Solid floating foundation
It happens that the owners do not need a basement, then digging a pit is not done, and the monolithic foundation is made directly on the crushed stone cushion. Such a slab will serve as the floor for the first floor and at the same time as the foundation. Therefore, insulation work to protect the foundation is also sexual treatment.
This type of foundation for a house is called a floating foundation. Because they are cast above the freezing zone of the soil, actually on the surface. Therefore, they experience all the vibrations of the underlying ground that occur during freezing in winter and thawing in spring. All loads occurring in the soil are transferred to the foundation, and the house, together with the foundation, either rises or settles.
Until recently, such options were used in the construction of shops and pavilions, but now this foundation option is often used when building a country house, especially where the soil is heaving.
Rolled waterproofing under the foundation slab
Moisture-proof materials are produced on various bases:
- bitumen;
- polymer.
They are supplied in rolls and fixed in various ways:
- by fusing onto concrete using burner heating;
- by gluing using a special mastic.
The traditionally used material is roofing felt. It is a cardboard base impregnated with bitumen.
Rolled. A long-known method that is fully justified, although the durability of such waterproofing is not too great
The main advantages of the application are:
- cheap material;
- ease of fixation.
The list of disadvantages significantly exceeds the list of advantages. Weaknesses of the material:
- fragility at negative temperatures;
- insufficient strength;
- limited service life;
- tendency to cracking at bends;
- low elasticity of the hydrophobic layer.
Modern waterproofing materials are replacing outdated roofing felt:
- glass ruberoid;
- stekloizol;
- hydroisol;
- rubemast.
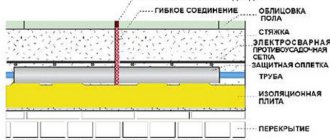
Installation is quite quick and simple; all you need is a burner to heat up the mastic. Waterproofing the slab with roll-up waterproofing is done by laying a protective layer on a compacted gravel-sand backfill. In this case, an overlap of 15–20 cm should be ensured. Concrete can be poured onto the waterproofing material. After hardening, it is necessary to waterproof the top and end surfaces.
To do this you need:
- Clean them from dust.
- Cover with mastic.
- Cut the canvas.
- Glue the roll moisture protection.
To perform the work, you can use any type of rolled waterproofing materials.
The process of waterproofing a monolithic foundation slab
Foundation waterproofing can be done in several ways. And, of course, each option has its advantages and disadvantages. Currently the most popular are:
The operating principle of penetrating waterproofing.
- Coating. Very easy to apply, good results, long service life.
- Penetrating. Quite a new option. A distinctive feature of this composition is that after its application, crystals form in the concrete, which prevent water from penetrating into the structure.
- Waterproofing in rolls. A classic option that has been used for quite a long time. It is worth noting here that the service life of roll waterproofing is relatively short.
During the installation of a slab foundation, a problem very often arises regarding the waterproofing of the bottom slab. This is due to its fairly large area. In most cases, this problem is solved through roll or coating waterproofing.
As already noted, not so long ago roofing felt was used for waterproofing. This is a material in a roll in which bitumen is applied to a cardboard base. It is worth saying that roofing felt cannot boast of its durability, because... bitumen quickly loses its elasticity, and cardboard does not have high strength.
Composition of roll waterproofing.
At the present stage, materials are used in rolls, but already including fiberglass or fiberglass. Moreover, the bitumen contains modifying additives that make the material more elastic.
Waterproofing in a roll is quite convenient to lay under the foundation slab. It does not require a special screed. The seams that appear between the strips of material must be glued with bitumen mastic. Installation is relatively quick. For installation, you only need a burner so that you can heat the mastic.
This mastic must be applied using a roller or brush. The whole problem is that in order to waterproof the very bottom part of the foundation, you need to put a cement screed on a bed of sand and crushed stone, on which bitumen mastic is subsequently applied. After the slab has been poured, a layer of waterproofing must be applied to its sides and top.
In the same way, you can create a layer of waterproofing using penetrating compounds. The result of this application is the sealing of the concrete pores. Crystals form inside the concrete base, which prevent moisture from penetrating inside. Currently, this waterproofing option is considered optimal and modern.
Types of waterproofing
Today, there are several ways to effectively waterproof a foundation. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Roll is the oldest and most traditional method, however, it has not lost its relevance. It is a dense base with a layer of bitumen applied to it. It is considered the simplest and most inexpensive method of waterproofing. However, it is also the most short-lived.
- Coating - consists of uniformly applying bitumen mastic with a brush or roller over the entire surface of the foundation. It is considered a more practical, durable, but also labor-intensive method of waterproofing. Often used in combination with other waterproofing methods.
- Penetrating is the most modern and effective method. It consists of applying a special composition to the concrete, which is impregnated into the concrete. In its pores, the composition crystallizes, sealing the pores of the material, which does not allow moisture to penetrate inside the concrete.
Most types of monolithic slab waterproofing are based on the principle of limiting the ingress of moisture using bitumen-based materials. Regardless of the type of coating, the material must have integrity and tightness in order to completely prevent contact of moisture with concrete. In modern construction, there are several ways to protect the foundation of a house, but the most common is still waterproofing the foundation slab with rolled materials.
The impact of moisture on the foundation
Anyone who has even a superficial understanding of the properties of building materials, in particular concrete, knows the pattern - under constant exposure to moisture, it continues to gain strength over several years. This fact may cast doubt on the need for waterproofing the foundation.
However, not everything is so simple - the fact is that you need to take into account some more factors:
- The presence of metal reinforcement in the foundation structure - as is known, in addition to concrete, the foundation structure also contains a reinforcing frame made of steel rods.
Penetration of moisture into metal rods and its constant exposure leads to corrosion. Metal, turning into rust, increases in volume almost 3 times. This leads to the formation of pressure in the inner layers of concrete and gradually destroys it from the inside. Photo 1. Consequences of reinforcement corrosion in a reinforced concrete structure - Capillarity is the rise of moisture through the pores in the concrete structure, initially to the inner layers, and then upward to the wall materials.
The result is an increase in heat loss through damp walls, constant dampness inside the premises, the formation of fungi and mold, and the destruction of finishing materials. Capillary suction of moisture is effectively cut off by horizontal waterproofing of the foundation. Figure 2. Effect of capillary suction of moisture - Alternating positive and negative temperatures - when moisture freezes, it also increases in volume and over time destroys the concrete base from the inside.
Photo 3. Consequences of alternating exposure to plus and minus temperatures on concrete (an example is shown on prototypes) - Groundwater is dangerous not so much in itself, but because of the sulfates, salts and acids it contains. These chemically aggressive elements cause so-called “concrete corrosion” - over time, it begins to crumble and reinforced concrete structures lose their performance characteristics.
Terms and materials
When planning a construction project, it is very important to know the optimal conditions for laying a particular type of foundation. It is not always rational to install a strip base, since it is very capricious to certain characteristics of the ground. Ideal recommendations and factors for filling a slab device are the following indicators:
- High rate of seasonal heaving of the earth in the territory;
- The area has excessive moisture;
- High surface water on a construction site.
Attention! The monolithic slab has proven itself worthy not only in conditions when other foundations cannot be erected, but also in fairly heavy buildings.
Modern methods of protecting the base
Modern construction technologies provide three methods, including:
- penetrating: a special mixture is applied to the surface and crystallizes. A film is formed that has a hydrophobic effect, which prevents the penetration of moisture;
- roll: the method is popular in the CIS countries, whose residents use simple technology. The average service life is 2 - 3 years, no more. When using cheap material, the period is reduced to one year. It consists of covering an area with a special layer under the influence of external temperature (gas burner). Despite the short service life, this method is suitable for covering large areas;
- coating: a simple way to protect the base. Chosen due to low cost.
Principles to follow when defending:
the waterproofing layer must be intact, without damage, without defects; protection is laid at the stage of laying the foundation, or after the concrete mixture has hardened; you should not hesitate with installation, since concrete tends to accumulate moisture; where there is a high probability of groundwater, strengthen waterproofing; the formwork will take on excess moisture, thereby reducing the risk of flooding; consider installing additional drainage to drain water; When choosing a material, pay attention to the characteristics of the building material. Some liquids contain allergic agents for the human body
Those who are susceptible feel discomfort.
Materials for foundation waterproofing
Waterproofing the foundation of a house can be done using various materials. The choice is made mainly depending on the class of the room and the degree of protection from exposure to water.
Initially, you need to understand the existing classes of premises:
- Class 4 – in private housing construction, premises with this class are practically never found. This class includes rooms with a constant, clearly established temperature and humidity regime - for example, archives, libraries, laboratories, etc.
- Class 3 – the most common in individual construction. This category includes residential premises, offices, commercial and social facilities. They are subject to high requirements regarding the microclimate; the presence of a natural or forced ventilation system is mandatory. The thickness of the walls must be at least 250 mm.
- Class 2 – these are utility rooms equipped with a ventilation system. Only minor evaporations are allowed here, without wet spots. In these rooms it is possible to install electrical appliances with standard operating voltage. Walls must have a thickness of 200 mm
- Class 1 – technical premises in which power supply is not provided. Even minor leaks are acceptable here. The standard wall thickness should be more than 150 mm.
Table 1. Types of waterproofing materials used depending on their degree of protection against water and their compatibility with rooms of different classes
| Waterproofing material | Resistance to cracking (on a 5-point scale) | Degree of protection against moisture | Room class | |||||
| Verkhov-Dka | soil moisture | groundwater aquifer | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Polyester based bitumen membranes | 5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | – |
| Mounted polymer waterproof membranes | 5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Coating polymer and bitumen-polymer mastics | 4 | + | + | + | + | + | + | – |
| Coating polymer-cement compositions (flexible) | 4 | + | – | + | + | + | + | – |
| Coating cement compositions (hard) | 3 | + | – | + | + | + | – | – |
| Impregnation waterproofing | 3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | – |
Main principles of moisture protection
Before we talk about moisture protection technology, a few words should be said about the basic principles that should be followed, no matter what method you use. The list of the most important requirements is as follows:
take care of the maximum density and tightness of the insulating layer - it must be solid and have no cracks, tears or holes;
A monolithic (slab) block has the ability to absorb water, as a result of which a poor-quality base can be obtained
where there is reason to assume the greatest activity of groundwater, provide additional protection; a well-made blind area will take on the negative effects of precipitation; if groundwater passes close to the surface, take care to install an additional drainage layer, which will reduce the water level underground and prevent the destruction of the slab; When choosing the material that will be used to waterproof the slab, pay attention to the height of the foundation.
If you want your building to stand for many years, follow these requirements when installing hydrophobic protection
This is critical to making your efforts successful and meaningful.
How to waterproof a monolithic slab ↑
This problem can be solved in several ways. Each type of waterproofing has its own pros and cons. Today the most common are:
- Coating. Quite easy to use, gives good results, and is durable.
- Penetrating. It is a more modern way of cutting off moisture. It differs in that when it is applied, the composition reacts with concrete, as a result of which, upon subsequent contact with moisture, it crystallizes and seals the smallest pores of the concrete.
- Rolled. A long-known method that is fully justified, although the durability of such waterproofing is not too great.
The main problem in constructing a slab foundation is waterproofing the slab from below, since it has a significant area. Typically, this work is carried out in two ways - using roll or coating materials.
Previously, roofing felt was used in construction - a rolled material in which bitumen was applied to a cardboard base. Its durability was low, since the paper base quickly deteriorated; this material had low bending strength, as well as resistance to high and low temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, etc. The bitumen used in its production also did not have sufficient viscosity and elasticity. As a result, the material quickly cracked and the waterproofing barrier lost its tightness.
Modern materials for installing roll waterproofing - rubemast, stekloizol, etc. – are made on the basis of fiberglass or fiberglass. This gives them much greater strength. The composition of the bitumen with which the base is impregnated includes modifying additives - due to this, the material becomes elastic, has significant bending strength, and resistance to temperature changes.
Rolled waterproofing under the foundation slab is convenient to use, as it is simply laid on the gravel-sand backfill, without requiring additional screed. The joints between the strips of material are carefully glued using bitumen mastic. Installation is quite quick and simple; all you need is a burner to heat the mastic. Along the perimeter of the foundation, strips of waterproofing material are bent upward by about 10-15 cm.
Coating waterproofing using bitumen mastics is a more modern way of cutting off water from a monolithic slab. It involves applying modified bitumen to a concrete base using a brush, roller, sprayer, etc. The difficulty is that to waterproof the base of the foundation, it is necessary to lay a layer of cement screed on the sand-crushed stone bed, on which a layer of bitumen mastic is applied. After pouring the slab itself on top of it, waterproofing is applied to the sides and top of the foundation.
A similar method is used to perform penetrating waterproofing of a monolithic slab. A cement screed is laid on the sand and gravel base, which is covered with rolled waterproofing materials. After the slab is poured, penetrating insulation is applied to the side and top surfaces. The principle of its operation is a chemical reaction between calcium hydroxide (lime), which is contained in concrete, capillary moisture located in the thickness of concrete and the active substances that make up the waterproofing material. As a result, the pores of the concrete are sealed with crystalline compounds, preventing the penetration of water. Moreover, this reaction continues for a long time, continuing the “self-healing” of microscopic cracks in the thickness of the concrete. This method of waterproofing a monolithic slab foundation is the most effective, high-tech and modern.
Advantages of a monolith
Today, a concrete slab is considered the most versatile and durable material.
Today, a concrete slab is considered the most versatile and durable material, which is why the demand for its installation is growing. Plus, we can highlight a number of advantages in the functioning of the design:
- Versatility of use. This material is well compatible with all materials from which the house is built.
- Installation work can be performed on any type of soil;
- High reliability indicator, which manifests itself when the monolith is handled correctly;
- It is not necessary to carry out geological diagnostics before starting construction;
- Resistant to soil heaving;
Why is waterproofing needed?
Waterproofing a monolithic slab is necessary primarily to maintain the stability and stability of the building. It is necessary to protect the foundation, since it often suffers from groundwater and underground moisture, which over time simply destroys the foundation of the house. Today there are quite a lot of means for waterproofing; almost anyone can use it for a monolithic foundation. The choice is determined only by the desire and capabilities of the homeowner.
When deciding whether waterproofing is necessary, it should be taken into account that any material or structure that has direct contact with the soil is subject to the following effects:
- Underground water flows. The water level, its pressure and the degree of impact may change, so the possibility of undermining the foundation cannot be ruled out, which often leads to its destruction.
- Filtration water flows. In this case, we mean rain runoff, melt water runoff and other types of flows, including random ones.
- From the side of moisture, which is located in the soil. The soil accumulates water after precipitation, as well as moisture from groundwater, and then begins to lift it upward under the influence of pressure, saturating the concrete.
Waterproofing the foundation slab helps solve some problems and eliminate the effect of moisture on concrete:
- Prevent the appearance of rust in reinforced structures that are used to strengthen concrete. Waterproofing material allows you to protect the foundation of the house from water penetration, and thereby ensure its long-term operation.
- Protect the building itself from water penetration inside. For example, water often enters basements, crawl spaces, etc. through an unprotected base.
To select the appropriate material for waterproofing the foundation slab, it is necessary to make some measurements and research. For example, it is necessary to determine air humidity, as well as the presence of groundwater, its movement and pressure. This will allow you to select a material that can best protect the base from possible danger.
- Placement of the monolith on the ground surface, without penetration into the soil.
- If a special cushion was made from non-metallic materials under the base of the slab.
- If, according to soil studies, the groundwater level does not rise higher than one meter.
- In cases where drains are located along the perimeter of the base, forming a closed loop.
- When backfilling the edges of the slab is done using sand.
- If a blind area is made on the soil.
In such a situation, it is believed that flows of water from rain or melting snow will not cause harm, since they are collected using a blind area. Moisture that accumulates in the soil cannot harm concrete, since non-metallic materials will prevent this. In addition, capillary suction does not occur, since there is a protection layer of sand.
In practice, many builders recommend providing better waterproofing under the foundation slab, since sometimes unexpected phenomena can occur, and water flows from below acquire greater pressure, which non-metallic materials or sand cannot withstand.
Types of monolithic foundations
Waterproofing a monolithic foundation can increase the operational life of a building and increase its level of strength
A slab monolith device can be built with or without a basement. For the two options, the methods for performing waterproofing will differ significantly. Today, vertical and horizontal methods of protection are known, as well as the following types of the slab itself:
- Base with and without grillage;
- Monolith for the basement space;
- Swedish stove with insulation;
- Components with stiffening ribs.
Cutting off moisture inside the house ↑
Waterproofing only begins with the foundation: moisture must be cut off in the structure itself. This is especially true for multi-storey panel buildings, for which floods and floods are common. There is also capillary filtration of moisture, primarily in rooms subject to constant moisture - bathrooms, toilets, kitchens.
Waterproofing of floor slabs is carried out in different ways, the main ones being roll, coating and penetrating waterproofing.
Roll materials are used mainly in kitchens and bathrooms. Before laying the decorative coating (most often it is ceramic tiles), a cement screed is applied to the laid waterproofing. It protects the material from damage and serves as the basis for high-quality tile laying. In “wet areas”, roll waterproofing is laid on the floor with an overlap of at least 20 cm on the lower part of the wall. This avoids moisture penetration in case of large leaks.
Coating waterproofing is easier to use because... applied to the prepared base using a sprayer or brush. Its advantage is a longer service life, and also that in this case there is no need for additional screed, therefore, the floor level rises slightly.
Penetrating waterproofing is the most reliable way to protect floor slabs from moisture penetration
These materials have another important advantage: manufacturers produce special joint compounds that are laid directly into the joints between the slabs. This method of waterproofing is the most reliable
Another plus is that it can be applied to mineral substrates, which include plastered surfaces, therefore, it can be used after finishing the rough finishing of walls and floors.
Waterproofing is installed at the rough finishing stage
Related Posts
- Foundation waterproofing
- We protect brickwork from moisture using penetrating waterproofing
- Slab foundation construction technology
- Membrane waterproofing: choosing the “right” coating
- Solid slab foundation
- Waterproofness of concrete
- Waterproofing the basement from the inside from groundwater
- Technologies, secrets, recipes
- How to make a slab foundation with your own hands
- Ways to strengthen the foundation
- Adding liquid glass to concrete. 2021 instructions
- Cold application bitumen mastic for waterproofing and gluing roofing felt: consumption and technical characteristics + photo
- How to make markings with your own hands for the foundation: rules
- All about rubble stone
- Penetrating concrete waterproofing
- How to build without a foundation
- Installation of formwork for the fence foundation
- Technology for constructing a foundation slab from A to Z
- Liquid plasticizer or liquid soap?
- Foundation for a greenhouse: how to do it right?
- Repair and replacement of the old foundation of a wooden house
- What should be the depth of the foundation?
- Installation of the foundation “insulated Swedish slab”
- Pouring the foundation in winter
- Example of calculating a slab foundation
Read with this
- Foundation waterproofing
- We protect brickwork from moisture using penetrating waterproofing
- Slab foundation construction technology
- Membrane waterproofing: choosing the “right” coating
- Solid slab foundation
- Waterproofness of concrete
- Waterproofing the basement from the inside from groundwater
- Technologies, secrets, recipes
- How to make a slab foundation with your own hands
- Ways to strengthen the foundation
Reasons for the need for a hydrobarrier
It is worth considering that the concrete used to build the foundation has a porous composition that easily absorbs liquid
Today it is no secret that water is aggressive. This quality is especially evident in relation to building materials. It is worth considering that the concrete used to build the foundation has a porous composition that easily absorbs liquid. Ground water flow, entering the slab, will also bring impurities of minerals, salts, and chemicals into it. These substances negatively affect the monolith and destroy it.
There is also the opposite problem, when the liquid, on the contrary, washes salts out of concrete, thereby compromising its strength. Also, if the waterproofing is of poor quality, this leads to the absorption of moisture by the material. The final negative consequence is the penetration of mold and mildew into the house.
Vertical waterproofing of the foundation with your own hands: types of insulation