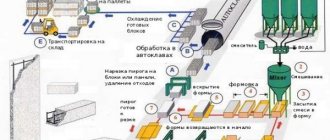
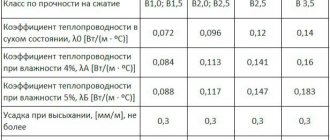
Description of the properties of aerated concrete
No matter how trite it sounds, the service life of a house made of aerated concrete depends on two things: the quality of the materials used and compliance with construction technologies. Technologies mean not only the correct installation, but also the structuring of the layers of the wall pie, taking into account the properties of a particular type of concrete.
Let's figure out what's so special about aerated concrete. Let us pay attention to its component composition and hardening conditions. It is impossible not to mention them, since it is due to the manufacturing technology that the properties of the material are formed - and they can vary significantly.
Features and properties of aerated concrete
Aerated concrete is a building material from the category of cellular concrete. Its peculiarity is its structure - it is not monolithic, like traditional brands of material, but porous, similar to a sponge. The presence of a large number of bubbles gives the material special properties inherent in cellular concrete:
- light weight;
- high heat-saving ability;
- the ability to dampen sounds, both airborne and transmitted through structures.
In addition to its positive qualities, aerated concrete also has negative properties:
- low strength (compared to dense building materials);
- high hygroscopicity;
- lack of both tensile and compressive strength.
Thanks to these properties, aerated concrete houses are of great interest among builders, but are also the subject of fierce debate. The most difficult aspect is the ability to absorb and retain large amounts of moisture, which automatically puts the material at risk.
The main disadvantage of the material, from the point of view of structural strength, is the instability of the structure. The constant presence of a certain amount of moisture provokes minute changes in the size of the dense part of its structure. In addition, there is a significant risk of destruction caused by frosty expansion of ice, which is very important for Russian climatic conditions.
The presence of moisture causes shrinkage of the aerated block in the first months after the start of operation. The block manufacturing technology requires exposure for 12 hours in an autoclave. The material is processed with superheated steam under high pressure, so the aerated concrete at the exit has high humidity. Gradually it dries out, which causes shrinkage.
Another feature of aerated concrete is its weak load-bearing capacity. The porous structure, which gives a lot of positive qualities, causes a decrease in the density of the material. High loads lead to compression of aerated concrete due to the collapse of internal cavities. If you reduce their number, the load-bearing capacity will increase, but at the same time, the useful qualities will significantly decrease - the material will become heavier, and the ability to retain heat will disappear. Therefore, manufacturers produce different brands of aerated concrete:
- structural, with increased density and load-bearing capacity, but with relatively high thermal conductivity;
- structural and thermal insulation, combining heat-saving abilities with sufficiently high strength;
- thermal insulation, intended for the construction of internal partitions or increasing the thickness of external walls by laying an additional layer from the inside.
Autoclaved aerated concrete has the least shrinkage. Accordingly, it is able to maintain its performance qualities longer, which helps to increase its service life.
How to make a wall from aerated concrete correctly
The service life of the gas block is affected by the likelihood of its secondary moisture. This applies only to heated buildings, inside of which a lot of steam is generated during the winter. Aerated concrete has a high level of vapor permeability, and vapors, even despite the insulation of the inner surface, still get into the thickness of the masonry.
That’s why it’s so important to insulate the walls as much as possible from the inside, and to allow steam to escape freely from the outside. Accordingly, for the facade you need to select a finish that will ensure this. The only insulation materials are mineral wool, and the only adhesive finishing materials are thin-layer plaster for cellular concrete.
Vitaly Kudryashov
Builder Author of the portal full-houses.ru
Ask a Question
Decorative aerated concrete tiles have also appeared on sale, which will be an excellent choice for a house built from aerated concrete. All other finishing materials must be installed according to the ventilation facade system, with a gap for normal air exchange.
Strength and Durability
The question: how many years will a house made of aerated concrete last, is asked by every developer who considers autoclave blocks as a wall material. There is a lot of information and sometimes it is diametrically opposed. Manufacturers often guarantee a hundred years, citing as an example buildings built in the last century in European territories. Their opponents, citing seemingly unshakable arguments, argue that in 15-20 years they will have to build a new house. Is this so, and who is right here?
- The truth is always somewhere in the middle, but history is always the best judge. In Russia, the era of aerated concrete began not with private, but with multi-story housing construction. True, the gas-block masonry here is not load-bearing, but only performs enclosing functions. The loads are taken by the reinforced concrete frame.
- However, houses built in the mid-eighties began to be taken out of service as early as 2015 due to wear and tear. It turns out that they served for only 30 years, maximum 35, which is very little for a permanent building. However, over the past years, aerated concrete production technologies have undergone great changes.
- You can verify this even when comparing the requirements of the standards for the production of cellular concrete: the previous 25485 and the latest 31359. In the old one, from 1989 (although it has not ceased to be valid today), the minimum strength class for autoclaved blocks with a density of D500 is set as B1 - more it is possible, but less is not possible.
- However, such strength is not enough for the construction of load-bearing walls of even a one-story house, so this material could only be thermal insulation. In the new GOST, introduced in 2007 specifically for autoclaved concrete, with a density of 500 kg/m3, blocks must correspond to strength class B2. In this case, you can build a house on two floors.
- The conclusion from the above is obvious: in old high-rise buildings, the masonry was initially less durable, hence the unenviable service life. Today, not only D500 blocks, but also D400 and even D300 correspond to class B2 - although the standard allows strength class B075 for this density. However, with this indicator, the material will only be thermal insulating, which is why manufacturers strive for higher indicators that ensure sales.
Vitaly Kudryashov
Builder Author of the portal full-houses.ru
Ask a Question
Class B2 allows not only to build two-story houses, but also to ensure the best ability of masonry to resist heat transfer due to lower density and thermal conductivity. So, technical characteristics when purchasing masonry material for construction are of paramount importance.
How durable is it?
Standard durability of the material
It is necessary to immediately clarify that it is inappropriate to talk about the durability of the material, since we should always talk about the durability of the structure. The durability of aerated concrete blocks stored in a warehouse cannot be compared with the durability of walls or other elements of buildings in use. Therefore, when talking about the duration of preservation of working qualities, it is necessary to take into account the conditions and circumstances of use of the material. There are many factors at play here, both external and internal.
The regulatory document determining the durability of aerated concrete is GOST 25820-2014 “Lightweight concrete. Technical conditions". According to its requirements, the service life of cellular concrete must be at least 50 years. However, this requirement applies only to material that is in favorable conditions and does not experience excessive loads. In practice, this is not always possible to achieve.
Durability of houses in practice
In practice, the service life of aerated concrete buildings can have very different values. The network contains information about private low-rise buildings in Europe, whose age has exceeded 80 years. Many houses from this material were once built in the Baltic states; today their age is 45-50 years. However, referring to this information when determining the service life of a house made of gas silicate blocks is, to say the least, incorrect. In order to be able to rely on available information, it is necessary to have data regarding the brand of aerated concrete, the parameters of buildings, their operating conditions, etc. Without this additional information, it is impossible to correctly determine the service life of aerated concrete blocks. Moreover, there is no reason to guarantee the service life of the material in the Russian climate.
What affects the durability of a house made of aerated concrete
Now let’s figure out why structures lose strength and durability:
Humidity and steam
Water is the main destroyer for any structure, and aerated concrete is the most vulnerable in this regard due to its porous structure. Therefore, the primary task is to prevent wetness or stagnation of moisture. For this:
- It is not advisable to put the blocks into use immediately after purchase, and you should not store them in the open air for a long time.
- A cut-off waterproofing must be installed under the first row to prevent capillary leakage of moisture.
- Exterior finishing should begin after the interior, and preferably not immediately.
- If you plan to insulate the facade with foam plastic or finish it with dense cladding, you must wait at least six months.
- To protect against the effects of steam, the selection of all wall pie materials is carried out according to the principle of increasing vapor permeability from the inside to the outside. That is, the materials on the facade must either have a density lower than that of aerated concrete, or be installed with a ventilated gap.
Convection of air currents
Single-layer masonry is characterized by the phenomenon of air permeability. If the walls are blown through, it means that moisture can penetrate with the air. And this not only disrupts the comfort of living in the house, but also reduces the durability of the masonry.
In many ways, air convection depends on the quality of installation of the blocks, in which a certain number of vertical joints may remain unfilled or poorly filled with mortar (glue). It also matters what shape the blocks were used for masonry. If they are tongue-and-groove, then their vertical planes are not filled with glue according to the technology.
The main protection of masonry from air permeation is plaster. If a different finishing option is chosen for the outside and there is no insulation, it is enough to plaster the walls from the inside. And it is better if it is vapor-proof plaster - for example, polymer cement or acrylic. Outside, you should use only compounds with a high coefficient of vapor permeability: mineral, silicone, silicate.
How to increase the service life of aerated concrete
The service life of a house made of gas silicate blocks depends on a combination of environmental conditions, design accuracy and quality of construction. All these factors have an impact on the lifespan of the building. It is necessary to take care of increasing the service life at the design stage. It is necessary to provide the house with a reliable supporting structure (foundation), motionless and rigid. In addition, the external walls must be properly finished using vapor-permeable materials or dense cladding with a ventilation gap.
When performing finishing work, one must take into account the basic rule - the vapor permeability of all layers of the wall pie should increase from the inside to the outside. If you simply paint an aerated concrete wall with impenetrable paint, the moisture will be trapped inside the walls and begin to accumulate and destroy the house. Drying walls is much more difficult than creating conditions for them to get wet - aerated concrete dries rather slowly, and in the conditions of a house in use, it is very difficult to change the humidity regime of the material.
An important element that affects the condition of walls and other structures is ventilation. It removes exhaust air with excess humidity from the premises, freeing the walls from excess load. Modern plastic windows and sealed doors stop the process of natural ventilation, therefore, care must be taken to install forced exhaust and supply ventilation systems. Dry aerated concrete is much stronger and therefore more durable.
Summarize. The service life of aerated concrete, according to GOST, is up to 50 years. This value was obtained during laboratory tests. In practice, such durability is not always confirmed, since optimal conditions are required to obtain the expected results.
The user cannot change the climate or soil composition, but he can prepare in advance to repel possible threats. It is necessary to design a reliable foundation, calculate structures so that there is a reserve of bearing capacity. In addition, aerated concrete walls must have a reliable exterior finish that cuts off rain moisture from the wall material. If all these conditions are met, you can expect the building to have the longest possible service life.
Insufficient foundation rigidity and improper reinforcement
Aerated concrete masonry does not resist bending loads well, and as a result of their impact, cracks appear in it. The house, of course, will not collapse, but repairs may be required. If the cause of cracking is an incorrectly laid or insufficiently rigid foundation, the consequences can be much more serious.
That's why:
- The foundation must only be monolithic.
- The rigidity of the masonry is ensured by reinforcing the most loaded areas (bottom row, window sill, supports under lintels, corners and intersections of walls).
- An armored belt is made under any structure supported on masonry (not only floor slabs, but also beams and rafters).
On walls longer than 6 meters, reinforcement is made along the entire height every 100 cm.