Problematic and weak-bearing soils occupy a significant area of Russian territory.
The use of traditional strip foundations in these conditions is difficult or even impossible and more efficient options for supporting structures are required.
The most successful solution is pile foundations, which can provide strong support on dense soil layers located at a considerable depth.
Such foundations allow the construction of massive and tall buildings in areas where the creation of strip foundations is almost impossible.
The most common option for implementing such structures is a pile-grillage foundation, which should be discussed in more detail.
What is a pile-grillage foundation?
A pile-grillage foundation is one of the main options for implementing a pile foundation, consisting of a system of vertical supports and a strapping belt in the upper part.
The supports (piles) are immersed in the ground, bypassing the upper unreliable layers, reaching dense layers and forming stable, fixed anchor points.
The strapping belt - the grillage - acts as a kind of strip foundation , but not installed on the entire length of the sand cushion, but rigidly fixed to the tops of the piles. The grillage beams, as well as the tape, are located under all the load-bearing walls of the house, forming a strong support system.
As a result, the load from the weight of the house is taken by the grillage and transmitted through a system of piles to dense layers of soil.
This distinguishes a pile-grillage foundation from a pile-tape foundation, which has a very similar design, but differs in that the tape, in addition to the piles, also rests on the ground surface, somewhat relieving the vertical supports.
A completely different type of load transfer occurs, so these two types of foundation should not be confused.
IMPORTANT!
Despite the significant difference in the design of different types of piles, almost all types of pile foundations are pile-grillage foundations.
Pile-grillage foundation for aerated concrete
When choosing aerated concrete for the construction of a residential building, developers decide on the type of foundation that is most optimal for such a building material. The porous structure of aerated blocks makes them relatively light, which means there is no need to build large, heavy foundations.
In order for the foundation of the house to be reliable, you need to choose the right type and calculate the construction technology. For all types of foundations, there are criteria by which the possibility of using a particular foundation is assessed. This is an indicator of the heaving of the soil, the depth of its freezing, the height of groundwater, the total weight of the building (walls, ceilings, roofing and interior).
In areas of weak soils, heaving and floodable, with a large freezing depth, an excellent solution for a lightweight house made of aerated concrete is a pile-grillage foundation. Its arrangement does not require large volumes of excavation work, results in affordable sums and allows installation without the use of special equipment, on your own.
This type of foundation is based on piles, the installation and arrangement of which takes less time than, for example, a concrete strip. At the same time, the uniform distribution and transfer of loads and deformations from the house to the ground is carried out by a reinforced concrete grillage.
In order to use the screw method of installing piles to create this type of foundation, they are chosen to be steel, with a pointed tip and a screw to simplify the screwing process. Then, using a special tool, you can install the piles yourself. Reinforcement is installed into the installed pile and concrete solution is poured. This is the most expensive of pile foundations.
Cast-in-place and bored piles can be used for aerated concrete. Rammed ones are created directly on the site: holes of the required depth are made in the calculated locations, asbestos-cement pipes are inserted into them and filled with concrete. To increase strength, additional reinforcement is used. Bored piles are manufactured in a factory and installed directly on the site.
When installing piles of any type, you need to be absolutely sure that they rest on solid ground, and that during the installation process there is no shedding of soil inside the pipe or formwork. Piles of any type protrude above the soil surface along with reinforcement threads. A waterproofing material (most often roofing felt) is laid on top of each pile and the installation of formwork and reinforced belt for the grillage begins. A grillage for an aerated concrete house is a monolithic reinforced concrete strip between piles, connecting them into a single system. The height of the grillage above the ground is from 10 to 40 cm and the distribution of loads is as follows: a high grillage is the load on the lower layers of the soil, a low grillage is the load on the grillage itself.
Is it suitable for a house made of aerated concrete?
The bearing capacity of pile-grillage foundations can reach very high values, limited only by the properties of the soil and the capabilities of the piles.
Increasing their number or creating support platforms under the lower ends of the shafts can significantly increase the bearing capacity and reduce the specific load on the ground, increasing the efficiency of the structure.
Aerated concrete weighs almost 5 times less than the weight of brick, and its strength is 4-5 times lower.
This means that a house made of aerated concrete cannot be multi-story, and its weight is much lower than that of buildings made of brick or ordinary concrete.
Therefore, the capabilities of a pile-grillage foundation for a house made of aerated concrete are not just sufficient , but even excessive, allowing you to safely use this type of support structure.
Types of foundations for a house made of aerated concrete
Screw piles can be installed on any soil and with any relief.
Lightweight concrete with gas filling has the disadvantage of fragility; because of this quality, the walls crack at the slightest subsidence of the soil under the foundation. Strip foundations can only be made at shallow depths, because low-slung foundations will be pushed out by lateral soil pressure. In deep supports, the sides experience indirect stress, and the light weight of the structure cannot keep the structure from being pushed out by the heaving layer.
The foundation of a house made of blocks on screw piles is least subject to the forces of pulling, twisting and bending, because the walls have a small surface and rest with their tip on a solid layer of earth. The support rods have sufficient rigidity and are little deformed during the construction of the house and operation. The foundation of a building made of aerated concrete is chosen taking into account its stability in the ground, so that the walls do not experience fault loads.
Columnar
Columnar base
Columns are placed at important points around the building's perimeter. Little money is spent on such a basis, but its application is limited by certain conditions. You cannot install poles if the house is being built on a slope with a large difference in heights on one site. Landslide and loose soils are not suitable for columnar foundations.
Requirements for the foundation:
- a durable layer of soil with a low level of soil liquid is used;
- the heel of the element is located below the freezing mark by 20 - 30 cm;
- towards the bottom of the column it expands like a glass to increase the square of support;
- The rigidity of the structure is provided by a reinforced reinforced concrete grillage.
The pillars can be square or round, the material is wood or reinforced concrete, sometimes they make metal supports with insulation. The grillage is made by pouring into the formwork with the preliminary installation of the reinforcement cage.
Monolithic
Foundation slab
It is a solid slab of concrete with stiffening ribs in which metal rods are installed for reinforcement. Mounted so that the bottom and side surfaces do not come into direct contact with the soil and do not absorb moisture. To do this, various cushions are made of sand, gravel, crushed stone, and geotextiles are placed under the base.
Types of monolithic slabs:
- the in-depth version is made below the freezing mark and is used in the construction of buildings with a basement;
- a floating type or a non-recessed one is placed on the surface if there is no basement.
In the construction of the foundation slab, two concrete layers are made (preparation and slab), a reinforcement cage in cross members for rigidity, a metal mesh is installed over the entire area, waterproofing and protection from the cold are laid. Concrete grades M250 and M300 are taken and anti-frost modifiers and additives against moisture absorption are added to the mixture.
Tape
Strip foundation
A buried monolithic foundation is not used for a house with walls made of aerated concrete; a foundation is made with a shallow immersion depth. Shallow concrete strips are placed so that their base is in the freezing zone of the soil. This option is suitable for dense soil, but in swelling layers it will be squeezed out when frozen. If the layer contains moisture or is fed by it from rain and snow, over time the shift will lead to the appearance of cracks on the walls.
It is not advisable to build a strip foundation under long-length aerated concrete walls. Concrete does not work well in bending and stretching, so increasing the length leads to a loss of strength. It is necessary to lay sand and crushed stone bedding, lay geotextiles and make thermal insulation of structures.
Base structure
The pile-grillage foundation is a support system, which includes:
- Pile system . These are vertical rods, metal, concrete or wood. They are immersed in the ground until firm contact with solid layers occurs. Alternatively, the so-called “hanging” piles held in the ground due to the frictional force of the soil and the side walls of the shaft. Suspension piles are used less frequently because they require a long shaft, which is not always possible. In addition, friction piles are prone to gradual settlement, especially in waterlogged soils.
- Grillage . It performs a double function - it connects all the trunks into a single rigid system, which greatly increases the load-bearing capacity of each unit, and also acts as a support line for load-bearing walls, external and internal. There are wooden (timber), metal and concrete grillage structures used in conjunction with the appropriate type of piles and wall material.
Features of the design of a pile-strip foundation for a house made of aerated concrete
A pile-strip foundation is a combination of a simple pile foundation and a shallow strip foundation.
Different parts of such a foundation harmoniously complement each other, each performing its own task - the piles are held deep in the ground, and the tape takes on the load from the building, evenly distributing the pressure created by its mass.
Therefore, such a foundation is excellent for heaving soils with a deep frost horizon, as well as for soils with a soft, mobile top layer, for example, sandy.
Even with strong movement of soft, loose soil, the piles will hold the house in place and will not move even a few centimeters.
If the soil on the site raises concerns that the building may begin to “float” due to the instability of the upper layers of the soil, or it will sink in the winter due to a high level of heaving, then it is necessary to use the pile-tape option, which ensures that the house or other building standing on it, will be stable in any climatic and geological changes. Since aerated concrete is a relatively lightweight material, in combination with a pile-strip foundation it is an excellent solution for building houses on difficult soils.
Read also: Pile grillage foundation pros and cons, features, advantages and disadvantages
The design of such a foundation is a strip that runs under all the load-bearing walls of the house without interruption, buried approximately 60-80 cm depending on conditions, and continues deep into the piles.
Large-diameter pipes are most often used as piles, which are reinforced inside in the same way as tape, and then filled with concrete.
The number of such “legs” is determined by the load on the foundation and the characteristics of the soil, but should be no less than two meters. The depth is determined by the freezing horizon and the thickness of the layer of soft, mobile soil with a high level of heaving.
Pile reinforcement
Reinforcement of piles occurs in conjunction with the tape and special attention is paid to the places where the belt of the tape intersects with the one going into the pipe.
In these places, the fastening must be especially reliable and resistant to bending effects in case the house “leads” to the side.
Wells for pipes
Wells for pipes are subject to primary waterproofing, usually performed using roofing felt, and at the bottom of each of them a base is created for a concrete pile.
Such measures increase the stability of the entire foundation mass and more or less protect the pile pipes from corrosion.
In many cases, instead of metal pipes, asbestos-cement pipes are used to create piles.
They are also a good option, as they are resistant to frost and humidity, but it won’t hurt to waterproof them. To do this, a pipe is formed from roofing material, which is lowered into the well and, after being released, straightens along the walls, creating more or less acceptable protection.
It is also possible to use rubble stone as a basis for filling wells, which is poured into the formwork and filled with cement mortar or concrete with fine gravel. This option requires less concrete, but is a little more expensive due to the cost of rubble stone.
Read also: Drilling technology for pile foundations, useful tips
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of a pile-grillage foundation include:
- Relatively simple construction technology.
- Possibility of independent production and installation of all elements.
- There is no need to hire a large team of construction workers.
- Material consumption is noticeably lower compared to the recessed type of tape.
- The dependence of the foundation on soil heaving processes is practically absent.
- The rigid connection of piles and grillage forms a system that is resistant to all loads and does not react even to trains passing nearby.
- You can work almost all year round, excluding days with frost below -10°.
- Lack of contact with frozen soil contributes to heat retention of house structures.
- Possibility of construction on a slope or fold of the terrain.
- The cost of such a foundation is noticeably lower than the cost of building a traditional belt.
The disadvantages of a pile-grillage foundation include:
- The possibility of creating a basement or ground floor is practically non-existent.
- If the weight of the house exceeds 50 tons, you should choose a different base option.
- It is necessary to carry out a thorough and professional analysis of the soil, calculate its bearing capacity and other features in order to accurately determine the number of piles and the shape of the pile field.
- In the absence of vertical heaving loads, lateral impacts on the pile remain and create considerable forces that can deform or destroy the support.
- During construction it is necessary to use special equipment.
NOTE!
Most of the disadvantages are characteristic of all types of pile foundations and are a feature of the supporting structure of this type.
Pile-grillage foundation
The foundation is a concrete base, often reinforced, that serves as a reliable basis for building a house, preventing subsidence and premature destruction.
A pile is a technological element of the foundation of a building, a rod of various shapes (cylinder, square, screw), made of wood, metal, reinforced concrete, buried in the ground to give strength to the foundation. Rod supports immersed in the ground bypass problematic rocks, reaching hard, stable layers, forming reliable, stationary nodes for tying the load-bearing base to the ground.
A grillage is an additional element of columnar, pile structures, formed in the day zone. Strengthens load-bearing elements (pillars, piles), evenly distributes the main and additional load created by the house. Made from a reinforced concrete belt, looped along the contour.
Piles with grillages are used on complex terrain, in conditions of heaving, weak soil rocks.
- If you need to build a house next to a pond, there is only one solution - a pile foundation.
- If the soil noticeably “walks” in winter, there is a reasonable suspicion that the soil has a complex multilayer structure; a pile foundation with a grillage is the solution.
In heaving soils, it is necessary to either build “floating” surface foundations or deepen them to significant depths, which is impractical. SRFs combine properties and characteristics, with the loss of physical activity - the weight values are less than those of buried analogues, it is impossible to build a ground floor or basement.
In terms of price gradation, SRF belongs to the middle category, located between shallow and buried foundations. If we compare the cost with its main competitor (slab foundation), then SVF is different - it costs less on building materials, and no excavation work is required.
Existing types
There are different design options for a pile-grillage foundation:
- Driven piles.
- Bored piles.
- Screw piles.
Driven piles are driven using special machines . They can be made of reinforced concrete, metal or wood, although the latter option is already very rare.
For self-installation, bored and screw piles are suitable, which can be made directly on the site (bored) or purchased ready-made and driven into the ground using muscular force.
The greatest load-bearing capacity is provided by driven concrete piles manufactured at specialized enterprises using special technology.
At the same time, the installation of such piles is the most labor-intensive and complex procedure, requiring the participation of professional and experienced builders with the appropriate equipment.
Most often, bored piles are used, which are a monolithic concrete casting into a pre-prepared well .
All work can be done with your own hands, and the dimensions of the well and the features of its base make it possible to form a large-area support platform, inaccessible to frost heaving loads.
Screw piles have been used relatively recently, so most users regard them with some doubt.
The barrel is made of a thick-walled pipe (4-5 mm), the lower part has a pointed tip with one or more spiral-shaped cutting blades. Immersion is carried out by screwing into the ground to a certain depth .
The procedure is simple, but requires an understanding of the essence of the process and practical experience, otherwise you can ruin the pile and not achieve the desired effect.
At the same time, working with screw supports is the fastest, requiring no preliminary preparation or excavation work.
If you avoid technological errors, the only problem remains corrosion, from which it is very difficult to protect a metal barrel.
Feasibility of use for a house made of aerated concrete
The load-bearing capacity of such a foundation reaches high values, which may be limited by soil characteristics and the capabilities of pile supports.
By increasing the number of pillars or forming support platforms under the supports, you will increase the load-bearing capacity and reduce the specific load on the soil, thus increasing the efficiency of the entire structure.
As you know, aerated concrete blocks weigh five times less than brick material, but their strength is also lower. This suggests the conclusion that multi-storey buildings are not built from aerated concrete, and the capabilities of the pile-grillage foundation used will be not only acceptable, but also in some places excessive.
Grillage options
The grillage design can consist of different materials:
- Wood.
- Metal.
- Reinforced concrete.
The most difficult option (and the most durable) is a concrete belt. It is created using almost the same methods as the strip base, only not in a trench, but at some distance from the surface.
It is much easier to install a wooden grillage, which is a beam 150: 200 or 200 by 200 mm.
The beams are connected in half a tree, installed on the pile heads and secured with bolted joints.
A metal grillage is attached to the pile heads for welding. The process is the fastest, but cutting thick and massive beams is quite a difficult task, and their weight often requires the use of lifting equipment .
For a house made of aerated concrete, the best option would be to create a wooden grillage, although in each case a specialized calculation must be made.
Installing a foundation on piles for a house made of aerated concrete
Let us consider the features of the technological stages of constructing a pile-strip foundation for a house made of aerated concrete.
Before starting work, it is necessary to perform the appropriate calculations, with the help of which the need for materials is determined. At the same time, to obtain reliable information, the type of foundation and the characteristics of the soil composition on the site are taken into account.
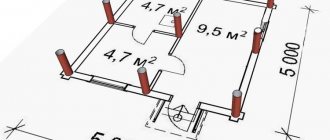
Plan the placement of piles in the corner sections of the object, at the central support points of the load-bearing walls. In this case, the installation step should be from one and a half to two meters.
The screw pile can withstand axial loads of up to twenty-five tons.
Having prepared everything necessary, cleared the construction site and completed preliminary markings, we proceed to the construction of a foundation on screw piles for a house made of aerated concrete.
Screw piles can be installed using two methods - manual or mechanized. The first option involves screwing the elements to a level of up to two meters with a cross-section not exceeding 10.8 cm. Larger supports are mounted using special installations.
Manual method
In this case, use a hand drill, levers and a building level. The installation process is as follows:
- a pit is prepared at the drilling site to facilitate the process;
- levers (cuts of steel pipes) are inserted into the technological holes of the pile;
- the rotation is performed by a pair of workers, the third constantly checks the vertical position of the support;
- Using an angle machine, the pile is trimmed to the required level and the head is welded on.
Mechanized method
In this case, special equipment is used with a power unit capable of grasping the head of the pile and ensuring its rotation. The speed of work depends on the size of the pile pillars and the characteristics of the soil composition.
The use of such an installation entails additional costs, but helps reduce the time for installing poles.
How to calculate the depth of immersion of piles
The immersion depth of piles is a value obtained experimentally. It is impossible to calculate the depth of dense layers; it is a random variable .
Therefore, the only criterion is drilling a test well or driving a test pile, which makes it possible to determine the depth of hard soil rocks.
This is a requirement of SNiP, and all other methods are an illiterate approach that is dangerous for the building and the people living in it.
IMPORTANT!
The depth determined by the trial method is one of the values used in further calculations.
Calculation example
The calculation of a pile-grillage foundation consists of determining the number of piles. It is obtained by dividing the weight of the house (calculated) by the load-bearing capacity of one support .
That is, if the conditional weight of the house is 10 tons, and the load-bearing capacity of the pile is 1 ton, then 10 piles will be needed.
The distribution pattern of supports depends on the configuration of the house . The main and most critical areas that determine the stability and reliability of the foundation are the corners.
When designing, first, one pile is provided for each corner, the point of contact with load-bearing walls and other loaded units.
After this, the remaining supports are evenly distributed, achieving the most even distribution of the load..
Experienced designers always provide some margin of safety for the foundation so that the foundation can withstand additional operational loads or weight from extensions.
Features of gas silicate blocks as a building material
When designing a foundation for a house made of blocks, it is necessary to take into account the features of this structural material:
- loads - gas silicate concrete is lighter than commercial concrete, but the weight of the box is much greater than that of a log house or frame, reinforcement of the structure is mandatory;
- small format - any masonry is susceptible to the slightest ground movements, so walls can only be supported on monolithic structures;
- moisture permeability - the base part of the foundation must be at least 40 cm from the ground and have reliable horizontal waterproofing.
Even with small settlements in the seams and the blocks themselves, cracks may open. Therefore, it is forbidden to erect masonry on grillages made of I-beams or channels.
Important! Gas silicate is not recommended for use on plinths. Therefore, on slab foundations and low grillages, it is advisable to make a plinth from reinforced concrete or ceramic bricks before laying cellular concrete blocks.
Construction technology
Let's consider the most common type of pile-grillage foundation, which you can create with your own hands. This is a support structure on bored piles.
Procedure:
Preparation
The area is cleared of foreign objects and plants. Pegs are marked and installed at the points where the piles are installed .
It is necessary to check the equality of the diagonals so as not to violate the accuracy of right angles.
Then the wells are drilled using special machines or a hand drill (if possible).
The lower sections of the wells are slightly expanded to form cushions that expand the base of the supports and reduce the specific pressure on the ground.
After this, sleeves are inserted into the wells - a type of formwork consisting of plastic pipes or a double layer of roofing material rolled into a pipe of the required diameter.
Reinforcement, pouring concrete
The reinforcement frame is created on the surface. It is a spatial lattice, the length of which is slightly greater than the depth of the wells, and its dimensions allow it to enter the hole quite freely .
After installing the reinforcement, the wells are filled with concrete grade M200 and higher. The poured material is bayoneted to remove air bubbles.
Pouring can be done at a temperature not lower than +5° (ideally +20°). After filling, the wells are kept for 20-28 days until they gain structural strength .
If you rush and start further work earlier, you can weaken the strength of the supports and create a serious threat to the foundation.
Creating a grillage
The most durable type of grillage is a concrete grillage . It is poured into formwork installed at the required height above the ground level.
The formwork is assembled from wooden panels, covered with polyethylene on the inside, and an armored belt is installed, which is rigidly connected to the reinforcement protruding from the piles.
This will make it possible to create a rigid monolithic structure that is resistant to all loads and capable of carrying fairly heavy houses.
Concrete is poured simultaneously, curing and other measures take 28 days.
After this, the outer part of the base is waterproofed using bitumen mastic or hot bitumen , and the foundation work is considered complete.
Installation technology
How to calculate a pile-grillage foundation for aerated concrete
The calculation is carried out on the basis of current SNiP and includes two parts:
Calculation for a pile field
- Dimensions of pile supports. They depend on the area and weight of the aerated concrete structure and the type of soil on the site. The size of the supports must be chosen in such a way as to effectively absorb the load from the structure and prevent its settlement. Piles are installed not only around the perimeter, but also under all load-bearing walls of the future house. The cross-section of bored supports is determined according to the table:
The load-bearing capacity of bored piles depending on the cross-section is given in the table:
Grillage calculation
For the grillage it is determined:
- Length - equal to the length of the perimeter of the load-bearing walls.
- Width - equal to the thickness of the wall of a house made of aerated concrete blocks.
- Height is assumed to be 0.5-0.7 meters.
Preparation for the installation of a pile-boring foundation
The site for a pile-grillage foundation requires minimal planning. Vegetation is removed, stumps are removed, and debris is removed. The marking is carried out in accordance with the drawing using a cord and pegs, which are driven into the places of future piles.
The set of tools and equipment depends on whether the concrete mixture will be produced at the construction site or ordered at the factory. The mandatory list includes:
- shovel or mini-excavator;
- tape measure and building level;
- crochet hook for reinforcement;
- concrete pump or trays for pouring the mixture;
- vibrating tool for compacting concrete.
The list of materials includes:
- concrete M250 or M300 - for pouring piles and grillage;
- reinforcement with a cross section of 12-14 mm;
- panels or finished formwork;
- pipes - for casing piles.
Pouring bored piles
Stages of constructing a pile field:
Creating a grillage
A monolithic grillage is made in the same way as a regular strip foundation. The main difference is that the grillage is buried into the ground no more than 10 cm. Stages of creating the grillage part:
- pile heads - coating waterproofing;
- the sole of the grillage is laid on a bedding layer, on top of which waterproofing or roofing material is laid;
- The top of the grillage tape is coated with liquid waterproofing material or lined with rolled material.
Kawabanga!
Proper care of concrete after pouring in summer and winter, rules for caring for the concrete mixture The external and internal walls of the grillage are subject to insulation. It is better to use moisture-resistant and durable polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam or plastic as insulation.