Structures for various purposes, built from block material, are becoming increasingly popular. There is nothing strange about this - the blocks are durable, environmentally friendly, easy to process, and perfectly retain thermal energy. Many developers strive to use this particular option of building material, but have doubts about the choice of foundation. It should be noted that the most acceptable option in this case is a foundation on piles. Today we will figure out how to lay gas blocks on a pile foundation.
General requirements for a foundation for an aerated block house
The final choice is determined by the ability of the foundation to fulfill its main function:
- maintain the stability of the shape of the structure and give it rigidity;
- distribute the load effects from the total weight of the object on the soil composition;
- do not allow the structure to settle unevenly, eliminate the formation of distortions and cracks;
- minimize the forces of heaving soils, prevent possible deformation;
- level out the lateral load effects on the walls and basement.
Taking into account soil conditions in the design of the foundation of a house made of aerated concrete
The strength of aerated concrete is 3-5 times less than the strength of brick. Therefore, when using this material, great attention must be paid to the uniform settlement of the building.
Brickwork (especially reinforced) provides sufficient rigidity to the building, compensating for uneven deformations of the foundation by redistributing pressure on the foundation structure.
In aerated concrete masonry built on a lightweight “standard” foundation, cracks may appear even with minor uneven deformations. To avoid this in the absence of knowledge about the peculiarities of the soil conditions of the construction site, it will be necessary to increase the rigidity (power) of the foundation structure, due to which it will become comparable (including in cost) to the foundation of a brick building.
Thus, construction without knowledge of soils will turn into either an extremely dangerous or unreasonably expensive undertaking.
1.1. Physical and mechanical properties of soils, the ability of the foundation to withstand design loads
The physical and mechanical properties of soils characterize their physical state and ability to deform and not collapse under the influence of external loads, and therefore are decisive in determining the ability of the foundation to withstand design loads.
The foundation only transfers the load from the above-ground part of the structure to the soils at the base. Therefore, regardless of the type of structure, the ability of the foundation structure to absorb design loads will be determined primarily by the bearing capacity of the soil at the base, and only then by the design parameters of the foundation itself (which are again assigned taking into account the soil conditions of the construction site).
1.2. Chemical properties of soils and service life of the foundation
The chemical properties of soils are determined by the chemical changes occurring in them and characterize their ability to participate in chemical interactions with various substances. The service life of the foundation depends on them.
For example, the foundation structure must be in operation for 50 years, and it will be installed in clay soils, which are characterized by high aggressiveness towards steel. If you use screw piles with a trunk wall thickness of 3.5-4 mm, the maximum service life will be 20 years at best. Such piles can only be used for 50 years in soils with a low degree of corrosion aggressiveness.
There is an opinion that if you use a protective coating, the service life of screw piles can be increased. Unfortunately, it is not. Firstly, there is a high probability that the coating will be damaged during the installation of the pile due to the abrasive effect of the soil and will cease to perform its function. Secondly, even if this does not happen, the maximum service life of the coating itself will be no more than 10-15 years.
Thus, both in the case of the ability to withstand design loads and in the case of service life, it is impossible to predict anything without having knowledge of soil conditions (Table 1). The only thing we can talk about more or less confidently (and even then not always) is the number of screw piles.
Table 1 - Basis for assigning parameters of screw piles
| Parameter | Reasons for appointment |
| steel grade | Requirements for rigidity, strength; soil conditions, including data on the corrosive aggressiveness of soils (CAG); operating conditions (more details: “What does the steel grade affect?”). |
| Barrel wall thickness, mm | Data on CAG; requirements for rigidity, strength (more details “Calculation of barrel wall thickness”). |
| Barrel diameter, mm | Data on CAG; requirements for rigidity, strength, stability (more details “Corrosion: causes, methods of protection”). |
| Length, mm | Indicators of the estimated freezing depth and load-bearing capacity of soils (read more “How to choose the length of piles for the foundation?”). |
| Blade diameter, mm, number of blades | Data on loads from the structure (in accordance with stability requirements), bearing capacity of soils (more details “Features of calculation of multi-blade modifications”). |
| Blade configuration | Data on the physical and mechanical properties of soils: porosity, degree of saturation with water, consistency, granulometric composition, etc. (more details “Key principles for selecting blade parameters”). |
1.3. Geotechnical studies and measurements of soil corrosion aggressiveness
To obtain information about the physical, mechanical and chemical properties of soils sufficient for the design of screw pile foundations, specialists from the research and development department, based on numerous studies and current regulatory documents, have developed procedures adapted to the needs of low-rise construction:
- geotechnical (dynamic sounding) and geological-lithological studies;
- measuring the corrosive aggressiveness of soils.
These methods are described in more detail in the article “Geotechnical and geological-lithological studies and measurements of soil corrosion aggressiveness.”
Also, by summarizing a large amount of data, a method for production monitoring of the load-bearing capacity of screw piles by the value of torque (VKM), as well as a device for performing these measurements, was developed (Patent No. 151668). It allows you to control the quality of work performed without resorting to expensive control field tests of soils using full-scale piles.
Often, the test screwing procedure, in which the torque value is indirectly determined, is positioned as an independent geological study, but this approach is incorrect. The results of a test drive are highly dependent on the time of year, and in addition, driving in several places on the site does not provide any information about the type and properties of the soil under the pile and the variability of soil conditions within the building area.
Advantages and disadvantages of pile supports for a gas-block house
The foundation on screw supports has certain advantages:
- construction is progressing at a rapid pace. To build such a foundation, one to two weeks is enough;
- installation work can be carried out in any weather conditions;
- the ability to carry out construction work in areas with difficult soils and elevation changes, with high groundwater levels and freezing of the ground;
- significant savings in labor costs and financial resources;
- long operational period.
Comparison of pile-screw and block foundations
Every house has an important part that often does not attract attention, but on which the durability and even the possibility of existence of the entire structure depends. This is its foundation. And the choice of its type must be taken very seriously, taking into account many factors. For example:
- Type of soil, features of the site and its location (hill, slope or lowland).
- Climatic conditions of this region.
- The type of building and its design, as well as the degree of load on the support of the entire structure.
- Types of communications that will be provided to the building.
Let's look at several types of foundations that are currently very popular.
Comparison of pile-screw and block foundations
Pile-screw foundation
It is an excellent way out of a situation where the groundwater in the area comes too close to the surface or the soil here is problematic . Building another type of foundation in such an area would be very expensive. At the same time, large financial costs do not guarantee that uneven settlement of the house will not occur in the spring.
There is no standard for the manufacture of screw piles. They come in various lengths and diameters, with threads and blades or combined threads, solid and hollow, with a cap at the top of round, rectangular and other shapes, etc.
Comparison of pile-screw and block foundations
Advantages of a pile-screw foundation. There is no need to carry out excavation work , so time and money are saved for preparing access roads for specialized equipment. Installation work can be carried out at any time of the year , including winter. doesn’t take more than 48 hours to “screw in” the piles , and all the work can be done by a group of three workers. You can always add a new structure to a house on a pile-screw foundation.
Foundations on screw piles are used for both residential and industrial premises . The piles are screwed into the ground using construction equipment or manually, since due to their design the pillars practically make their own way in the soil.
If the structure was not concreted after installation, KSAmet screw piles are very easy to dismantle and move to another location for reuse .
Comparison of pile-screw and block foundations
More information about KSAmet screw piles: https://vsksamet.ru/
Block foundation
Experts recommend installing this type of support for owners of sites: with sandy soil of high and medium density; in areas with rocky formations; in places with gravel-pebble or crushed stone deposits.
To lay a block foundation, a base must be made - a sand cushion 15-20 cm high. For this purpose, a frame knocked down from wooden boards 30-40 cm wide is installed at the bottom of the pit, onto the bottom of which coarse sand is poured level.
When installing a block foundation, you need to know an important point - the laying of pillow blocks is done from the corners of the walls . The external units are installed first and only then the internal ones. The correct installation of all elements must be checked using a level and plumb line, as well as along the axes of the previous blocks. The thickness of the seams should in no case exceed 1.5 cm. If it is not possible to insert another element between the blocks, the gaps are filled with monolithic inserts of the required size.
Advantages of a block foundation. One of the most important advantages of this type of support is the speed of its construction , as well as the ability to install load-bearing walls immediately after completion of the work. The relatively low price is also very much appreciated , as well as a fairly large selection of types of blocks : solid and hollow, pillow blocks, blocks with cutouts for communications, etc. Ready-made elements with holes significantly simplify and reduce the cost of further work on installing all the necessary communications into the building.
Due to the fact that crushed stone is used in the manufacture of blocks, this support is resistant to acidic rocks . The high frost resistance of the element materials allows the use of this type of foundation in places with harsh climatic conditions.
Disadvantages of a block foundation. If we compare the cost of this support with a columnar type of foundation, it will be quite high. The complexity of waterproofing work is due to the large number of seams. Since reinforced concrete and other types of blocks are quite massive and heavy, all work related to their movement and laying requires the use of special equipment .
Comparison of pile-screw and block foundations
| What else can We do for you? |
| Call: 8-800-700-59-17 Free for All Russia |
| Contacts of Kaluga: |
| Call: +7 (4842) 59-59-16 - Central office. |
| Email: |
Features of pile installation
Houses made of aerated concrete blocks are built in most cases on construction sites with shallow groundwater levels. In this case, the foundation is prepared on screw supports or bored piles, connecting into a single structure using a monolithic grillage.
Both types of piles differ from columnar elements:
- dimensions. With a smaller cross-section, their length is slightly longer;
- materials used in production;
- installation options.
The laying of the pile foundation is carried out somewhat deeper than the level at which the freezing point of the soil composition, marked in the area of construction work, is located.
Screw piles
If a problem area with heaving or weak-bearing soil is allocated for development, then it is better to build a house made of aerated concrete on a pile foundation on screw pile supports. They can be installed even in frozen ground or under surface objects.
At the lower end of the metal pile there are welded blades or coils, with the help of which screwing into the ground is faster and the expansion of the support cushion is ensured. The helical blade in this case is a kind of anchor, firmly fixed in the ground.
The upper part of the pipe has special holes and caps (the latter can be mounted separately, after installing the piles). If the deepening is carried out to a level not exceeding two meters, the piles are screwed in manually. In other cases, you will have to use special equipment.
The process of installing screw pile supports is completed by concreting their cavities. This not only gives additional strength to the structure, but also protects the internal walls from corrosion.
When working with screw supports, it is recommended to take into account:
- the length of the section equipped with blades;
- depth of freezing of the ground;
- the level at which a solid soil layer is located.
Remember that the piles must sink at least thirty centimeters into dense soil. When screwing them in, it is necessary to keep the position at the vertical level under control, since even minimal distortions are not acceptable.
The main advantages of screw supports are quick installation, excellent load-bearing capacity, cleanliness on the construction site during work, and the possibility of installation in an area with differences in height.
Bored piles
The second option for a pile foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is bored supports. They are preferred on uneven terrain or when the ground is deeply frozen.
Wells for supports are prepared manually or by drilling. Using a special tool, you can go five meters or more deep and make widening at the bottom to fill the support areas.
In accordance with the diameter of the pile support, formwork is prepared from roofing felt material. The length of the workpiece should exceed the same size of the pile by twenty to thirty centimeters. The prepared “pipe” is installed in the well; a frame of reinforcing bars is placed inside it, the height of which takes into account the dimensions of the future grillage.
Everything is filled with concrete mortar, which is carefully compacted with vibrators.
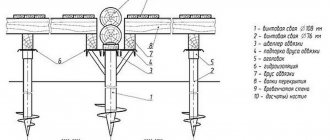
What is a pile-grillage foundation
A pile-grillage foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is a foundation structure that includes a system of vertically installed supports in the ground and a piping connecting them in the part above the ground. The supports are immersed deep into the ground, bypassing unreliable layers and trying to reach dense soil, where they turn into motionless, stable anchor points.
A grillage is a strapping belt that acts as a kind of strip foundation mounted on a sand cushion and rigidly fastened to the top of the piles. Like the tape, grillage beams are placed under all load-bearing walls of the structure, creating a high-strength support system. Thus, the load of the house is taken by the grillage, and then transferred to dense layers of soil through a system of piles.
A grillage foundation differs from a pile-strip foundation in that the tape slightly unloads the vertical supports, transferring part of the load to the ground surface.
Here a different principle is used and two types of grounds must be distinguished. At the same time, almost all types of pile foundations are pile-grillage, despite the differences in the design of the types of piles.
Houses made of aerated concrete, which are planned to be built on sites with close groundwater, are most often built on screw or bored piles, which are connected to each other with a monolithic grillage.
Main differences from columnar structures:
- Execution material.
- Installation method.
- Dimensions – longer length, smaller diameter.
Pile foundations are always laid deeper than the maximum level of soil freezing, which is recorded in a particular region.
Is it suitable for a house made of aerated concrete?
The bearing capacity of a pile-grillage foundation is quite high and limitations exist only in the capabilities of the piles and the properties of the soil. As the number of piles increases or by creating support platforms under the lower part of the ends of the shafts, the load-bearing capacity can be significantly increased, while simultaneously reducing the specific load on the soil. This increases the efficiency of the entire structure.
Aerated concrete has a mass that is 5 times less than brick and a strength that is 5 times lower (subject to the construction of walls with similar parameters). Therefore, houses made of aerated concrete are usually built 1-2 floors high, but their weight is significantly less compared to brick structures.
Due to the light weight and construction features, the possibilities of a pile-grillage foundation for an aerated concrete house are not only sufficient, but to some extent even excessive. At the same time, sufficient rigidity is achieved, which is very important for aerated concrete, which does not accept shrinkage and requires a fixed base structure, which a strip foundation cannot always achieve.
Base structure
The pile-grillage foundation system includes two main elements - piles and grillage. Both parts of the structure are designed to absorb and distribute the load, but there are some features that are important to study before installing the base.
What does a pile-grillage foundation consist of:
- Piles are vertical rods (supports) made of concrete, wood or metal that are driven into the soil until they reach the hard layers and ensure firm contact with them. So-called “hanging piles” can be used, which are held in the ground due to the side walls of the trunk and the friction force of the soil. But they are used less often, since the length of the barrel in this case must be large and this cannot always be achieved. It is also important that hanging piles can gradually sag (especially for waterlogged soils), which is unacceptable for aerated concrete.
- Grillage - simultaneously performs two important functions: connecting all the trunks into one rigid system (which greatly increases the load-bearing capacity of each unit) and acting as a support line for internal/external load-bearing walls. Grillage structures can be made of concrete, metal, wood (timber) - the choice depends on the material used to build the house.
Advantages and disadvantages
A pile-grillage foundation, like any other, has certain features and nuances that must be carefully studied before construction begins.
The main advantages of the pile-grillage foundation system:
- A relatively simple technology that even beginners can handle.
- The ability to carry out all the work yourself - from the manufacture of elements to their installation.
- No need to attract a large number of employees.
- Relatively lower consumption of materials (if we take into account the buried tape, for example).
- No influence on the properties of the base by soil heaving.
- The ability to rigidly connect the piles to the grillage and achieve the most load-resistant system that will not react even to trains passing nearby.
- Ability to perform work almost all year round - with the exception of conditions with air temperatures less than 10 degrees below zero.
- Good heat conservation of the house structure due to the lack of contact with frozen soil.
- Houses with such a foundation can be built on folds of the terrain and slopes.
- The price of the base is relatively low (again, when compared with the classic tape).
Key disadvantages of the pile and grillage system:
- It is not possible to create a basement or basement.
- If the total weight of the house is more than 50 tons, it is better to choose a different type of foundation.
- The importance of correctly performing all calculations based on accurate soil data to determine the optimal number of piles and grillage shape.
- Even if there are no vertical heaving loads, there remain lateral impacts on the pile, which provide considerable forces and can deform or even destroy the column.
- The need to use special equipment during construction, which increases foundation costs.
It is worth noting here that all the main disadvantages are characteristic of all types of pile foundations, since they are among the features of structures of this type.
Existing types
There are several types of piles and each of them differs in certain nuances. Typically, screw, bored and driven piles are used to create a pile-grillage type foundation. Driven piles are installed into the ground using special equipment. They can be made of wood, metal, reinforced concrete. Self-assembly involves screw and bored piles; the latter are often made directly on site or purchased ready-made. Such piles are driven into the soil using muscular force.
The highest load-bearing capacity is found in concrete driven piles, which are made in factories using special technology. Installation of such supports is quite labor-intensive and complex, requiring the participation of experienced builders and equipment.
Bored piles are more popular; they are made in the format of concrete supports poured into a prepared well. It’s quite possible to do all the work yourself, and thanks to the size of the well and certain features of its base, it becomes possible to create a large-area support platform that will be inaccessible to the effects of frost heaving loads.
The use of screw piles in the installation of foundations began relatively recently. The barrel is made of a metal pipe with a wall thickness of 4-5 millimeters with a pointed tip at the bottom or several blades (made like a spiral). The piles are immersed by screwing them into the soil to the required depth.
The procedure is simple, but requires some effort and skill. Screw piles are the fastest to install and do not require preliminary excavation work. If installed correctly, the only problem with screw piles is protecting the metal from corrosion.
Grillage options
The grillage structure can be made of a variety of materials - metal, wood, reinforced concrete. The last option is the strongest and most durable, but also the most difficult to implement. It is created similarly to a strip reinforced concrete base, but not in a trench in the ground, but at a certain distance from the ground surface.
A wooden grillage is much easier to install. To create it, timber 150 by 200 and 200 by 200 millimeters is used. All beams are combined into half a tree, mounted on the pile heads, and then secured with strong bolted connections.
The metal grillage is connected to the pile heads by welding. The process is very fast, but cutting massive and thick beams is a rather complex process. While their mass often becomes the reason for the need to use lifting equipment.
For an aerated concrete house, the best choice would be a wooden or reinforced concrete grillage, and in both cases it is necessary to perform careful and accurate calculations, and then, based on them, create the most detailed project possible.
Pile tying
A pile foundation for a house made of gas silicate blocks must have a grillage. This necessity is dictated by the fact that it is impossible to install aerated concrete on piles, especially screw ones, without carrying out additional measures.
Heads prepared from pieces of larger cross-section pipes and steel sheets, the thickness of which is 1 cm, are welded along the upper edges of the screw posts. The heads will have to be prepared in advance for each pile support.
Additionally, a solid base is prepared, for which metal elements are used or a reinforced concrete belt is poured. The first option is more convenient because it involves the use of rolled blanks, which are fixed to the ends by welding.
The issue with a grillage made of reinforced concrete is more difficult to resolve. Technologically, the process looks like this:
- all screw piles are cut to the same height, a shallow trench is prepared along all load-bearing walls and interior partitions, and formwork panels are placed;
- if an air grillage is to be poured, additional supporting elements are installed on which the bottom is laid under the reinforced concrete strip, and the side walls are attached;
- as soon as the preparation of the formwork is completed, a frame base made of reinforcement with a cross-section of eight to ten millimeters, connected by crossbars made of knitting wire, is placed in it;
- Concrete solution is poured and compaction is performed. The poured grillage is covered and, in hot weather, periodically moistened during the first week.
A grillage for piles greatly facilitates the construction of a house made of aerated concrete on a screw foundation.
Existing types
There are different design options for a pile-grillage foundation:
- Driven piles.
- Bored piles.
- Screw piles.
Driven piles are driven using special machines . They can be made of reinforced concrete, metal or wood, although the latter option is already very rare.
For self-installation, bored and screw piles are suitable, which can be made directly on the site (bored) or purchased ready-made and driven into the ground using muscular force.
The greatest load-bearing capacity is provided by driven concrete piles manufactured at specialized enterprises using special technology.
At the same time, the installation of such piles is the most labor-intensive and complex procedure, requiring the participation of professional and experienced builders with the appropriate equipment.
Most often, bored piles are used, which are a monolithic concrete casting into a pre-prepared well .
All work can be done with your own hands, and the dimensions of the well and the features of its base make it possible to form a large-area support platform, inaccessible to frost heaving loads.
Screw piles have been used relatively recently, so most users regard them with some doubt.
The barrel is made of a thick-walled pipe (4-5 mm), the lower part has a pointed tip with one or more spiral-shaped cutting blades. Immersion is carried out by screwing into the ground to a certain depth .
The procedure is simple, but requires an understanding of the essence of the process and practical experience, otherwise you can ruin the pile and not achieve the desired effect.
At the same time, working with screw supports is the fastest, requiring no preliminary preparation or excavation work.
If you avoid technological errors, the only problem remains corrosion, from which it is very difficult to protect a metal barrel.
Kawabanga! Monolithic reinforced concrete plinth; features and construction technology
Installing a foundation on piles for a house made of aerated concrete
Let us consider the features of the technological stages of constructing a pile-strip foundation for a house made of aerated concrete.
Before starting work, it is necessary to perform the appropriate calculations, with the help of which the need for materials is determined. At the same time, to obtain reliable information, the type of foundation and the characteristics of the soil composition on the site are taken into account.
Plan the placement of piles in the corner sections of the object, at the central support points of the load-bearing walls. In this case, the installation step should be from one and a half to two meters.
The screw pile can withstand axial loads of up to twenty-five tons.
Having prepared everything necessary, cleared the construction site and completed preliminary markings, we proceed to the construction of a foundation on screw piles for a house made of aerated concrete.
Screw piles can be installed using two methods - manual or mechanized. The first option involves screwing the elements to a level of up to two meters with a cross-section not exceeding 10.8 cm. Larger supports are mounted using special installations.
Manual method
In this case, use a hand drill, levers and a building level. The installation process is as follows:
- a pit is prepared at the drilling site to facilitate the process;
- levers (cuts of steel pipes) are inserted into the technological holes of the pile;
- the rotation is performed by a pair of workers, the third constantly checks the vertical position of the support;
- Using an angle machine, the pile is trimmed to the required level and the head is welded on.
Mechanized method
In this case, special equipment is used with a power unit capable of grasping the head of the pile and ensuring its rotation. The speed of work depends on the size of the pile pillars and the characteristics of the soil composition.
The use of such an installation entails additional costs, but helps reduce the time for installing poles.
Installation technology
How to calculate a pile-grillage foundation for aerated concrete
The calculation is carried out on the basis of current SNiP and includes two parts:
Calculation for a pile field
- Dimensions of pile supports. They depend on the area and weight of the aerated concrete structure and the type of soil on the site. The size of the supports must be chosen in such a way as to effectively absorb the load from the structure and prevent its settlement. Piles are installed not only around the perimeter, but also under all load-bearing walls of the future house. The cross-section of bored supports is determined according to the table:
The load-bearing capacity of bored piles depending on the cross-section is given in the table:
Grillage calculation
For the grillage it is determined:
- Length - equal to the length of the perimeter of the load-bearing walls.
- Width - equal to the thickness of the wall of a house made of aerated concrete blocks.
- Height is assumed to be 0.5-0.7 meters.
Preparation for the installation of a pile-boring foundation
The site for a pile-grillage foundation requires minimal planning. Vegetation is removed, stumps are removed, and debris is removed. The marking is carried out in accordance with the drawing using a cord and pegs, which are driven into the places of future piles.
The set of tools and equipment depends on whether the concrete mixture will be produced at the construction site or ordered at the factory. The mandatory list includes:
- shovel or mini-excavator;
- tape measure and building level;
- crochet hook for reinforcement;
- concrete pump or trays for pouring the mixture;
- vibrating tool for compacting concrete.
The list of materials includes:
- concrete M250 or M300 - for pouring piles and grillage;
- reinforcement with a cross section of 12-14 mm;
- panels or finished formwork;
- pipes - for casing piles.
Pouring bored piles
Stages of constructing a pile field:
Creating a grillage
A monolithic grillage is made in the same way as a regular strip foundation. The main difference is that the grillage is buried into the ground no more than 10 cm. Stages of creating the grillage part:
- pile heads - coating waterproofing;
- the sole of the grillage is laid on a bedding layer, on top of which waterproofing or roofing material is laid;
- The top of the grillage tape is coated with liquid waterproofing material or lined with rolled material.
Kawabanga!
Rules for vibrating concrete The external and internal walls of the grillage are subject to insulation. It is better to use moisture-resistant and durable polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam or plastic as insulation.
Technology of laying gas blocks
How is aerated concrete installed on a pile foundation? A waterproofing layer is placed under the first block row so that the stones do not absorb moisture from the grillage. After this, a number of blocks are laid out on cement mortar; subsequently, an adhesive mixture is used for this purpose.
Masonry work is carried out from the corners, between which the cord is stretched. If it is necessary to fill a row completely, an additional element of the required size is cut out of a solid block. All subsequent rows are performed with a half-block dressing, as is the case with brickwork.
The glue is applied to the surface of the blocks with a spatula or a carriage whose width corresponds to the size of the stone. The seam is not made thick, because the glue has excellent adhesive properties. To level the blocks laid in a row, use a rubber or wooden mallet.
To prevent cracks on the surface of the walls, a reinforcement method is used. This operation is performed during the construction of any large building, and for an aerated concrete house built on a pile foundation, it will not be superfluous. Not all rows are subject to reinforcement, but only certain ones that are considered the most vulnerable. These include areas with lintels, support points, the first masonry row, and areas located under the openings of window blocks.
Reinforcement is performed along the length of the upper part of the aerated block stone.
The following materials are permitted for this work step:
- double steel wire frame connected by crossbars. It is laid in one layer;
- reinforcing bars with a cross-section of six to eight millimeters. They are laid in two parallel rows, having previously cut grooves in the block material.
Features of installing a foundation on screw piles for foam block houses
In general, laying a pile-screw foundation for houses made of foam block is similar to that for any buildings and includes:
- Foundation planning taking into account loads
- Preparing the site for the foundation
- Screwing in screw piles
- Concreting piles, trimming to level
- Installation of grillage on piles
We have already mentioned the features of foam block as a building material. They need to be taken into account when laying the foundation.
Since foam block houses can be much heavier than houses made of timber or frame houses made of wood, an appropriate margin of safety must be included in the calculation of a pile-screw foundation. In most cases, for a standard two-story foam block house, piles with a diameter of at least 108 mm and a wall thickness of 4-5 mm are chosen. Calculation of the load-bearing capacity of each pile shows that their number should be greater than for a frame house of the same size.
Often, to give additional strength to the foundation, not an ordinary wooden grillage is installed on the piles, but a concrete one, even up to laying a monolithic slab on the piles. Thus, there is a qualitative combination of the properties of a pile-screw and monolithic foundation. Using such foundations, it is possible to build quite massive houses on them.
You can read about such foundations on our website, here.
The depth of piles is also required to be relatively greater than in foundations for lighter buildings.
As for the installation of screw piles, of course, the mechanized method is preferable; the developer needs to prepare for this. This is due to both the high standard number of piles in a pile field and the parameters of the piles, as well as the depth of their screwing. Manually laying the foundation for a fairly large house made of foam block is a labor-intensive task, and it will take more time than using a pile drill. This will save money on paying for heavy equipment, but will increase the salary share of builders if the installation is done manually. However, options are possible for light buildings.