Elevator passenger
An elevator is a lifting and transport device that transports elevator passengers or goods in a vertical direction along rigid steel elevator guides . Typically, an elevator moves inside an elevator shaft . The elevator speed ranges from 0.15 m/sec to 10 m/sec and higher. The elevator's lifting capacity reaches 20 tons.
An elevator car usually has a square or rectangular shape, it has walls, a floor of the car
and ceiling.
Entrance to the elevator is through automatic elevator doors - elevator portal .
The electrical circuit of the elevator assumes that the elevator can be controlled by any elevator passenger independently, but before that, he must familiarize himself with the rules for the design and operation of elevators .
Brief characteristics of the elevator control system
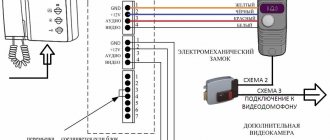
. The control system for this elevator (Fig. 3.7) is a single external one, with an alarm call to the cabin from the loading platforms.
To control the electric drive of the elevator, a contactor NKU type YASZH5401 is used.
The elevator is controlled using push-button control stations.
If the elevator is controlled from one stop, a PKL41UZ type push-button station with “Up” or “Down”, “Call”, “Stop” buttons and a “Busy” signal lamp is used. When controlling an elevator from two stops, a PKL31UE type push-button station with “Up” or “Down”, “Call”, “Stop” buttons and a “Busy” signal lamp is used. The control station buttons are self-returning. On a loading platform that is not equipped with a control station, a calling device with a Kn button is installed, which has one closing contact with self-reset. While it is being held, the ZvV bell is activated.
The cabin has a fixed floor, without load control. Closing the cabin doors or the device that makes it impossible to move the load beyond the overall dimensions of the cabin floor is not controlled by the switch.
The shaft doors are opened and closed manually. The door shutter is controlled by the door shutter switch, but their locking by an automatic (crossbar) lock is not controlled.
The unit for determining the location of the cabin and sending a signal for its precise stop on the upper or lower loading platform is made on the basis of floor switches 1EP and 2EP installed in the shaft. There is a tap on the cabin that acts on the roller of the floor switch lever when the cabin enters the precise stop zone of the loading platform. The positions of the ED switch lever are presented in the table.
Contact
| Lever position | |||
| Left | 0 | Right | |
| 1 | + | — | — |
| 2 | — | — | + |
| 3 | — | + | + |
| 4 | + | + | — |
Application
. + — contact is closed; — contact is open; left -
after going up the cabin; right - after going down the cabin; 0 - at the moment of impact on the EP of the cabin lift. If the cabin passes the exact stop level of the loading platform, the VK limit switch is triggered, turning off the elevator control circuit. In the elevator circuit there are contactors for the direction of movement up and down (KV and KN, respectively), which control the electric motor Ml.
Rice. 3.7. Schematic electrical diagram of a small freight elevator for two stops with a load capacity of 100 kg with a nominal cabin speed of 0.5 m/s
Elevator operating program
. 1. When you press the 2KN-1 button for calling the loading platform, the electric bell ZvV is turned on, signaling the requirement to direct the cabin to this stop.
2. When you press the Kn “Up” or Kn “Down” button, the cabin is directed up or down, after which it makes an exact stop at the specified loading area.
3. When you press the Kn “Stop” button, the moving cabin should stop.
Operating principle of the elevator electrical circuit
. The elevator is prepared for operation by turning on switch B1 and circuit breaker BA1.
In this case, the mains voltage is supplied:
• three-phase - via wires LZ1, JI32 and JI33 to the main contacts of the KV and KN contactors;
• single-phase - via wire JI33-L43 to fuse Pr1 and then to the elevator control circuit;
• two-phase - via wires JI22 and JI23 to fuses Pr2 and then via wires JI82 and JI83 to the step-down transformer TrZ.
A voltage of 220 V AC is supplied to the control circuit (at a network voltage of 380 V): the network phase (380 V) is supplied to wire 1 (101), and wire 0 (104) is connected to the neutral wire of the network.
From the output of the low voltage winding of the transformer TrZ through the fuse PrZ via wires 03 (803) and 02 (102), an alternating two-phase voltage of 24 V is removed, which is supplied to the power circuit of the signal lamps 1LP-1, 2LP-1 and LZ, the cabin call bell ZvV and plug connectors ShR1, ShRZ - ShR5.
Action of the electrical circuit when pressing the control and call buttons
. The diagram is designed for the case when the cabin and push-button control station are at the first stop. Let us assume that the cabin with the doors of the first stop shaft open needs to be directed to the upper stop. To start it, it is necessary to close the doors of the first stop shaft, after which the electrical contacts 1DSh-1 and 2DSh-1 are closed, and press the call button Kn “Up”. The action of the electrical circuit is as follows:
HF contactor power circuit: 1 - 2 - 2-2 - 2DSh-1 - 3 - 4 - VL - 6 - VK - 8 - 1DSh-1 - 10 - 12 - Stop button - 15 - Up button - 16 — 2EP-2 — 17 — KN — (03) — KV coil.
After turning on the HF contactor, the button can be released, since the power supply circuit of the HF coil will pass through the 3-contact HF (15-16). The cabin begins to move upward. When entering the precise stopping zone of the second loading platform, the cabin lift moves the 2EP lever to the zero position, at which the electrical contact 2EP-2 opens and the HF contactor is turned off. Then Ml and EmT are switched off and the cabin stops. Starting the cabin from the KN “Down” button is similar, only in this case the KN contactor is turned on.
To give an audible signal to call the cab to the first stop, if it is at the second, press the 2KN-1 button. The ZvV bell is turned on via circuit 03 - 2Кн-1 - 23 - ZvV bell. In this case, at the first stop, a sound signal is received and, if the warning lamp LZ is not illuminated, the cabin is started down.
Operation of light signaling circuits
. The elevator is equipped with a light alarm. Signal lamps 1LP-1 and 2LP-1 are installed at the first stop next to the control station; they indicate the number of the loading area on which the cabin is currently located. The signal lamp 1LP-1 is turned on by contact 1EP-3 (03-21-1), and 2LP-1 by contact 2EP-4 (03-21-2). The LZ signal lamp, mounted in the control station, is turned on when the shaft door is open by contact 1DSh-1 or 2DSh-1 (03-22), and when the cabin moves - by 3-contact KV or KN (03-22).
Control questions
1. Explain why, after turning on the KV or KN contactor, you can release the Kn “Up” or Kn “Down” button.
2. Explain why the fourth contact 2EP is introduced into the circuit of the KV coil, and the third contact 1EP into the circuit of the KN coil.
3. In what cases does the JI3 warning light turn on?
4. In what cases does the 1LP-1 warning light turn on?
5. In what cases does the VK contact (6^8) open? Where is it installed on the elevator?
6. Why is it impossible to start the cabin when the shaft door is open, the safety devices or the limit switch are activated?
content .. 81 82 83 ..
Elevator device
The elevator system consists of:
✔ Elevator cabins are a closed elevator compartment in which an elevator passenger , the height of the cabin is usually 2100-2200 millimeters, the size of the elevator cabin should allow it to comfortably transport several passengers
✔ Elevator doors – passenger elevators have elevator cabin doors and elevator shaft doors
✔ Elevator guides - elevator guides made of steel along which the elevator cabin and counterweight ( the weight of the elevator guides is about 50 kg/meter)
✔ Elevator winches are the elevator drive that gives the elevator speed
✔ Elevator cable - elevator ropes on which the elevator cabin is suspended. The elevator traction rope has a 14-fold safety factor. ropes for elevators are made of steel wire
✔ Elevator control stations - the brain of the elevator, which controls it and sets the speed of the elevator , sets the acceleration of the elevator car and controls the elevator circuit
✔Elevator safety devices
✔ Speed limiter - an elevator device that controls the speed of the elevator
✔ Elevator catchers - catching jammed grips of the elevator cabin. Mandatory for a modern elevator
✔ Elevator passports - a technical document that every elevator must have. The elevator passport contains all the necessary information about the elevator
Features of the design of freight elevators
All types of elevator equipment are designed primarily for transporting various types of cargo. At the same time, they work both on ascent and descent. In addition to the fact that all elevators operate on the same principle, their designs are somewhat different. Depending on its purpose, each type of lifting equipment is equipped with separate, unique elements. However, a characteristic feature of all is the mandatory presence of a mechanism that drives steel cables, which facilitate the movement of the cargo or passenger cabin. What is particularly different about the design of a freight elevator is that its design contains additional pulleys with double entwining cables. This precaution, in a stronger grip on the pulley wheels, ensures high safety when lifting fairly heavy loads.
Depending on the engineering decisions made by the manufacturer, some models of freight elevators are equipped with a gearless winch. Such structures are usually installed by specialists at those facilities where great attention is paid to the efficiency of transporting large quantities of cargo. If the winch does not have a gearbox, the synchronous movement of the pulley wheel and the motor shaft is maintained. Elevators with a gear winch have a lower speed, and therefore are mainly installed in low buildings, cottages and private houses.
of great importance in the design of freight elevators . When placed at the top, the design of the lift can be somewhat simplified. This position of the drive helps to reduce the load experienced by the shaft and, in addition, prevents the formation of bends on the ropes, which significantly increases their service life. When the drive mechanism is located at the bottom, favorable conditions are created for employees to carry out high-quality repairs and install the winch on a separate base, which significantly reduces the sound emanating from the operating elevator. True, in this case it will be necessary to significantly lengthen the traction ropes and additionally install a system of deflecting blocks. Due to the deviation of the cables in the desired direction, they may become kinked, which in this case causes a reduction in their service life. In addition, it creates a load on the elevator shaft and complicates the design of the elevator as a whole.
Who produces elevators in Russia
The production of most domestic elevators is concentrated at two elevator-building plants - JSC Shcherbinsky Elevator Construction Plant (JSC ShchLZ ) and JSC Karacharovsky Mechanical Plant (JSC KMZ ); a certain number of elevators are produced in Russia by the American company OTIS .
In Russia, elevators are produced with a load capacity of up to 5000 kg and speeds of up to 2 m/s. Foreign elevator factories can produce elevators with a load capacity of up to 20 tons and a speed of up to 10-15 m/sec (such elevators are needed for high-rise buildings - for example, the elevator speed in the Ostankino tower is 7 m/sec).
Elevators. Classification. Kinematic diagrams, operating principle of a passenger elevator
An elevator is a type of lifting machine designed for vertical or inclined movement of goods or people on special platforms moving along rigid guides.
Classification:
1.Intended use:
· Passenger elevators
. For transporting people.
· Freight elevators
. For transportation of goods with accompanying personnel
· Hospital elevators
. Elevators for medical institutions
· Cargo-passenger
. For transporting people and goods
· Loading platforms
. For transportation of goods, materials and equipment.
· Freight with a guide
. For transportation of goods and accompanying persons.
· Freight without a conductor
. For transportation of goods only.
· Small cargo
. usually in restaurants and cafes, libraries, warehouses, etc.
· Industrial
. For installation in buildings with dusty environments containing corrosive gases, explosive and fire hazardous environments and for hazardous industries
2By design:
· Releasers
. In such an elevator, the ropes wrap around the cabin from below.
· Sidewalk
. The cabin moves out of the floor. The sidewalk elevator can be squeezed.
· Freight with monorail
, built into the cabin.
· Freight (small store
).
· Elevators accessible for disabled people
.
· Pneumolifts
. They work using air that is pumped inside the cylinder in the section below the cabin.
· Hydraulic
.
· Cottage
. They differ from conventional serial passenger elevators in the following: low energy consumption, the ability to work autonomously in case of power outages in the house
· Construction hoists
. Designed for lifting and delivering various loads inside building openings or onto the roof[12].
· Parking systems
cars.
· Panoramic
. They do not have their own elevator shafts. From the cabin of the panoramic elevator, passengers have a view of the external space
· Home elevators
. Elevators are installed in apartments and residential buildings powered by a regular 220V AC network
3.According to the drive design:
· Electrically driven:
· With drum winches
. They have a rigid connection between the cabin and the counterweight with the drum.
· Winches with rope pulley
. They do not have a rigid connection between the cabin and the counterweight with the traction pulley.
· With hydraulic drive.
· With pneumatic drive.
According to the drive design, winches with gear drive and gearless drive are distinguished. Winches with a gear drive are used on elevators with low speeds, while gearless winches are used, on the contrary, on elevators with high speeds.
Kinematic schemes:
a and b - with a lower location of the winch;
c and d - with the upper location of the winch;
d and f - with an upper winch and a counterweight;
g - with a lower location of the winch and a counterweight;
z and i - with an upper winch with a traction pulley and a counterblock;
k - release;
l - with pulley suspension of the cabin and counterweight.
Operating principle of a passenger elevator:
The winch, using traction ropes connected to the passenger elevator car, moves the elevator car across floors.
A counterweight is provided for part of the payload and for balancing the passenger elevator cabin. The passenger elevator cabin and counterweight move in a special shaft. Inside the shaft, cabin and counterweight guides are fixed, which fix the cabin and counterweight to the horizontal plane. The building structure in which the winch is located is called the machine room. A control station with contactors, switches and other devices and devices is installed in this machine room.
In elevators with high lift heights, chains are installed to balance the variable mass of traction ropes.
The devices are powered via an overhead cable.
The doorways are closed with shaft doors, the cabin is equipped with doors. Depending on the control system, terminal boxes and a deceleration sensor are installed in the shaft, and a precision stop sensor is installed in the cabin.
1 cargo winch
2 counterweight
3 cable (rope)
4 passenger cabin