What materials can be used for work
Let's look at the most popular materials:
- Gidroizol - is used as a sheet material that matches its own technical parameters with standard roofing felt.
- Stekloizol - used to protect the foundation, it is based on fiberglass, which is a very moisture-resistant component.
- Gidrostekloizol - has in its structure elements of the two products listed above, it is used to work by gluing or even burning with a gas burner.
- Glassine is a little different from other insulators, since the base is cardboard, which is impregnated with oil.
- Roofing felt - you can use the simplest one, or high-quality euroroofing felt. Quite often it is the ideal choice of homeowners, as it intelligently combines excellent quality and affordable cost.
- Materials based on bitumen, namely resins. It does not have pores in its own structure; after heating and further cooling, it forms a thin elastic film on the surface of the processed product, which is waterproof.
- Technoelast is a rolled product that has an important quality (it protects the surface from the appearance of microscopic organisms - mold and mildew.
- Polymer-based membranes. It has a huge service life, reaching half a century, and at the same time weakly resists mechanical damage, but the base will be very good.
- Rubber with a liquid consistency is convenient because when it is used, seams will not form on the surface, and the insulation itself will have a homogeneous and evenly distributed structure.
- Uniflex is a product made on the basis of foil. In addition to the protection function, it reflects heat, namely, it provides increased heat conservation.
- Elon is a material based on two layers, it perfectly resists the influence of temperature, and can also withstand radiation.
- Benite mats are mineral insulators of environmentally friendly origin. Considered extremely reliable.
- Dry mixtures have a cement component and are used much less frequently. These include products such as calmatron, penetron and hydrotex.
Insulation of the strip base can be successfully done using all the insulators listed above.
Materials for horizontal waterproofing and technology for their installation
Horizontal cut-off can be made from different materials with different characteristics and methods of construction. The choice of the right material depends on the type of structure and the material from which it is made.
Rolled adhesive waterproofing
Pasted waterproofing is made mainly of bitumen-polymer materials. There are lining rolls based on fiberglass impregnated with a bitumen-polymer binder and protected on both sides with polypropylene material, and there is a self-adhesive baseless material, it is obtained by applying a self-adhesive bitumen-polymer binder to an anti-adhesive film, followed by covering the binder on the front side with a polymer film .
Adhesive waterproofing is supplied in rolls of various sizes and colors. Pasting sheets are intended for the installation of cut-off waterproofing , as well as for the protection of foundations, walls, floors and basements from the inside and outside.
Structure of adhesive waterproofing
Advantages of adhesive insulation:
- Easy installation, which does not require special equipment;
- Long service life;
- No hot work.
Technology for installing self-adhesive pasting materials on the horizon:
- It is necessary to clean the base from dust and dirt;
- Prime the bases with bitumen primer;
- Open the self-adhesive roll from top to bottom;
- Stick the rolls on a horizontal or vertical surface, pressing them to the base. When installing vertical waterproofing, it is necessary to secure the upper edge of the sheet with a metal edge strip.
Detailed instructions for installing adhesive waterproofing on a horizontal base can be downloaded by clicking on the link: Installation instructions for adhesive insulation
Roll fused waterproofing
Rolled fused sheets are produced by double-sided application of a bitumen binder, consisting of bitumen, filler and various additives, onto a fiberglass or polyester base. The bitumen layers on top and bottom are protected by easily combustible polyethylene film.
Welded rolls are supplied in various sizes and are intended for work related to waterproofing foundations, roofs, walls and other structures.
Advantages:
- Durability;
- Can withstand relatively heavy loads;
- Good heat resistance;
- Frost resistance;
- Non-toxic.
Installation technology:
- Surface preparation;
- Prime the surface using a bitumen primer;
- Fusing rolls using a torch.
Detailed instructions for installing built-up waterproofing can be downloaded by clicking on the link: Instructions for installing a waterproofing membrane made of bitumen-polymer roll materials
Penetrating waterproofing
Penetrating compounds are made from special cements, graded aggregates, organic additives and chemically active substances. Penetrating materials are known to crystallize in the pores of treated concrete. Due to their unique properties, penetrating agents are able to stop the passage of water through concrete structures, as they form poorly soluble crystals in the filled capillaries and pores at the treatment site.
Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly;
- Complies with the hygienic standards in force in the Russian Federation.
Device technology:
- The surface to be treated must be moistened abundantly;
- Apply the penetrating composition using a brush or roller;
- Moisten the area where the material was applied generously every 10-16 hours for 4-6 days.
Scheme of operation of penetrating compounds in the concrete structure:
Scheme of operation of penetrating compounds in the structure of concrete
Injection waterproofing
Injection waterproofing involves the use of various epoxy resins and helium compounds to be introduced into the body of the structure or its cold seams. Injection formulations differ in varying degrees of viscosity, flexibility and behavior of the material when in contact with water.
Selecting the correct injection formulation to suit the specific project requirements is the first key success factor and can have a significant impact on the efficiency of the job completed.
Injection itself is the procedure of pumping cement, polyurethane, epoxy or acrylate material into damaged or cracked structures to reliably seal, eliminate leaks, repair damaged structures and restore their waterproofness for a long time.
Advantages of the injection method:
- Can be used to seal various substances such as concrete, brick, stone and other natural substances;
- Can be used at any stage of construction, including during initial construction or later for life extension or renovation, depending on the specific requirements of the project;
- Can be used both outside the room, foundation or basement walls, and inside;
- Suitable for waterproofing the body of a structure, as well as for waterproofing seams (cold, concreting, expansion joints, etc.);
- Injection waterproofing is one of the most effective methods of eliminating leaks from inside a private home or building.
Important: There are three main success factors that go into ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of injection projects. It is very important that the correct combination of injection materials, injection equipment and injection method is selected.
Scheme of operation of horizontal injection waterproofing:
Scheme of operation of horizontal injection waterproofing
You can read more about injection in the article – “Injection waterproofing”
Liquid rubber
Liquid rubber consists of modified bitumen, latex, binders and other polymers. When a surface is horizontally coated with liquid rubber, a waterproof coating is formed that can withstand the movement of any structure and even the shrinkage of the foundation of a house, since liquid rubber has an excellent coefficient of elongation and elasticity.
Advantages of liquid rubber:
- No seams;
- Elasticity above 800%;
- 100% adhesion to the surface;
- Ability to cover an area of 400 m2 per day (using spraying).
Technology of horizontal water protection device:
- Removing sharp corners and flaking elements;
- Surface anesthesia;
- Application of primer (primer);
- Spraying or applying liquid rubber.
horizontal application of liquid rubber
You can read more about liquid rubber in the article – “Waterproofing with liquid rubber”
Differences between the main types of insulation in the table
Open table
The following table compares the main types of waterproofing:
| Liquid rubber | Roll welded and pasted | Penetrating | |
| Presence of seams | No | Yes | No |
| Adhesion to horizontal base | 100% | 40% | 100% |
| Elasticity coefficient | 600-800% | 20-90% | No |
| Installation method | Spray or brush and roller | Fusing with a torch | Brush and roller |
| Application according to foundation type (recommendation) | Slab Belt | Tape | Not recommended |
| Material life | 40 years | 10-30 years | 5-6 years |
| Warranty period for work | 7 years | 3-5 years | 1-2 years |
Types of waterproofing
Protection of the foundation from moisture can be horizontal or vertical. For both types of waterproofing, different materials can be used, which will be discussed further.
Horizontal
The peculiarity of this insulation is that it is performed only during the construction of the foundation of the house. First of all, it protects the foundation from the effects of groundwater.
The horizontal insulation option is made from a variety of membrane materials on a bitumen, polymer or synthetic basis. The most commonly used material for this type of protection is roofing felt. If a basement is planned in the house, most often horizontal waterproofing will be carried out simultaneously along the upper and lower sides of the floor slab.
Vertical
Vertical moisture protection can be done in an already built house. This type of protection is needed to prevent groundwater from affecting the foundation material of the house.
As mentioned above, not all types of foundation require such insulation. However, when constructing a strip and column base of a building, vertical waterproofing is always needed. To install vertical insulation, you can use different methods and materials, which will be discussed in more detail below.
Pasted insulation
For this type of protection, roll materials are used, which are attached by fusing or gluing. Fused materials have an adhesive layer that heats up and sticks to the surface. To secure the material without an adhesive base, it is necessary to use bitumen mastic, which will act as a connecting component.
The following materials are used to perform adhesive insulation:
- Glassine. The average price for 1 roll is 150 rubles. The material is made on the basis of thick cardboard, which is impregnated with a bitumen composition. Glassine does not make the most reliable and durable insulation, but it is a great way to save money;
- Ruberoid. The average price for 1 roll is 350 rubles. This material is a leader among rolled types of insulation, as it has a low price and a long service life;
- Bitumen-polymer material. This is the most reliable and durable option, but it costs more than others. The average price for one roll of bitumen-polymer material is 1,000 rubles. As an example of such insulation, the following common options can be cited: TechnoNIKOL, Linokrom, Gidroizol, Bikrost and Stekloizol.
Coating insulation
To insulate the foundation in this way, bitumen-based mastic is most often used (average price - 350 rubles per 20 liters). In addition to simple bitumen compositions, you can buy more modern options in construction stores:
- Polymer resins;
- Bitumen-polymer resins;
- Bitumen-rubber mastics.
Conventional bitumen mastic differs from modern compositions in that it is unstable to low temperatures (it cracks in the cold).
More modern mixtures have additional additives that allow them to be resistant to cold. They have only one drawback - the high price (on average from 3,000 rubles for 20 liters).
Penetrating insulation
Penetrating insulation prevents moisture from entering the concrete capillaries, thereby increasing the strength of the top layer of this material.
This insulation option is only suitable for concrete foundations. If you use penetrating compounds on brick or stone, they will not work.
The most popular compositions for penetrating insulation are these:
- Penetron (on average 1,500 rubles per 5 kilogram);
- Peneplug (on average 1,200 rubles per 5 kilogram);
- Hydrohit (on average 1,000 rubles per 5 kilogram);
- Penecrit (on average 1,300 rubles per 5 kilograms).
It is recommended to use this protection technology for new homes, since penetrating mixtures must be applied to thoroughly cleaned, degreased and smooth surfaces.
Mounted insulation
Mounted waterproofing is used mainly for strip foundations, if it is necessary to protect the basement from high groundwater pressure.
The best option for mounted insulation is considered to be a steel caisson. This option involves lining the walls and floor of the basement from the inside using steel sheets, the thickness of which is 4-6 mm. This is a rather expensive option, so it is used extremely rarely.
Technology of horizontal waterproofing according to the type of foundation
The technology and method of waterproofing the horizon may vary depending on the type of foundation and its structure, since each foundation has its own characteristics.
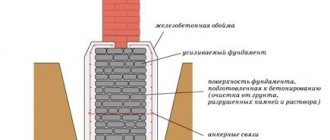
Horizontal waterproofing of strip foundation
Waterproofing on the horizontal surface of a strip foundation is recommended to be made from glued, fused or mastic materials, the latter forming a reliable seamless coating with 100% adhesion to the base. When choosing coating materials, it is best to use liquid rubber or high-quality mastics applied in 2-3 layers.
When performing work related to insulating a strip foundation, horizontal protection must be applied in 2 places: 1. between the foundation base and foundation blocks (No. 1 in the diagram) 2. between the blocks and the subsequent wall (No. 2 in the diagram).
The horizontal protection of the tape will serve as a cut-off and will not allow capillary moisture to rise through the blocks and exit indoors in the form of a wet or damp spot.
Installation diagram of horizontal waterproofing strip foundation:
Installation diagram of horizontal waterproofing strip foundation
Horizontal waterproofing of slab foundations
When installing a slab foundation, a rigid base is first installed, on which a slab, the so-called footing, will be erected, and it is on it that the first contour of horizontal insulation is applied. After pouring the slab, before erecting the walls, horizontal waterproofing is applied to the slab (2nd circuit). After the walls are erected, the vertical waterproofing is joined to the horizontal, thereby forming a water lock.
To protect the slab foundation on the horizon, the following materials may be suitable:
- Welded;
- Membrane;
- Pasting;
- Coating;
- Liquid rubber.
Recommendation: when using liquid rubber as waterproofing, the result is an elastic, seamless rubber coating with complete adhesion to the surface, which makes this material an ideal option for long-term protection of slabs and other foundation elements from water and moisture. Characteristics such as the absence of seams make liquid rubber a more reliable and durable coating, and elasticity will prevent the material from cracking or coming apart at the seams when the foundation shrinks.
Diagram of the installation of different horizontal waterproofing of a slab foundation
Scheme of horizontal and vertical waterproofing of a slab foundation
Horizontal protection of pile columnar foundation
In a pile construction, waterproofing is laid only at the end of the pile at the junction between the end of the foundation and before the construction of the walls of the house. The location of the insulation may vary depending on what the grillage is made of.
- Bored piles under the building made of concrete and concrete grillage – Insulation is laid between the installed grillage and the constructed wall of the house. This system is used to prevent the impact of structures with different characteristics.
- Metal screw piles with a grillage made of wood - in this case, insulation is placed on the top of the piles to separate the metal and the subsequent structure.
Scheme of laying waterproofing in a pile foundation on the horizon
Scheme of horizontal waterproofing of a pile foundation
Waterproofing methods
There are two main ways to waterproof a strip foundation - horizontal and vertical methods, each of which is carried out using a specific technology, using certain materials.
Horizontal
It is necessary to think about how to waterproof a horizontal strip foundation at the design stage of the structure. Preparatory activities can take up to 17 days (in addition to the main work). Horizontal insulation protects the foundation from capillary groundwater in the corresponding plane. It must include a drainage system, equipped when groundwater occurs at a high level.
A solid base is made under the tape, and a layer of waterproofing is mounted on it. Often, for this purpose, a cushion is created that is thicker than the future foundation. The simplest option (suitable for a bathhouse, garage, etc.) is to make a screed of cement and sand in a 1:2 ratio.
Technology for arranging horizontal waterproofing:
- Filling the bottom of the pit with sand in a layer up to 30 centimeters thick, tamping.
- Fill the cushion with a cement screed in a layer of 6-8 centimeters, harden for 2 weeks.
- Covering the screed with bitumen mastic, installing roofing felt sheets on top of the bitumen layer, repeating layers of mastic + roofing felt. Cement screed is poured on top in a layer of 6-8 centimeters and hardens.
- Construction of the foundation.
In some cases, drainage may be necessary: if the depth of the structure is below or at the level of groundwater, when the permeability of the soil is low and moisture can accumulate in it.
Performing drainage:
- 100 centimeters from the base, along the perimeter of the structure, a pit is dug up to 30 centimeters wide and 25 centimeters deeper than the depth of pouring the foundation. The pit should have a slope towards the drainage basin, where water will accumulate.
- Covering the bottom with a layer of geotextile, overlapping it with the walls by at least 60 centimeters.
- A layer of gravel 5 centimeters thick is laid.
- Installation of a drainage pipe with a slope to the catchment area of about 5mm/1 linear meter.
- Filling the pipe with a 25 centimeter layer of gravel, wrapping the sandwich with the geotextile edges left earlier, backfilling.
Such measures allow water to enter the pipe, eliminating the possibility of it clogging. Moisture will flow freely into the reservoir.
Vertical
This type of waterproofing of a strip foundation involves treating ready-made foundation walls with different materials. Work can be performed both during the construction of the building and after its completion. In addition, vertical insulation from water can be primary (when special hydrophobic additives are used in the construction of the structure to increase the resistance of concrete to moisture) or secondary (if the first type of insulation was not performed).
Depending on the installation site, vertical waterproofing can be external or internal. To accomplish the task, plastering and coating compounds, paint and varnish coatings, various sealing impregnations, lining materials, antiseptics, biocides, etc. are used.
The need for vertical waterproofing:
- When the foundation is affected by moisture from the soil, which is retained in the soil by adhesive or capillary forces and remains there permanently, regardless of the levels of groundwater and filtration water.
- If melt and rain water fills the pores in the soil and gets deep into the ground, seeping into the depth of the foundation.
- When the surface layer of underground moisture lies close.
Usually, not only the underground part of the foundation is isolated, but also the above-ground part, in order to exclude the influence of water rising up through the capillaries.
Which method is most optimal?
Experienced craftsmen, answering the question of whether it is necessary to waterproof a strip foundation, claim that both types are necessary and desirable. Both horizontal and vertical protection are required - only in this case can a long service life of the building be guaranteed and the absence of any structural damage.
Restoration of horizontal waterproofing
If at the construction stage the horizontal cut-off waterproofing between the wall and the foundation was not made or was made with violations, then its restoration after the walls have been erected is possible only with the use of injection waterproofing .
When injecting from inside a constructed basement, plinth or other room, the polyurethane injection resin under pressure penetrates into the space between the foundation and the constructed wall, thereby restoring horizontal waterproofing, which also serves as a cut-off for water and moisture that cannot rise capillarily up the wall.
Waterproofing restoration technology on the horizon using injection:
- Dismantling of finishing elements that interfere with reaching the base of the cold seam of the slab-to-wall junction. Such elements can be tiles, screed, drywall and plaster on the inside walls of the basement;
- Installation of a small fine at the junction of the wall and the foundation surface;
- Layer-by-layer compaction of expanding sealant into the made groove. This procedure is necessary so that when polyurethane resin is injected into a seam, the composition spreads horizontally into the wall itself, and does not come out back through a weak joint;
- Drilling holes at an angle of 45 degrees to the center of the cold seam or the junction of the foundation and the wall;
- Installation of injectors or packers into drilled holes;
- Connecting the injection pump to the installed packers and injecting the injection composition;
- Dismantling of installed packers and sealing the holes with a special expanding sealant;
Detailed recovery scheme:
Scheme for restoring horizontal waterproofing using the injection method
Methods of vertical moisture insulation
Waterproofing of the foundation of the house is required to be carried out in accordance with SP 28.13330.2012. For these purposes the following materials are used:
- paint and varnish and impregnating compositions;
- mastics;
- waterproof plaster mixtures;
- self-adhesive or weld-on products in rolls.
Protected base
Based on the installation technology of the protective coating being created, waterproofing is divided into the following types:
- welded;
- coating;
- plastering;
- injection;
- impregnation;
- sprayed.
Use of coating materials
Do-it-yourself foundation waterproofing with coating materials is carried out using bitumen-polymer or bitumen mastics. When applied, a waterproof layer is formed on the surface.
When there is hydrostatic pressure, then coating materials are used as follows:
- bitumen mastics are used if the pressure does not exceed 2 meters;
- when it is from 2 to 5 m, then they work with bitumen-polymer compositions.
Applying mastic
Mastics are applied to the work surface in several layers: from 2 to 4. This is determined by the depth of the foundation:
- if it is up to 3 m, then a layer 2 mm thick is formed;
- when the depth is up to 5 m, then the height of the protective coating is chosen from 2 to 4 mm.
The advantages of the material are as follows:
- relatively low price;
- no special skills are required to apply mastics;
- high degree of elasticity and adhesion.
But the service life of the created bitumen coating is about 6 years. Then it becomes covered with cracks. To increase the period, polymer substances are added to the composition of the product.
The coating technology consists of the following manipulations:
- prepare the working surface of the foundation, clearing it of dirt;
- reinforce joints using fiberglass tapes;
- processed using a roller (brush), primer (primer);
- wait for it to dry completely;
- then apply the required number of layers of mastic.
Pasting with roll products
This method involves both the use of only rolled products and their use in conjunction with mastics. The traditional working material in this area is ordinary roofing felt. It has been replaced by modern roll products with improved performance characteristics. An example of this is products from. The service life of the created waterproofing when used is up to 50 years.
The average thickness of the protective coating layer is 5 mm. It is determined by the type of waterproofing material used. The material can be applied in 2-3 layers.
Work with roll materials as follows:
- clean the surface of the foundation from dust and dirt;
- treated with a primer;
- cut fragments of the required length from the roll;
- apply adhesive mastic;
- fix the pieces on the surface of the base.
Fusing of rolled insulation
If fragments of material are fixed by heating them with a torch, then the method of fixation by fusing is obtained.
Plastering with waterproof mixtures
Another way to protect against water is to use waterproof plaster mixtures. Compositions such as hydroconcrete and polymer concrete are used.
The technology of work is similar to plastering walls using beacons. In this case, the thickness of the applied layer should be at least 2 cm.
The advantages of the option are:
- comparative cheapness of working material;
- no need to create a perfectly flat surface;
- ease of work.
Plastering the foundation
The disadvantages of this method are the following:
- the level of resistance to moisture is inferior to rolled and coating materials;
- Waterproofing made in this way has a short service life: after about 5 years it begins to crack.
Waterproofing technology
First, you will have to determine a set of waterproofing works, taking into account a number of conditions:
- soil heterogeneity;
- groundwater level at the site;
- operational conditions of the future building.
If the groundwater level is more than a meter below the foundation, a horizontal waterproofing layer of roofing felt coupled with a vertical coating layer will be sufficient. And if the groundwater is closer than a meter from the base of the foundation, but does not reach the basement, the scope of work will have to be expanded:
- perform horizontal waterproofing in 2 layers, coating the space between the layers with mastic;
- Vertical insulation should be equipped not only by coating, but also by pasting.
If you have enough budget, all surfaces of the foundation and basement should also be treated with penetrating waterproofing compounds.
In extreme cases, when the groundwater level is higher than the foundation or a particular area is characterized by heavy rainfall, it will be necessary to design a drainage system in addition to waterproofing measures.
conclusions
Protecting the foundation from negative moisture influences is a responsible and quite complex matter. And if you decide to install waterproofing yourself, you should remember that the keys to success in this situation are:
- correct choice of material;
- competent determination of the method of waterproofing;
- as well as compliance with the sequence and timing of the necessary work.
If you do everything correctly, follow the instructions and listen to the opinions of experts, you can hope that the rebuilt foundation and the house above it will last a long time, without requiring major repairs.
( 67 votes, average: 4.90 out of 5)
How to make a wooden gazebo with your own hands: step-by-step instructions
Building a cellar with your own hands: step-by-step instructions