Many private developers decide to build without a design, as a result of which they have many different questions. Some of the most relevant and discussed are the so-called hidden work performed at the stage of the zero cycle device. Correcting them afterwards is either impossible or too expensive, so mistakes can be more than annoying. Let's consider how and where film is used to waterproof the foundation, and in what cases this material is simply useless.
Features of foundation waterproofing
The main goal that needs to be achieved using a foundation waterproofing device is to:
- protect the structure from waterlogging and subsequent freezing, because the resulting ice destroys the integrity of the concrete stone;
- protect the reinforcement inside the concrete from corrosion, which also contributes to the destruction of concrete.
There are two types of such protection: primary and secondary. Primary protection is provided by raw materials (for example, the use of special types of cement), additives with certain properties, and compliance with additional design requirements. One of the measures to protect the reinforcement is a protective layer of concrete provided during the design.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Please note: All types of surface treatment, including laying film under the foundation slab, are considered secondary protection. It is used mainly when primary measures do not provide the required operating conditions. But since modern technologies make it possible to obtain excellent plastic concrete with a water permeability grade of at least W6, there is most often no need for such protection.
Although, a lot depends on the type of foundation, groundwater level, and the presence or absence of a basement. In a building with a basement, waterproofing is mandatory. Moreover, it should not be just some kind of insulation that does not allow water to pass through, but a material with a vapor-proof effect. After all, in the soil water is present not only in a liquid state, more often it is steam, which, penetrating through the walls of the basement, moistens the premises. In a basement, a polymer film for the foundation and floor will be the best choice; in a house without a basement, it is a completely unnecessary element that increases the cost.
For shallow or surface installations, secondary protection from moisture may only be needed for the foundation slab, under the sole. It has a very large bearing area, so waterproofing is done horizontally. And it is needed not so much to protect the slab as to prevent the monolith from losing moisture during the pouring process.
Protecting the base of a slab foundation
Why do you need a film under the foundation, where is it placed?
Not only the part of the foundation laid in the ground needs waterproofing, but also the base, which resists rain and melt water. It is very important to protect house structures from capillary moisture - that is, to prevent its absorption by the surfaces of overlying structures. For this reason, waterproofing is performed not only in the vertical plane, but also in the horizontal.
If we classify waterproofing according to the method of exposure to water, then it can be:
- Non-pressure. Eliminates the temporary effects of moisture that appears only in certain seasons. They are mainly installed under the base of the foundation and under the floors along the ground.
- Anti-pressure. It is carried out in the presence of hydrostatic pressure of groundwater, and protects not only horizontal surfaces, but also vertical ones (strip foundations and basement walls supported on a foundation slab).
- Cut-off (anti-capillary). The capillary rise of moisture occurs vertically; it can move from the lower structure to the upper one. Accordingly, this type of waterproofing is located only horizontally and is laid in the joints between structures adjacent to each other.
There are several methods of waterproofing: coating (liquid bitumen and glass, mastics and rubber), impregnation (deep penetration compounds), injection (hydroactive resins), rigid (plasters and gunite). However, the most in demand in low-rise construction are roll materials, which include polyethylene film for waterproofing the foundation. It is mainly used to seal formwork - to prevent laitance from leaking out, or as an anti-capillary barrier.
Vertical waterproofing is installed mainly on the walls of the basement, and the material for it is selected depending on the presence or absence of groundwater, its aggressiveness and the degree of soil moisture. If the groundwater level is stable below the base of the foundation and the basement floor, it is enough to treat its walls with bitumen mastic or liquid glass. It is impossible to perform such waterproofing from below, so a film or other rolled material is used as a pressure-free barrier under the foundation.
In the presence of pressure water, the level of which is above the basement floor, continuous waterproofing is performed under it and extending onto the walls using two layers of rolled material glued to mastic. So that the protective shell does not have to experience hydrostatic pressure and bend, it is covered from the outside with a rigid layer of asbestos-cement sheets or brickwork, and EPS insulation.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
Waterproofing in the basement can be external or internal. The external one is installed before or during the construction of the foundation. The internal one is installed afterwards, but it does not protect the basement walls from getting wet, but only minimizes the penetration of vaporous moisture into the premises.
What film is needed for waterproofing, and where is it useless?
Whether it is necessary to put a film under the foundation, and which one, you will understand by reading the table below:
| At what stage of the work is waterproofing installed? | Purpose of its use | Type of waterproofing, location | Materials used |
| Development of soil for foundation construction. | Prevent the spread of the bulk cushion of sand or crushed stone and their mixing with continental soil, especially clayey soil. | It is laid on the bottom of a pit or trench, in a horizontal position with the installation on the walls. |
|
| Installation of bulk cushions made of ASG, sand, crushed stone. | Protect the pillow from drying out, and the base of the foundation from capillary rise of moisture from the pillow. | It is placed horizontally on top of the pillow, followed by placement on vertical surfaces. |
|
| On a slab foundation with preliminary concrete preparation. | Protection of the slab from hydrostatic water pressure and capillary rise of moisture. | Fused or glued to the preparatory concrete slab. |
|
| For point foundations (piles or pillars). | Protection against capillary rise of moisture. | Surface insulation - the ends and heads of the piles are coated or wrapped. | Driven piles are usually coated with liquid bitumen; monolithic ones can be protected with a sleeve made of bitumen roll material. Roofing felt and similar materials can be used under the sole of the posts installed in the pit. When pouring the grillage, the formwork is covered with polyethylene film; after its removal, coating or adhesive waterproofing can be used. |
| Prefabricated monolithic foundations made of FBS and FL and FP cushions. | Avoid moisture entering the basement through joints and capillary rise. | Suture, horizontal and vertical waterproofing. | If there is a basement, first install external waterproofing from roll material in combination with mastic. Before putting the building into operation, the joints between the blocks are caulked using a self-expanding cord and a cement-based repair compound. Then, depending on the chosen finishing option, final waterproofing (impregnation or film) is performed. |
| Pouring monolithic strip foundations. | Prevent laitance from leaking out. | The entire internal cavity of the formwork is lined. |
|
| Waterproofing the basement part of a strip foundation or grillage. | Insulation of the structure from rain and melt moisture. | Depends on the exterior finish option. | Both coatings and rolled materials can be used. In case of insulation with slab or sprayed polymer material, additional waterproofing is not required. |
| Internal waterproofing of basement walls and floors. | Prevent the formation of condensation and mold. | Horizontally along the floor, and vertically along the walls. | Coating and penetrating compounds are mainly used. |
We've figured out where to install the waterproofing, all that remains is to figure out which film to use for the foundation.
Modern roll waterproofing
In the vast majority of foundation construction, roll materials are used as the main or additional hydraulic barrier. These are non-woven and polymer fabrics rolled into rolls that are glued or fused to the insulated surface.
- Materials with bitumen impregnation can be made on the basis of cardboard or fiberglass canvas. The second option has a higher tensile strength, which is why it is used more often for laying under the base of the foundation - where short-lived material cannot be replaced.
- Film (the definition of this term sounds like “thin shell”), which has a small thickness, is not suitable for this purpose; it can only be used when constructing a sub-concrete slab, which is designed to ensure the integrity of the waterproofing carpet.
- If there is no such protection under the sole, it is better to use a polyvinyl chloride membrane with a profile due to which it simply stretches when the ground moves, but does not tear.
Under the insulation layer is a PVC membrane, on top of it is a bitumen roll materialExpert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
If, instead of a footing, insulation is provided under the main foundation slab, there will be two horizontal insulating layers: a PVC membrane on the bottom, and a thin polyethylene film can be laid on top of the EPS.
- Geotextiles are non-woven fabrics made from thermo- or hydro-bonded polyester or polypropylene fibers, or fabrics made from polyester threads. Basically, geofabrics are used as a separating layer between clayey continental soil and bulk sandy or coarse-grained soil (gravel, crushed stone). This prevents the bulk cushion from silting up with clay, since its particles are able to accumulate moisture and swell, thereby provoking frost heaving.
- Clay has water-resistant properties, and when there is a threat of the foundation being washed away by groundwater, it has long been used to construct clay castles. Today, bentonite clay granules are used in the manufacture of innovative roll materials for waterproofing. These are WATERPROOF AQUIZOL mats sewn from geotextile fabric, filled with bentonite granules in a biodegradable cardboard shell. The main advantage of this material is that the cracks that form when the layer dries out can self-destruct when moistened. Bentonite mats are very effective for insulating slab foundations and ground floors.
- Polyethylene films are completely waterproof and, it would seem, are ideal waterproofing. So it is, but only until the shell breaks. If the integrity of the coating is compromised, the entire waterproofing effect is lost, so films are used to a very limited extent in relation to the foundation. Basically, they line the inside of the formwork to prevent the loss of moisture from the concrete.
Although, there are also reinforced polyethylene sheets, which are reinforced with a mesh frame over the entire area. This film is usually used when constructing a slab foundation, laying it as protection against mechanical damage on top of a ready-made waterproofing carpet - after all, installers who assemble the reinforcement frame have to walk on it and move materials. The film sheets are glued together with sealing mounting tape.
Pros and cons of polyethylene films
When choosing a material, the buyer tries to weigh all its advantages and disadvantages, and this is the list of polyethylene films in relation to foundation insulation:
| Plus | Minus |
| Low price. | Fear of ultraviolet radiation. |
| Easy installation. | Polyethylene is not suitable for waterproofing foundations due to its low mechanical strength. |
| Light weight. | Damaged by rodents. |
| Polyethylene foams, and in this form it is the most effective insulation with water-repellent properties. It is mainly used for internal insulation of basement walls and rooms with high humidity. |
Film price
Most often, polyethylene is used to seal formwork so that the concrete poured into it does not lose moisture. For this purpose, a film with a thickness of 150 microns is usually used. Polyethylene is sold in rolls 1.5 m wide, the film is usually folded in half, the spread is 3 meters. The cost of a roll 100 m long at the beginning of May 2021 is about 2800 rubles. Rolls of 25, 50, 65 and 85 m are also available for sale. The price of 1 m² is about 19 rubles. Reinforced film of the same thickness costs at least 39 rubles/m².
Feasibility of application
The part of the foundation structure located in the ground is exposed to ground moisture to a greater extent, as a result of which it gradually becomes unusable. If proper protection is not created, the concrete will gradually become saturated with moisture and begin to crumble, reducing the safety margin of the entire structure.
To maintain its integrity, it is economically feasible to use film waterproofing of the foundation to maintain its structure in normal operating condition.
In addition, the material used for this purpose performs the following functions:
- creates the basis for a waterproofing layer. It is necessary to use a diffusion membrane that is considered moisture-proof, but has the ability to allow steam to pass through;
- used as an additional layer to provide complete insulation from moisture between the soil composition and the insulation or between the screed and the insulating material. In such cases, PVC film, which has good density and thickness, is used to waterproof the foundation.
Technology of waterproofing slab foundations using surfacing method
Waterproofing of the slab under the sole with films and thin polymer membranes is carried out only in the presence of a rigid, durable base, the role of which is played by concrete preparation. This is a slab no more than 10 mm thick, poured from lean concrete directly onto the ground.
- Before installing the waterproofing, the surface is cleaned of dirt, stains and cement film, if necessary, washed with a Karcher and dried. Existing cracks and cavities are sealed with a repair solution, after which the entire surface is treated with a primer (primer composition).
- It can be applied to the base when the concrete moisture content is no more than 4%; one layer is usually sufficient. You need to wait until the primer has completely dried (there should be no traces left on the tampon attached to it), after which you can begin installing the bitumen-polymer membrane.
- Before rolling out the rolls on the base, it is necessary to carry out markings; the main task is to avoid displacement of the sheets in the end seams. If the outside temperature is below +15 degrees, the membrane should lie in a warm room for at least a day. Immediately before laying, the rolls are rolled out on a concrete base and given time to straighten. Rolling is done in one direction.
- The floating method involves the use of a gas burner, the flame of which melts the back side of the canvas and heats the base. Heating is carried out evenly, which helps to avoid un-glued areas. The sufficiency of heating is indicated by an indicator pattern on the lower surface of the film.
- The main sign of correctly performed gluing is the slight flow of liquefied bitumen from under the longitudinal edge of the web. The side overlaps of the canvases must be at least 100 mm, the end overlaps - 150 mm. Waterproofing is carried out in two layers, the top row sheets are rolled out in the same direction as the bottom ones, but with the seams shifted.
- The area of the waterproofing carpet must be larger than the area of the main foundation slab that will be poured on top of it. After the formwork is removed, you will also have to waterproof the vertical surfaces, for which you need to make the correct connections.
- To do this, sides are made of modified sand-cement mortar between the horizontal and vertical surfaces at an angle of 45 degrees. The transition is smooth; all that remains is to glue the membrane onto the vertical surface of the base, covering the stepped edge of the slab.
The principle of waterproofing a slab foundation
If the base of the slab is not monolithic, but is made of brick or concrete blocks, the free edge of the waterproofing carpet can be rolled up and glued first to the vertical surface of the end of the slab, and then placed on the upper horizontal surface so that the membrane is under the masonry. In the place where the basement walls adjoin the slab, you also need to make a side of elastic mortar, after which you can begin to vertically waterproof the base.
Advantages and disadvantages of waterproofing films
Being a worthy alternative to bitumen coating waterproofing, the presented types of film coating have found wide application in the installation of horizontal and vertical protection of foundation walls from moisture penetration. However, before deciding and choosing the most suitable material, you should familiarize yourself with the results of preliminary geological studies of the soil, and also weigh all the disadvantages of waterproofing films, namely:
- high risk of damage to film waterproofing due to its relatively low mechanical strength;
- thorough preparation of the surface before laying an insulating coating on it;
- the presence of joining seams, which are problem areas in protection;
- possible damage to integrity as a result of chemical effects of groundwater;
- susceptibility to film damage by rodents.
However, due to its excellent waterproofing properties, as well as its relatively low cost, the use of film coatings to protect foundations is popular in the construction of not only private buildings, but also industrial facilities.
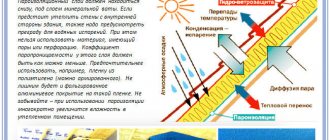
Diffuser membranes
It is also a multi-layer material. Among the features is that the product allows hydroid steam to pass through, but remains completely waterproof. These types of waterproofing films for foundations are widely used for roofing work. The material has a distinctive feature - steam is removed from a special heat-insulating layer to the outside. Due to this feature, the product protects the foundation from moisture, various types of destruction and putrefactive processes. These products are used in very damp areas. These are saunas, baths, restaurants, cafes.
There is also a super-diffuser film on sale, which has high technical characteristics and protective capabilities. The price between a regular membrane and its “super” modification differs little. Therefore, for greater reliability and guarantee of maximum protection, experts recommend purchasing super-diffuser types.
Main advantages of the material
When arranging the foundation, the film provides a large number of positive aspects. This material has the following advantages:
- The material is resistant to moisture and mold.
- The corrugated structure prevents the film from moving away during installation.
- Does not decompose and does not rot.
- Easy to install.
- Cheap cost.
In addition to the advantages, there are also disadvantages, which are listed in the following list:
- The coating reacts negatively to ultraviolet rays. With constant exposure of the film to such light, the service life of the material is significantly reduced. In an open space, the material used will last no more than one year.
- There is a high probability of compromising the integrity of the material during installation work. Thus, all the positive properties of waterproofing will immediately disappear.
- The film is a very attractive product for rodents. Therefore, you should not store it in places accessible to mice.
Even despite the shortcomings, with careful and correct installation of such foundation waterproofing, you can reliably protect the foundation for future construction from excess moisture.
Types of construction waterproofing films
Products used to provide waterproofing protection to foundation structures are produced by both domestic and foreign manufacturers. They are divided into the following types:
- regular roll. The thickness parameter varies between 0.6 – 2 mm. This type of film has found wide application in the national economy as a covering material for greenhouses and greenhouses. The use of such a film for waterproofing the foundation is a cost-effective solution, but for its successful use, appropriate conditions must be created, because the material is subject to mechanical stress. Today, manufacturers add special additives to such material to increase its strength;
- reinforced This film is produced in multilayer rolls. The layer located in the center is distinguished by a non-woven base or the presence of a polypropylene mesh, and the outer layers are sealed. There are perforated and non-perforated types, differing in quality characteristics and cost. The perforated layer has small holes that allow water to pass through and is used for waterproofing roofing slopes. The non-perforated version does not allow moisture to pass through. The reinforcing layer creates protection against deformation effects, increasing the service life of the material. Reinforced film, designed to protect roofs and foundations, is produced in rolls and has various color shades. When purchasing such material, you should pay attention not to its thickness, but to the density indicator, focusing on data of 100 - 250 g per square meter;
- diffusion membrane. Multilayer material that allows hydroid steam to pass through and retains water. The film is used when arranging roofing ceilings, since it, by removing steam, reliably protects structures from rotting processes. Superdiffusive film material has found application in rooms with high levels of humidity, while its cost is practically no different from the original version. Therefore, when waterproofing the foundation with film, it is recommended to use the second option, as the most reliable.
Types of films
There are several main types of films and membranes intended for waterproofing:
1. Simple rolled polyethylene film is produced in a thickness of 0.6-2 millimeters. This is the cheapest material in the category, the most vulnerable to mechanical stress. Today, in the manufacture of polyethylene, special additives are used to increase strength.
2. Reinforced rolled polyethylene. Multilayer film, the core of which is polypropylene mesh or non-woven material.
The use of a reinforcing layer increases the strength of the material and increases the service life.
Available perforated and non-perforated. The perforated layer has micropores that allow water to pass through: this film is used as a vapor barrier for roofs and facades. Waterproofing the foundation with reinforced polyethylene film is made of a non-perforated type; it does not allow moisture to pass through. The main criterion for choosing this film is density. The preferred option for foundations is at least 100 grams per meter (up to 250).
3. Diffusion membranes. Also multilayer, they have vapor-conducting properties, but are waterproof.
The most suitable option for rooms and structures with high humidity is a superdiffusion membrane.
4. Polyvinyl chloride. Waterproofing the foundation with PVC film is one of the most common.
The thickness of about a millimeter provides the material with a sufficient margin of safety.