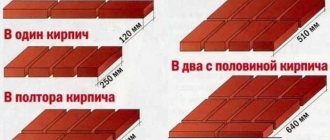
Base - the foot of a building with a height of 0.2 to 2 meters, lying on the foundation. The main purpose of this structural element is protective, namely, the creation of an effective barrier to moisture and cold coming from the ground. In addition, the base performs an architectural function: for some architectural styles, the building, even with a small base of 0.5 meters, looks much better than without it. A building without a base looks squat and unfinished. This does not apply to modern minimalism, where, on the contrary, the basement of the house is lowered or made invisible.
In addition to protecting the house from dampness and cold, the structural element solves the following problems:
- Creates the desired level of the first floor, which is especially important for low or deeply recessed foundations.
- Forms a flat horizontal surface, which facilitates the subsequent laying of aerated concrete blocks.
- Evenly distributes the load from the building onto the foundation, extending the service life of the foundation and load-bearing walls.
- With sufficient height, it allows you to create a basement floor - additional space in the house where you can place utility rooms.
As you can see, the answer to the question of whether a brick plinth is needed for aerated concrete is clear: Its use is determined by the hydro-geological features of the site, as well as the chosen architectural style of the residential building.
How to build a basement from foam blocks?
An economical and practical alternative to brick, stone and other expensive materials is foam concrete plinth blocks.
They are made from concrete with the addition of water, sand and a foaming agent (natural tree resin, plant and animal proteins, and their synthetic analogues).
Basic rules for installing foam block structures
- Foam concrete starting from D600 (at least) is suitable for the base;
- The masonry should be reinforced with metal rods in the horizontal and vertical directions. The blocks are connected together with a reinforced belt;
- the base is installed on a reinforced concrete foundation strip 30-50 centimeters above the blind area. It is preferable to place it on a buried foundation;
- waterproofing is necessary on the outside (street) side to prevent rainwater from entering the basement;
- The blocks are connected using a special glue for foam concrete. This allows you to make narrow, sealed seams and prevent the appearance of cold bridges.
Detailed procedure
The procedure for constructing a basement floor made of foam concrete:
1. Waterproof the tape with bitumen mastic and weldable material.
2. Place cement mortar on top to level the surface of the tape and fasten the foam concrete blocks to the waterproofing substrate.
3. Place two reinforcing bars with a cross-section of 8 millimeters longitudinally into the cement joint.
4. Laying blocks starts from the corner. The first row is laid according to the level and the marking cord stretched along the outside of the base. It is recommended to moisten the underside of the blocks with water for better setting of the cement. Adjustments can be made with a rubber hammer.
5. Subsequent rows are placed on glue prepared from a dry mixture. Before installation, the solution must be kept in its finished form for about 15 minutes.
6. The glue is applied to the horizontal and end surfaces of the already laid block in a thin layer using a notched trowel.
7. The blocks are laid with the seams staggered, shifting the top row relative to the bottom by 10 centimeters.
8. When building a two-story house, before applying glue, you need to lay reinforcing bars in grooves in every third or fourth row.
Designing an additional floor
As a rule, the design of a house made of foam blocks with a basement consists of the following premises: a storage room, a boiler room, a garage with a separate exit, a workshop. On the ground floor you can design a spacious terrace, the floor of which will also be part of the roof of the basement. One of the possible project options is shown in the photo below.
On the lower floor you can also place a sauna or bathhouse, a gym or a billiard room. If the height of the ceilings in the room is more than two meters, you can plan to place living rooms, a kitchen or a living room in the basement. When planning rooms for non-technical purposes, it is recommended to include windows in the design for natural lighting.
In the case where the site has a multi-level terrain, and the level of the room is at its lowest point, it is best to place a garage in the basement. This way you will be able to save on work on the construction of the exit.
Another way to save money during construction is to arrange the floor above the basement in the form of an attic. At the same time, the walls are made thinner and, accordingly, lighter, and additional thermal insulation is provided with one of the insulation materials.
Materials for the construction of the plinth
For our company, the construction of country houses and cottages from foam blocks with a turnkey basement in Moscow is one of our many services.
The technology has been worked out to the smallest detail. Our specialists are well versed not only in the peculiarities of the construction of the basement floor itself, but also in the correct choice of building materials.
The ground floor essentially continues the foundation. Therefore, experts often use concrete blocks from which the walls of the house are laid.
For the floor, you can use cement screed or ready-made concrete slabs. We carry out the cladding using wood materials, having previously treated it with protective agents.
At the customer’s request, the company’s specialists will install windows and doors in the protruding plinth. It is best when they face south, west or east.
Advantages of foam blocks
The following advantages of this material can be highlighted:
- Foam concrete is one of the most inexpensive materials for construction. The use of foam blocks allows you to build a basement floor at the lowest cost.
- The size of the foam block is much larger than a standard brick, and its weight is light due to its cellular structure. Laying such blocks is quite easy and construction takes less time.
- The technology allows you to create blocks of any shape, which further simplifies installation. Foam concrete can be cut and perforated for domestic needs without much effort.
- The foam blocks are connected to each other with special glue. This allows for minimal seams and prevents cold from penetrating through the gaps.
- The use of foam blocks retains heat in the room and reduces heating costs. Foam concrete also has good soundproofing qualities.
- Closed-cell material prevents moisture and steam from entering the basement. It does not rot or expand from water during the cold season.
- Foam blocks do not burn. Unlike concrete, the surface of the foam block does not split when exposed to high temperatures and the reinforcement is more reliably protected from heating in the event of a fire.
- Foam concrete is an environmentally friendly material that does not emit toxic fumes during the operation of the premises.
Construction of foundation walls
The next step is to install the plinth blocks for the walls. Also, the base wall can be poured into formwork and fixed on top of the cushion. The material of blocks for walls has its advantages. Reinforced concrete monolithic blocks, from which the basement floor is made from FBS blocks, guarantees the strength of the structure, and the base made of expanded clay concrete material is characterized by high heat transfer.
As a result, the building material from which a basement floor can be built from foam blocks is selected based on strength, performance characteristics and cost-effectiveness.
Construction of the plinth wall begins after the foundation slab is completely removed. Base blocks are laid along the marked line, from the corners to the center, using the dressing rule. The monolith is poured into formwork, assembled on top of the base and reinforced with transverse struts. Vertical reinforcement rods for a monolithic wall made of reinforced concrete are welded to the outlets from the base slab.
Laying the plinth
The foundation is ready and you can begin laying the base. It is better not to make a base from foam blocks, since they are afraid of humidity and cannot withstand heavy loads, but the entire frame of the house will stand on them, along with the floors and roof. Therefore, it is better to make a base from cinder block, sand concrete blocks or bricks.
First, corner blocks are laid along the hydraulic level, and a cord is pulled between them. The first row is laid on roofing felt waterproofing with cement mortar to increase strength and smooth out unevenness.
Laying the plinth
Since we used a foundation that is higher than ground level, there is no need to be afraid of moisture, so we partially made the basement floor from foam blocks: they will go inside, and the brick wall will be duplicated from the outside to the end of the basement. They can be laid in parallel. Then the brick will take on part of the load.
To ensure that the wooden floors do not sag over the base and are rigid, you need to make an additional support point in the center. To do this, columns are laid out in 1 brick to install a load-bearing concrete beam.
Note! Every 3-4 rows of masonry need to be reinforced. To do this, you need to manually make grooves in the blocks for laying reinforcement. At the junction of external and internal walls, reinforcement is done in each row.
Above the basement windows, ceilings made of 65 mm corners are used, on which foam blocks are then laid. Also be sure to place a quarter in the opening using bricks to install the windows.
Ground floor
Armopoyas
To distribute the load evenly between the floors and mauerlats, an armored belt is made. This is a reinforced concrete layer that is made around the perimeter of the entire building.
Formwork for armored belt
To fill it, you can use ordinary wooden formwork or permanent formwork made from sawn thin foam blocks.
Wall masonry
The construction of the basement is completed, and now we are starting to build the 1st floor. We continue to lay the walls of foam blocks in the same way.
When we come to covering windows, there are several ways to do them:
- Use reinforced foam concrete lintels from the manufacturer (their price per cube is approximately 3 times more expensive than conventional foam blocks);
- Use U-shaped blocks as permanent formwork;
- Make permanent formwork with your own hands from blocks of smaller thickness.
Option 3 is the cheapest, especially since when purchasing pallets, there are extra blocks of a different thickness left (they are used as additional ones).
Instructions for installing ceilings:
- First, supporting bridges are made. To do this, you can place the boards on a couple of blocks, as shown in the photo.
Installing supports for pouring a beam
- Then formwork is laid from thin blocks in the shape of an inverted letter “P”.
- There will be a 100 mm block inside, 150 mm outside, and a 150 mm block sawn in half inside.
Permanent formwork
- The reinforcement is tied together in the shape of a long parallelepiped and inserted inside. Then everything is poured with concrete.
The formwork for the armored belt between floors is made in the same way. The second floor in the house is an attic. We lay 4 rows of blocks (1 meter), the mauerlats and rafters will be installed on it.
To do this, we reinforce it with a continuous armored belt around the entire perimeter. For convenient installation of the Mauerlats in the armored belt, you need to make embedded studs.
The process of laying foam blocks
- Waterproofing – treatment with mastic, fusing of roofing material;
- Applying cement mortar over the waterproofing layer (leveling the foundation, fastening blocks);
- Laying reinforcing bars into the seam with mortar (their optimal diameter is 8 mm);
- Pull the string tightly along the outer edge of the base so that the masonry is even;
- Foam blocks begin to be placed from the corners and are pressed tightly with a rubber hammer;
- Subsequent rows are placed on a special glue, which is first diluted from the dry mixture and left to stand. It is applied to the horizontal surface of the blocks and their ends;
- For buildings with a height of more than one floor, the blocks must be strengthened with reinforcement in the grooves before applying glue (on every 3-4 row);
- Upon completion of the construction of the basement floor, it is additionally reinforced with concrete and waterproofing.
Waterproofing
After completing the foundation, it urgently needs to be isolated from the effects of water; this can be done using ordinary rolled roofing felt; it must be laid in several layers. Again, this moment completely depends on the type of soil and the depth of groundwater, but the roofing material spreads over the deposited Bikrost SKP mastic. After insulation, a layer of masonry concrete mixture, no more than 10 mm thick, is laid on its surface; it will serve as a kind of connecting link between the foam concrete blocks and the main foundation of the building.
Waterproofing the basement
Scheme for finishing walls made of aerated concrete blocks.
The finished base must be insulated. To do this, use a special waterproofing material or roofing felt. Rolls of material are laid in several layers and filled with cement. Depending on the location of the groundwater level and the type of soil located on the construction site, the waterproofing process is carried out in 2-3 stages.
First of all, the resulting structure is covered with bitumen mastic. In the future, to waterproof the resulting structure, craftsmen advise laying Bikrost SKP. This economy-class roll material is based on fiberglass or a polyester base of oxidized bitumen. On both sides it is coated with protective layers of coarse-grained powder and polymer film. It is applied by fusing, using a propane torch. This technology significantly reduces the layering of the resulting waterproof carpet. This method not only simplifies the procedure compared to laying roofing felt, it also makes it a safer and more economical method.
General characteristics of projects
A typical design of a house made of foam blocks with a basement most often involves the construction of the following elements:
- Basement floor with an area of 30 to 50 m2, in which storage rooms, workshops, boiler rooms, etc. are located . In some cases, a garage is also located here, but then a separate exit is provided for the car (see diagram below).
- Ground floor with living room, sitting area, bathroom and kitchen . Part of the first floor is sometimes reserved for a spacious porch or open terrace.
- Second floor with several bedrooms and sometimes an additional bathroom.
Note! In some cases, in order to save materials and optimize costs, the second floor is made into an attic, with thinner and lighter walls. In this case, special attention must be paid to high-quality thermal insulation.
As a rule, all load-bearing structures are made of foam blocks of different thicknesses. At the same time, the outside walls are finished with facing bricks, and the part of the basement floor protruding above the ground floor is finished with ceramic tiles, clinker or special siding with additional thermal insulation.
This design has a number of advantages:
- The first and most important thing is the price. The use of foam concrete blocks can significantly reduce the cost of building a house, so it is better to spend the excess on finishing and communications.
- Thermal insulation. The low thermal conductivity of foam blocks provides us with an acceptable temperature even in an unheated basement. What can we say about a full-fledged basement?
Projects of houses with a base made of foam blocks
| Deferred (0) Compare (0) > |
Look at the projects of houses with a base made of foam blocks and aerated concrete. The range of projects has a wide range. You can ask our managers for help in selection.
Square
up to 150 m2150-250 m2250-400 m2from 400 m2All
No subcategories
Reset filters
Advanced Search
There are 286 projects in this category.
Sorting:
- Square
- Price
- Rating
- Novelty
- Comments
- Sales
T-388-1P
T-388-1P project of a two-story aerated concrete house with a basement and a garage measuring 16 by 17
| 392.81 m2 | 16.3 x 17.1 m |
| RUB 51,300 |
R-149-1P
R-149-1P project of a two-story aerated concrete house with a basement and attic measuring 8 by 11
| 149 m2 | 7.5 x 10.6 m |
| RUB 21,000 |
B-173-1P
B-173-1P project of a two-story house made of foam blocks with a basement and a garage measuring 8 by 8
| 173.92 m2 | 8.4 x 8 m |
| RUR 33,250 |
B-170-1P
B-170-1P project of a two-story house made of foam blocks with a base measuring 7 by 11
| 169.48 m2 | 7 x 10.9 m |
| RUB 26,600 |
B-169-1P
B-169-1P project of a two-story house made of foam blocks with a basement and attic measuring 9 by 9
| 174.34 m2 | 8.6 x 9 m |
| RUB 23,750 |
L-174-1P
L-174-1P project of a two-story house made of foam blocks with a base measuring 9 by 8
| 177.93 m2 | 9 x 7.5 m |
| RUB 33,300 |
D-308-1P
D-308-1P project of a two-story cottage made of foam concrete with a basement and a garage measuring 17 by 14
| 308.4 m2 | 17.2 x 13.8 m |
| RUB 31,000 |
L-414-1P
L-414-1P project of a two-story aerated concrete house with a basement and a garage measuring 16 by 14
| 485.89 m2 | 15.9 x 14.4 m |
| RUB 57,500 |
T-260-1P
T-260-1P project of a two-story house made of foam blocks with a basement and a garage measuring 15 by 11
| 260.33 m2 | 14.7 x 11.1 m |
| RUB 45,500 |
H-131-2P
H-131-2P project of a two-story house made of foam concrete with a basement and a garage measuring 10 by 10
| 203.48 m2 | 10.2 x 9.6 m |
| RUB 41,300 |
G-306-2P
G-306-2P project of a two-story cottage made of foam concrete with a basement and a garage measuring 12 by 12
| 306 m2 | 11.9 x 11.8 m |
| RUB 47,900 |
E-531-1P
E-531-1P project of a three-story aerated concrete house with a basement and attic measuring 15 by 22
| 531.4 m2 | 15.5 x 21.8 m |
| 60,000 rub. |
E-341-1P
E-341-1P project of a three-story house made of foam concrete with a basement and attic measuring 19 by 15
| 341.1 m2 | 19.2 x 14.9 m |
| 45,000 rub. |
R-199-2P
R-199-2P project of a one-story house made of foam blocks with a basement measuring 14 by 12
| 167.98 m2 | 13.7 x 12 m |
| RUB 36,000 |
R-132-1P
R-132-1P project of a one-story aerated concrete house with a basement measuring 12 by 14
| 131 m2 | 12 x 13.7 m |
| RUB 32,000 |
U-363-1P
U-363-1P project of a two-story aerated concrete house with a basement and a garage measuring 18 by 12
| 362.85 m2 | 18.1 x 12.3 m |
| 40,000 rub. |
Y-300-1P
Y-300-1P project of a two-story cottage made of foam concrete with a base measuring 16 by 14
| 303 m2 | 16.1 x 13.6 m |
| RUB 35,000 |
C-189-1P
C-189-1P project of a two-story house made of foam blocks with a basement and attic measuring 8 by 11
| 189.84 m2 | 8 x 10.5 m |
| RUB 36,000 |
G-306-1P
G-306-1P project of a two-story cottage made of foam concrete with a basement and a garage measuring 12 by 12
| 306 m2 | 11.9 x 11.8 m |
| RUB 49,900 |
A-289-1P
A-289-1P project of a two-story house made of foam blocks with a basement and attic and a garage measuring 13 by 11
| 289.2 m2 | 13.2 x 10.5 m |
| RUB 38,000 |
A-337-1P
A-337-1P project of a two-story house made of foam concrete with a basement and attic and a garage measuring 15 by 12
| 337.2 m2 | 14.8 x 12.1 m |
| RUB 38,000 |
A-308-1P
A-308-1P project of a two-story cottage made of foam concrete with a basement and attic and a garage measuring 14 by 12
| 308.8 m2 | 13.5 x 11.7 m |
| RUB 38,000 |
G-388-1P
G-388-1P project of a two-story aerated concrete house with a basement and a garage measuring 15 by 17
| 388.1 m2 | 15.2 x 16.9 m |
| RUB 50,900 |
G-302-1P
G-302-1P project of a two-story cottage made of foam concrete with a basement and a garage measuring 15 by 11
| 302.2 m2 | 14.8 x 11 m |
| RUB 44,900 |
A-207-1P
A-207-1P project of a one-story house made of foam concrete with a basement and a garage measuring 17 by 31
| 207 m2 | 17.1 x 31.2 m |
| RUB 24,700 |
A-510-1P
A-510-1P project of a three-story aerated concrete house with a basement and attic and a garage measuring 20 by 16
| 509.9 m2 | 20.1 x 15.7 m |
| RUB 32,775 |
U-075-1P
U-075-1P project of a one-story house made of foam block with a basement measuring 17 by 8
| 75 m2 | 16.7 x 7.6 m |
| 23,000 rub. |
R-319-1P
R-319-1P project of a two-story house made of foam concrete with a base measuring 24 by 32
| 319 m2 | 23.7 x 31.7 m |
| 70,000 rub. |
R-225-1P
R-225-1P project of a two-story aerated concrete cottage with a basement and attic and a garage measuring 15 by 17
| 226 m2 | 15.4 x 17 m |
| RUB 38,000 |
U-240-3P
U-240-3P project of a two-story aerated concrete house with a basement measuring 12 by 14
| 236.82 m2 | 11.5 x 13.7 m |
| RUB 38,000 |
263831042734196317781500155215651608164237923794379538203558356135713584365437163717373037433745374637583767377637883402
| 105.64 m2 | |
| Box 4.014 million Warm contour 4.648 million White box | |
| More details | |
| 122.73 m2 | |
| Box 4.842 million Warm contour 5.354 million White box | |
| More details | |
| 115.97 m2 | |
| Box 5.012 million Warm contour 6.546 million White box | |
| More details | |
| 216.47 m2 | |
| Box 8.558 million Warm contour 10.056 million White box | |
| More details | |
Previous Next
House projects Brick Foam concrete Wooden
Single-storey Double-storey With basement With attic
For narrow areas Houses with a garage With a flat roof
With discounts
New projects
Payment options:
| by card | according to account |
About the company About us Advertising in the catalog News Articles
What are foam blocks?
Foam blocks are large-sized lightweight bricks that consist of sand, water, cement and foam. They are obtained by introducing a special substance into the cement mortar, which causes the bubbling process. As a result of the chemical reaction, hydrogen is released, which ensures the porosity of the cement mortar. Foam concrete of various densities is produced industrially. The production of foam blocks is carried out using one of two methods. The first method is based on pouring foam concrete mixture into special molds. This technology makes it possible to obtain blocks of any shape and volume. It is used in the construction of buildings of unusual design, the facade of which has an unusual shape. The second method involves cutting the source material into pieces of the required size.
Stages of construction work
Work on the construction of houses made of foam blocks takes place in the following sequence:
- Removal of design dimensions to the area;
- Geological studies of the territory;
- Construction of the foundation;
- Installation of wooden formwork and pouring concrete;
- Casting of columns of the first floor;
- Walling.
The construction of a house made of foam concrete is carried out both in the warm and cold seasons. This material is easy to transport and affordable for a wide range of Russians. A medium-sized construction takes an average of three months. This is significantly faster than building a brick house. In addition, it is easy to make holes in foam blocks for communication systems and electrical wiring.
Photo examples of built houses