Foundation waterproofing is a measure to protect house structures from the influence of water and moisture. The destructive effect of water on foundations built without effective waterproofing can often be observed even today - this is the presence of water in the basement of the house, fungus and mold on the walls not only of the first floor, but also above, general dampness in the house and an unhealthy microclimate. Almost all structures of the house (except perhaps the internal walls) are protected from moisture: enclosing walls and junctions of windows and doors; ceilings and floors; but foundation structures, floors and walls of basements, and the basement require special attention.
All types of foundations need to be protected from water, and from all types of water: underground or ground water and surface water (precipitation, snowmelt, flood water near rivers and lakes). Foundations and other house structures are protected from surface water by blind areas, as well as by comprehensive measures for the organized drainage of water from the roof and a drainage and storm sewer system. Blind areas and roof drains are made in any residential building. Groundwater at a constant high level is not present in every area, but this does not eliminate the need to waterproof the underground parts of the house. The depth of groundwater in relation to the foundation cannot be stable, the water rises seasonally, and flood waters are possible near reservoirs.
The selection of foundation waterproofing depends on its type and on the quality of pressure and aggressiveness of groundwater, but the latter can only be learned from a hydrogeological study. Groundwater can be of various types:
- Pressure groundwater is under pressure, it is compressed by waterproof rock or massif, and its pressure can be sufficient to rise and flow to the surface if the integrity of the waterproof layer is damaged.
- Low-pressure waters are under less pressure; their conditions can be close to both pressure and non-pressure at different times of the year.
- Gravity groundwater always comes into contact with the air through open pores and capillaries to the surface of the earth.
- Suspended groundwater is classified as non-pressure water; it is located above the main level of groundwater and can be in the form of “lakes” isolated from each other, local accumulations of water.
The occurrence of aquifers within one construction site can be very complex and have both pressure and non-pressure waters. If hydrological surveys have not been carried out, then it is impossible to predict the nature of groundwater, and the most dangerous groundwater for buildings is pressure water with chemically aggressive properties for concrete. Therefore, at any level of groundwater, the base for the foundation is made according to the same scheme: a cushion made of compacted inert material with strong drainage properties, most often it is a sand-crushed stone preparation with a geotextile protective layer. Such a foundation serves as a damper, contributing to the uniform distribution of loads from the house to the foundation and from the soil to the foundation; and also serves as a barrier against capillary groundwater.
Effective methods of waterproofing different types of foundations
Korovin Sergey Dmitrievich
Master of Architecture, graduated from Samara State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 11 years of experience in design and construction.
Water destroys the building structures, rendering them unusable and reducing their service life. This is especially true for the underground part of the house, which is exposed to several types of moisture at once. Outside, rain and melt water have a destructive effect on it, and in the soil, groundwater causes trouble, the level of which can vary depending on the season. Waterproofing methods for the foundation of a building depend on its type and method of manufacture (installation of tape, slab, pillars or piles).
Types of moisture insulation
All types of foundation moisture insulation can be combined into three: vertical, horizontal and blind area.
Vertical waterproofing
The vertical walls of the foundation are insulated entirely: both above and below the ground. This process is carried out using different technologies and materials.
Horizontal waterproofing
Horizontal moisture insulation is designed to protect the foundation of the house from groundwater. In some cases, it is advisable to only protect the lower part of the foundation base where it abuts the ground.
Sometimes it is possible to protect only the upper level, where the plinth connects to the load-bearing walls.
If the groundwater in the area in the spring is capable of rising above the base, then it is necessary to isolate the level above it with preliminary arrangement of drainage.
Blind area
The blind area has its own function in matters of waterproofing - it is the right means for draining rain and melt water from the foundation walls. In addition, do not forget about the decorative nature of the blind area.
How does moisture affect
There are several ways in which water can lead to the destruction of a concrete foundation:
- Washing out of particles from the structure, formation of irregularities and potholes due to aggressive components in rain or groundwater.
- Destruction when water penetrates into the body of the foundation and freezes there. The fact is that water is the only substance on the planet that, when entering a frozen state, expands and does not decrease in volume. Getting into the capillaries, it puts strong pressure on the foundation from the inside, which leads to the appearance of cracks and crevices.
That is why waterproofing the foundation is important and should be carried out immediately after the construction of the structure.
Waterproofing the base with modern materials
When waterproofing in a vertical plane, modern materials based on quartz filler and Portland cement exhibit high qualities. It perfectly increases the water resistance of the surface, prevents the penetration of water during the hardening process, and accelerates the setting of the material.
To waterproof the base, I recommend applying it to a degreased, pre-cleaned surface, which can be damp. A 3 mm thick waterproofing material is applied using a roller or brush. When this layer dries, which will take about 2 hours, I advise you to apply a second layer of waterproofing to increase its strength.
If the groundwater level in your area is close to the surface, I would advise you to waterproof the basement by covering the walls with rolled modern materials - geomembrane or glass insulation. They are very effective, especially if your project plans to build a basement.
In addition to roll materials for protection against moisture, penetrating waterproofing can be successfully used. Its meaning is that a special composition, penetrating wet microcracks and pores, clogs them and crystallizes. Moreover, if new cracks form, the penetrating material fills them too. This process is continuous and continues until the active substances are present in the protective composition.
In addition to the listed water-repellent materials, a water plug is effectively used when waterproofing the base. This is a dry mixture based on active chemical additives, fillers and hydraulic cements, which can successfully eliminate leaks in a concrete wall. What is the operating principle here? An aqueous solution of a water plug is applied to a cleaned and degreased surface, slightly moistened with water. To do this, 1 kg of dry mixture must be mixed with 220 ml of water heated to 70 degrees. Within 2 minutes, the solution is thoroughly mixed and immediately applied to the surface. At the same time, it expands and does not allow water to enter.
Types of moisture protection by location
In general, the foundation waterproofing device is divided into three groups:
- horizontal;
- vertical;
- blind area device.
Depending on the type of base, several methods can be used simultaneously.
Horizontal is designed to prevent moisture from penetrating between different levels. It can be made of various materials. Provided for all types of foundations (strip, slab, pillars, piles).
Vertical is needed so that groundwater cannot influence the foundation. Not all types of grounds require such protection. Required only for strip and column supports of the house. Horizontal protection is provided for all types (strip, slab or free-standing supports).
The blind area protects the base from the penetration of rainwater and melted snow in the spring. Here the width of the structure is essential. If it is insufficient, the moisture will be removed a short distance and will be able to reach the foundation. This type of protection reduces the load on all others, allowing them to increase their service life.
The need to waterproof the foundation
If the house is being built in a swampy area or where the groundwater level is always high, waterproofing is definitely needed. But if the site chosen for construction has dry soil, is it necessary to use moisture protection technology? In this situation, everything will depend on the type of foundation.
When waterproofing is not needed
When installing a pile-screw foundation, protection from moisture will not be required, but only if industrial piles are used. If the material is made independently, waterproofing will still be required.
A foundation built from a shallow-depth tape does not require additional protection from moisture, but there is a small exception here: if there is no blind area, then waterproofing will be needed.
When you can't do without moisture protection
Waterproofing must be installed when installing slab, strip and column foundations, as well as if a basement floor is being built. If the soil under the building has even a little moisture, and at the same time comes into contact with the surfaces of the walls in the basement, where there is no protection from moisture, fungus and mold will soon appear in the room.
Vertical and horizontal insulation
Foundation waterproofing can be done using different means of protection. Separately, it is worth considering vertical and horizontal types and the design of the blind area, since the materials in these cases will vary quite significantly.
Protection of the recessed part of the building with vertical and horizontal insulation suggests that materials can be used in the following ways:
- pasting;
- coating;
- penetrating;
- plastering;
- injection;
- mounted;
- structural (additives to concrete).
It is worth separately understanding what material to use in each case.
Pasting
This type of structure protection is carried out using roll versions with bitumen binder. Fused or bonded material may be used. Fused types imply the presence of an adhesive layer, which is heated at high temperatures and adheres to the surface. To attach insulation to the base without an adhesive layer, you will need to use bitumen mastic as a connecting substance.
Pasting materials include:
The last group is the most reliable option, but the price of such material can be quite high.
But here it is worth taking into account their long service life, which will reduce the frequency of repairs. The advantages of the pasting method include the fact that it can be used for various surfaces:
- concrete;
- tree;
- metal;
- asphalt concrete;
- old waterproofing coating (during repairs).
Coating insulation
In this case, waterproofing the foundation is most often performed using bitumen mastics. To protect the buried part of the building and the walls of the house, one-component and two-component compounds are used. In addition to bitumen, you can now find more reliable and modern options on the building materials market:
- polymer resins;
- bitumen-polymer resins;
- bitumen-rubber mastics.
Unlike regular bitumen, which cracks at low temperatures, these mixtures with additional additives are resistant to cold. The disadvantage of more modern options is their price, which cannot compete with conventional bitumen-based mastic. The latter is best used to protect house structures with deep groundwater.
Penetrating insulation
Waterproofing the foundation in this way prevents moisture from entering the concrete capillaries. This increases the strength of the surface layer of concrete. Waterproofing a strip foundation in this way is often carried out using an additional coating or adhesive layer.
On average, the penetration depth is 15-25 cm, but some materials can go as deep as 90 cm. It is important to note that such methods are only suitable for concrete. They are useless when used on brick and stone.
The most common compositions for this steel processing method are:
- "Penetron";
- "Peneplug";
- "Hydrohit";
- "Penecritus."
- "Osmosed."
Waterproofing technology depending on the type of foundation
Each type of building support requires certain protection options. Before waterproofing the foundation, you need to find out what is required for the full range of measures.
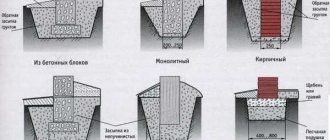
Strip foundation protection
Waterproofing of strip foundations differs for monolithic and prefabricated versions. First, let's look at the prefabricated version. To prevent damage to the underground walls of the house and flooding of the basement, the following measures will be required:
- installation of a reinforced seam between factory-made foundation slabs and concrete blocks of the basement walls;
- laying rolled material in the first seam between the blocks, which is located below the basement floor level;
- the rolled material is mounted along the edge of the foundation at the junction of the walls and the supporting structure;
- vertical insulation of the underground part of the tape from the outside;
- blind area device.
How to carry out waterproofing depending on the type of foundation
When choosing a waterproofing option and a suitable material for it, you need to take into account the type of foundation, its design features, as well as the presence or absence of a basement, and its functional purpose.
There is no point in talking about the process of waterproofing all types of foundations, so we will focus on only one of them. This will be a detailed description of the process of creating a moisture-proof layer for a strip foundation.
Waterproofing strip foundation
Almost any method of waterproofing is suitable for this type of foundation, so when choosing the appropriate option, you need to take into account the climatic conditions of the area where the building is being built.
If the climate is fairly mild, without large temperature changes and high humidity, there is no need for complex and expensive waterproofing options.
The most suitable method in such a situation would be coating with bitumen mastic. Moreover, the technology for applying the special mixture is quite simple. It consists of 4 stages:
- Preparatory;
- Surface priming;
- First layer;
- Finishing layer.
Surface preparation
- Fill large pores on the surface of the foundation with cement-sand mortar;
- Remove the “ridges” that appear in the cracks of the formwork;
- Dry the surface of the foundation;
- Remove oil, grease and other types of stains;
- Clean the surface of the foundation from dust.
Application of primer
The bitumen mixture will have maximum adhesion to the surface of the foundation only when a primer is applied to it. For this purpose, special primers are used.
Unlike conventional primers, such compositions have a dark tint, so there is no need to add color to control the untreated part of the surface.
After the soil is applied to the surface of the foundation, you must wait until it dries completely. Please note that the drying time of the primer is not always the same for different manufacturers, as it all depends on the composition of the mixture. Therefore, before starting priming, carefully read the instructions.
First layer of mastic
You can apply mastic in two ways: by spray or by hand (roller, brush or spatula). Applying the waterproofing layer manually is much cheaper, since the sprayer is quite expensive.
If you decide to rent a device for the duration of waterproofing work, keep in mind that you will have to wash it after use, which is also not very convenient.
Apply the composition from bottom to top in vertical stripes, overlapping the previous layer by 3 - 5 cm. Try to apply the layer evenly, so that its thickness is the same over the entire surface. To do this, it is necessary to level out smudges and sagging. The thickness of the layer depends on the depth of the foundation and can be:
- 2 mm. at a depth of up to 3 meters;
- 2-4 mm. at a depth of 3 to 5 meters.
Finishing layer of mastic
To improve the adhesion of the mastic to the surface of the base, and securely fasten them together, before applying the second layer, the entire surface of the foundation (including the corners) is covered with reinforcing mesh. A polymer or fiberglass mesh is suitable for this.
Types of waterproofing
Protection of the foundation from moisture can be horizontal or vertical. For both types of waterproofing, different materials can be used, which will be discussed further.
Horizontal
The peculiarity of this insulation is that it is performed only during the construction of the foundation of the house. First of all, it protects the foundation from the effects of groundwater.
The method and material for its manufacture depend on the type of base and the characteristics of the soil. Under a wooden house, horizontal protection from moisture is mandatory, regardless of what kind of foundation will be built.
The horizontal insulation option is made from a variety of membrane materials on a bitumen, polymer or synthetic basis. The most commonly used material for this type of protection is roofing felt. If a basement is planned in the house, most often horizontal waterproofing will be carried out simultaneously along the upper and lower sides of the floor slab.
Vertical
Vertical moisture protection can be done in an already built house. This type of protection is needed to prevent groundwater from affecting the foundation material of the house.
As mentioned above, not all types of foundation require such insulation. However, when constructing a strip and column base of a building, vertical waterproofing is always needed. To install vertical insulation, you can use different methods and materials, which will be discussed in more detail below.
Pasted insulation
For this type of protection, roll materials are used, which are attached by fusing or gluing. Fused materials have an adhesive layer that heats up and sticks to the surface. To secure the material without an adhesive base, it is necessary to use bitumen mastic, which will act as a connecting component.
The following materials are used to perform adhesive insulation:
- Glassine. The average price for 1 roll is 150 rubles. The material is made on the basis of thick cardboard, which is impregnated with a bitumen composition. Glassine does not make the most reliable and durable insulation, but it is a great way to save money;
- Ruberoid. The average price for 1 roll is 350 rubles. This material is a leader among rolled types of insulation, as it has a low price and a long service life;
- Bitumen-polymer material. This is the most reliable and durable option, but it costs more than others. The average price for one roll of bitumen-polymer material is 1,000 rubles. As an example of such insulation, the following common options can be cited: TechnoNIKOL, Linokrom, Gidroizol, Bikrost and Stekloizol.
Coating insulation
To insulate the foundation in this way, bitumen-based mastic is most often used (average price - 350 rubles per 20 liters). In addition to simple bitumen compositions, you can buy more modern options in construction stores:
- Polymer resins;
- Bitumen-polymer resins;
- Bitumen-rubber mastics.
Conventional bitumen mastic differs from modern compositions in that it is unstable to low temperatures (it cracks in the cold).
More modern mixtures have additional additives that allow them to be resistant to cold. They have only one drawback - the high price (on average from 3,000 rubles for 20 liters).
Penetrating insulation
Penetrating insulation prevents moisture from entering the concrete capillaries, thereby increasing the strength of the top layer of this material.
On average, the depth of penetration of special mixtures into concrete is 15-25 cm.
This insulation option is only suitable for concrete foundations. If you use penetrating compounds on brick or stone, they will not work.
The most popular compositions for penetrating insulation are these:
- Penetron (on average 1,500 rubles per 5 kilogram);
- Peneplug (on average 1,200 rubles per 5 kilogram);
- Hydrohit (on average 1,000 rubles per 5 kilogram);
- Penecrit (on average 1,300 rubles per 5 kilograms).
It is recommended to use this protection technology for new homes, since penetrating mixtures must be applied to thoroughly cleaned, degreased and smooth surfaces.
Mounted insulation
Mounted waterproofing is used mainly for strip foundations, if it is necessary to protect the basement from high groundwater pressure.
The best option for mounted insulation is considered to be a steel caisson. This option involves lining the walls and floor of the basement from the inside using steel sheets, the thickness of which is 4-6 mm. This is a rather expensive option, so it is used extremely rarely.
Coating waterproofing of the foundation
This technology is one of the most inexpensive. The material used in the work is based on bitumen. It is applied to the surface of the foundation either with a construction brush, or with a roller or spatula. The material itself can be purchased ready-made; in the construction environment it is called bitumen mastic. You can also make such mastic yourself by melting bitumen and adding diesel fuel to it in a ratio of approximately 1/5 - 1/3. Purchased mastic is used according to the instructions for use from the manufacturer. To prepare it you will need a solvent.
Before applying mastic to the surface, the latter is first cleaned of dirt and dust. The protection is laid out in several layers, each of which is laid out after the previous layer has completely hardened. The thickness of the finished waterproofing should be approximately 5 mm. Despite its cheapness, coating waterproofing of the foundation does not allow achieving reliable and durable protection, especially when making mastic yourself. In addition, this method requires a lot of labor.
Special building mixtures can also be used as a material for coating waterproofing, including components that enhance the water resistance of the applied layer. Sometimes this technology is called plaster waterproofing. Its advantages include ease of construction and low time consumption, its disadvantages include low durability and a low degree of water resistance. The recommended use of such insulation is to level surfaces before applying a higher-quality layer to them. Plaster is applied using the usual methods - with a spatula or trowel; reinforcing mesh can be used to increase durability.
Where to start and how to waterproof the foundation?
The foundation is an important component of any structure, the quality and stability of which determines the durability of the building as a whole. Why use insulation? The foundation is exposed to many negative factors - one of them is moisture, which destroys the structure. Do-it-yourself foundation waterproofing, done correctly using technology, will help you cope with this trouble.
There are two types of moisture that affect the base:
- melt water and precipitation entering the ground from the outside;
- bottom waters, their level is variable, depending on the season.
Which waterproofing to choose for the foundation? The base is selected based on the type of base and material; slab and column supports are protected from moisture in different ways.
Destructive effect of water
It acts on the base in several ways:
- if there are aggressive components in the bottom or rain moisture, then potholes and defects caused by the leaching of solid particles may appear in the base body;
- is destroyed by freezing of moisture that has penetrated into the base material. The only element in nature that expands when exposed to sub-zero temperatures is water. Penetrating into micropores, it puts a strong load on the base from the inside, resulting in cracks, crevices, and breaks;
- washing away the soil with water leads to distortion and subsidence of the structure, which can lead to the destruction of walls.
Now it becomes clear why waterproofing the base is needed. For this reason, the base must be insulated as soon as the structure is ready.
Types of insulation used
Three groups of arrangement for protecting the constructed foundation from groundwater can be distinguished:
- horizontal waterproofing of the foundation inside the house;
- creating a blind area.
Foundation waterproofing materials for construction are different. There are such bases that several types of protection are used in combination to protect them:
- Cut-off foundation waterproofing is used for foundations on pillars and strip foundations.
- Horizontal foundation waterproofing – suitable for all types of foundations. With its help, the influence of moisture in the interlevel space is limited. This insulation is made from different materials, depending on the construction budget.
- The blind area is constructed to protect the base from rain or melt water. It is advisable to make the structure wide enough, otherwise moisture will penetrate to the base and put additional stress on other types of insulation.
Horizontal and vertical waterproofing
These two types of foundation protection should be examined separately; the materials for waterproofing the foundation are very different from those used in the construction of the blind area.
Insulation of the buried part of the support is carried out by several types of protection:
- by coating;
- pasting;
- plastering;
- penetrating compounds;
- performed by installation;
- structural;
- injection.
You need to understand which foundation waterproofing materials to use for a certain type of foundation and how horizontal foundation waterproofing is constructed.
Coating method in isolation
Coating waterproofing of the foundation is carried out with bitumen-based mastics. Two-component and one-component compositions are used to coat part of the base located in the ground and the walls of the building. In addition, many new, modern and high-quality insulating materials have recently appeared:
- polymer-based and bitumen-polymer resins;
- bitumen and rubber mastics.
Thanks to additives in bitumen, the material tolerates low temperatures well and does not crack like regular bitumen when frozen. The disadvantage of modern materials is their high cost, so private developers use the foundations of the house as insulation.
Pasting
How to waterproof a foundation using adhesive compounds? A popular and frequently used type of protection is the use of various materials in rolls mounted on a binder layer of bitumen, for example hydroglass insulation. The adhesive protection can be installed in two ways – gluing or fusing.
Welded waterproofing involves the use of a gas burner, with which the top layer will be heated to a viscous state, after which the material is glued to the base plane. If there is no adhesive base on the roll insulation, then mastic is used as an external adhesive. It is necessary to choose the right material.
Before installing insulation, the surface is primed.
Pasting materials are:
- Roofing felt is considered an obsolete insulation material, but is still widely used. Due to its low cost and the ability to quickly recover if damaged. This is cardboard, the surface of which is treated with bitumen;
- glassine is a good waterproofing material based on thick construction cardboard, treated on both sides with bitumen. This cannot be said to be reliable insulation, but the cost of roll coating allows you to save;
- roofing felt is a leader among insulating materials, good insulating characteristics and an affordable price make the material in demand among developers. But it is worth noting that the service life is short;
- materials based on polymers, with bitumen impregnation, the base of which is fiberglass or polyester. There are several common insulation options: “Gidrostekloizol”, “Linocom”, “Tekhnokol”, “Bikrost” and so on.
The most reliable options for foundation waterproofing are the materials listed in the last list, but often their use entails additional costs. Hydroglass insulation is especially in demand, its technical characteristics and the latest production technologies allow you to insulate the foundation inside an old house for a period of 30 years.
But it is worth noting that these materials last quite a long time, which allows you to save on the frequency of repairs. Another positive point is the ability to use hydroglass insulation for any building materials:
- metal;
- concrete;
- tree;
- asphalt concrete;
- hydrostekloizol is used for repeated and restoration of waterproofing without dismantling the old coating.
Rolled waterproofing for foundations
With this method of producing a protective layer for the foundation, special materials are applied to the base. They are usually rolled into rolls, hence the name of the technology. Bitumen or polymer modifiers are used as the outer layer, and the base can be either paper (for example, in roofing felt), or fiberglass or polyester. Rolled waterproofing for foundations is not a cheap method of protection, but in terms of coating quality and durability it has very high performance.
The roll can be applied to the surface by gluing or melting. Bitumen mastics are used as an adhesive composition. When fusing, a gas or gasoline burner is used to heat the roll laid on the surface. The disadvantages of roll waterproofing include the complexity of the work, which requires certain skills. Its installation can be simplified by the use of self-adhesive roll materials, which have recently appeared on the construction market.
Vertical waterproofing of the foundation with your own hands: types of insulation
Since the strength and durability of the entire structure depends on the design of the foundation, its design and execution must be approached with special care. But even a strong and properly designed foundation can collapse over time under the influence of surface and ground moisture. To protect structures from the harmful effects of water, you need to perform waterproofing. Since waterproofing the foundation with your own hands must be done according to all the rules, you should learn about the types of waterproofing work, the intricacies of the process and choose the right materials. To ensure that the process of independently waterproofing the base goes correctly, we offer useful videos throughout the article.
Waterproofing a columnar foundation with your own hands
Preface . Do-it-yourself waterproofing of a columnar foundation is carried out during the construction stage. The durability of the entire building depends on the quality of the insulation of the concrete structure. Experienced builders know how to waterproof a columnar foundation using rolled materials. And we will share this important information with you on this page of our online magazine.
Every building needs a proper foundation. The choice of the type of concrete structure required depends on the category of soil, the depth of groundwater and the depth of soil freezing. It is recommended to make a columnar foundation on difficult heaving soils, as well as when constructing frame or wooden houses, since this type of construction is much cheaper than a strip foundation.
Features of waterproofing
To choose the right measures to protect the base from moisture, you should consider a number of factors:
- depth of groundwater;
- the presence of soil heaving forces in winter;
- soil composition;
- design features of the foundation and building.
The choice of the type of foundation waterproofing is primarily related to the level at which groundwater flows:
- If the underground aquifer is located more than 1 m below the foundation cushion, then to effectively isolate and protect the base it is enough to perform vertical and horizontal waterproofing by gluing two layers of roofing material onto bitumen mastic.
- When the aquifer passes at a depth of less than 1 m from the foundation base (provided that the water does not reach the basement level), the set of waterproofing measures will be slightly wider. In this case, in addition to vertical and horizontal waterproofing with roofing felt, it is worth using penetrating compounds that will protect structures from capillary moisture.
- If the groundwater level is higher than the bottom of the foundation or construction is carried out in a flooded area, then in addition to the measures listed in the second paragraph, a drainage system will have to be implemented that will effectively drain water from building structures.
Horizontal waterproofing
This method of protecting the foundation of a private house is considered the simplest to implement, and therefore the most widely used.
The main objectives of horizontal waterproofing are:
- Resistance to groundwater if a protective layer is laid under the base of the foundation.
- Protection from capillary damp action when waterproofing is laid in the transitions of the foundation walls into the load-bearing walls of the structure itself (private residential building).
This method of waterproofing is used in the construction of almost any structure, regardless of what features the soil on the site has, and what the total amount of rainwater is.
Traditionally, horizontal waterproofing is a layer created from pieces of rolled materials laid on top of each other several times.
Stages of work
To perform horizontal waterproofing efficiently, you should adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
First you need to prepare the base. To do this, all treated surfaces are cleaned and leveled (if necessary). Then dry thoroughly.- Then follows the application of primer primers, which provide additional protection for the foundation and the maximum possible adhesion of the main waterproofing material to the base.
- At the next stage, the actual application of the waterproofing composition occurs. Most often, roll materials are used, which are laid overlapping. If necessary, waterproofing sheets or pieces are heated.
- Next, the surfaces are treated with additional coating materials. And in order for them to provide the proper level of protection, they must be allowed to dry thoroughly. This will take 7 days, no less. Therefore, if construction deadlines are running out, it is better not to use this method of waterproofing.
Do-it-yourself horizontal insulation
When making a monolithic strip foundation, which is most often used in individual construction, horizontal waterproofing is done in two places:
- at the same level with the waterproofing layer of the basement or slightly below it (along the top of the foundation pad);
- at the junction of the foundation and the wall.
Important: since horizontal waterproofing can only be done at the construction stage, it is worth taking care of this in a timely manner.
The first layer of waterproofing is performed after installing the foundation cushion in the form of a monolithic reinforced concrete strip. Quite often this layer of waterproofing is at the same level as the basement floor waterproofing. Work on the device is carried out as follows:
- After making a monolithic foundation pad, the concrete should stand for a couple of weeks.
- Then the upper surface of the foundation pad is coated with bitumen mastic.
- The 1st layer of material is laid on it.
- After this, the surface is again covered with bitumen mastic and a second layer of roofing felt.
Sometimes, to further increase the moisture resistance of concrete, it is iron-plated. The procedure is performed like this:
- The freshly poured concrete is allowed to sit for a couple of hours.
- Then sifted cement is poured on top of it. The height of the cement backfill is 10-20 mm. The surface is leveled.
- After some time, the cement becomes wet as it absorbs moisture from the concrete.
- After this, the concrete surface is allowed to dry in the same way as ordinary concrete mortar (covered with film and periodically moistened with water).
Upper horizontal waterproofing is done after installing the foundation, before laying the walls. This process is shown in detail in the video below. The waterproofing layer will not allow capillary moisture to penetrate from the foundation structures into the walls of the house. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- The horizontal surface of foundation structures is lubricated with bitumen.
- After this, the first layer of material is spread.
- Then we apply the coating a second time, and roll out the roofing material again.
- We do not cut off the ends of the roofing felt from the inside of the building, but put them on the walls and connect them to the waterproofing of the first floor floor, if one is planned.
You can learn how to do horizontal waterproofing from the following video:
Drainage system
If the geological conditions of the area are such that vertical and horizontal insulation alone is not enough, then a drainage system is installed around the perimeter of the building, which will collect surface and ground water and drain it from the building structures into a separate well.
Instructions for installing a drainage system around the house can be viewed in the video below. The work is carried out like this:
- First of all, you need to dig a trench along the perimeter of the future house at a distance of at least 70 cm. The depth of the trench depends on the height of groundwater passage. The width of the ditch is 0.3-0.4 m. The bottom of the trench should have a slope towards the drainage well.
- We cover the bottom of the ditch with geotextiles. We wrap the edges of the material onto the walls of the trench to a height of 0.8-0.9 m.
- Then pour a layer of gravel 5 cm high along the entire length of the ditch.
- You can begin laying the perforated drainage pipeline. The slope of the pipes is half a centimeter per 1 linear meter.
- Now pour out a layer of gravel 0.2-0.3 m high. The material should be washed first so that the drainage holes in the pipes do not become clogged.
- Now we lay the protruding edges of the geotextile on top of this layer.
- We connect the pipes to the well and fill the trench with soil.
Important: the arrangement of the drainage system does not have to be carried out during the construction of the building. It can be done several years after the start of operation of the house, if necessary.
You will find useful recommendations for installing a drainage system in this video:
Types of vertical insulation
Do-it-yourself vertical waterproofing of the foundation can be done using different materials and their combinations. You can use one of the methods suggested below or use two options at once.
Bitumen insulation
The method of coating waterproofing the base is considered the simplest and most accessible. To do this, we use bitumen resin, which we prepare from block bitumen in the following sequence:
- Pour bitumen (70%) and waste (30%) into a container and place it on a gas stove or fire to heat it up.
- When the solution acquires the consistency of liquid sour cream, you can begin coating the vertical surface of the foundation. At the same time, during the work, the container must be heated at all times so that the composition does not cool down.
Apply the mixture to a pre-leveled surface using a brush or roller. We begin work from the foundation base and finish 150-200 mm above the ground surface. In this case, it is necessary to apply bitumen in several layers so that the final thickness is at least 30 mm.
This bitumen composition can last about 5 liters. It will then crack and crumble, allowing moisture from the soil to leak into the concrete structures. This is due to the fact that bitumen itself hardens and cracks at sub-zero temperatures.
If you take bitumen-polymer mastics, then the service life of such insulation will be much longer. At the same time, there are mastics on sale that are applied cold or hot. The consistency of these mixtures also varies. Thick, rigid mixtures are applied with a spatula or trowel, while liquid compositions can be sprayed or applied with a roller.
Pasted insulation
Typically, roll materials are used in conjunction with the coating method, but can also be used separately. Most often, roofing felt is used for these purposes. The work is carried out as follows:
- Before gluing the roofing felt to the wall, it is treated with mastic or primer, as described above.
- Strips of material are heated by a burner and attached to the vertical plane of the foundation structure. The overlap of adjacent sheets should be 150-200 mm.
Attention: before fusing the roofing material, the edges of the horizontal waterproofing are folded down onto the vertical surface and pressed against it. Strips of roofing material are fused on top of them.
In addition to fusing, roofing felt can be attached to special mastics. After applying the mastic and gluing the first sheet, repeat the procedure.
Video guide for performing vertical waterproofing of foundations: