flash point.
- Oxidation index (acid number) of a transformer liquid dielectric . Since the presence of acids leads to damage to the insulation of the transformer windings, it is important to determine their presence. The acid number displays the amount (in mg) of potassium hydroxide (KOH) required to remove traces of acid in 1 gram of product.
Change in electrical properties
Essentially, transformer oil is a dielectric medium; accordingly, its quality indicators will be its insulating characteristics. These include:
- Dielectric strength indicator . This is a characteristic of breakdown voltage, the norms of which are established depending on the class of electrical equipment. The permissible relationship between operating and breakdown voltage is shown below.
Table 1. The ratio of operating and breakdown voltage.
| Electrical installation voltage class (kV) | Breakdown voltage standard for electrical insulating oils (kV) |
| ≤15,0 | 30,0 |
| From 15.0 to 35.0 | 35,0 |
| From 60.0 to 150.0 | 55,0 |
| From 220.0 to 500.0 | 60,0 |
| 750,0 | 65,0 |
- Dielectric losses in insulation , occurring due to the dissipation of electricity in insulating materials under the influence of an electric field.
- The presence of water and mechanical impurities (indicated as a percentage).
Electrical indicators, like physical ones, change over time, which requires checking them for compliance with the standards of RD 34.45-51.300-97.
Norms
The standardized indicators must correspond to the following quantitative values according to the following criteria:
- breakdown voltage, for equipment operating in the range from 60 to 220 kV - up to 35 kV, from 20 to 35 kV - up to 25 kV;
- the presence of mechanical impurities is not allowed;
- acid number – up to 0.25 mg per 1 g of composition;
- stability against oxidative processes with similar units of measurement - within 0.005 mg;
- mass fraction of sedimentary components – should be absent;
- acid number of oxidized material – up to 0.1 mg;
- flash point – up to 150°C;
- dielectric loss tangent – up to 7 percent;
- moisture and gas content - in accordance with factory standards;
- sodium test – up to 0.4 points;
- pour point – up to -45°С;
- kinematic viscosity – from 9 to 1300 m³/s, depending on the temperature parameters of the composition.
Also read: Stray currents
If the indicators do not meet the standards, the use of this material risks breakdown of the equipment insulation and overheating, as a result of which the transformer may fail.
Working fluid that does not meet the established criteria is subjected to purification, as a result of which the indicators are returned to normal, with the possibility of further use of the oil.
Modern industry produces many filter units that allow you to purify oil for its subsequent use.
Testing transformer oil allows you to check the quality of the material and eliminate the risk of an emergency situation, which is not excluded if the composition does not comply with the established standardized indicators.
Test procedure and methodology
There is an established procedure for testing transformer oil, it includes three stages:
- Receiving samples . To select a sample, you must follow the appropriate guidelines.
- Carrying out tests according to the chosen method . This can be a complete or partial physicochemical analysis or determination of electrical strength (electric current permeability) under conditions of a certain temperature.
- Summing up the analysis . The test report indicates the results of the tests carried out, and a conclusion is drawn up on the compliance of the tested oil with accepted standards.
Having understood the testing procedure, let’s consider the main methods.
Methodology for testing transformer oil for breakdown
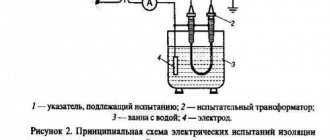
Breakdown tests of transformer oil are carried out in electrical laboratories using a special technique and taking into account the requirements of PUE, PTEEP and GOST.
To determine the breakdown voltage indicator, a special installation for testing transformer oil is used, which consists of a high-voltage transformer, control equipment and a special vessel - an oil punch.
Before carrying out test work, check that the device is grounded and that there are no problems with the alarm or locking system. Tests are carried out by certified specialists using personal protective equipment.
Test activities are carried out by sequentially performing the following actions:
- transformer oil sampling;
- preparation of a special cell;
- visual inspection of the selected oil;
- determination of breakdown voltage indicator;
- processing of test results, mathematical calculations.
All work must be carried out in strict compliance with safety regulations, during dry weather, using clean utensils and working equipment. Upon completion of the work, a transformer oil test report is drawn up.
Abbreviated chemical analysis
This test procedure includes:
- Quality check based on the appearance of the sample taken . This rapid analysis can determine the presence of water and sludge.
- Determination of breakdown voltage . We will consider this test separately.
- Determination of acid number . This test is carried out in a special laboratory; we will not discuss the technical side of the analysis, since it is of interest only to specialists. What this indicator reflects was described above.
- Determination of flash point . In modern special laboratories, automatic instruments are used for this purpose, allowing the ignition temperature of oil to be recorded over a wide range. In particular, the device shown in the figure below is capable of measuring the ignition temperature in the range from 40.0°C to 370°C. Automatic flash point recording device TVZ-LAB-11
- An analysis called the “water extract reaction” . Using this method, you can determine the presence of alkali and acid in the sample taken. The oil is considered to meet the standard if the reaction shows a neutral result.
Types of transformer oil breakdown tests
An assessment of the condition of the insulating liquid is given based on the results of the tests, which are divided into 3 types:
- Electric strength test. During the work, a visual inspection is carried out, the presence of foreign liquid and mechanical impurities is determined, as well as the breakdown voltage indicator, which determines the reliability of the insulation that the oil provides in electrical installations.
- Oil analysis - abbreviated. In addition to testing for electrical strength, the oil's flash point and acid number, indicating its aging, are determined.
- Oil analysis - complete. Includes strength testing, abbreviated analysis and determination of a number of other parameters - the amount of liquid and solids, the content of acids, alkalis, gases, pour point, etc.
Professional testing of transformer oil for breakdown according to the approved methodology is carried out by the certified LabTestEnergo laboratory. All work is carried out by certified specialists within the framework of approved methods, after which the customer is issued an official protocol. You can order services and find out the price of testing transformer oil for breakdown on our company’s website.
Complete chemical analysis
Insulating oil is subjected to full testing in cases where even one of the characteristics becomes critical or an intensive aging process is noticed. Thanks to a complete physical and chemical analysis, it is possible to determine with great accuracy the permissible period of technical operation, establish the probable cause of aging and recommend a restoration procedure. In a full test, all tests of the abbreviated analysis are performed and the following characteristics are additionally checked:
- Checking the permissible level of dielectric losses , an increase in which indicates the presence of aging products and/or contamination above the permissible norm. The result of this test is the dielectric loss tangent.
- Determination of the amount of impurities formed during operation and reducing the dielectric strength. This characteristic can be obtained in various ways, of which the simplest are visual inspection and gravimetric method. But, unfortunately, these two methods do not allow assessing the particle size distribution of impurities, and it is on this indicator that the electrical strength characteristic depends.
Modern laboratories include automatic ultrasonic units that make it possible to determine the quantitative content of impurities with great accuracy.
Automatic analyzer of the amount of mechanical impurities GRAN-152
- Determination of the amount of moisture contained in a sample. Based on this indicator, it is possible to determine the insulating properties of the tested product and obtain information about the permissible service life. By the presence of moisture and its quantity, it is possible to determine the fact of depressurization of the transformer tank and its frequent operation in overloaded mode. An image of an automatic analyzer device that allows you to determine the quantitative moisture content is shown below.
Aquameter KFM 3000 moisture content meter - Analysis to determine the composition of gases dissolved in a sample (gas content). This indicator is reflected in the dielectric density of transformer oils. Below is a mobile gas analyzer that allows you to determine the absorption composition.
Transport X portable transformer oil gas analyzer - Test for the presence of antioxidant additives . The result of the analysis allows us to determine the need to replace or regenerate the tested oil.
- Determination of oxidation stability (stability of the dielectric mixture). The analysis is carried out by treating an oil sample with an air mixture (a special catalyst may be added). After this, the characteristics after oxidation are taken and compared with those that were originally.
Scope of testing and what properties are tested
During the testing process, the main characteristics of the material are checked for compliance with the requirements of regulatory documentation. There is a check based on the following criteria:
- Flash point - as this indicator increases, the volume of evaporation increases, as a result of which the oil becomes more viscous, and the specific percentage of explosive gases in its composition increases.
- The pour point is the opposite indicator to that noted above. Its reduction complicates the functioning of oil transfer pumps, switching devices and other elements of oil systems.
- Acid number - shows the level of caustic potassium content in the material. The number of milligrams of a given component required to neutralize free acids in 1 g of the composition is determined. The final value of the indicator is obtained by calculation.
- Dielectric density is the primary criterion indicating the degree of contamination of the composition. Conducted 6 times to determine the average.
- Dielectric loss tangent – determines the dielectric and insulating properties of the working fluid.
- Color characteristics - by these you can determine the properties of the composition and its quality.
- The presence of third-party mechanical contaminants - this criterion is related to the acid number and shows the degree of aging of the oil, as a result of which it loses its specified properties.
- The content of moisture and gases also indicates the degree of aging of the working fluid.
Also read: Methods of protection from electromagnetic radiation
In addition to the listed work, density measurements are carried out with a hydrometer and the presence of sulfur is determined. But these indicators are not standardized.
Determination of electrical strength
This indicator can be called the main parameter describing the insulating properties of a liquid dielectric. The strength of transformer oil is calculated using the formula: E = UNP / h, where UNP is the breakdown voltage value, h is the interelectrode gap. The results from the sample are taken using a special device, such as the one in the figure below.
Electrical strength monitoring device KPN-901
It is characteristic that the breakdown voltage measurement indicators do not depend on the conductivity of the oil, but both of these characteristics are sensitive to moisture and gas content, as well as the presence of process impurities. As soon as the listed indicators go beyond acceptable limits, an increase in conductivity and a decrease in electrical strength are observed.
Scope and frequency of tests
According to current standards, oil is tested in the following cases:
- During the storage of electrical devices . The frequency of testing depends on the voltage class of the equipment. For example, oil in devices up to 35.0 kV is tested every six months, and in equipment designed for 110.0 kV or more, tests are carried out every 4 months. If the filling was carried out with fresh transformer oils, then checking the electrical strength is sufficient, otherwise a shortened chemical analysis is performed.
- Before starting work . A sample from the equipment tank must be taken before turning on transformers or other devices that use oil. The scope of testing is specified by the manufacturer of electrical equipment.
- During the operation of oil switches , high-voltage transformers, special current measuring devices, etc. The frequency of testing depends on the purpose of the equipment and the voltage class. For example, for power transformers up to 35.0 kV, tests are carried out at the following frequency:
- Once put into operation 5 times during the first month, with 3 tests to be performed in the first two weeks, remaining in the next two weeks.
- Next, measurements are taken at intervals of 4 months.
Frequency of oil testing in power transformers
Type of test Voltage 110 kV and higher (power over 630 kVA) Voltage 110 kV and higher (power up to 630 kVA) Voltage 35 kV Block transformers, TSN and transformers with an average annual load of at least 50% of the rated load. (35 kV) Voltage 35 kV and above Voltage 35 kV and below HARG1) During the first 3 days; 2) After 10 days; 3) 1, 3, 6 months after switching on, then 2 times a year. During the first 3 days after switching on—During the first 3 days. after switching on - after 1 and 6 months. after switching on - then at least 2 times a year - Before commissioning - Before and after completion of major and restoration repairs of the transformer and/or work with oil - Punchdown UAfter commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least 1 time in 2 years It is allowed not to test———During the first month of operation (1 time in the first half and 1 time in the second half of the month) and after a year. Further, at least once every 4 years Flash point After commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least 1 time in 2 years It is allowed not to test - - - At least 1 time in 4 years Moisture content After commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least 1 time in 2 years It is allowed not to test———At least 1 time in 4 years Mechanical impurities After commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least once every 4 years————Acid number After commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least 1 time in 2 years It is allowed not to test———At least 1 time in 4 years Acids and alkalis After commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least once every 4 years It is allowed not to test————Tangent After commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least 1 time in 4 years It is allowed not to test————Ionol, Agidol At least 1 time in 4 years It is allowed not to test————Furan 1 time in 12 years. After 24 years of operation: 1 time every 4 years. It is also recommended to determine if significant amounts of CO and CO2 are detected in transformer oil by chromatographic analysis of dissolved gases———By the decision of the technical manager Total gas content For transformers with film protection after commissioning: 1) 110-220 kV - after 10 days and 1 month; 2) 330-750 kV - after 10 days, 1 and 3 months. 3) In the future - at least once every 4 years—————Degree of polymerization In case, according to indirect assessment methods (presence of furan derivatives in transformer oil, results of chromatographic analysis of furan compounds dissolved in oil, CO and CO2 gases, results of physical - chemical analysis of oil, results of measuring the dielectric parameters of insulation) there are sufficient grounds to expect significant wear of solid insulation For critical transformers that have worked within the time limits established by the regulatory and technical documentation (block transformers, auxiliary transformers), under the above conditions———Stability against oxidationBefore commissioning ————Example of a test report with explanation
Let us give as an example a test report for operational transformer oil, with a separation of the main information fields.
Example of a transformer oil test report
The protocol contains the following information:
- “Header”, where the document number, its name are displayed, the brand of oil and test standards according to a specific GOST are indicated.
- A table with the name of the tests performed and their results.
- Conclusion of the examination.
- The name and seal of the laboratory that performed the tests, the date of the document and the signature of the person in charge.
Source
Acceptance testing standards.
Scope of acceptance tests of transformer oil.
In accordance with the requirements of the PUE, transformer oil is tested at the installation site of electrical equipment to the following extent:
1. Oil analysis before filling into equipment.
2. Oil analysis before turning on the equipment.
3. Testing the oil from the apparatus for stability when mixing it.
Oil analysis before filling into equipment.
Before filling into the equipment, each batch of transformer oil received from the plant must undergo one-time tests for all indicators given in table. 2.14, except clause 3. The values of the indicators obtained during testing must be no worse than those given in table. 2.14.
Oils manufactured according to technical conditions not specified in the table. 2.14 must be tested according to the same indicators, but test standards should be adopted in accordance with the technical specifications for these oils.
Oil analysis before turning on the equipment.
Oil refilled into equipment must be subjected to a stored analysis before it is energized after installation. The abbreviated oil analysis includes: determination of the minimum breakdown voltage, qualitative determination of the presence of mechanical impurities and suspended carbon, determination of the acid number, determination of the reaction of the aqueous extract or quantitative determination of water-soluble acids and determination of the flash point. Test standards are presented in paragraphs. 1-6 tables 2.14, and for 110 kV equipment, in addition, in clause 12 of table. 2.14.
Testing oil from devices for stability when mixing it.
When pouring fresh conditioned oils of different brands into electrical equipment, the mixture is checked for stability in mixing proportions, and the stability of the mixture should be no worse than the stability of one of the mixed oils, which has less stability.