The main task of the foundation is to take the load from the house and distribute it evenly onto the ground. Therefore, when laying the foundation, it is necessary to take into account the type of soil and the location of the groundwater level (GWL). The last indicator may be too high, that is, the water is close to the soil surface.
Pouring a foundation under such conditions is difficult and costly. Therefore, the work contractor is faced with the question of what kind of foundation is needed for a private house if groundwater is close? This question affects not only the type of foundation structure, but also an additional choice that concerns the laying depth: below the groundwater level or above.
Groundwater influence
In the construction environment there is such a term - cement bacillus. This is when a concrete structure is destroyed under the influence of negative factors, which include groundwater. But we must understand that it is not the water itself that negatively affects concrete, but the salts and various chemicals dissolved in it. They penetrate into the concrete body, where they interact with cement or fillers, breaking their bonds with each other. Hence the appearance of all kinds of plaque, dark spots and unpleasant odors.
High groundwater level is a problem even at the stage of digging a pit. Water collects inside, which softens the bottom, which leads to a decrease in the bearing capacity of the soil. If this happens, you will first have to think through and install a drainage system, with the help of which it will be possible to pump out the water.
There are technologies that do not require drying the site. To lay the foundation, a pile method is used with driving pillars into the depths of the earth to dense layers. Not a bad option, but expensive and time-consuming. Without special equipment, such a foundation cannot be built. For private housing construction, this technology is rarely used. Therefore, the construction of a foundation with a high groundwater level is approached from the perspective of drainage.
And one more negative point. The dangerous time for such areas is winter with sub-zero temperatures. Freezing of the soil in winter turns into a dangerous situation for the foundation. Frost heaving and high groundwater level can destroy the foundation structure of a house in one season.
Groundwater: impact on the foundation of a building
Before determining the type of house foundation suitable for construction in water-filled soils, it is worth understanding what negative consequences a high groundwater level has for building structures buried in the ground and what to do to reduce the risk of building collapse.
The main components of any foundation are concrete and reinforcement, so it is worth considering the negative impact of groundwater in relation to these materials.
As for the metal foundation structures of a house, it is safe to say that water can cause significant damage to the metal, which is destroyed by corrosive processes that occur when the metal parts of the foundation come into contact with water.
Aggressive soil waters, which contain various chemicals that accelerate corrosion processes, increase the degree of destruction.
High level of water occurrence
Aggressive waters also cause considerable damage to the concrete structures of the foundation of a house - the concrete is destroyed very quickly, deposits, delamination of the concrete body, and cracks appear on the structures.
Chemicals dissolved in water can render even the strongest foundation of any home unusable in a short period of time. So what to do if groundwater is close to the surface?
The bearing capacity of the soil is significantly reduced when groundwater occurs close to the surface of the site. A wet foundation during the construction of a house complicates the work on building the foundation already at the stage of digging a pit or trenches. Water-filled soil under the supporting foundation is fraught with the occurrence of deformations and uneven subsidence of the erected structure. What way out is there? Before constructing a foundation belt in wet soil, it is best to plan the construction of reliable drainage that can cope with the removal of soil water from the supporting foundation of the house.
At a construction site with a high groundwater level, a dangerous phenomenon can be observed - ascending suffusion (leaching of mineral components from the soil). What to do in this case? In this situation, it is best to provide a number of effective measures to drain the soil before starting construction work, and to begin with, determine the actual groundwater level at the construction site.
Determining the level
The groundwater level, that is, the indicator itself, is recorded in a geological organization, which has a branch in any large city. You can get information on the State Regulations there. Or you can measure the level yourself. To do this, you will have to dig a hole 3 m deep. Or drill a well to the same depth. A hole diameter of 20 cm will be normal, which will only require a garden drill.
Measurements should be taken in the spring, when the snow has melted. This is the period when the groundwater level is at its maximum peak point. Cover the hole with film to prevent precipitation from getting into it. And after a day you check how much water has accumulated in it. You can check with a pole: lower it all the way so that it touches the bottom. We pulled out and measured the dry area from the wet one to the mark that determines the ground level (the mark must be placed when measuring in the hole). This is the UGV.
- If this indicator is more than 2 m, it means that in the area where the house is being built there is a moderate groundwater level. The foundation can be laid without additional measures.
- If the length of the dry section is less than 2 m, then the water level is high. We will have to think through a water drainage system, construct it, and provide the foundation structure with protective materials.
- It is the second position - with high groundwater - that will require the work manufacturer to select the type of foundation.
Determining groundwater levels and possible concerns
Groundwater level
The construction of a foundation with a high groundwater level must be stable and reliable. The extent of the threat of subsidence and destruction of the building is determined long before the start of construction work. For this purpose, in the spring or autumn (at a time when the amount of moisture contained in the soil reaches its maximum level), in the place where, in accordance with the construction plan, the basement will be equipped, a hole should be dug at least 3 m deep.
Dig a hole at least 3 m deep
To obtain accurate data, you will need to reliably protect the pit from weather precipitation. After a few weeks, a certain amount of water will appear and settle at the bottom. Perhaps the bottom will remain dry, and then the foundation does not require additional protection.
If the water is located at a distance above 2 m from the surface, it is necessary not only to calculate the depth at which the foundation will be built, but also to choose the right design.
What should the foundation be like in case of high groundwater, experts can say after conducting geological surveys.
Piles will raise the level of the house to a safe height.
Among the existing foundation structures on high-level groundwater, pile structures are especially popular and trusted by consumers.
Their arrangement will help ensure high-quality and reliable protection of the foundation of the house from the negative influence of groundwater:
- flooding of basements;
- destruction of concrete structures;
- the occurrence and development of fungus and mold;
- violation of the integrity of the foundation itself when freezing during the cold season.
At a high groundwater level, the walls of the pit can float.
In addition, a high groundwater level causes the walls of the pit to float and a sharp reduction in the bearing capacity of the soil. This will require additional work to develop an effective drainage system, including wells and catch basins.
The most dangerous process is the leaching of minerals from the soil, which significantly worsens the strength characteristics of the soil and leads to a change in its structure. Installing a foundation in such conditions has a number of limitations. Calculation of the depth at which the supporting structure will be poured is carried out taking into account the qualitative characteristics of the soil:
- loams;
- sandy;
- clayey;
- mixed.
The level of heaving and the depth of soil freezing depend on this. If the freezing depth is less than the ground level, then there is no need to make adjustments for soil characteristics when planning.
The calculation is carried out with adjustments for soil type and possible subsidence of soft soils.
The data obtained most often forces one to abandon the construction of a strip structure, since the associated work will be very labor-intensive and require significant material costs.
Soil freezing depth and groundwater level
The presence of high groundwater flow affects several positions related to foundation laying. They are clearly stated in SNiPs. And most often in the rules there is a correlation between groundwater level and the level of soil freezing. Because these two indicators are the main factors that reduce the strength of a concrete structure. Here are a few positions.
- If the water level is less than the freezing level, then the foundation is calculated according to the usual scheme, that is, only for the load from the house.
- If the soil at the construction site is weak, soft and mobile, then the foundation is laid below the UPG. In this case, a drainage system must be organized to drain groundwater.
- If the groundwater level is very high, then it is not recommended to build a strip foundation.
- If there is frequent flooding in the building area, then the only acceptable option is a house on stilts. In this case, the pillars are driven into the ground below its freezing level.
If the groundwater level is high enough and the area is drained, then there is a high probability of soil subsidence. This especially happens on sandy soils.
GWL closer than 0.5 m
In this situation, the only solution is piles. There are three options: ready-made monolithic, screw made from steel pipe and bored.
- The ideal option is monolithic. They have been used in construction for a long time; they have increased load-bearing capacity and can easily withstand frost heaving. In addition, there is no need to think about soil drainage. True, this will require special equipment.
- Screw ones have become very popular today. In small private housing construction, such foundations for high groundwater are the optimal and cheap solution. Their only drawback is not the highest load-bearing capacity. Therefore, you will have to calculate the number of piles and the distance between them. It is recommended to install screw piles to a depth of no more than 3 m.
- As for bored structures, this is a good option that has a high load-bearing capacity. But this technology also has its downside - a large amount of drainage measures will have to be carried out.
From 0.5 m or more
When choosing the type of foundation, preference should be given to the slab model.
The thing is, if we are talking about a house, columnar structures in such a situation will not be able to provide the necessary load-bearing capacity of a large structure. You can use a strip foundation, but only a shallow one, which is usually built for small, lightweight buildings. In principle, it will withstand a frame cottage. In this case, it is recommended to build a foundation with an expanded base.
On the question of how to make a foundation slab. When pouring it to a depth of up to half a meter, you need to understand that its thickness and method of reinforcement will depend on the number of floors of the building, as well as on the type of materials from which the walls will mainly be built. In this case, you will have to think about thermal insulation technology. By the way, this is an important stage in the construction of the slab.
Replacing the soil will help increase the load-bearing capacity of the slab. It is taken out to the groundwater level and instead filled with sand or crushed stone with careful compaction.
If the soil on the site is very weak, then the cushion under the foundation of the house for high groundwater is filled in until its materials displace excess moisture and stop sinking deeper.
1.5 m or more
Comparing the conditions described above, it should be noted that in this case it is possible to use strip and slab foundations on groundwater. But both structures must be shallow-depth.
With or without basement
You will have to abandon a basement on swampy soils.
When designing the construction of a house on a site with a high groundwater level, you should not plan a basement. Under such conditions, constant flooding is guaranteed. Moreover, this very process can lead to the destruction of the foundation.
If the desire to arrange a basement is very strong, then it is better to do it separately from the house. In this case, it should be waterproofed and insulated, and if an embankment is made on top, then such a basement will last for a very long time.
Some types of foundations do not provide a basement at all. For example, when building a columnar foundation, it is not recommended to make a basement under the house.
Options for close proximity to groundwater
Options for foundations with close groundwater have already been given above. In principle, the slab structure in this case is the most commonly used structure. There is no need to build drainage ditches or think through protection methods, because everything is carried out using standard technology.
High groundwater - building a house without a basement
Everything here is quite simple if you use a surface or shallow slab as a base. That is, a house is being built without a basement on the ground floor, and the walls rise immediately from the slab. Here is the sequence of work carried out:
- A pit is dug up to the groundwater level;
- A cushion of sand and crushed stone is filled with a tamper;
- Waterproofing with roll material;
- Installation of reinforced frame;
- Pouring concrete.
If an insulated base is being constructed, then insulation is placed under the frame. In areas with high levels of subsoil water, this is an ideal foundation option.
Which foundation is better
If the level of water passage on the acquired site is quite high, then you should carefully consider the type of supporting structure.
When determining the type of foundation, be sure to take into account how deep the soil freezes.
When laying a slab in an area with a high groundwater level, do not forget to waterproof the foundation.
So, let's consider all types of load-bearing structures that are, in principle, suitable for an area with such geological conditions. Let's evaluate all their pros and cons:
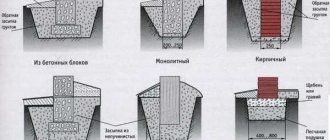
- The foundation is slab. This foundation does not need to be laid deep. All seasonal soil changes have almost no effect on the slab. But if you do not waterproof it, then water will erode the slab foundation in weak spots, and it will crack over time. In such cases, it is necessary to protect the slab foundation from the effects of groundwater. To ensure the insulation process, roofing felt is used. Roofing felt is spread on a special bed of sand and gravel and only then they begin to pour the slab foundation. You can also arrange a slab on a bulk rise made of gravel and clay.
- A columnar foundation is the optimal solution for arranging the foundation for a house on the water. It is not very expensive compared to other types, even if the pillars are laid deeper than the freezing level of the soil. But for heavy multi-tiered houses, a columnar foundation is not suitable.
- A shallowly buried strip foundation, which is called a floating foundation, can withstand houses with heavy loads well.
Which type of base is best to choose depends on various factors, but the only requirement for all is high-quality waterproofing.
Protection from high groundwater level
In the construction of foundations on such soils, three types of waterproofing are used, with the help of which it is necessary to protect the structure of the foundation and the house itself.
- Coating, when bitumen mastics are applied to the foundation itself in several layers, due to which a smooth waterproof layer is formed on the surface of the structure.
- Rolled, when the structure is covered with waterproofing films or membranes in several layers.
- Plastering, when cement mixtures containing waterproofing additives are applied.
The thickness of the waterproofing layer is determined based on the occurrence of groundwater. The higher their level, the thicker the insulating coating.
What to do if the groundwater level is located close to the surface
Before starting construction on the site, it is necessary to perform geological studies and determine the location of moisture. You can do this yourself using hole fragments or hand drilling. To correctly determine the groundwater level, you will need to dig up the ground 50 cm below the expected level of the base of the foundation.
Depending on which of the above problems you need protection from, choose the method of carrying out the work. In most cases, you will need to consider more than one consequence. For example, frost heaving and destruction of the surface from excessive moisture.
Methods to combat frost heaving
The construction of a foundation at high groundwater levels will be successful if the following protective measures are taken:
- partial or complete replacement of soil;
- bedding made of non-foaming materials;
- insulation of the structure;
- removal of moisture from the boundaries of the house.
Advice! Replacing the soil layer is a labor-intensive and costly undertaking. It is recommended to consider it if there are other reasons. For example, soil strength is a significant reason for replacement. It is better to remove very fine sands and unreliable foundations from the site, and instead fill them with coarse or medium sand, which does not retain moisture at the surface and is classified as a conditionally non-heaving soil.
A backfill of coarse sand or crushed stone not only reduces the likelihood of heaving, it strengthens and levels the soil before making foundations. In some cases, it is enough to make a bedding 30-50 cm thick, but sometimes you will have to use more material. In practice, there have been cases when crushed stone literally sank into the ground. In this case, you need to sprinkle it until the base becomes strong.
The standard depth of the foundation is set below the freezing mark (determined according to SP 22.13330.2011). But, if the water is located close to the surface, it will not be possible to do it according to the standards without reducing the water level. In general, you need to mark the base of the foundation so that it is approximately 50 cm above the ground level. Depending on the location of the water horizon, we are talking about shallow (with a ground level below 1.5 m) or non-buried (with a ground level below 0.5 m) foundations. When located above 0.5 m, pile foundations are used.
Important! Building supports located above the frost depth will require thermal insulation. It would be correct to carry out a set of measures, including thermal insulation, drainage (water disposal) and proper designation of the sole mark.
Construction of a foundation on a floating cushion
What is a floating pillow? This is a thick layer of base made of several materials, which are separated from each other by insulating films. For high groundwater it is done very often. Here's the sequence:
- Coarse sand is poured into the bottom of the pit or trench and compacted well.
- Backfilling is done in layers with compaction of each layer. In this case, the final result is a layer 50 cm thick.
- A waterproofing film is laid, preferably roofing felt.
- Crushed stone is poured and compacted to a thickness of 30 cm.
- Another layer of roll waterproofing.
- Filling the screed with a thickness of 10 cm.
After which you can pour the monolithic reinforced concrete structure of the foundation itself. The pillow creates conditions under which the foundation can move relative to it. Such a foundation is often called a floating monolithic foundation.
When the water is close. Foundation on difficult soil
October 28 at 18:50 16158 Denis Galochkin
When the plot is purchased, the developer rushes to start designing and begin building the house. But, unfortunately, there are a number of factors that can seriously affect the construction plan. One of them is the high groundwater level. Let's try to figure out what this danger is, what it threatens and, most importantly, how to deal with this bad geological condition.
As a researcher
When purchasing a plot, an inexperienced person may simply not be interested in how close the groundwater is to the surface. This is how classic situations arise when there is no one to blame but yourself. How to be? You should start by getting to know your neighbors in misfortune: asking what materials and technologies they used to build the structures. In addition, you will have to conduct a geological survey to find out the type of soil on the site and the level of surface water. This should be done when the maximum amount of moisture accumulates in the soil - in early spring or autumn after long rains. You should choose a place where a cellar or cesspool will be located in the future (so as not to work in vain) and dig a hole 3 m deep and 1 square meter in cross section. m, cover it with a lid to prevent rainwater from getting inside. After a few days, check the level of accumulated water. If the liquid never appears or is barely visible at the bottom, then groundwater can be ignored during construction. If the moisture rises to a level above 2 m, you will have to seriously think through the design of the foundation.
The construction of a screw pile foundation does not require the use of large equipment, unlike other types of foundations.
The type of soil should also be determined, as this is important when surface water levels are high. From a small area it is necessary to remove a layer of turf and fertile soil, and then extract two handfuls of earth: from a shallow depth (about 200 mm) and from the freezing depth (for Moscow and the Moscow region this figure varies from 1.8 m in the south to 2.5 m in the north). Next, you need to slightly moisten the handfuls and try to roll them in your hands. A sample of clay soil will quickly take shape like plasticine. Cracking of the soil indicates loam, and soil breaking up into separate balls will most likely turn out to be sandy loam. Sand is the easiest to recognize - this crumbling substance cannot be rolled at all. Any type of foundation can be built on coarse sand, while clay (heaving soil) requires serious calculations when choosing a foundation.
Why should we be afraid of surface groundwater at all? Firstly, the salts contained in the water will destroy concrete, and dampness will provoke the appearance of mold on the walls. Secondly, not only the foundation will suffer - the water will reach the basement and basement of the house. Thirdly, water located above the soil freezing level will turn into ice at subzero temperatures, increase in volume and shift soil layers, which will lead to destruction or shifts of the foundation. What kind of foundation can be built under such conditions?
EXPERT OPINION
Vladimir KRYUCHKOV, specialist of the screw supports department, construction
When building a foundation in conditions of high groundwater levels, you may encounter a problem such as cement bacillus, when water with a high content of sulfates destroys and loosens the foundation of the house. Unlike a concrete foundation, screw piles, manufactured in a factory according to specifications, are completely sealed. Ground water can get inside the support only in the case of through corrosion, that is, in fact, at the end of their service life, after about 100–120 years. Increasing the strength and preventing corrosion of piles is also facilitated by pouring a cement mixture into their shaft. Constant contact of screw supports with groundwater will not reduce their service life, since they are designed for operation in critical circumstances. It would be more correct to say that, on the contrary, favorable conditions will extend the service life of the pile foundation. It is worth mentioning that screw supports are often used in reservoirs for the construction of berths, piers, and walkways. At the same time, part of their trunk is constantly in the water. The strength characteristics of the piles are such that no additional protective measures are required to extend their service life.
On chicken legs
The most budget option for a foundation is a pile foundation. It is even suitable for construction on marshy and peat soils. Piles (reinforced concrete, screw or other type) are installed at the location of the future load-bearing walls of the house at the same distance from each other and are buried into the ground below the freezing level of the soil so that the pillars rest on solid, stable layers of soil. From above, the piles are tied into a single contour with a grillage - a concrete strip on which the load-bearing walls will rest. Before this, the upper part of each support must be waterproofed in order to cut off the rise of capillary moisture.
The pile foundation resists frost heaving of the soil well without changing its geometry, and the small volume of excavation work will allow significant savings on its construction, especially if you use TISE - an individual construction technology. It involves manual drilling of a hole under the pile to a depth of 2.5–3 m, followed by reinforcement, installation of a cushion of sand and crushed stone, and pouring with concrete. However, this method requires pre-draining the well before filling it with solution.
When the groundwater level is high, special attention should be paid to waterproofing slab and prefabricated foundations. To cut off moisture, you can use both roll and coating materials - bitumen mastics, waterproofing mixtures.
Pile foundations have a number of disadvantages. The first of them is the impossibility of building a basement or ground floor (there is no base plate and walls for these structures). Second, this type of foundation is more suitable for lightweight houses - frame, wooden, or built from lightweight concrete. Third, the construction of a pile foundation is not always possible, since the heel of each pile must rest on a solid layer of soil. At what depth it is located and whether it exists at all in a particular area, only a specialist can answer.
Over the seas, over the waves
If the construction of a pile foundation is impossible due to the lack of solid load-bearing soil layers, the solution may be to construct a so-called floating foundation. Structurally, it consists of a flat concrete slab of small thickness, laid on a sand cushion. In this case, the weight of the house will balance the heaving pressure of the soil, and in the event of uneven changes in the soil, the slab will behave like a raft on the waves - it will rise or fall without causing deformation of the structure.
To install such a foundation, first mark the area, determining the area to be poured. Then select soil to a depth of 0.4–0.5 m. Having carefully leveled the bottom of the pit, arrange a cushion of sand and crushed stone 0.2–0.4 m thick with mandatory compaction. Then the base is waterproofed by laying rolled material or laying EPS boards, which, in addition to cutting off moisture, will also insulate the structure. After that, along the perimeter of the future foundation, formwork is built from boards, a reinforcing lattice is mounted and filled with concrete mortar M200 or M300, bayoneting each layer. The thickness of the slab is calculated individually for each specific site, since it is necessary to take into account both the type of soil and the weight of the main structure.
Unfortunately, this type of foundation also has disadvantages. Firstly, as in the case of a pile foundation, you will have to forget about the possibility of constructing a basement or ground floor. Secondly, the construction of a floating slab is possible only on an area with a slope of no more than 5°.
Every whim for your money
If you definitely want a house with a spacious basement or ground floor, then a prefabricated foundation is built from reinforced concrete blocks on a support pad (concrete slab). To do this, a pit is dug under the entire future house to a depth below the location of groundwater. It is more advisable to carry out the work in the summer, so that as little moisture as possible accumulates at the bottom of the pit. If the foundation is installed in the fall or spring, walls are built around the perimeter of the pit from buried polymer or metal piles connected to each other with special locks, and the moisture formed at the bottom is constantly pumped out. When the pit is dug, the bottom is carefully leveled and compacted and a footing is poured - a thin leveling layer of concrete mortar. In parallel with it, a drainage system of perforated PVC pipes wrapped in geotextile is installed along the perimeter, which will collect soil moisture and drain it into the drainage well. A layer of rolled waterproofing is laid on the footing, leaving allowances for the walls along the edges. Then formwork is installed around the perimeter of the support cushion, a reinforcing frame is mounted inside it and filled with ready-made concrete mortar. After the slab has gained the necessary strength, the foundation walls are erected - structures made of reinforced concrete blocks are installed under the future load-bearing walls. On the outside they are covered with several layers of rolled waterproofing.
The main disadvantage of such a foundation is its high cost due to the large volume of excavation work and concrete mixture. In addition, errors in the installation of the drainage system or waterproofing can lead to flooding of the basement and wetness of the walls of the building.
To summarize, it should be said that construction in conditions of high groundwater levels is possible, but you should definitely enlist the support of specialists who will accurately determine the geology of the site and perform the correct calculations for the foundation of the future structure. Remember, high surface water is not an obstacle, but merely a condition of construction.
- Discuss
News smi2.ru
Related articles:
- Where and when will there be a new metro station and international bus station in Moscow?
We found out where and when a new metro station and international bus station will be built in Moscow. - When they can take away your apartment for debts
We talked with a lawyer and found out what will happen if you don’t pay the rent and think that no one will take it from you, because it’s yours. - When a fake is better than the original
“To buy something unnecessary, you must first sell something unnecessary.” The wise remark of Matroskin the cat sometimes applies to very necessary things - for example, real estate. The construction boom of recent years has generated an extensive supply on the primary market.
Save your time!
Subscribe to the weekly newsletter and receive the most important real estate news of the past week from market experts
Comments:
Sorry, no comments found.
Tape
The strip foundation on soils with high groundwater level is poured in exactly the same way as described in the previous sections. It is important to understand here that a strong base in the form of a tape is a large material cost. They mainly concern the consumption of concrete and reinforcement. At the same time, they try to construct the tape itself with an expanded sole.
If you try to save on something, the end result can lead to a weakening of the foundation structure, and, consequently, problems with the house itself will begin to arise. Therefore, one cannot deviate from the construction technology and the exact sequence of construction operations.
Pile type
As already mentioned, a pile foundation with a high groundwater level is the optimal solution. The main thing is to choose the right type of elements to be installed.
As practice shows, when constructing a large, heavy house, monolithic reinforced concrete pillars are used, which are manufactured at reinforced concrete factories.
This technology is called TISE. It’s true that this is not the cheapest technology of all piles, but it is the most reliable.
And although a screw foundation is cheaper, it does not provide the necessary load-bearing capacity for a heavy structure. It must be taken into account that waterproofing in a screw pile or other type of device is a mandatory measure.
Choosing a foundation depending on the soil
The soil and foundation are interconnected. Liquids below the surface can dissolve salts and gases, causing them to become corrosive and can destroy the concrete foundation of the house. The rate of destruction depends on the speed of water movement. Therefore, special cement is used.
If the water rises higher than the base of the water pressure, it will lead to foundation failure or shifting.
Used for the base:
- Shallow foundation of various designs:
- Pile open;
- Pile-grillage.
Gradual filling
In case of high groundwater levels, it is recommended to lay the foundation deeper, as provided for by freezing depth standards. Fulfilling this condition will partially make the construction of a strip foundation economically unprofitable, but possible. If the soil is complex in composition and has floating features, a monolithic reinforced concrete base is laid. Depending on the soil, a shallow strip foundation can be simplified.
Minimum assumptions in the design of shallow foundations:
- Prefabricated structures are stacked next to each other without connecting (with semi-solid clay and silty and fine sand with an average degree of water saturation);
- Assembly structures rigidly connected to each other. In this case, pouring concrete into water will allow the joints to be concreted (for clay soils and sands saturated with water).
- Monolithic concrete and monolithic cushion (soft-plastic clay soils);
- The monolithic base is rigidly connected, reinforced with reinforcement or reinforced concrete belts (for fine and dusty sands saturated with water).
In areas with high capillary rise, as well as those with the possibility of flooding from spills during hurricane winds or melting snow during the season, it is more desirable to lay a pile or pile with a grillage type of foundation under the house. It is not advisable to install a cellar when the groundwater level is high when building a house.
Pit filled with concrete
The foundation for the house must be such that its durable characteristics are not affected by groundwater, which can suddenly either rise or fall. And since there is a possibility of contact with water, the concrete must have high strength. It must contain an additive for water resistance. By choosing the correct water-cement ratio, porosity is reduced.
It is also mandatory to carry out high-quality waterproofing when laying concrete. Water with chemicals and salts dissolved in it causes corrosion and also easily provokes delamination. The so-called “cement bacillus” in the form of a white coating, reminiscent of light frost, dissolves cement.