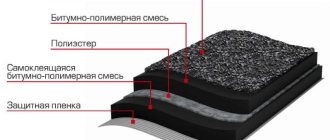
Structural elements of buildings and structures for various purposes are made from various materials: reinforced concrete, structural steel, brick, wood, fiberboard and chipboard, natural and artificial stone, glass, PVC and others. Depending on their hydrophysical properties, they differ in service life and have different safety margins. Bitumen waterproofing is one of the simplest and most inexpensive ways to increase the useful life of structures and their elements made of various materials.
Bitumen waterproofing: types of materials
All elements of buildings and structures need to organize waterproofing protection - external, internal, above-ground and underground:
- basements;
- foundation;
- floor;
- pipelines and highways;
- internal walls, joints and seams;
- external facades;
- roof;
- ventilation shafts;
- tanks;
- etc.
Bitumen belongs to the group of technical materials that are obtained by distilling crude oil during the oil refining process. Bituminous waterproofing today is represented by a wide range of materials that exist in many forms and types, but they all have a number of properties:
- good adhesion to various types of surfaces;
- protection of the base in conditions of high humidity, extremely high or low temperatures;
- the ability of the material to create an adhesive base;
- anti-corrosion properties;
- water resistance;
- heat resistance;
- long service life.
And most importantly, such material is one of the most inexpensive ways to organize reliable waterproofing on objects of any purpose.
Coating waterproofing technology
- The surface of the foundation is cleaned from dust and dirt. Sharp protrusions, corners and edges must be rounded to a radius of at least 3 cm using a grinder, otherwise the mechanical pressure of the soil or structures will cause damage to the waterproofing layer. If internal corners are to be coated, it is necessary to make fillets of triangular cross-section - with their help, the pressure of the backfill on the waterproofing layer is reduced. Cracks and seams are expanded to a solid base and sealed with cement mortar. Sinks are also covered with cement mortar - when covered, air remains in them, and after some time bubbles form, when they rupture, the continuous waterproofing layer is broken.
- To improve the adhesion of the waterproofing film to the base, so-called primers are used - primers designed for a specific type of coating. For bitumen mastics based on organic solvents, primers with the same type of solvent are used; for water-based compositions, water-soluble primers are used. The primer is applied to a dust-free base using a roller, and the corners are additionally coated with a brush. The drying time of the primer usually does not exceed several hours.
- Under bitumen and bitumen-polymer mastics, the first layer is applied with a quick-drying bitumen varnish, which ensures good adhesion. The varnish is applied with a brush, vertical strokes, or spraying over the entire surface of the foundation. Wait for it to dry completely.
- Prepare the mastic for application. The one-component solution is stirred and, if necessary, diluted with an appropriate solvent. Two-component mastic is mixed according to the instructions on the package.
- Apply the first layer of mastic with a wide brush, roller or spatula. The mastic is applied without gaps, carefully covering the corners to form a solid and tear-free coating. The direction of the strokes is vertical. Apply two or three layers of mastic in the same way, always waiting until it completely hardens. When working in sub-zero temperatures, the mastic must be slightly heated to improve its ductility.
- In the case of new buildings, it is necessary to reinforce the waterproofing to avoid damage during shrinkage. To do this, use fiberglass or fiberglass, gluing them onto the first layer of mastic so that they are completely moistened with it. It is also necessary to reinforce corners, fillets, and sharp protrusions with a chamfer with fiberglass.
- Bitumen mastic for hot use must be preheated to a temperature of 160-180 degrees in a metal container. Apply it with a spatula, leveling with a hard brush. Hot bitumen mastic is usually used for horizontal waterproofing of foundations, where a thicker layer and rapid hardening of the bitumen layer are required.
- After the mastic has completely dried, they begin to insulate the foundation or backfill the soil. For backfilling, sand should be used without foreign inclusions - they can damage the waterproofing layer. To reduce stagnation of moisture near the foundation walls and reduce hydrostatic pressure in areas with high groundwater levels, drainage is performed before backfilling.
Coating waterproofing is also used as additional protection for the foundation and as a sublayer for adhesive waterproofing. In this case, the preparation of the foundation surface is carried out in a similar way, including rounding sharp corners and making chamfers, installing fillets, as well as priming and coating with varnish or the first layer of mastic. Next, the adhesive waterproofing is performed.
Mastic and primer for additional protection are selected depending on the roll material: for roofing felt with a bitumen coating - bitumen-based mastic, for polymer materials - water-soluble mastic based on rubber and dispersed petroleum products, since bitumen is an aggressive material in relation to polymer coatings and can cause their destruction. Also, bitumen mastics based on organic solvents should not be used as unprotected waterproofing before insulating the foundation with polystyrene foam and polystyrene. It is better to choose a water-based polymer-based composition or cover the waterproofing with a cement primer.
Hot bitumen waterproofing
Hot waterproofing with bitumen involves a number of preparatory works. Solid pieces of material must first be melted, and only then the liquid composition must be applied to the surface using a special tool. This type of moisture insulation has a number of disadvantages:
- costs for preparing the liquid mixture;
- unpleasant odors, smoke and soot formation during preparation of the composition;
- if handled carelessly, thermal and chemical burns cannot be ruled out during preparation and application of the composition;
- the need to carry out waterproofing work in a short time - the composition quickly becomes viscous;
- you need special equipment or a platform to maintain the bitumen solution in a liquid state throughout the entire working process;
- long waiting time during the transition of bitumen from a viscous state to hardening;
- increased consumption of the composition for processing m2 of surface.
The use of such waterproofing is advisable at large facilities, where it is possible to use special equipment or organize a separate place for heating the bitumen. The consumption of bitumen per 1 m2 of waterproofing applied in one layer is about two kilograms.
Cold waterproofing based on bitumen
This category includes various types of mastics. Bitumen waterproofing mastic is a plastic adhesive paste consisting of various insulating components: bitumen, liquid rubber, polymers, mineral chips, resin, plasticizers, additives, etc.
Coating bitumen waterproofing is available in ready-made form, does not require preparation of the mixture, is easy to use and safe. In addition, it has a number of other advantages:
- adhesion to all types of surfaces;
- plasticity, elasticity;
- fast hardening;
- mechanical strength;
- ability to withstand significant temperature changes;
- resistance to ultraviolet rays and weathering;
- corrosion resistance;
- antibacterial and hydrophobic properties.
Depending on the main component, a whole range of bituminous materials for waterproofing can be distinguished, produced in the form of various compositions:
- bitumen mastic - protects against the effects of water and high humidity, but is not recommended for floors that are subject to significant temperature changes. In such conditions it simply collapses;
- bitumen-rubber paste fits perfectly on any base, does not delaminate, and has excellent adhesion. The mastic is environmentally friendly and can withstand heating up to +70°C, maintaining its properties;
- bitumen-rubber mastics - have high adhesion, are elastic, plastic, and can resist mechanical loads. They can withstand ambient temperature changes from -30°C to +130°C. This bitumen-based waterproofing with the addition of rubber is most often used for roofing, concrete, reinforced concrete, and as an adhesive when laying rolled materials.
Waterproofing mastics are supplied ready-made or produced in the form of a two-component material - a dry mixture and a solvent resin. Depending on the polymers and fillers included in the composition, such pastes can be universal or highly specialized.
Features of application
Waterproofing of foundations is required to prevent capillary penetration of water from the soil, as well as surface water, into the building through the thickness of concrete, as well as to extend the service life of the foundation.
Waterproofing the foundation with bitumen mastic is one of the oldest and most common methods of protection. The mastic applied in layers reliably protects underground structural elements from the harmful effects of water, which is always present in any soil.
If you decide to do the waterproofing work yourself, then the use of bitumen mastic can be called the optimal solution.
Construction bitumen as a material is a viscous structure of natural origin, which includes hydrocarbon ingredients and their various derivatives.
Depending on the included components, several types of mastic are produced:
- Bituminous;
- Bitumen-polymer;
- Polymer.
To waterproof small areas with your own hands, it is most convenient to use coating waterproofing, the basis of which is ordinary bitumen.
The waterproofing coating mixture is not durable, but is considered the most convenient, economical and quick-drying material. Bitumen mastic is environmentally friendly, easy to apply to surfaces, and has good adhesion.
Types of bitumen-based mastics
Today, among the abundance of mastics, we can highlight:
- Waterproofing. The paste contains mineral fillers, bitumen emulsions, synthetic resins and polymers. Such materials are used for moisture protection of individual parts of buildings and structures (walls, roofs, foundations, balconies, basements, pipes, metal and reinforced concrete elements).
- Bitumen-kukersol. They include Kukersol varnish, resin, latex emulsions, polymers and mineral fillers. They are used to fasten roofing coverings and provide additional protection. Among the features is the creation of a monolithic coating without joints or seams.
- Bitumen-rubber. The composition contains several types of petroleum bitumen, rubbers, mineral fillers, polymers, additives and solvents. Mastic is used for roof waterproofing, is used as an adhesive layer for roofing felt, roofing felt and other rolled materials, and can be used to organize the protection of structures, structures or their parts.
- Polymer. This bitumen-based mastic is used to protect plumbing structures, sewers, wells, and drinking water tanks. Eco-friendly material does not emit toxic and harmful chemicals.
- Sealing. They are a reliable means for treating seams, joints, crevices, cracks in reinforced concrete, concrete, steel and wooden structures.
- Fireproof. The paste is widely used for insulating stoves, fireplaces, and chimneys, since it is resistant to heating up to +1600°C.
- In addition, there are universal, soundproofing, butyl rubber, acrylic, epoxy and other types of mastics.
Such mastics are applied in a uniform thin layer to a previously prepared surface, which is cleaned of dust and dirt, and also dried. The bitumen consumption per 1 m2 of waterproofing applied in one layer is 1 – 2 kg (depending on the purpose of the mastic).
Applying hot coating material
- The procedure for applying hot bitumen to any surface must be carried out in special clothing in order to avoid body burns.
- Carefully monitor the movements of applying bitumen and protect the work area from children and unauthorized persons.
- Use temperature-resistant tools
- Do not use containers that may contain water.
Often this type of material is applied to a surface that has been previously cleaned of dust and dirt. This will increase the coefficient of adhesion of the liquid and provide maximum moisture - stability of the surface.
Apply the soluble material evenly and sparingly, taking into account the solidification time of the liquid. When working with hot bitumen, you should pay attention to its condition and monitor the tool.
In most cases, after some time, the material begins to harden in the container and strongly adhere to the coating tool. Under no circumstances should you use a tool that can become deformed due to temperature changes; this can lead to accidents during operation.
The most popular tools for using this material are: heat-resistant brushes, brooms and spatulas. To use a brush in the process of applying bitumen, you should take into account the length of its handle.
It should be long enough and strong enough to prevent hot substances from getting on your hand. On flat horizontal surfaces, you can use a regular household broom and spatula. These handy tools do a good job of evenly applying hot material to the surface.
Bitumen roll material for roof waterproofing
Bitumen roll material for roof waterproofing is represented by both timeless classics - roofing felt, roofing felt and glass roofing felt, and new polymer multilayer membrane materials on a self-adhesive basis:
- roofing felt Flexible moisture-proofing material on a cardboard base, impregnated with coal tar, without topping or with fine-grained and coarse-grained topping of mineral sand (GOST 30547-97);
- roofing felt Flexible material on a cardboard base, impregnated with petroleum bitumen with dusty, fine-grained and coarse-grained filling of talc and soapmagnesite (GOST 10923-93);
- glass roofing material Flexible insulating material on a fiberglass fabric base, impregnated with petroleum bitumen with dusty, fine-grained and coarse-grained filling of vermiculite sand, mica, talc and soapmagnesite (GOST 15879-70);
- glassine Waterproofing material without coating, made on a cardboard base impregnated with petroleum bitumen (GOST 2697-83);
- modern moisture-proofing roll polymers are an improved analogue of roofing felt. Depending on the manufacturer, they have different names: glass chrome, glass elast, elastobit, rubitex, stekloizol and so on.
Regardless of whether bitumen-based coating waterproofing or rolled bitumen material is used, the coating is effective, strong and durable, and its reliability is beyond doubt and has been tested for decades.
Application nuances
The prepared mixture is applied using a brush or roller, depending on the complexity and volume of work. In more rare cases, mastic is applied using a wide spatula.
Work order:
- Apply the material overlapping so that the layers overlap each other by 5-10 cm.
Application with a spatula
- A new layer is applied after the previous one has cooled slightly.
- For rooms where there is a swimming pool, or for roofing work, 2-4 layers of similar insulation are used, which are then further reinforced with fiberglass mesh and further insulated.