0
6279
18.11.2013
To determine which foundation is suitable for sandy soil, you must carefully examine the soil itself. Sand, as you know, can have different particle sizes: from large ones, up to a millimeter, to very small ones, more like dust.
Coarse sand is an excellent basis for any type of foundation; it drains water well, is practically not susceptible to frost heaving, and is resistant to seasonal movements. Sand with small particle sizes is dust when dry, and when moistened, it does not allow water to pass through, like coarse sand, but absorbs and retains it. Dirt is formed, which when frozen due to the high water content greatly increases in size. Therefore, fine-grained silty sands are very susceptible to frost heaving, and this must be taken into account when calculating the foundation.
Construction of a foundation on sandy soil
The second factor that complicates construction on fine-grained sands and sandy loams is their tendency to form quicksand in areas with close groundwater. Before starting construction, you need to order a geodetic study of the soil from companies specializing in this, otherwise the costs of correcting errors may exceed the costs of the foundation itself.
Types of sandy soil
Sandy soils are a loose mixture of small fractions of quartz and other minerals with a clay content of no more than 3%. As a product of rock destruction, sandy substrate is divided by density into groups such as dense, medium density and loose. Depending on the composition and grain fraction, sandy soils are divided into 4 types.
Dusty
The substrate is very fine sand - more than 3/4 of the composition contains particles less than 0.1 mm - with a high content of clay inclusions. This mass does not allow moisture to pass through well, which causes instability of the thickness and a tendency to subsidence and swelling. On such an unreliable fine sand foundation, a strip foundation reinforced with piles is most often used.
Fine grain
This category of sandy soil contains 3/4 elements larger than 0.1 mm. The substrate is relatively stable as a support for the foundation structure if reliable waterproofing is used. The fine-grained layer absorbs moisture well and is susceptible to frost heaving. When laying the base of a building, a depth greater than the calculated freezing depth of the soil is required.
Large
Soil mass with coarse sand is a reliable base option for foundation construction. 1/2 of the total number of fractions have dimensions greater than 0.5 mm, the substrate has excellent water permeability, and frost heaving forces are minimal.
gravelly
Soil layers, 1/4 of the composition of which are grains larger than 2.0 mm, have a high potential for the construction of foundation structures. The gravelly substrate does not retain water, the soil layers are not subject to horizontal displacements, and there is no frost heaving effect.
Sandy soil research before construction
Before creating a base, you will need to carefully examine the soil.
To understand which type of foundation is best suited for building a house, you need to examine the soil for the presence of sand. There are several types of sand that differ in grain size:
- The coarse-grained type of sand is a good basis for building almost any foundation. Its advantages include a high level of moisture removal, lack of heaving during frosts, and resistance to seasonal shifts.
- Fine-grained sand is able to retain moisture and not allow it to pass through. During this process, dirt is formed, which can lead to an increase in the size of the soil. This factor must be taken into account during construction. Also, soil based on fine-grained sand has a high tendency to heave.
Depending on the percentage composition of sand in the soil, there are several varieties:
- Soil consisting of dusty sand. Such a foundation is least suitable for erecting buildings on it. The bearing capacity of this type of soil directly depends on moisture levels. When there is a large amount of moisture on silty sand, its characteristics change, causing it to turn into clay.
- Constructing a building on shallow sandy soil can also lead to a decrease in load-bearing capacity after moisture. To avoid this, experts recommend waterproofing the pit using plastic film. About 75% of such soil consists of sand with a size of 0.1 mm.
- Soil with medium and high sand fraction. Such soil consists of particles with a size of about 0.5 mm. This type of foundation has excellent load-bearing capacity. This option is the optimal solution for the construction of any building.
- Sandy soil with a gravelly appearance. The composition of such a base consists of more than 24% sand with a fraction greater than 2 mm. This soil is not prone to heaving and has good properties.
When studying sandy soil, it is necessary first of all to pay attention to the bearing capacity, which directly depends on the density of the base. The greater the density of the soil, the greater the load it can withstand. If the soil is moistened, the bearing capacity will be reduced.
It is also necessary to take into account that the deeper the base is laid, the less shrinkage the building will undergo. During the construction of the foundation, it is necessary first of all to produce high-quality waterproofing. Regardless of the type of sand, the waterproofing process is mandatory.
Sandy soil is rarely heaving, as moisture passes through it. Therefore, almost any foundation can be built on such a basis. If the area is characterized by a high moisture content, then you will need to create a drainage system and insulate the building around the perimeter.
The choice of foundation depends on quite a large number of factors.
In some cases, there is a high probability of changes in the structure of sandy soil in depth. In this regard, during research it is necessary to study deep samples of the earth. Since the sand base has a low moisture level, it freezes extremely rarely.
Pros and cons of sandy soil when building a foundation
If the sandy soil is evenly distributed with sufficient layer density, it will become a good basis for the construction of foundation structures.
Features of sandy soils:
- Coarse quartz sand can withstand significant loads.
- Soils with gravelly and coarse sand tend to become compacted in a short time under the weight of the foundation, which causes rapid shrinkage of the structure.
- Coarse sands do not freeze, are not subject to swelling, are easy to develop, and compact well.
- Fine-grained sand with admixtures of clay as a base for a foundation is not particularly reliable.
- When erecting structures on silty sand soil, high-quality reinforcement of the base is required.
The substrate has different levels of water permeability depending on the characteristics of the mass. The suitability of the soil for construction is determined by the abilities of the predominant sand fraction - the larger the particles, the more reliable the basis for arranging the foundation structure.
It is worth considering that sandy soil is not always homogeneous: at the top there may be a layer of coarse sand, while further there is a layer of fine fractions.
Types of foundations on sandy soil
When arranging buildings on sandy soil, various types of foundation structures are relevant, the selection of which takes into account the characteristics of local conditions.
Tape
When constructing a strip foundation, a shallow or in-depth version of the foundation is used. For relatively small buildings in the form of one-story houses, bathhouses and extensions on coarse sandy, stable soils, a foundation base made of shallow tape up to 40-60 cm deep is installed. The structure can be monolithic or prefabricated. If it is necessary to create a basement floor, a recessed strip foundation is laid; the degree of immersion of the underground walls varies between 3-4.5 m.
Pile-strip foundation on sandy soil
Pile-tape
When building on unreliable soils with a predominance of fine-grained or silty sands, the shallow strip foundation is reinforced with piles, and the supporting structures are installed to a depth of a stable soil layer. It is recommended to drive piles every 200 cm. The trench is filled with crushed stone, waterproofed, reinforced and filled with concrete mortar.
Pile
Pile foundations are often used for structures built on fine sand. Depending on the terrain and the complexity of construction, pile-screw devices, cast-in-place piles or bored-in-place versions of products are used. The structure is strong and stable, since the piles are installed below the soil freezing level.
Bored pile foundation
Tiled
The foundation for a building of this category involves pouring a reinforced concrete platform under the entire area of the house. The tiled support structure is a priority in cases where construction is planned in conditions of extreme soil instability. In such cases, other types of foundations do not meet the technological requirements of construction, and it is necessary to lay a slab foundation, despite the fact that this is a costly option for arranging the base of the building. As a result, the support area is maximized and the independence of the foundation from the influence of heaving forces is enhanced.
Pouring a slab foundation
Choosing a foundation for sandy soil
Coarse sand allows you to build almost any foundation on it. But the most economical solution would be to create a strip base with a shallow base. This solution is often used for buildings where a basement is not planned or for wooden structures.
The shallow tape base is divided into:
- made;
- monolithic.
If a foundation on sand needs to be built as soon as possible, it is better to choose the first option. To create such a base you will need to use special reinforced concrete blocks. They are fastened together using a concrete mixture. The cost of work with this choice will be slightly reduced, but the quality will be noticeably inferior to the monolithic option.
The monolithic base is created directly on site. To do this, you will need to equip the formwork, install a frame based on reinforcement in it and fill the entire area with concrete.
A recessed strip base is used when it is necessary to build a building with a plinth or basement. With this choice, you will need to equip an additional drainage system that will prevent the penetration of moisture. You will also need to create high-quality waterproofing for the walls and floor of the basement.
A pile or slab foundation will allow you to save a lot of money when building a house on sand. In addition to its low cost, such a base is quite simple to construct, so that even a beginner in the construction craft can handle the work.
The choice of foundation must be carried out taking into account the type of soil and the level of groundwater. The depth of arrangement of the base depends on the depth of soil freezing.
A technologically correctly constructed foundation is the key to long-term operation of the building. It is better not to skimp on the base, as this can lead to its cracking and destruction.
Features of foundation construction technology depending on the type of soil
With the help of the correctly selected type of foundation and compliance with foundation construction technologies, you can create a strong support for construction on any type of sandy soil.
Dusty and fine-grained
To build a house on silty and fine sand, due to the extreme instability of the layers, it is necessary to create the strongest possible foundation. In such cases, it is permissible to build a slab foundation. To do this, the fertile layer of soil is removed and a concrete slab is cast, the scale of which is slightly larger than the area of the planned building. The structure does not collapse under the influence of seasonal changes in the soil, since this type of foundation is able to move along with the soil, which is why it is called a floating foundation.
Another more common way to create a solid foundation for construction on silty and fine sandy soil is to use a monolithic shallow-type strip foundation. It is recommended to make it trapezoidal in shape with lines expanding downwards. This helps to significantly reduce the effect of frost heaving on the foundation of the house.
Before pouring the foundation tape, the trench is equipped with a waterproofing layer. When laying a base structure under a building on fine sand and dusty soils, drainage work is especially important. Closed systems that are equipped with drainage pipes are recommended as effective methods.
When working on the construction of the base of heavy buildings on fine and silty sand, it is worth using a pile-tape option for arranging the foundation:
- carry out markings, dig a pit, install formwork;
- in places where the tape intersects, wells are drilled to a depth of stable soil layers;
- pipes based on asbestos cement are installed in the wells, the structures are properly leveled, and reinforced with spacers;
- the pipes are filled with concrete 1/3, slightly raised to form a thickening at the bottom. Next, the pipes are filled with solution, having previously lowered the fittings into them.
Formwork and reinforcement for pile-strip foundations
Piles can be poured without installing pipes, if the environment is not very humid and the wells are not filled with water:
- the lower part of the well is expanded using a special plow;
- reinforcing material is lowered into the well and filled with solution;
- After the pile structures have hardened, they begin to pour the tape into the formwork.
Experts note that after pouring the foundation on fine-grained and silty sand, the structure must stand for six months before continuing construction work.
Large and gravelly
Since coarse sandy soils have a reliable level of bearing capacity, any types of foundation structures are relevant here:
- if you plan to build a house without a basement, a shallow-type tape version is most often used;
- a columnar base is suitable for a structure made of light materials in the form of frame structures, wooden houses or panel structures;
- For massive buildings with a basement, a deeply recessed strip foundation is used.
Columnar foundation for a frame house
When laying a columnar or strip version of the base, foundation blocks or ceramic bricks are also used.
On a shallow strip foundation on coarse sand, you can put a building made of foam blocks or wood, a frame/panel type structure, or a small brick house. In this case, the depth of laying the sole varies in the range of 40-70 cm.
Do-it-yourself technology for pouring monolithic shallow tape:
- Site preparation. After removing the fertile layer of soil, they will level the surface.
- Marking. The work is carried out based on the house design.
- Preparing the trench. Dig a trench 60-80 cm deep. The width of the recess is equal to the thickness of the planned walls plus 20 cm, that is, 5 cm on both sides of the wall for structural stability and 5 cm for the formwork.
- Pouring formwork with concrete mortar.
Trenches for foundation construction
For formwork, plywood sheets, edged boards, corrugated sheets are used, the inner surface is lined with polyethylene, and reinforcing materials are used to strengthen the composition.
When constructing massive buildings or houses with a residential ground floor or basement, a deep foundation strip is laid. Moreover, the base under a brick house is installed 20 cm below the soil freezing level. The deep strip foundation is provided with a waterproofing layer on all sides, including the lower surface. Good drainage is also required.
Foundation on coarse and medium-grained sands
The case is simple, and any type of foundation will do. If groundwater runs low, at a depth of 1.80 m or more, a strip foundation, a columnar foundation, or a combination of both is optimal. Monolithic reinforced shallow tape (MZLF) or a foundation made of prefabricated FBS concrete blocks are suitable for houses made of stone, brick and blocks with several floors and a basement. For lighter frame houses, or one-story buildings made of lightweight concrete blocks and timber, a support-column foundation, brick or block, will be sufficient.
Before starting construction, the site is always leveled and all debris is removed, and then the plant layer of soil is cut to a depth of about 20 cm.
A columnar foundation does not require complex technology. materials – concrete, rubble concrete, sand concrete, blocks are possible. The use of foundation blocks of size 200*200*400 mm allows you to do the work yourself, without the use of equipment. When using bricks for laying support pillars, you should remember that sand-lime brick and red brick with low frost resistance characteristics are unacceptable for foundations.
The construction of the foundation begins with clearing and marking the site. Supporting foundation pillars are located in the corners of the house, at the intersections of load-bearing walls, that is, at points with maximum load. The house plan is transferred to the area by installing cast-off posts, marking points by driving in pegs along which the cords are pulled - the axes indicated on the house plan.
The holes for the support pillars are dug strictly along the axes. For a monolithic option, after installing a crushed stone or sand-gravel cushion, roll waterproofing is installed, formwork and reinforcement frame are installed, then concrete is poured and compacted with a vibrator or bayonet. A grillage is placed on top of the supports.
For a columnar version made of brick or in a block design, trenches are deepened under the pillars to 400 mm, and a crushed stone cushion is made to prevent capillary suction of groundwater. The pillow is covered with waterproofing made of rolled material. The laying of support pillars is done with obligatory ligation; the dimensions of the pillars depend on the thickness of the future load-bearing walls. The finished masonry is coated twice with bitumen or bitumen mastic. Vertical waterproofing - cut-off is carried out with rolled material. Then they begin to build the walls.
The role of drainage when laying a foundation on sandy soil
When constructing the base of buildings on fine-grained and silty sandy soil, special attention is paid to drainage, since soils of this category do not drain water well. It is recommended to create closed systems using drainage pipes.
How to do drainage work yourself:
- holes are drilled on a plastic sewer pipe;
- the pipes are wrapped in geotextile, which helps prevent sand from penetrating and clogging the holes;
- A system of trenches is dug around the house and drainage pipes are laid in them.
When constructing closed drainage systems, drainage to the surface must be carried out. The drainage channels are filled with gravel, covered with geotextiles and a layer of turf.
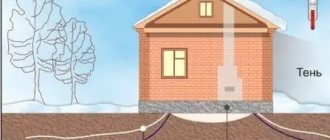
Hydro- and thermal insulation of the foundation
To protect the foundation from destruction under the influence of moisture and frost heaving forces, it is necessary to perform high-quality hydro- and thermal insulation of the structure.
Features of waterproofing the sole of the structure:
- For waterproofing, special materials are used in the form of water-based mastic or bitumen;
- To eliminate the risk of deformation of the insulating layer, mastic based on organic solvents should not be used.
When working on insulating the base, polystyrene foam boards are used. The insulation modules are easily connected and allow you to create dense protection from external influences. Expanded polystyrene panels are fixed to the sole structure using special glue.
The solution to the question of which foundation is better on sandy soil depends on the type of sand and the features of the structure. In the case of arranging a structure on coarse sandy or gravelly soils, greater freedom in choosing the option of the base for the building is assumed. For construction on fine-grained and silty sand, it is advisable to use only certain types of supporting structures, most often this is a strip, pile-strip or pile version of the foundation.